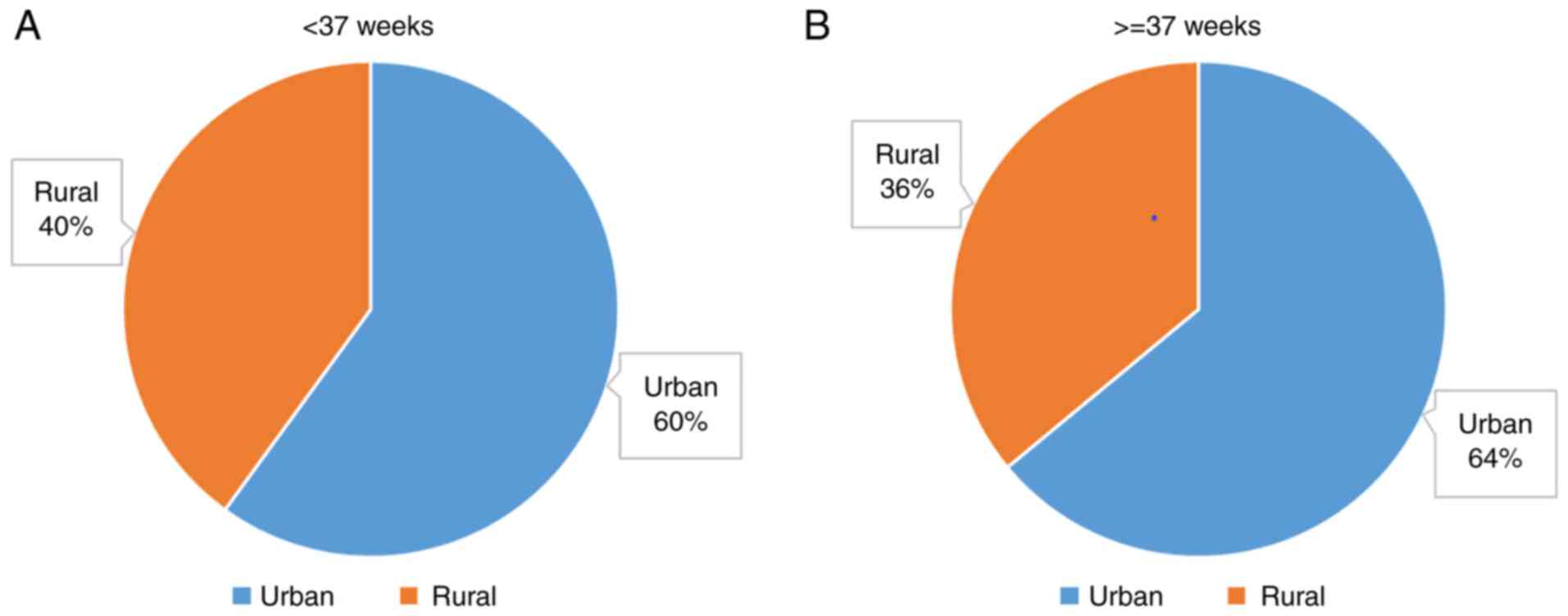
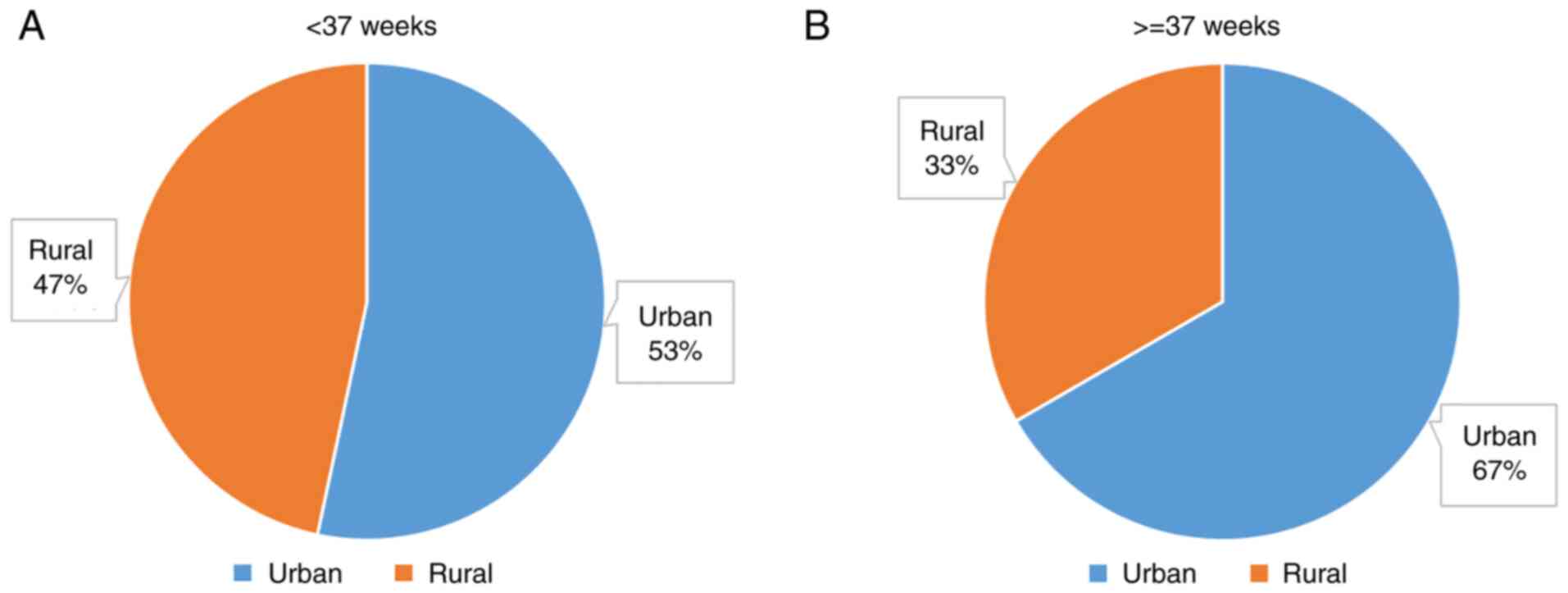
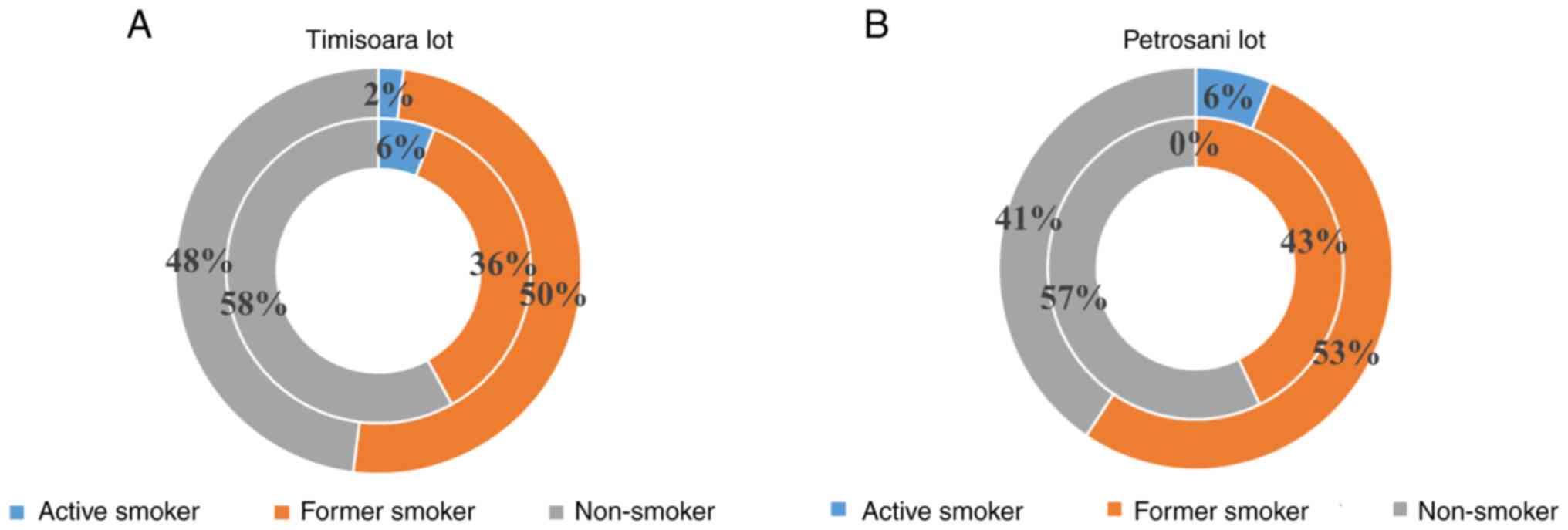
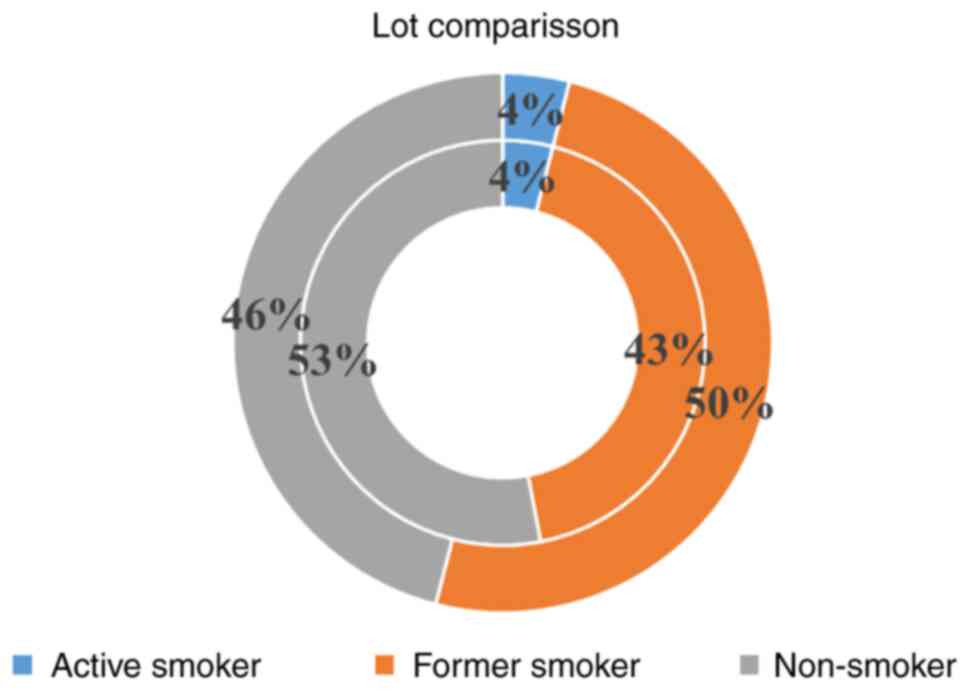
|
1
|
Cassady G and Barnett R: Amniotic fluid
electrolytes and perinatal outcome. Biol Neonat. 13:155–174.
1968.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lind T, Billewicz WZ and Cheyne GA:
Composition of amniotic fluid and maternal blood through pregnancy.
J Obstet Gynaecol Br Commonw. 78:505–512. 1971.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Harman CR: Amniotic fluid abnormalities.
Semin Perinatol. 32:288–294. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Brace RA and Wolf EJ: Normal amniotic
fluid volume changes throughout pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
161:382–388. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Elliott PM and Inman WH: Volume of liquor
amnii in normal and abnormal pregnancy. Lancet. 2:835–840.
1961.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Queenan JT, Thompson W, Whitfield CR and
Shah SI: Amniotic fluid volumes in normal pregnancies. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 114:34–38. 1972.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Underwood MA, Gilbert WM and Sherman MP:
Amniotic fluid: Not just fetal urine anymore. J Perinatol.
