|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer Statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Durzynska J, Lesniewicz K and Poreba E:
Human papillomaviruses in epigenetic regulations. Mutat Res Rev
Mutat Res. 772:36–50. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sawaya GF, Brown AD, Washington AE and
Garber AM: Current approaches to cervical-cancer screening. N Engl
J Med. 344:1603–1607. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sawaya GF, Smith-McCune K and Kuppermann
M: Cervical cancer screening: More choices in 2019. JAMA.
321:2018–2019. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Botezatu A, Iancu IV, Plesa A, Manda D,
Popa O, Bostan M, Mihaila M, Albulescu A, Fudulu A, Vladoiu SV, et
al: Methylation of tumour suppressor genes associated with thyroid
cancer. Cancer Biomark. 25:53–65. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Tasca L, Ostör AG and Babeş V: XII. Aurel
Babeş. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 21:198–202. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tan SY and Tatsumura Y: George
Papanicolaou (1883-1962): Discoverer of the Pap Smear. Singapore
Med J. 56:586–587. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Petry KU, Woermann B and Schneider A:
Benefits and risks of cervical cancer screening. Oncol Res Treat.
37 (Suppl 3):S48–S57. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
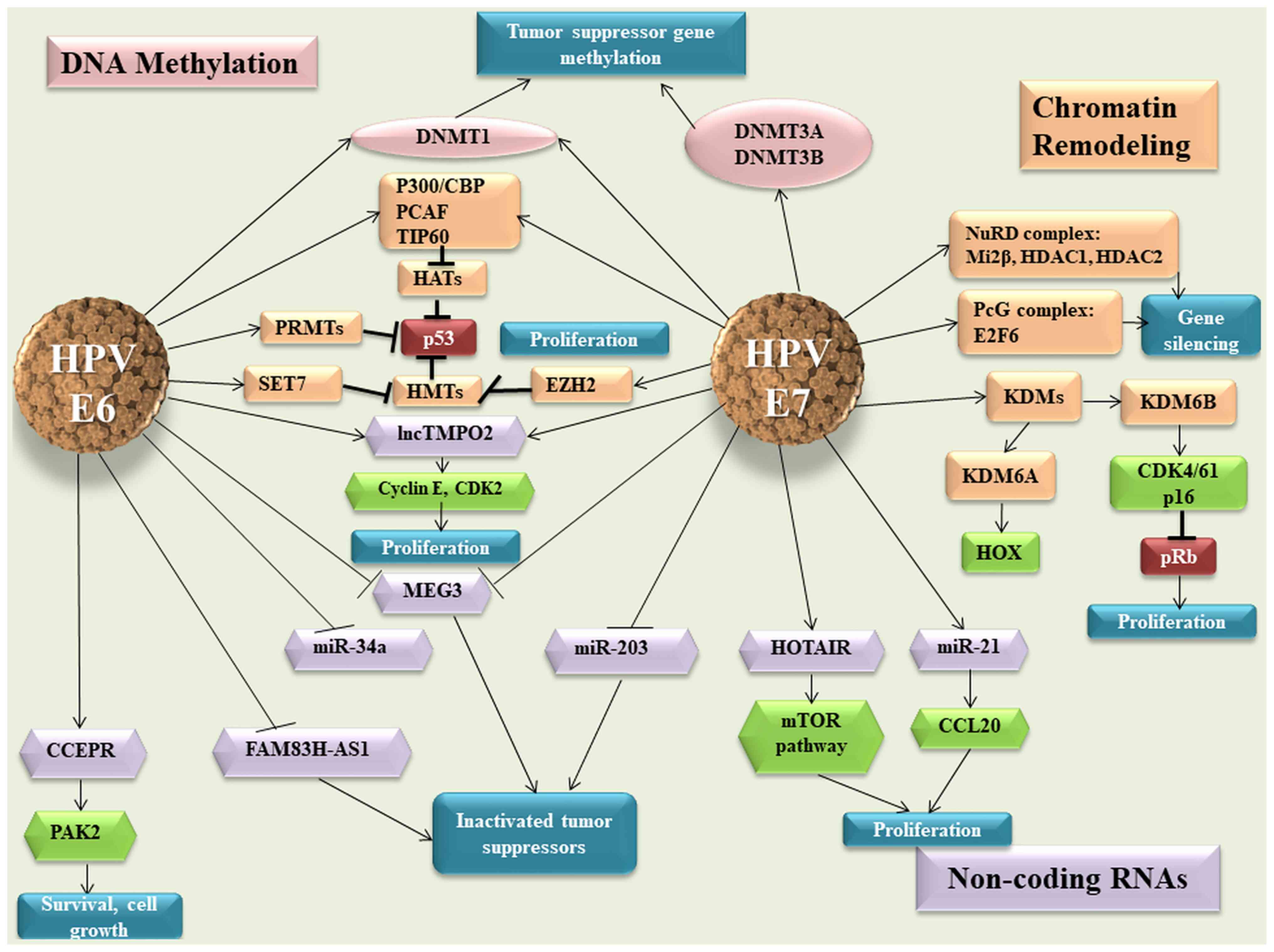
|
Lazcano-Ponce E, Lorincz AT, Cruz-Valdez
A, Salmeron J, Uribe P, Velasco-Mondragón E, Nevarez PH, Acosta RD
and Hernandez-Avila M: Self-collection of vaginal specimens for
human papillomavirus testing in cervical cancer prevention (MARCH):
A community-based randomised controlled trial. Lancet.
