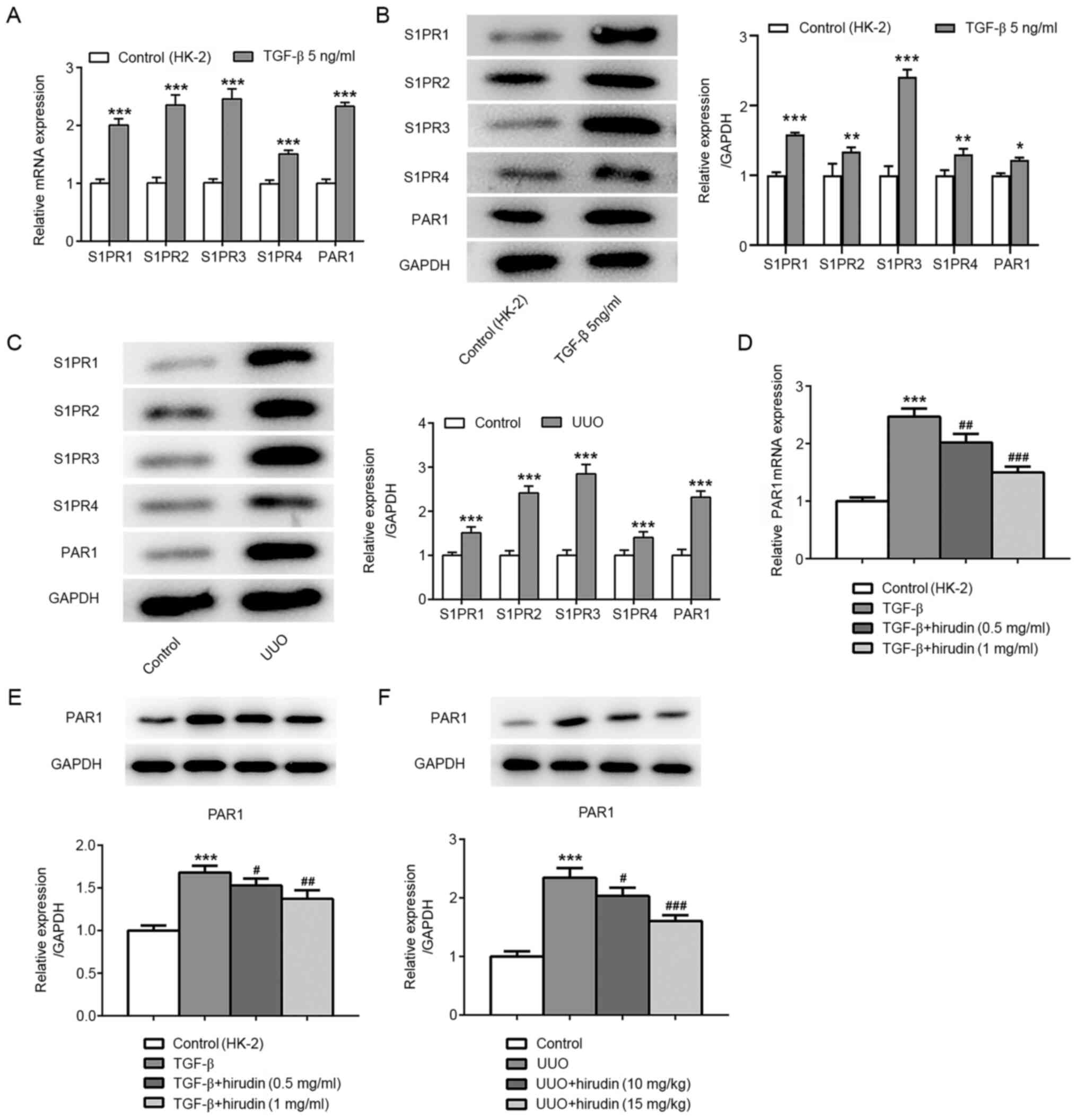
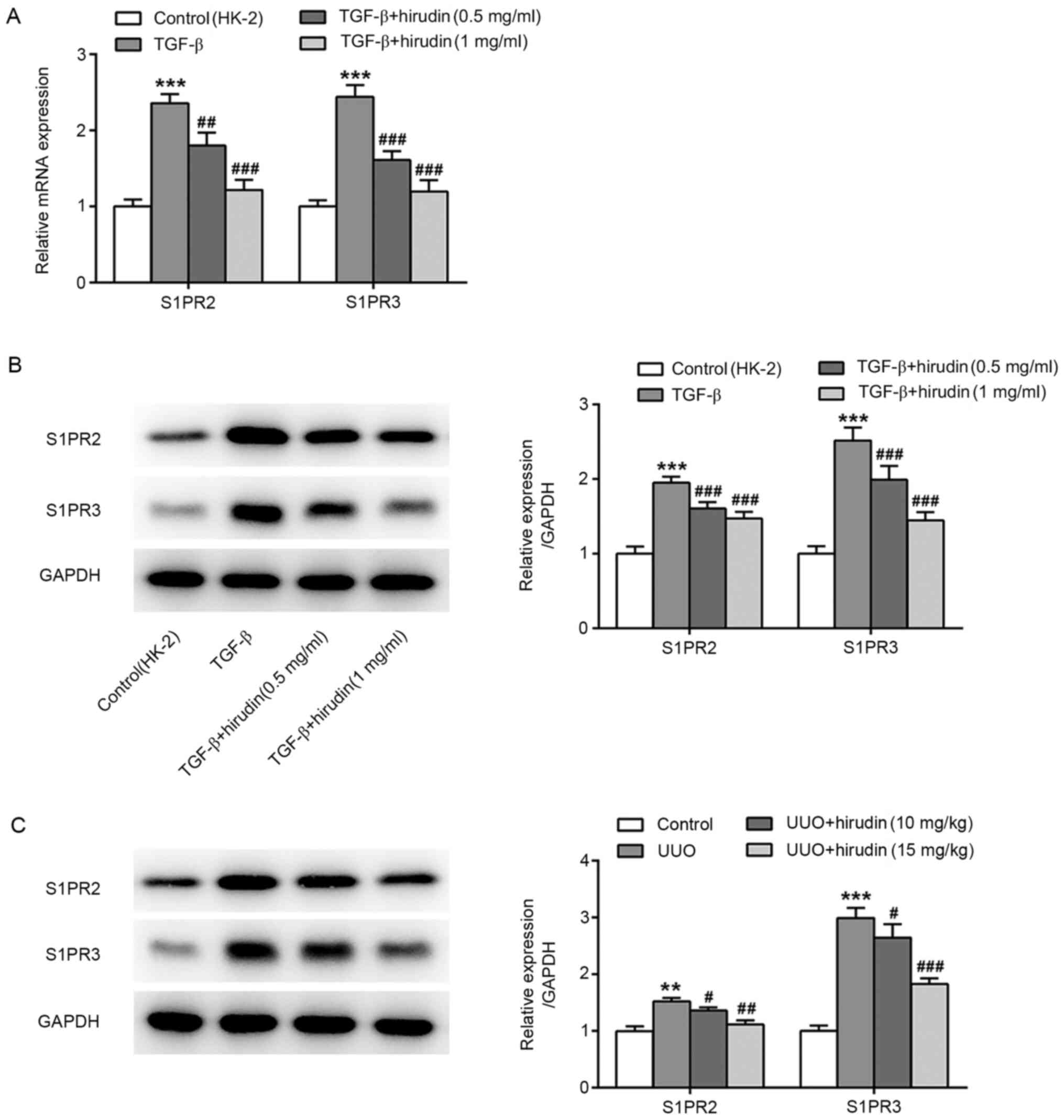
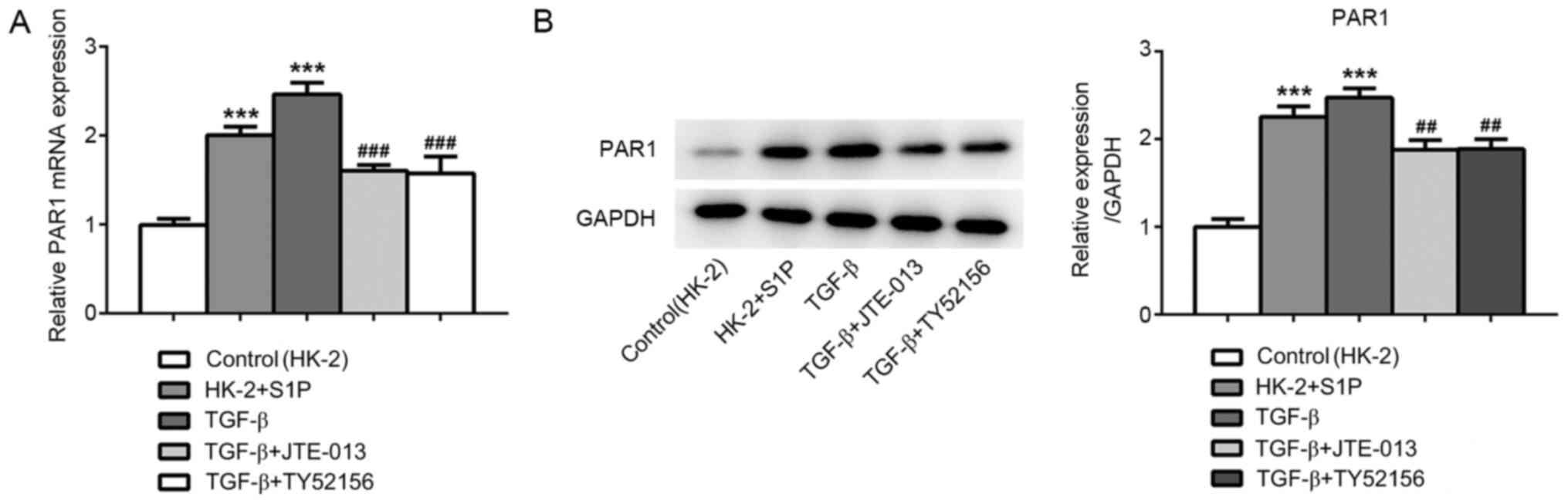
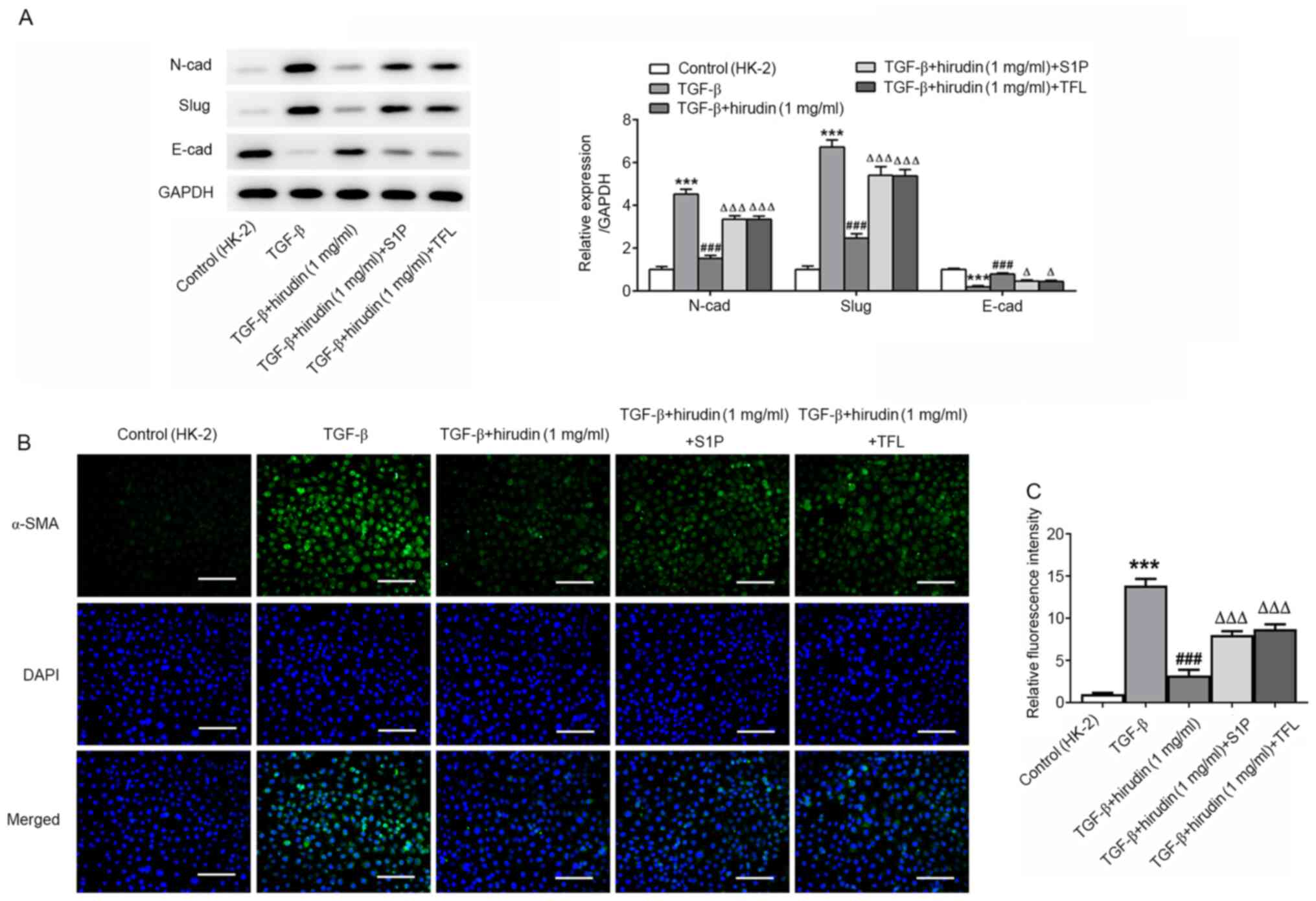
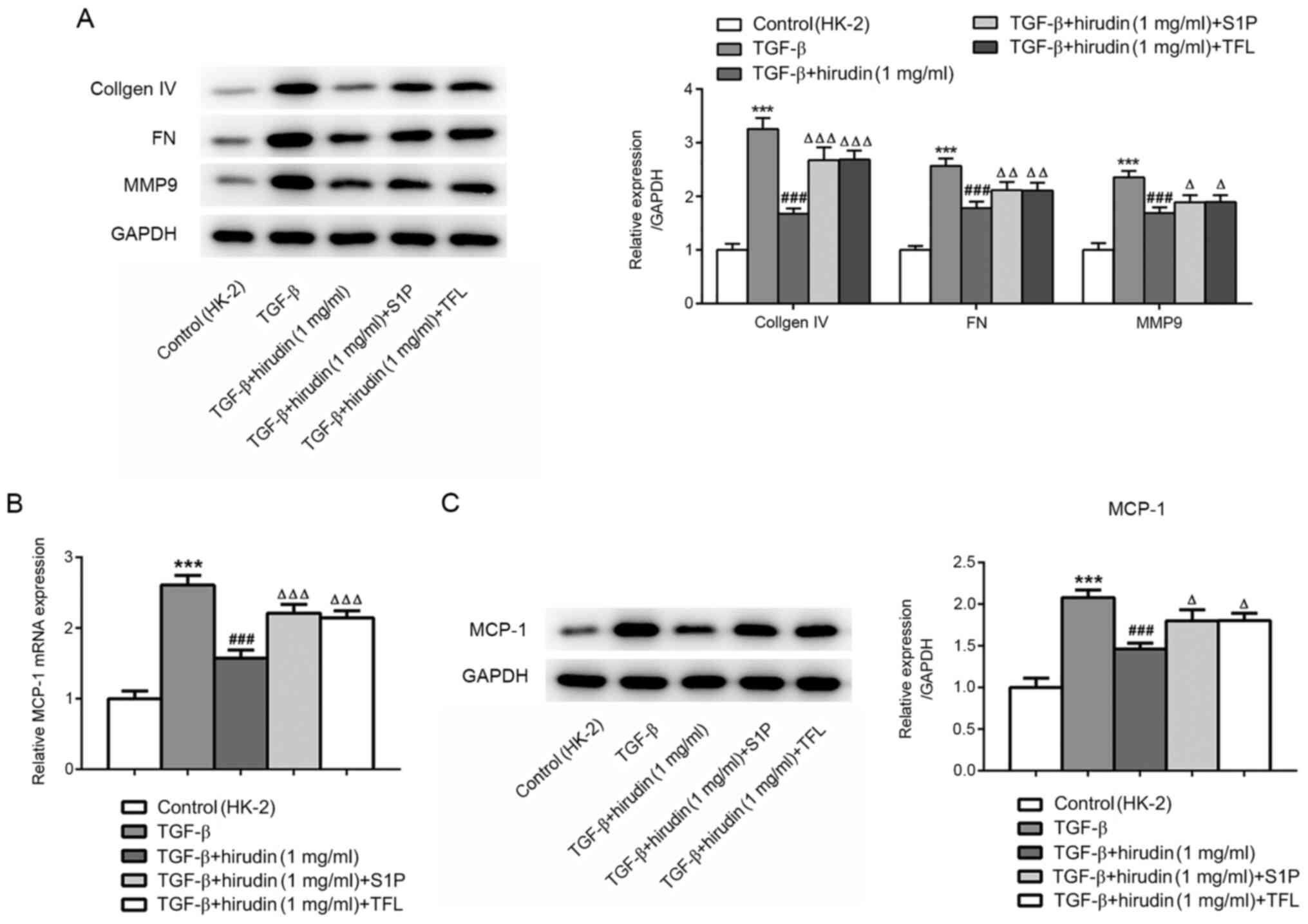
|
1
|
Martínez-Klimova E, Aparicio-Trejo OE,
Tapia E and Pedraza-Chaverri J: Unilateral ureteral obstruction as
a model to investigate fibrosis-attenuating treatments.
Biomolecules. 9(9)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wen Y, Rudemiller NP, Zhang J, Jeffs AD,
Griffiths R, Lu X, Ren J, Privratsky J and Crowley SD: Stimulating
type 1 angiotensin receptors on T lymphocytes attenuates renal
fibrosis. Am J Pathol. 189:981–988. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li R, Guo Y, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Zhu L and