25:341–348. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Curran MA, Nijland MJ, Mann SE and Ross
MG: Human amniotic fluid mathematical model: Determination and
effect of intramembranous sodium flux. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
178:484–490. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Massa G, Proesmans W, Devlieger H,
Vandenberghe K, Van Assche A and Eggermont E: Electrolyte
composition of the amniotic fluid in Bartter syndrome. Eur J Obstet
Gynecol Reprod Biol. 24:335–340. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fotiou M, Michaelidou AM, Masoura S,
Menexes G, Koulourida V, Biliaderis CG, Tarlatzis BC and
Athanasiadis AP: Second trimester amniotic fluid uric acid,
potassium, and cysteine to methionine ratio levels as possible
signs of early preeclampsia: A case report. Taiwan J Obstet
Gynecol. 55:874–876. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Weiss M, Frenkel Y, Dolev E, Barkai G,
Mashiach S and Sela BA: Increased amniotic fluid divalent cation
concentrations in preeclampsia. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol.
6:71–77. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Dawson EB, Evans DR and Nosovitch J:
Third-trimester amniotic fluid metal levels associated with
preeclampsia. Arch Environ Health. 54:412–415. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Honkonen E, Näntö V, Hyörä H, Vuorinen K
and Erkkola R: Trace elements and antibacterial activity in
amniotic fluid. Neonatology. 50:21–26. 1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Scane TM and Hawkins DF: Antibacterial
activity in human amniotic fluid: Relationship to zinc and
phosphate. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 91:342–348. 1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shankar AH and Prasad AS: Zinc and immune
function: The biological basis of altered resistance to infection.
Am J Clin Nutr. 68 (Suppl 2):447S–463S. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Dawson EB, Evans DR, Harris WA and Van
Hook JW: Amniotic fluid B12, calcium, and lead levels associated
with neural tube defects. Am J Perinatol. 16:373–378.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Asefi Y, Gohari Mahmoudabad A, Habibian
Sezavar A, Mirshahvaladi S, Abyadeh M and Abyareh M: Association
between maternal cadmium exposure and preterm birth: A
meta-analysis. Int J Environ Health Res. 7:1–10. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Xu L, Dai H, Skuza L and Wei S:
Comprehensive exploration of heavy metal contamination and risk
assessment at two common smelter sites. Chemosphere.