378:1868–1873. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Koliopoulos G, Nyaga VN, Santesso N,
Bryant P, Martin-Hirsch P, Mustafa RA, Schünemann H, Paraskevaidis
E and Arbyn M: Cytology vs. HPV testing for cervical cancer
screening in the general population. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
8(CD008587)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Schmitz M, Eichelkraut K, Schmidt D,
Zeiser I, Hilal Z, Tettenborn Z, Hansel A and Ikenberg H:
Performance of a DNA methylation marker panel using liquid-based
cervical scrapes to detect cervical cancer and its precancerous
stages. BMC Cancer. 18(1197)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wentzensen N, Schiffman M, Palmer T and
Arbyn M: Triage of HPV positive women in cervical cancer screening.
J Clin Virol. 76 (Suppl 1):S49–S55. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
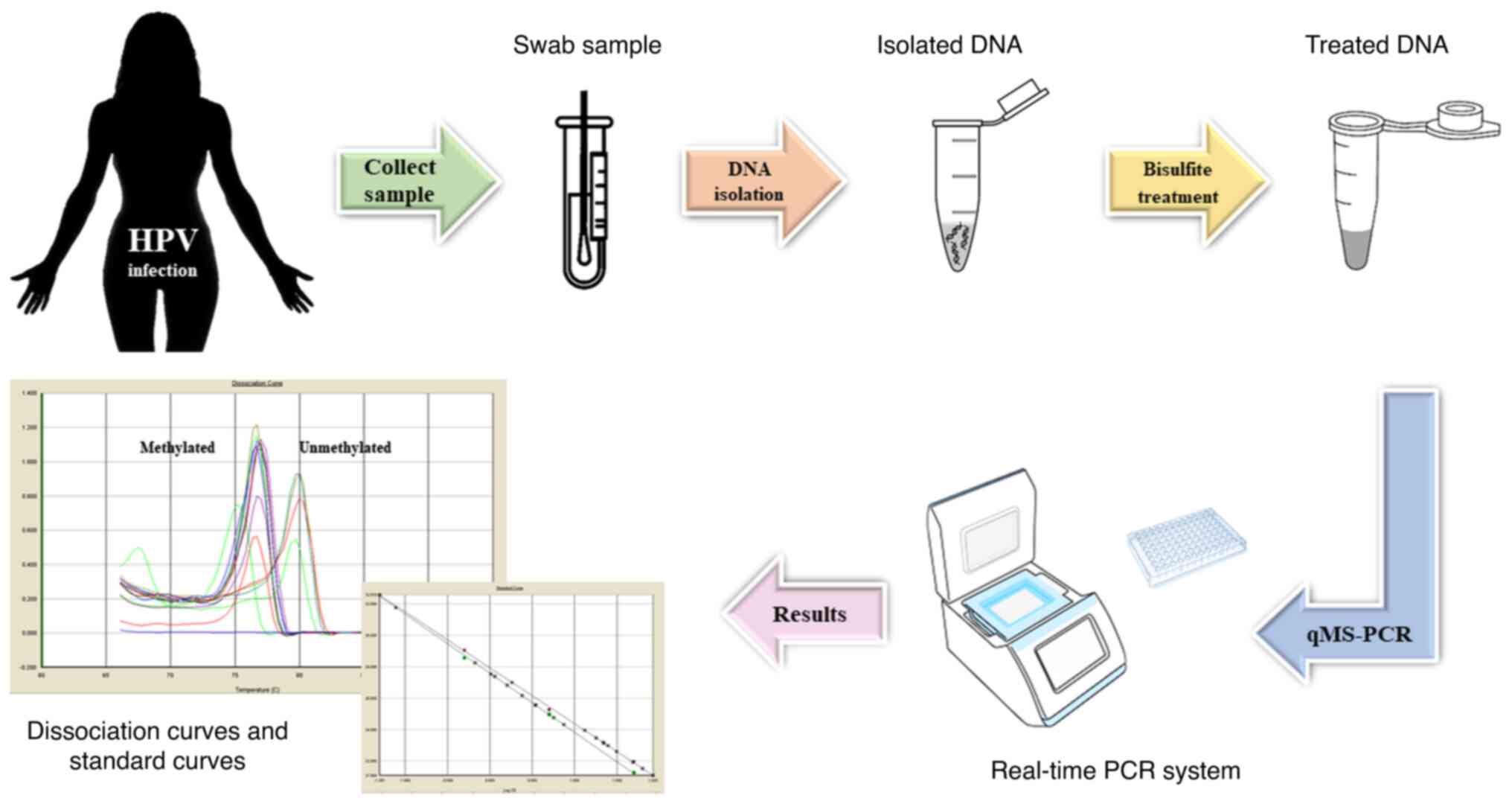
|
Dillner J, Rebolj M, Birembaut P, Petry
KU, Szarewski A, Munk C, de Sanjose S, Naucler P, Lloveras B, Kjaer
S, et al: Long term predictive values of cytology and human
papillomavirus testing in cervical cancer screening: Joint European
cohort study. BMJ. 337(a1754)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Saslow D, Solomon D, Lawson HW, Killackey
M, Kulasingum SL, Cain J, Garcia FAR, Moriarty AT, Waxman AG,
Wilbur DC, et al: American Cancer Society, American Society for
Colposcopy and Cervical Pathology and American Society for Clinical
Pathology screening guidelines for the prevention and early
detection of cervical cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 62:147–172.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Bian M, Cheng J, Ma L, Cong X, Liu J, Chen
Y and Chen X: Evaluation of the detection of 14 high-risk human
papillomaviruses with HPV 16 and HPV 18 genotyping for cervical
cancer screening. Exp Ther Med. 6:1332–1336. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tian Y, Wu NYY, Liou YL, Yeh CT, Cao L,
Kang YN, Wang HJ, Li Y, Chu TY, Li W, et al: Utility of gene
methylation analysis, cytological examination and HPV-16/18
genotyping in triage of high-risk human papilloma virus-positive
women. Oncotarget. 8:62274–62285. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fudulu A, Albulescu A and Anton G: Human
papillomaviruses' proteins with clinical utility. J Immunoassay
Immunochem. 40:81–90. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Clarke MA, Gradissimo A, Schiffman M, Lam
J, Sollecito CC, Fetterman B, Lorey T, Poitras N, Raine-Bennett TR,
Castle PE, et al: Human papillomavirus DNA methylation as a
biomarker for cervical precancer: Consistency across 12 genotypes
and potential impact on management of HPV-positive women. Clin
Cancer Res. 24:2194–2202. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gai W and Sun K: Epigenetic biomarkers in
cell-free DNA and applications in liquid biopsy. Genes (Basel).
10(32)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Dagogo-Jack I and Shaw AT: Tumour
heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 15:81–94. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Baylin SB and Jones PA: Epigenetic