Yan T: Salidroside ameliorates renal interstitial fibrosis by
inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Int J Mol
Sci. 20(1103)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lv W, Fan F, Wang Y, Gonzalez-Fernandez E,
Wang C, Yang L, Booz GW and Roman RJ: Therapeutic potential of
microRNAs for the treatment of renal fibrosis and CKD. Physiol
Genomics. 50:20–34. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Nastase MV, Zeng-Brouwers J, Wygrecka M
and Schaefer L: Targeting renal fibrosis: Mechanisms and drug
delivery systems. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 129:295–307. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Humphreys BD: Mechanisms of renal
fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 80:309–326. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chen Y, Mu L, Xing L, Li S and Fu S: Rhein
alleviates renal interstitial fibrosis by inhibiting tubular cell
apoptosis in rats. Biol Res. 52(50)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Nogueira A, Pires MJ and Oliveira PA:
Pathophysiological mechanisms of renal fibrosis: A review of animal
models and therapeutic strategies. In Vivo. 31:1–22.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ma Z, Wei Q, Zhang M, Chen JK and Dong Z:
Dicer deficiency in proximal tubules exacerbates renal injury and
tubulointerstitial fibrosis and upregulates Smad2/3. Am J Physiol
Renal Physiol. 315:F1822–F1832. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Forbes MS, Thornhill BA, Minor JJ, Gordon
KA, Galarreta CI and Chevalier RL: Fight-or-flight: Murine
unilateral ureteral obstruction causes extensive proximal tubular
degeneration, collecting duct dilatation, and minimal fibrosis. Am
J Physiol Renal Physiol. 303:F120–F129. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Isaka Y: Targeting TGF-β signaling in
kidney fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. 19(19)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang J, Zhu H, Huang L, Zhu X, Sha J, Li
G, Ma G, Zhang W, Gu M and Guo Y: Nrf2 signaling attenuates
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and renal interstitial
fibrosis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Exp Mol Pathol.
111(104296)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wakui M, Fujimori Y, Nakamura S, Kondo Y,
Kuroda Y, Oka S, Nakagawa T, Katagiri H and Murata M: Distinct
features of bivalent direct thrombin inhibitors, hirudin and
bivalirudin, revealed by clot waveform analysis and enzyme kinetics
in coagulation assays. J Clin Pathol. 72:817–824. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Deng F, Zhang J, Li Y, Wang W, Hong D, Li
G and Feng J: Hirudin ameliorates immunoglobulin A nephropathy by
inhibition of fibrosis and inflammatory response. Ren Fail.