285(131350)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Ilechukwu I, Osuji LC, Okoli CP, Onyema MO
and Ndukwe GI: Assessment of heavy metal pollution in soils and
health risk consequences of human exposure within the vicinity of
hot mix asphalt plants in Rivers State, Nigeria. Environ Monit
Assess. 193(461)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Alsubih M, El Morabet R, Khan RA, Khan NA,
Ul Haq Khan M, Ahmed S, Qadir A and Changani F: Occurrence and
health risk assessment of arsenic and heavy metals in groundwater
of three industrial areas in Delhi, India. Environ Sci Pollut Res
Int. 28:63017–63031. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wongsasuluk P, Chotpantarat S, Siriwong W
and Robson M: Human biomarkers associated with low concentrations
of arsenic (As) and lead (Pb) in groundwater in agricultural areas
of Thailand. Sci Rep. 11(13896)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wang Y, Qian P, Li D, Chen H and Zhou X:
Assessing risk to human health for heavy metal contamination from
public point utility through ground dust: A case study in Nantong,
China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2021 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
23
|
Llanos MN and Ronco AM: Fetal growth
restriction is related to placental levels of cadmium, lead and
arsenic but not with an-tioxidant activities. Reprod Toxicol.
27:88–92. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Smeester L, Martin EM, Cable P, Bodnar W,
Boggess K, Vora NL and Fry RC: Toxic metals in amniotic fluid and
altered gene expression in cell-free fetal RNA. Prenat Diagn.
37:1364–1366. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Bonithon-Kopp C, Huel G, Moreau T and
Wendling R: Prenatal exposure to lead and cadmium and psychomotor
development of the child at 6 years. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol.
8:307–310. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ebrahim K and Ashtarinezhad A: The
association of amniotic fluid cadmium levels with the risk of
preeclampsia, prematurity and low birth weight. Iran J Neonatol.
6:1–6. 2015.
|
|
27
|
Lewis M, Worobey J, Ramsay DS and
McCormack M: Prenatal exposure to heavy metals: Effect on childhood
cognitive skills and health status. Pediatrics. 89 (6 Pt
1):1010–1015. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Pogorelova TN, Linde VA, Gunko VO and
Selyutina SN: The imbalance of metal-containing proteins and free
metal ions in the amniotic fluid during fetal growth. Biomed Khim.
62:69–72. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Russian).
|
|
29
|
Campbell J, Wathen N, Macintosh M, Cass P,
Chard T and Mainwaring Burton R: Biochemical composition of
amniotic fluid and extraembryonic coelomic fluid in the first
trimester of pregnancy. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 99:563–565.
1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Leela KV and Babu K: Study of biochemical
parameters in amniotic fluid for assessment of foetal maturity in
cases of nor-mal pregnancy. J Evid Based Med Hlthcar. 3:8394–8399.
2016.
|
|
31
|
Gagnon R, Harding R and Brace R: Amniotic
fluid and fetal urinary responses to severe placental insufficiency
in sheep. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 186:1076–1084. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gómez de la F CL, Novoa P JM and Caviedes
R N: Bartter syndrome: An infrequent tubulopathy of prenatal onset.
Rev Chil Pediatr. 90:437–442. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In English,
Spanish).
|
|
33
|
Tong XL, Wang L, Gao TB, Qin YG, Qi YQ and
Xu YP: Potential function of amniotic fluid in fetal
development-novel insights by comparing the composition of human
amniotic fluid with umbilical cord and maternal serum at mid and
late gestation. J Chin Med Assoc. 72:368–373. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sabatier M, Garcia-Rodenas CL, Castro CA,
Kastenmayer P, Vigo M, Dubascoux S, Andrey D, Nicolas M, Payot JR,
Bordier V, et al: Longitudinal changes of mineral concentrations in
preterm and term human milk from lactating swiss women. Nutrients.
11(1855)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cruikshank DP, Pitkin RM, Reynolds WA,
Williams GA and Hargis GK: Calcium-regulating hormones and ions in
amniotic fluid. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 136:621–625. 1980.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Shah MC, Modi UJ, Bhatt RV and Mistry KP:
Amniotic fluid composition in abnormal pregnancies. Indian J
Pediatr. 50:271–274. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Pettit BR, Baker SP and King GS: The
composition of amniotic fluid in pregnancies complicated by fetal
anencephaly or Spina Bifida. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 86:637–641.
1979.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Mimouni F, Miodovnik M, Tsang RC, Callahan
J and Shaul P: Decreased amniotic fluid magnesium concentration in
diabetic pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 69:12–14. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Gortzak-Uzan L, Mezad D, Smolin A, Friger
M, Huleihel M and Hallak M: Increasing amniotic fluid magnesium
concentrations with stable maternal serum levels: A prospective
clinical trial. J Reprod Med. 50:817–820. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hovdenak N and Haram K: Influence of
mineral and vitamin supplements on pregnancy outcome. Eur J Obstet
Gynecol Reprod Biol. 164:127–132. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Adama van Scheltema PN, In't Anker PS,
Vereecken A, Vandenbussche FP, Kanhai HH and Devlieger R:
Biochemical composition of amniotic fluid in pregnancies
complicated with twin-twin transfusion syndrome. Fetal Diagn Ther.