determinants of cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
8(a019505)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lleras RA, Smith RV, Adrien LR, Schlecht
NF, Burk RD, Harris TM, Childs G, Prystowsky MB and Belbin TJ:
Unique DNA methylation loci distinguish anatomic site and HPV
status in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
19:5444–5455. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wentzensen N, Sherman ME, Schiffman M and
Wang SS: Utility of methylation markers in cervical cancer early
detection: Appraisal of the state-of-the-science. Gynecol Oncol.
112:293–299. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lorincz AT: Virtues and weaknesses of DNA
methylation as a test for cervical cancer prevention. Acta Cytol.
60:501–512. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Plesa A, Iancu IV, Botezatu A, Huica I,
Stoian M and Anton G: The involvement of epigenetic mechanisms in
HPV-induced cervical cancer, Rajamanickam Rajkumar, human
papillomavirus-research in a global perspective, IntechOpen,
London, 191-239, 2016. https://www.intechopen.com/chapters/50425. Accessed
June, 16, 2021.
|
|
26
|
Du J, Johnson LM, Jacobsen SE and Patel
DJ: DNA methylation pathways and their crosstalk with histone
methylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 16:519–532. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jin B and Robertson KD: DNA
methyltransferases, DNA damage repair and cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol.
754:3–29. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Williams K, Christensen J and Helin K: DNA
methylation: TET proteins-guardians of CpG islands? EMBO Rep.
13:28–35. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Schübeler D: Function and information
content of DNA methylation. Nature. 517:321–326. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Sina AA, Carrascosa LG, Liang Z, Grewal
SY, Wardiana A, Shiddiky MJA, Gardiner RA, Samaratunga H, Gandhi
MK, Scott RJ, et al: Epigenetically reprogrammed methylation
landscape drives the DNA self-assembly and serves as a universal
cancer biomarker. Nat Commun. 9(4915)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kanwal R, Gupta K and Gupta S: Cancer
epigenetics: An introduction. Methods Mol Biol. 1238:3–25.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Reinert T: Methylation markers for
urine-based detection of bladder cancer: The next generation of
urinary markers for diagnosis and surveillance of bladder cancer.
Adv Urol. 2012(503271)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
de Groot JS, Pan X, Meeldijk J, van der
Wall E, van Diest PJ and Moelans CB: Validation of DNA promoter
hypermethylation biomarkers in breast cancer-a short report. Cell
Oncol (Dordr). 37:297–303. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yi JM: DNA Methylation change profiling of
colorectal disease: Screening towards clinical use. Life (Basel).
11(412)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Etcheverry A, Aubry M, de Tayrac M,
Vauleon E, Boniface R, Guenot F, Saikali S, Hamlat A, Riffaud L,
Menei P, et al: DNA methylation in glioblastoma: Impact on gene
expression and clinical outcome. BMC Genomics.