41:104–112. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xie Y, Lan F, Zhao J and Shi W: Hirudin
improves renal interstitial fibrosis by reducing renal tubule
injury and inflammation in unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO)
mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 81(106249)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bae JS, Kim IS and Rezaie AR: Thrombin
down-regulates the TGF-beta-mediated synthesis of collagen and
fibronectin by human proximal tubule epithelial cells through the
EPCR-dependent activation of PAR-1. J Cell Physiol. 225:233–239.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sun XJ, Chen M and Zhao MH: Thrombin
contributes to anti-myeloperoxidase antibody positive IgG-mediated
glomerular endothelial cells activation through SphK1-S1P-S1PR3
signaling. Front Immunol. 10(237)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Mahajan-Thakur S, Sostmann BD, Fender AC,
Behrendt D, Felix SB, Schrör K and Rauch BH:
Sphingosine-1-phosphate induces thrombin receptor PAR-4 expression
to enhance cell migration and COX-2 formation in human monocytes. J
Leukoc Biol. 96:611–618. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang GL, Xia XL, Li XL, He FH and Li JL:
Identification and expression analysis of the MSP130-related-2 gene
from Hyriopsis cumingii. Genet Mol Res. 14:4903–4913.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hirata N, Yamada S, Shoda T, Kurihara M,
Sekino Y and Kanda Y: Sphingosine-1-phosphate promotes expansion of
cancer stem cells via S1PR3 by a ligand-independent Notch
activation. Nat Commun. 5(4806)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hsieh PF, Liu SF, Lee TC, Huang JS, Yin
LT, Chang WT, Chuang LY, Guh JY, Hung MY and Yang YL: The role of
IL-7 in renal proximal tubule epithelial cells fibrosis. Mol
Immunol. 50:74–82. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chen HA, Chen CM, Guan SS, Chiang CK, Wu
CT and Liu SH: The antifibrotic and anti-inflammatory effects of
icariin on the kidney in a unilateral ureteral obstruction mouse
model. Phytomedicine. 59(152917)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chen DQ, Cao G, Zhao H, Chen L, Yang T,
Wang M, Vaziri ND, Guo Y and Zhao YY: Combined melatonin and
poricoic acid A inhibits renal fibrosis through modulating the
interaction of Smad3 and β-catenin pathway in AKI-to-CKD continuum.
Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 10(2040622319869116)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen DQ, Feng YL, Cao G and Zhao YY:
Natural products as a source for antifibrosis therapy. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 39:937–952. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu X, Hong Q, Wang Z, Yu Y, Zou X and Xu
L: Transforming growth factor-β-sphingosine kinase 1/S1P signaling
upregulates microRNA-21 to promote fibrosis in renal tubular
epithelial cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 241:265–272.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yang Z, Xiong F, Wang Y, Gong W, Huang J,
Chen C, Liu P and Huang H: TGR5 activation suppressed S1P/S1P2
signaling and resisted high glucose-induced fibrosis in glomerular
mesangial cells. Pharmacol Res. 111:226–236. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Man XY, Chen XB, Li W, Landeck L, Dou TT,
Chen JQ, Zhou J, Cai SQ and Zheng M: Analysis of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition markers in psoriatic epidermal
keratinocytes. Open Biol. 5(150032)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xu R, Chen MY, Liang W, Chen Y and Guo MY:
Zinc deficiency aggravation of ROS and inflammatory injury leading
to renal fibrosis in mice. Biol Trace Elem Res. 199:622–632.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Posma JJ, Grover SP, Hisada Y, Owens AP
III, Antoniak S, Spronk HM and Mackman N: Roles of coagulation
proteases and PARs (protease-activated receptors) in mouse models
of inflammatory diseases. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 39:13–24.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liang D, Song Z, Liang W, Li Y and Liu S:
Metformin inhibits TGF-beta 1-induced MCP-1 expression through
BAMBI-mediated suppression of MEK/ERK1/2 signalling. Nephrology
(Carlton). 24:481–488. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Waasdorp M, de Rooij DM, Florquin S,
Duitman J and Spek CA: Protease-activated receptor-1 contributes to
renal injury and interstitial fibrosis during chronic obstructive
nephropathy. J Cell Mol Med. 23:1268–1279. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|