20:186–189. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Correia-Branco A, Rincon MP, Pereira LM
and Wallingford MC: Inorganic phosphate in the pathogenesis of
pregnancy-related complications. Int J Mol Sci.
21(5283)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Schlievert P, Johnson W and Galask RP:
Bacterial growth inhibition by amniotic fluid. VII. The effect of
zinc supplementation on bacterial inhibitory activity of amniotic
fluids from gestation of 20 weeks. Am J Obstet Gynecol.
127:603–608. 1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tomblin J, Davis B and Larsen B: Phosphate
content of human amniotic fluid and its relationship to bacterial
growth inhibition. Am J Reprod Immunol Microbiol. 13:33–35.
1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Pier SM: The role of heavy metals in human
health. Tex Rep Biol Med. 33:85–106. 1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chowdhury R, Ramond A, O'Keeffe LM,
Shahzad S, Kunutsor SK, Muka T, Gregson J, Willeit P, Warnakula S,
Khan H, et al: Environmental toxic metal contaminants and risk of
cardiovascular disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ.
362(k3310)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kim DW, Ock J, Moon KW and Park CH:
Association between Pb, Cd, and Hg exposure and liver injury among
Korean adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health.
18(6783)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Liu YH, Wang CW, Wu DW, Lee WH, Chen YC,
Li CH, Tsai CC, Lin WY, Chen SC, Hung CH, et al: Association of
heavy metals with overall mortality in a Taiwanese population.
Nutrients. 13(2070)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Durá Travé T, da Cunha Ferreira RM,
Monreal I, Ezcurdia Gurpegui M and Villa-Elizaga I: Zinc
concentration of amniotic fluid in the course of pregnancy and its
relationship to fetal weight and length. Gynecol Obstet Invest.
18:152–155. 1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Kumar V, Kumar A, Singh K, Avasthi K and
Kim JJ: Neurobiology of zinc and its role in neurogenesis. Eur J
Nutr. 60:55–64. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Boskabadi H, Maamouri G, Akhondian J,
Ashrafzadeh F, Boskabadi A, Faramarzi R, Heidar E, Pourbadakhshan
N, Shojaei SRH, Zakerihamidi M, et al: Comparison of birth weights
of neonates of mothers receiving vs. not receiving zinc supplement
at pregnancy. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 21(187)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Vickram S, Rohini K, Srinivasan S, Nancy
Veenakumari D, Archana K, Anbarasu K, Jeyanthi P, Thanigaivel S,
Gulothungan G, Rajendiran N and Srikumar PS: Role of zinc (Zn) in
human reproduction: A journey from initial spermatogenesis to
childbirth. Int J Mol Sci. 22(2188)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Jankovic-Karasoulos T, McAninch D, Dixon
C, Leemaqz SY, François M, Leifert WR, McCullough D, Ricciardelli
C, Roberts CT and Bianco-Miotto T: The effect of zinc on human
trophoblast proliferation and oxidative stress. J Nutr Biochem.
90(108574)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Vetchý MPJVKKD: Biological role of copper
as an essential trace element in the human organism. Ceska Slov
Farm. 67:143–153. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lisa SH, Akhter QS, Nessa A, Munna MA and
Eza LH: Serum copper level and its relation with blood pressure and
urinary protein level in preeclampsia. Mymensingh Med J.
30:473–477. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Sak S, Barut M, Çelik H, Incebiyik A,
Ağaçayak E, Uyanikoglu H, Kirmit A and Sak M: Copper and
ceruloplasmin levels are closely related to the severity of
preeclampsia. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 33:96–102.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Schaefer M and Gitlin JD: Genetic
disorders of membrane transport. IV. Wilson's disease and Menkes
disease. Am J Physiol. 276:G311–G314. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Tümer Z, Tønnesen T, Böhmann J, Marg W and
Horn N: First trimester prenatal diagnosis of Menkes disease by DNA
analysis. J Med Genet. 31:615–617. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Gu YH, Kodama H, Sato E, Mochizuki D,
Yanagawa Y, Takayanagi M, Sato K, Ogawa A, Ushijima H and Lee CC:
Prenatal diagnosis of Menkes disease by genetic analysis and copper
measurement. Brain Dev. 24:715–718. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Lorincz MT: Wilson disease and related
copper disorders. Handb Clin Neurol. 147:279–292. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Satish K and Trivedi AV: A Review on role
of nickel in the biological system. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci.