11(701)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
LeBlanc VG and Marra MA: DNA methylation
in adult diffuse gliomas. Brief Funct Genomics. 15:491–500.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang C, Li J, Huang T, Duan S, Dai D,
Jiang D, Sui X, Li D, Chen Y, Ding F, et al: Meta-analysis of DNA
methylation biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
7:81255–81267. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Shen N, Du J, Zhou H, Chen N, Pan Y,
Hoheisel JD, Jiang Z, Xiao L, Tao Y and Mo X: A diagnostic panel of
DNA methylation biomarkers for lung adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol.
9(1281)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yang M and Park JY: DNA methylation in
promoter region as biomarkers in prostate cancer. Methods Mol Biol.
863:67–109. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Fang J, Zhang H and Jin S: Epigenetics and
cervical cancer: From pathogenesis to therapy. Tumour Biol.
35:5083–5093. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Li C, Ke J, Liu J and Su J: DNA
methylation data-based molecular subtype classification related to
the prognosis of patients with cervical cancer. J Cell Biochem.
121:2713–2724. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hernández-López R, Lorincz AT,
Torres-Ibarra L, Reuter C, Scibior-Bentkowska D, Warman R, Nedjai
B, Mendiola-Pastrana I, León-Maldonado L, Rivera-Paredez B, et al:
Methylation estimates the risk of precancer in HPV-infected women
with discrepant results between cytology and HPV16/18 genotyping.
Clin Epigenetics. 11(140)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Lorincz AT: Cancer diagnostic classifiers
based on quantitative DNA methylation. Expert Rev Mol Diagn.
14:293–305. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Clarke MA, Luhn P, Gage JC, Bodelon C,
Dunn ST, Walker J, Zuna R, Hewitt S, Killian JK, Yan L, et al:
Discovery and validation of candidate host DNA methylation markers
for detection of cervical precancer and cancer. Int J Cancer.
141:701–710. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kremer WW, Van Zummeren M, Novianti PW,
Richter KL, Verlaat W, Snijders PJF, Heideman DAM, Steenbergen RDM,
Dreyer G and Meijer CJ: Detection of hypermethylated genes as
markers for cervical screening in women living with HIV. J Int AIDS
Soc. 21(e25165)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Verlaat W, Van Leeuwen RW, Novianti PW,
Schuuring E, Meijer CJLM, Van Der Zee AGJ, Snijders PJF, Heideman
DAM, Steenbergen RDM and Wisman GBA: Host-cell DNA methylation
patterns during high-risk HPV-induced carcinogenesis reveal a
heterogeneous nature of cervical pre-cancer. Epigenetics.
13:769–778. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kong L, Wang L, Wang Z, Xiao X, Xu T, Wu
H, Wu M, Liu P and Li L: DNA methylation for cervical cancer
screening: A training set in China. Clin Epigenetics.
12(91)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Shivapurkar N and Gazdar AF: DNA
methylation-based biomarkers in non-invasive cancer screening. Curr
Mol Med. 10:123–132. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Varghese VK, Shukla V, Kabekkodu SP,
Pandey D and Satyamoorthy K: DNA methylation regulated microRNAs in
human cervical cancer. Mol Carcinog. 57:370–382. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Botezatu A, Goia-Rusanu CD, Iancu IV,
Huica I, Plesa A, Socolov D, Ungureanu C and Anton G: Quantitative
analysis of the relationship between microRNA-124a,-34b and-203
gene methylation and cervical oncogenesis. Mol Med Rep. 4:121–128.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Ehrlich M: DNA hypomethylation in cancer
cells. Epigenomics. 1:239–259. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Yin FF, Wang N, Bi XN, Yu X, Xu XH, Wang
YL, Zhao CQ, Luo B and Wang YK: Serine/threonine kinases 31(STK31)
may be a novel cellular target gene for the HPV16 oncogene E7 with
potential as a DNA hypomethylation biomarker in cervical cancer.
Virol J. 13(60)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Thangavelu PU, Krenács T, Dray E and Duijf
PHG: In epithelial cancers, aberrant COL17A1 promoter methylation
predicts its misexpression and increased invasion. Clin Epigenet.
8(120)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
García AD, Abba MC, Briceño I, Aristizabal
FA and Arregui AC: DNA methylation pattern in high-grade cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia and cancer revealed by genomewide
methylation analysis of cervical DNA. Integr Mol Med. 4:1–13.
2017.doi: 10.15761/IMM.1000309.
|
|
55
|
Miller JL and Grant PA: The role of DNA
methylation and histone modifications in transcriptional regulation
in humans. Subcell Biochem. 61:289–317. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Greer EL and Shi Y: Histone methylation: A
dynamic mark in health, disease and inheritance. Nat Rev Genet.