5:719–727. 2016.
|
|
62
|
Savolainen H: Biochemical and clinical
aspects of nickel toxicity. Rev Environ Health. 11:167–173.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Zambelli B and Ciurli S: Nickel and human
health. Met Ions Life Sci. 13:321–357. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Moradnia M, Attar HM, Heidari Z, Mohammadi
F and Kelishadi R: Prenatal exposure to chromium (Cr) and nickel
(Ni) in a sample of Iranian pregnant women: Urinary levels and
associated socio-demographic and lifestyle factors. Environ Sci
Pollut Res Int. 28:63412–63421. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Wang XW, Gu JY, Li Z, Song YF, Wu WS and
Hou YP: Gestational age and dose influence on placental transfer of
63Ni in rats. Placenta. 31:305–311. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Hou YP, Gu JY, Shao YF, Song YF, Jing YH,
Wu WS and Pu S: The characteristics of placental transfer and
tissue concentrations of nickel in late gestational rats and
fetuses. Placenta. 32:277–282. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Kakhlon OR and Cabantchik ZI: The labile
iron pool: Characterization, measurement, and participation in
cellular processes(1). Free Radic Biol Med. 33:1037–1046.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Ganz T: Hepcidin, a key regulator of iron
metabolism and mediator of anemia of inflammation. Blood.
102:783–788. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Trumbo P, Yates AA, Schlicker S and Poos
M: Dietary reference intakes: Vitamin A, vitamin K, arsenic, boron,
chromium, copper, iodine, iron, manganese, molybdenum, nickel,
silicon, vanadium, and zinc. J Am Diet Assoc. 101:294–301.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Taylor CL and Brannon PM: Introduction to
workshop on iron screening and supplementation in iron-replete
pregnant women and young children. Am J Clin Nutr. 106 (Suppl
6):1547S–1554S. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Milman N: Iron in pregnancy: How do we
secure an appropriate iron status in the mother and child? Ann Nutr
Metab. 59:50–54. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Chigladze M: The predictive value of the
mother's risk factors in formation of fetal developmental delay.
Glob Pediatr Health. 8(2333794X21999149)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Fisher AL, Sangkhae V, Presicce P,
Chougnet CA, Jobe AH, Kallapur SG, Tabbah S, Buhimschi CS,
Buhimschi IA, Ganz T and Nemeth E: Fetal and amniotic fluid iron
homeostasis in healthy and complicated murine, macaque, and human
pregnancy. JCI Insight. 5(e135321)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Gulec S, Anderson GJ and Collins JF:
Mechanistic and regulatory aspects of intestinal iron absorption.
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 307:G397–G409.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Burke RM, Leon JS and Suchdev PS:
Identification, prevention and treatment of iron deficiency during
the first 1000 days. Nutrients. 6:4093–4114. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Bacon BR, Adams PC, Kowdley KV, Powell LW
and Tavill AS: American Association for the Study of Liver
Diseases. Diagnosis and management of hemochromatosis: 2011
practice guideline by the American association for the study of
liver diseases. Hepatology. 54:328–343. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Wessling-Resnick M: Excess iron:
Considerations related to development and early growth. Am J Clin
Nutr. 106 (Suppl 6):1600S–1605S. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Tellez-Plaza M, Guallar E, Howard BV,
Umans JG, Francesconi KA, Goessler W, Silbergeld EK, Devereux RB
and Navas-Acien A: Cadmium exposure and incident cardiovascular
disease. Epidemiology. 24:421–429. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Tellez-Plaza M, Jones MR, Dominguez-Lucas
A, Guallar E and Navas-Acien A: Cadmium exposure and clinical
cardiovascular disease: A systematic review. Curr Atheroscler Rep.
15(356)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Skolarczyk J, Pekar J,
Skórzyńska-Dziduszko K and Łabądź D: Role of heavy metals in the
development of obesity: A review of research. J Elem. 23:1271–1280.
2018.
|
|
81
|
Dobrescu A, Copaescu C, Zmeu B, Duta C,
Bedreag OH, Stoica L, Tarta C, Rogobete AF and Lazar F: Ghrelin
levels and hunger sensation after laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy
compared with laparoscopic greater curvature plication in obese
patients. Clin Lab. 66:2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Luevano J and Damodaran C: A review of
molecular events of cadmium-induced carcinogenesis. J Environ
Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 33:183–194. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Joseph P: Mechanisms of cadmium
carcinogenesis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 238:272–279.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Liu J, Zeng L, Zhuang S, Zhang C, Li Y,
Zhu J and Zhang W: Cadmium exposure during prenatal development
causes progesterone disruptors in multiple generations via
steroidogenic enzymes in rat ovarian granulosa cells. Ecotoxicol
Environ Saf. 201(110765)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Yi SJ, Xiong YW, Zhu HL, Dai LM, Cao XL,
Liu WB, Shi XT, Zhou GX, Liu AY, Zhao LL, et al: Environmental
cadmium exposure during pregnancy causes diabetes-like phenotypes
in mouse offspring: Association with oxidative stress in the fetal
liver. Sci Total Environ. 777(146006)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Zhu J, Huang Z, Yang F, Zhu M, Cao J, Chen
J, Lin Y, Guo S, Li J and Liu Z: Cadmium disturbs epigenetic
modification and induces DNA damage in mouse preimplantation
embryos. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 219(112306)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Liao Y, Zheng H, Wu L, He L, Wang Y, Ou Y,
Yang H, Peng S, Chen F, Wang X and Zhao J: Cadmium cytotoxicity and
possible mechanisms in human trophoblast HTR-8/SVneo cells. Environ
Toxicol. 36:1111–1124. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Amegah AK, Sewor C and Jaakkola JJK:
Cadmium exposure and risk of adverse pregnancy and birth outcomes:
A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of cohort and
cohort-based case-control studies. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol.