13:343–357. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Bannister AJ and Kouzarides T: Regulation
of chromatin by histone modifications. Cell Res. 21:381–395.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
D'Oto A, Tian QW, Davidoff AM and Yang J:
Histone demethylases and their roles in cancer epigenetics. J Med
Oncol Ther. 1:34–40. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Groves IJ, Drane ELA, Michalski M, Monahan
JM, Scarpini CG, Smith SP, Bussotti G, Várnai C, Schoenfelder S,
Fraser P, et al: Three-dimensional interactions between integrated
HPV genomes and cellular chromatin dysregulate host gene expression
in early cervical carcinogenesis. bioRxiv: Feb. 3, 2021 2021 (Epub
ahead of print). doi: 10.1101/2021.02.03.429496.
|
|
60
|
Sen P, Ganguly P and Ganguly N: Modulation
of DNA methylation by human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncoproteins
in cervical cancer. Oncol Lett. 15:11–22. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Mac M and Moody CA: Epigenetic regulation
of the human papillomavirus life cycle. Pathogens.
9(483)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Shadeo A, Chari R, Lonergan KM, Pusic A,
Miller D, Ehlen T, Van Niekerk D, Matisic J, Richards-Kortum R,
Follen M, et al: Up regulation in gene expression of chromatin
remodelling factors in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. BMC
Genomics. 9(64)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Kanwal R and Gupta S: Epigenetic
modifications in cancer. Clin Genet. 81:303–311. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Lu Y, Chan YT, Tan HY, Li S, Wang N and
Feng Y: Epigenetic regulation in human cancer: The potential role
of epi-drug in cancer therapy. Mol Cancer. 19(79)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Feng C, Dong J, Chang W, Cui M and Xu T:
The progress of methylation regulation in gene expression of
cervical cancer. Int J Genomics. 2018(8260652)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Rathinasamy B and Velmurugan BK: Role of
lncRNAs in the cancer development and progression and their
regulation by various phytochemicals. Biomed Pharmacother.
102:242–248. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Wang X, Wang HK, Li Y, Hafner M, Banerjee
NS, Tang S, Briskin D, Meyers C, Chow LT, Xie X, et al: microRNAs
are biomarkers of oncogenic human papillomavirus infections. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 111:4262–4267. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Jia W, Wu Y, Zhang Q, Gao GE, Zhang C and
Xiang Y: Expression profile of circulating microRNAs as a promising
fingerprint for cervical cancer diagnosis and monitoring. Mol Clin
Oncol. 3:851–858. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Kong Q, Tang Z, Xiang F, Jiang J, Yue H,
Wu R and Kang X: Diagnostic value of Serum hsa-mir-92a in patients
with cervical cancer. Clin Lab. 63:335–340. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Laengsri V, Kerdpin U, Plabplueng C,
Treeratanapiboon L and Nuchnoi P: Cervical cancer markers:
Epigenetics and microRNAs. Lab Med. 49:97–111. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Gibb EA, Becker-Santos DD, Enfield KS,
Guillaud M, Niekerk Dv, Matisic JP, Macaulay CE and Lam WL:
Aberrant expression of long noncoding RNAs in cervical
intraepithelial neoplasia. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 22:1557–1563.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Aalijahan H and Ghorbian S: Long
non-coding RNAs and cervical cancer. Exp Mol Pathol. 106:7–16.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Burgers WA, Blanchon L, Pradhan S, de
Launoit Y, Kouzarides T and Fuks F: Viral oncoproteins target the
DNA methyltransferases. Oncogene. 26:1650–1655. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Laurson J, Khan S, Chung R, Cross K and
Raj K: Epigenetic repression of E-cadherin by human papillomavirus
16 E7 protein. Carcinogenesis. 31:918–926. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Leonard SM, Wei W, Collins SI, Pereira M,
Diyaf A, Constandinou-Williams C, Young LS, Roberts S and Woodman
CB: Oncogenic human papillomavirus imposes an instructive pattern
of DNA methylation changes which parallel the natural history of
cervical HPV infection in young women. Carcinogenesis.
33:1286–1293. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Hsu CH, Peng KL, Jhang HC, Lin CH, Wu SY,
Chiang CM, Lee SC, Yu WC and Juan LJ: The HPV E6 oncoprotein
targets histone methyltransferases for modulating specific gene
transcription. Oncogene. 31:2335–2349. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Patel D, Huang SM, Baglia LA and McCance
DJ: The E6 protein of human papillomavirus type 16 binds to and
inhibits co-activation by CBP and p300. EMBO J. 18:5061–5072.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Bernat A, Avvakumov N, Mymryk JS and Banks
L: Interaction between the HPV E7 oncoprotein and the
transcriptional coactivator p300. Oncogene. 22:7871–7881.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Thomas MC and Chiang CM: E6 oncoprotein
represses p53-dependent gene activation via inhibition of protein
acetylation independently of inducing p53 degradation. Mol Cell.
17:251–264. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Avvakumov N, Torchia J and Mymryk JS:
Interaction of the HPV E7 proteins with the pCAF acetyltransferase.