31:299–317. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Gonzalez-Nahm S, Nihlani K, S House J, L
Maguire R, G Skinner H and Hoyo C: Associations between maternal
cadmium exposure with risk of preterm birth and low after birth
weight effect of mediterranean diet adherence on affected prenatal
outcomes. Toxics. 8(90)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Kaur M, Sharma P, Kaur R and Khetarpal P:
Increased incidence of spontaneous abortions on exposure to cadmium
and lead: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Gynecol
Endocrinol. 25:1–6. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Chan TF, Su JH, Chung YF, Hsu YH, Yeh YT,
Jong SB and Yuan SS: Amniotic fluid and maternal serum leptin
levels in pregnant women who subsequently develop preeclampsia. Eur
J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 108:50–53. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Akhtar E, Roy AK, Haq MA, von Ehrenstein
OS, Ahmed S, Vahter M, Ekstrom EC, Kippler M, Wagatsuma Y and Raqib
R: A longitudinal study of rural Bangladeshi children with
long-term arsenic and cadmium exposures and biomarkers of
cardiometabolic diseases. Environ Pollut.
271(116333)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Hunter P: A toxic brew we cannot live
without, Micronutrients give insights into the interplay between
geochemistry and evolutionary biology. EMBO Rep. 9:15–18.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Uthus EO: Evidence for arsenic
essentiality. Environ Geochem Health. 14:55–58. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Platanias LC: Biological responses to
arsenic compounds. J Biol Chem. 284:18583–18587. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Wisessaowapak C, Watcharasit P and
Satayavivad J: Arsenic disrupts neuronal insulin signaling through
in-creasing free PI3K-p85 and decreasing PI3K activity. Toxicol
Lett. 349:40–50. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Navas-Acien A and Guallar E: Measuring
Arsenic Exposure, Metabolism, and Biological effects: The role of
urine proteomics. Toxicol Sci. 106:1–4. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Wang SX, Wang ZH, Cheng XT, Li J, Sang ZP,
Zhang XD, Han LL, Qiao XY, Wu ZM and Wang ZQ: Arsenic and fluoride
exposure in drinking water: Children's IQ and growth in Shanyin
county, Shanxi province, China. Environ Health Perspect.
115:643–647. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Skogheim TS, Weyde KVF, Engel SM, Aase H,
Surén P, Øie MG, Biele G, Reichborn-Kjennerud T, Caspersen IH,
Hornig M, et al: Metal and essential element concentrations during
pregnancy and associations with autism spectrum disorder and
attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children. Environ Int.
152(106468)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Vahter M: Effects of arsenic on maternal
and fetal health. Annu Rev Nutr. 29:381–399. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Farzan SF, Chen Y, Wu F, Jiang J, Liu M,
Baker E, Korrick SA and Karagas MR: Blood pressure changes in
relation to arsenic exposure in a US pregnancy cohort. Environ
Health Perspect. 123:999–1006. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Ekong EB, Jaar BG and Weaver VM:
Lead-related nephrotoxicity: A review of the epidemiologic
evidence. Kidney Int. 70:2074–2084. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Navas-Acien A, Guallar E, Silbergeld EK
and Rothenberg SJ: Lead exposure and cardiovascular disease-a
systematic review. Environ Health Perspect. 115:472–482.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Park SK, O'Neill MS, Vokonas PS, Sparrow
D, Wright RO, Coull B, Nie H, Hu H and Schwartz J: Air pollution
and heart rate variability: Effect modification by chronic lead
exposure. Epidemiology. 19:111–120. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
White LD, Cory-Slechta DA, Gilbert ME,
Tiffany-Castiglioni E, Zawia NH, Virgolini M, Rossi-George A,
Lasley SM, Qian YC and Basha MR: New and evolving concepts in the
neurotoxicology of lead. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 225:1–27.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Bouchard MF, Bellinger DC, Weuve J,
Matthews-Bellinger J, Gilman SE, Wright RO, Schwartz J and
Weisskopf MG: Blood lead levels and major depressive disorder,
panic disorder, and generalized anxiety disorder in US young
adults. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 66:1313–1319. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Meyer PA, McGeehin MA and Falk H: A global
approach to childhood lead poisoning prevention. Int J Hyg Environ
Health. 206:363–369. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Lanphear BP, Hornung R, Khoury J, Yolton
K, Baghurst P, Bellinger DC, Canfield RL, Dietrich KN, Bornschein
R, Greene T, et al: Low-level environmental lead exposure and
children's intellectual function: An international pooled analysis.