Oncogene. 22:3833–3841. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Huang SM and McCance DJ: Down regulation
of the interleukin-8 promoter by human papillomavirus type 16 E6
and E7 through effects on CREB binding protein/p300 and P/CAF. J
Virol. 76:8710–8721. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Münger K, Baldwin A, Edwards KM, Hayakawa
H, Nguyen CL, Owens M, Grace M and Huh K: Mechanisms of human
papillomavirus-induced oncogenesis. J Virol. 78:11451–11460.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Jha S, Vande Pol S, Banerjee NS, Dutta AB,
Chow LT and Dutta A: Destabilization of TIP60 by human
papillomavirus E6 results in attenuation of TIP60-dependent
transcriptional regulation and apoptotic pathway. Mol Cell.
38:700–711. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Brehm A, Nielsen SJ, Miska EA, McCance DJ,
Reid JL, Bannister AJ and Kouzarides T: The E7 oncoprotein
associates with Mi2 and histone deacetylase activity to promote
cell growth. EMBO J. 18:2449–2458. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Longworth MS and Laimins LA: The binding
of histone deacetylases and the integrity of zinc finger-like
motifs of the E7 protein are essential for the life cycle of human
papillomavirus type 31. J Virol. 78:3533–3541. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Longworth MS, Wilson R and Laimins LA:
HPV31 E7 facilitates replication by activating E2F2 transcription
through its interaction with HDACs. EMBO J. 24:1821–1830.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
McLaughlin-Drubin ME, Crum CP and Münger
K: Human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein induces KDM6A and KDM6B
histone demethylase expression and causes epigenetic reprogramming.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:2130–2135. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Wang Y, Tong J, Lin H, Ma L and Xu Y:
CCHE1 accelerated the initiation of oral squamous cell carcinoma
through enhancing PAK2 expression by sponging miR-922. J Oral
Pathol Med. 49:636–644. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Sharma S, Mandal P, Sadhukhan T, Roy
Chowdhury R, Ranjan Mondal N, Chakravarty B, Chatterjee T, Roy S
and Sengupta S: Bridging links between long noncoding RNA HOTAIR
and HPV oncoprotein E7 in cervical cancer pathogenesis. Sci Rep.
5(11724)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Zhang J and Gao Y: Long non-coding RNA
MEG3 inhibits cervical cancer cell growth by promoting degradation
of P-STAT3 protein via ubiquitination. Cancer Cell Int.
19(175)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
He H, Liu X, Liu Y, Zhang M, Lai Y, Hao Y,
Wang Q, Shi D, Wang N, Luo XG, et al: Human papillomavirus E6/E7
and long noncoding RNA TMPOP2 mutually upregulated gene expression
in cervical cancer cells. J Virol. 93:e01808–18. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Wang X, Wang HK, McCoy JP, Banerjee NS,
Rader JS, Broker TR, Meyers C, Chow LT and Zheng ZM: Oncogenic HPV
infection interrupts the expression of tumor-suppressive miR-34a
through viral oncoprotein E6. RNA. 15:637–647. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Melar-New M and Laimins LA: Human
papillomaviruses modulate expression of microRNA 203 upon
epithelial differentiation to control levels of p63 proteins. J
Virol. 84:5212–5221. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Yao T and Lin Z: MiR-21 is involved in
cervical squamous cell tumorigenesis and regulates CCL20. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1822:248–260. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Kottaridi C, Leventakou D, Pouliakis A,
Pergialiotis V, Chrelias G, Patsouri E, Zacharatou A, Panopoulou E,
Damaskou V, Sioulas V, et al: Searching HPV genome for methylation
sites involved in molecular progression to cervical precancer. J
Cancer. 10:4588–4595. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Hsu YW, Huang RL, Su PH, Chen YC, Wang HC,
Liao CC and Lai HC: Genotype-specific methylation of HPV in
cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. J Gynecol Oncol.
28(e56)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Lorincz AT, Brentnall AR,
Scibior-Bentkowska D, Reuter C, Banwait R, Cadman L, Austin J,
Cuzick J and Vasiljević N: Validation of a DNA methylation HPV
triage classifier in a screening sample. Int J Cancer.
138:2745–2751. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Gu YY, Zhou GN, Wang Q, Ding JX and Hua
KQ: Evaluation of a methylation classifier for predicting
pre-cancer lesion among women with abnormal results between
HPV16/18 and cytology. Clin Epigenetics. 12(57)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Sahasrabuddhe VV, Luhn P and Wentzensen N:
Human papillomavirus and cervical cancer: Biomarkers for improved
prevention efforts. Future Microbiol. 6:1083–1098. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Wilting SM and Steenbergen RDM: Molecular
events leading to HPV-induced high grade neoplasia. Papillomavirus
Res. 2:85–88. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Au Yeung CL, Tsang WP, Tsang TY, Co NN,
Yau PL and Kwok TT: HPV-16 E6 upregulation of DNMT1 through
repression of tumor suppressor p53. Oncol Rep. 24:1599–1604.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Yeo-Teh NSL, Ito Y and Jha S: High-risk
human papillomaviral oncogenes E6 and E7 target key cellular
pathways to achieve oncogenesis. Int J Mol Sci.
19(1706)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Leonard SM, Wei W, Collins SI, Pereira M,
Diyaf A, Constandinou-Williams C, Young LS, Roberts S and Woodman
CB: Oncogenic human papillomavirus imposes an instructive pattern
of DNA methylation changes which parallel the natural history of
cervical HPV infection in young women. Carcinogenesis.