Environ Health Perspect. 113:894–899. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Bellinger DC: Very low lead exposures and
children's neurodevelopment. Curr Opin Pediatr. 20:172–177.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Saylor C, Tamayo-Ortiz M, Pantic I,
Amarasiriwardena C, McRae N, Estrada-Gutierrez G, Parra-Hernandez
S, Tolentino MC, Baccarelli AA, Fadrowski JJ, et al: Prenatal blood
lead levels and reduced preadolescent glomerular filtration rate:
Modification by body mass index. Environ Int.
154(106414)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Hsieh CY, Jung CR, Lin CY and Hwang BF:
Combined exposure to heavy metals in PM2.5 and pediatric
asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 147:2171–2180 e13. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Wang M, Xia W, Zeng Q, Zhang W, Qian X,
Bao S, Zhou A, Li Y and Xu S: Associations between prenatal and
postnatal lead exposure and preschool children humoral and cellular
immune responses. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf.
207(111536)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Lee S, Park SK, Park H, Lee W, Kwon JH,
Hong YC, Ha M, Kim Y, Lee B and Ha E: Prenatal heavy metal
exposures and atopic dermatitis with gender difference in
6-month-old infants using multipollutant analysis. Environ Res.
195(110865)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Bellinger DC: Teratogen update: Lead and
pregnancy. Birth Defects Res A Clin Mol Teratol. 73:409–420.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Goto Y, Mandai M, Nakayama T, Yamazaki S,
Nakayama SF, Isobe T, Sato T and Nitta H: Association of prenatal
maternal blood lead levels with birth outcomes in the Japan
Environment and Children's Study (JECS): A nationwide birth cohort
study. Int J Epidemiol. 50:156–164. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Wu SZ, Xu HY, Chen Y, Chen Y, Zhu QL, Tan
MH and Zhang MM: Association of blood lead levels with
preeclampsia: A cohort study in China. Environ Res.
195(110822)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Irwinda R, Wibowo N and Putri AS: The
concentration of micronutrients and heavy metals in maternal serum,
placenta, and cord blood: A cross-sectional study in preterm birth.
J Pregnancy. 2019(5062365)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Park J, Kim J, Kim E, Kim WJ and Won S:
Prenatal lead exposure and cord blood DNA methylation in the Korean
Exposome Study. Environ Res. 195(110767)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Tatsuta N, Nakai K, Kasanuma Y,
Iwai-Shimada M, Sakamoto M, Murata K and Satoh H: Prenatal and
postnatal lead exposures and intellectual development among
12-year-old Japanese children. Environ Res.
189(109844)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Tomska N, Kosik-Bogacka DI,
Łanocha-Arendarczyk N, Szylińska A, Kotfis K, Sipak-Szmigiel O and
Rotter I: Relationship between concentrations of elements and
geographic location in Poland. Ann Agric Environ Med. 28:283–290.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Khanam R, Kumar I, Oladapo-Shittu O, Twose
C, Islam AA, Biswal SS, Raqib R and Baqui AH: Prenatal
environmental metal exposure and preterm birth: A scoping review.
Int J Environ Res Public Health. 18(573)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Szukalska M, Merritt TA, Lorenc W,
Sroczyńska K, Miechowicz I, Komorowicz I, Mazela J, Barałkiewicz D
and Florek E: Toxic metals in human milk in relation to tobacco
smoke exposure. Environ Res. 197(111090)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Karakis I, Landau D, Gat R, Shemesh N,
Tirosh O, Yitshak-Sade M, Sarov B and Novack L: Maternal metal
concentration during gestation and pediatric morbidity in children:
An exploratory analysis. Environ Health Prev Med.
26(40)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Riaz M, Lewis S, Naughton F and Ussher M:
Predictors of smoking cessation during pregnancy: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Addiction. 113:610–622. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Gomez-Roig MD, Marchei E, Sabra S, Busardò
FP, Mastrobattista L, Pichini S, Gratacós E and Garcia-Algar O:
Maternal hair testing to disclose self-misreporting in drinking and
smoking behavior during pregnancy. Alcohol. 67:1–6. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Benowitz NL, Hukkanen J and Jacob P III:
Nicotine chemistry, metabolism, kinetics and biomarkers. Handb Exp
Pharmacol. 29–60. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
White AJ, O'Brien KM, Jackson BP and
Karagas MR: Urine and toenail cadmium levels in pregnant women: A
reliability study. Environ Int. 118:86–91. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|