33:1286–1293. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Kalantari M, Osann K, Calleja-Macias IE,
Kim S, Yan B, Jordan S, Chase DM, Tewari KS and Bernard HU:
Methylation of human papillomavirus 16, 18, 31, and 45 L2 and L1
genes and the cellular DAPK gene: Considerations for use as
biomarkers of the progression of cervical neoplasia. Virology.
448:314–321. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Brentnall AR, Vasiljević N,
Scibior-Bentkowska D, Cadman L, Austin J, Szarewski A, Cuzick J and
Lorincz AT: A DNA methylation classifier of cervical precancer
based on human papillomavirus and human genes. Int J Cancer.
135:1425–1432. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Brentnall AR, Vasiljevic N,
Scibior-Bentkowska D, Cadman L, Austin J, Cuzick J and Lorincz AT:
DNA methylation assay for HPV33 contributes independent triage
information to HPV16, HPV18, HPV31, and EPB41L3 for detecting
cervical pre-cancer. Cancer Biomark. 15:669–675. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Qiagen: Products: Cervical Cancer
Screening. https://www.qiagen.com/be/products/diagnostics-and-clinical-research/sexual-reproductive-health/cervical-cancer-screening/qiasure-methylation-test-kit-eu/#productdetails.
Accessed June 16, 2021.
|
|
108
|
Dippmann C, Schmitz M, Wunsch K, Schütze
S, Beer K, Greinke C, Ikenberg H, Hoyer H, Runnebaum IB, Hansel A
and Dürst M: Triage of hrHPV-positive women: Comparison of two
commercial methylation-specific PCR assays. Clin Epigenetics.
12(171)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Schmitz M, Eichelkraut K, Schmidt D,
Zeiser I, Hilal Z, Tettenborn Z, Hansel A and Ikenberg H:
Performance of a DNA methylation marker panel using liquid-based
cervical scrapes to detect cervical cancer and its precancerous
stages. BMC Cancer. 18(1197)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Kocsis A, Takács T, Jeney C, Schaff Z,
Koiss R, Járay B, Sobel G, Pap K, Székely I, Ferenci T, et al:
Performance of a new HPV and biomarker assay in the management of
hrHPV positive women: Subanalysis of the ongoing multicenter TRACE
clinical trial (n > 6,000) to evaluate POU4F3 methylation as a
potential biomarker of cervical precancer and cancer. Int J Cancer.
140:1119–1133. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Kan YY, Liou YL, Wang HJ, Chen CY, Sung
LC, Chang CF and Liao CI: PAX1 methylation as a potential biomarker
for cervical cancer screening. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 24:928–934.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Liou YL, Zhang TL, Yan T, Yeh CT, Kang YN,
Cao L, Wu N, Chang CF, Wang HJ, et al: Combined clinical and
genetic testing algorithm for cervical cancer diagnosis. Clin
Epigenetics. 8(66)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Witjes JA, Morote J, Cornel EB, Gakis G,
van Valenberg FJP, Lozano F, Sternberg IA, Willemsen E, Hegemann
ML, Paitan Y and Leibovitch I: Performance of the Bladder EpiCheck™
Methylation Test for Patients Under Surveillance for
Non-muscle-invasive Bladder Cancer: Results of a Multicenter,
Prospective, Blinded Clinical Trial. Eur Urol Oncol. 1:307–313.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Wasserstrom A, Frumkin D, Dotan Z, Bukin
E, Gadish T, Hanuka S, Knirsh R, Darawsha AE and Leibovitch I:
MP13-15 molecular urine cytology-bladder epicheck is a novel
molecular diagnostic tool for monitoring of bladder cancer
patients. J Urol. 195(e140)2016.
|
|
115
|
D'Andrea D, Soria F, Zehetmayer S, Gust
KM, Korn S, Witjes JA and Shariat SF: Diagnostic accuracy, clinical
utility and influence on decision-making of a methylation urine
biomarker test in the surveillance of non-muscle-invasive bladder
cancer. BJU Int. 123:959–967. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Su SF, de Castro Abreu AL, Chihara Y, Tsai
Y, Andreu-Vieyra C, Daneshmand S, Skinner EC, Jones PA, Siegmund KD
and Liang G: A panel of three markers hyper- and hypomethylated in
urine sediments accurately predicts bladder cancer recurrence. Clin
Cancer Res. 20:1978–1989. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Van Kessel KE, Beukers W, Lurkin I,
Ziel-van der Made A, van der Keur KA, Boormans JL, Dyrskjøt L,
Márquez M, Ørntoft TF, Real FX, et al: Validation of a DNA
Methylation-Mutation Urine Assay to Select Patients with Hematuria
for Cystoscopy. J Urol. 197:590–595. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Feber A, Dhami P, Dong L, de Winter P, Tan
WS, Martínez-Fernández M, Paul DS, Hynes-Allen A, Rezaee S, Gurung
P, et al: UroMark-a urinary biomarker assay for the detection of
bladder cancer. Clin Epigenetics. 9(8)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Maier S, Nimmrich I, Koenig T,
Eppenberger-Castori S, Bohlmann I, Paradiso A, Spyratos F, Thomssen
C, Mueller V, Nährig J, et al: DNA-methylation of the homeodomain
transcription factor PITX2 reliably predicts risk of distant
disease recurrence in tamoxifen-treated, node-negative breast
cancer patients-Technical and clinical validation in a multi-centre
setting in collaboration with the European Organisation for
Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) PathoBiology group. Eur J
Cancer. 43:1679–1686. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Imperiale TF, Ransohoff DF, Itzkowitz SH,
Levin TR, Lavin P, Lidgard GP, Ahlquist DA and Berger BM:
Multitarget stool DNA testing for colorectal-cancer screening. N
Engl J Med. 370:1287–1297. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Oussalah A, Rischer S, Bensenane M, Conroy
G, Filhine-Tresarrieu P, Debard R, Forest-Tramoy D, Josse T,
Reinicke D, Garcia M, et al: Plasma mSEPT9: A novel circulating
cell-free DNA-based epigenetic biomarker to diagnose hepatocellular
carcinoma. EBioMedicine. 30:138–147. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Chalasani NP, Ramasubramanian T, Bruinsma
JJ, Allawi HT, Olson M, Roberts LR, Kisiel J, Reddy KR, Lidgard GP,
et al: Combined methylated DNA and protein markers: An accurate
blood-based test for early-stage detection of Hepatocellular
carcinoma. Hepatology. 70 (Suppl 1)(109)2019.
|
|
123
|
Taggart D, Roy D, Li G, Liu D, Zheng L and
Zhang K: DNA methylation biomarkers for noninvassive detection of
hepatocellular carcinoma [abstract]. SITC 2018 Abstracts 263, 2018.
https://sitc.sitcancer.org/2018/abstracts/titles/poster/.
|
|
124
|
Johannessen LE, Brandal P, Myklebust T,
Heim S, Micci F and Panagopoulos I: MGMT Gene Promoter methylation
status-Assessment of two pyrosequencing kits and three
methylation-specific PCR methods for their predictive capacity in
glioblastomas. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 15:437–448.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Gilbert MR, Dignam JJ, Armstrong TS, Wefel
JS, Blumenthal DT, Vogelbaum MA, Colman H, Chakravarti A, Pugh S,
Won M, et al: A randomized trial of bevacizumab for newly diagnosed
glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 370:699–708. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Waterhouse RL Jr, Van Neste L, Moses KA,
Barnswell C, Silberstein JL, Jalkut M, Tutrone R, Sylora J, Anglade
R, Murdock M, et al: Evaluation of an epigenetic assay for
predicting repeat prostate biopsy outcome in African American men.
Urology. 128:62–65. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Weiss G, Schlegel A, Kottwitz D, König T
and Tetzner R: Validation of the SHOX2/PTGER4 DNA Methylation
Marker Panel for Plasma-Based Discrimination between Patients with
Malignant and Nonmalignant Lung Disease. J Thorac Oncol. 12:77–84.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Hao YX, Fu Q, Guo YY, Ye M, Zhao HX, Wang
Q, Peng XM, Li QW, Wang RL and Xiao WH: Effectiveness of
circulating tumor DNA for detection of KRAS gene mutations in
colorectal cancer patients: A meta-analysis. Onco Targets Ther.
10:945–953. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Moran S, Martínez-Cardús A, Sayols S,
Musulén E, Balañá C, Estival-Gonzalez A, Moutinho C, Heyn H,
Diaz-Lagares A, de Moura MC, et al: Epigenetic profiling to
classify cancer of unknown primary: A multicentre, retrospective
analysis. Lancet Oncol. 17:1386–1395. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Snoek BC, Splunter APV, Bleeker MCG,
Ruiten MC, Heideman DAM, Rurup WF, Verlaat W, Schotman H, Gent MV,
Trommel NEV and Steenbergen RDM: Cervical cancer detection by DNA
methylation analysis in urine. Sci Rep. 9(3088)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Darwiche N: Epigenetic mechanisms and the
hallmarks of cancer: An intimate affair. Am J Cancer Res.
10:1954–1978. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Locke WJ, Guanzon D, Ma C, Liew YJ,
Duesing KR, Fung KYC and Ross JP: DNA methylation cancer
biomarkers: Translation to the clinic. Front Genet.
10(1150)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Keller S, Ridinger J, Rupp AK, Janssen JW
and Altevogt P: Body fluid derived exosomes as a novel template for
clinical diagnostics. J Transl Med. 9(86)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Meng Y, Sun J, Wang X, Hu T, Ma Y, Kong C,
Piao H, Yu T and Zhang G: Exosomes: A promising avenue for the
diagnosis of breast cancer. Technol Cancer Res Treat.
18(1533033818821421)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Bolha L, Ravnik-Glavač M and Glavač D:
Long Noncoding RNAs as biomarkers in cancer. Dis Markers.
2017(7243968)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|