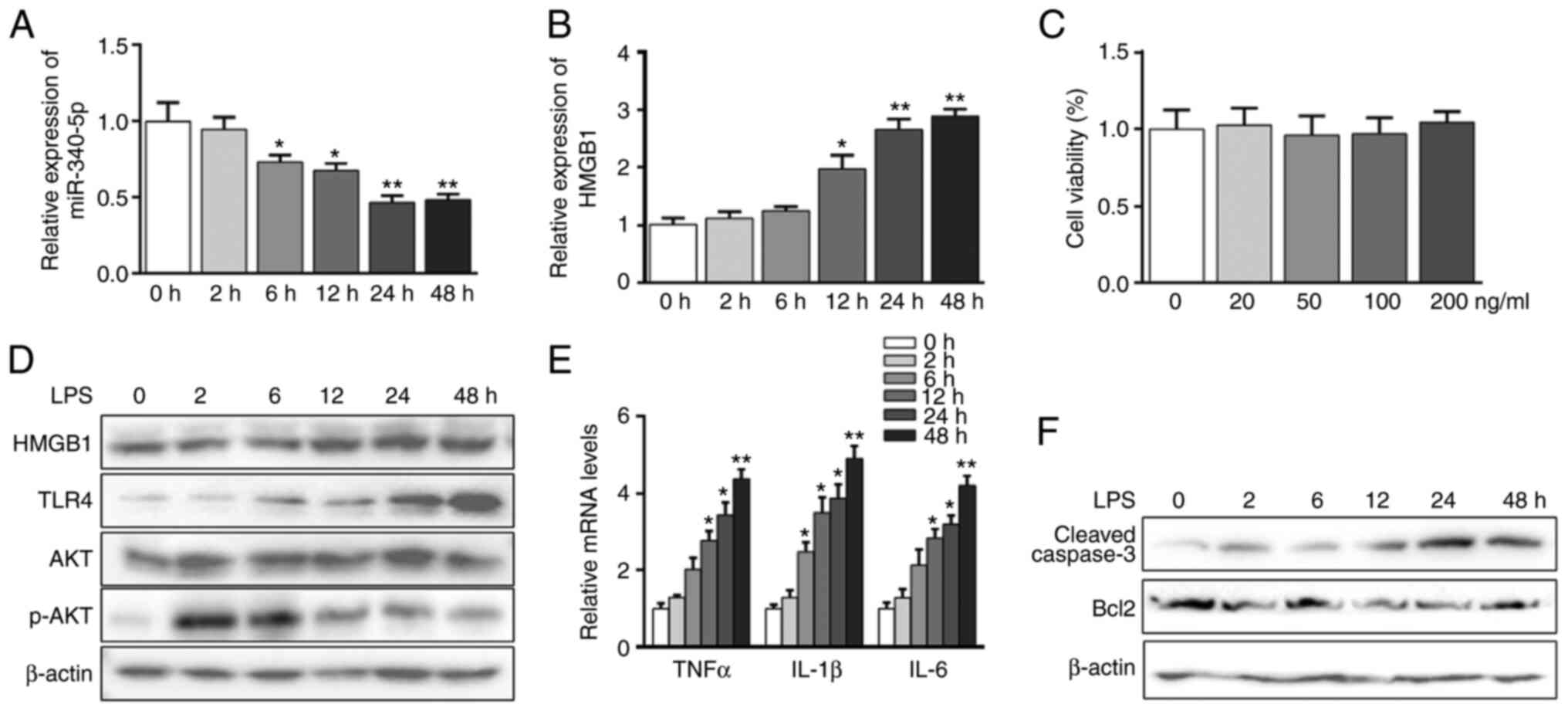
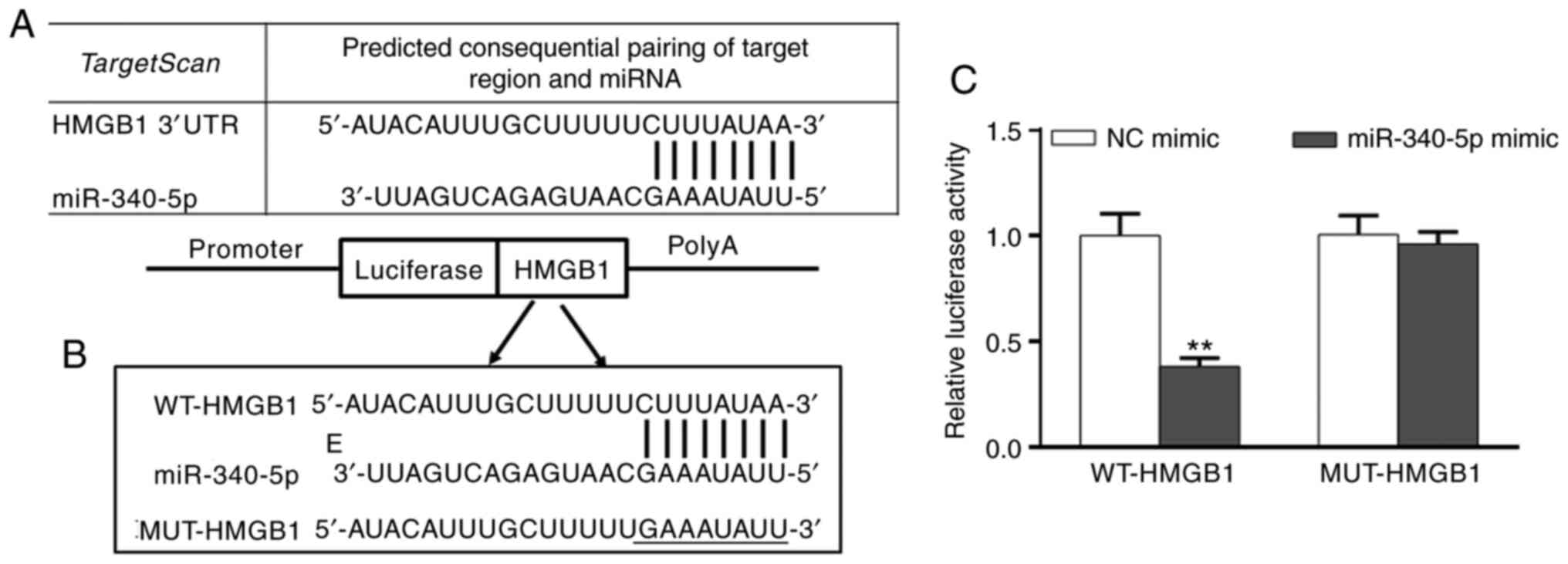
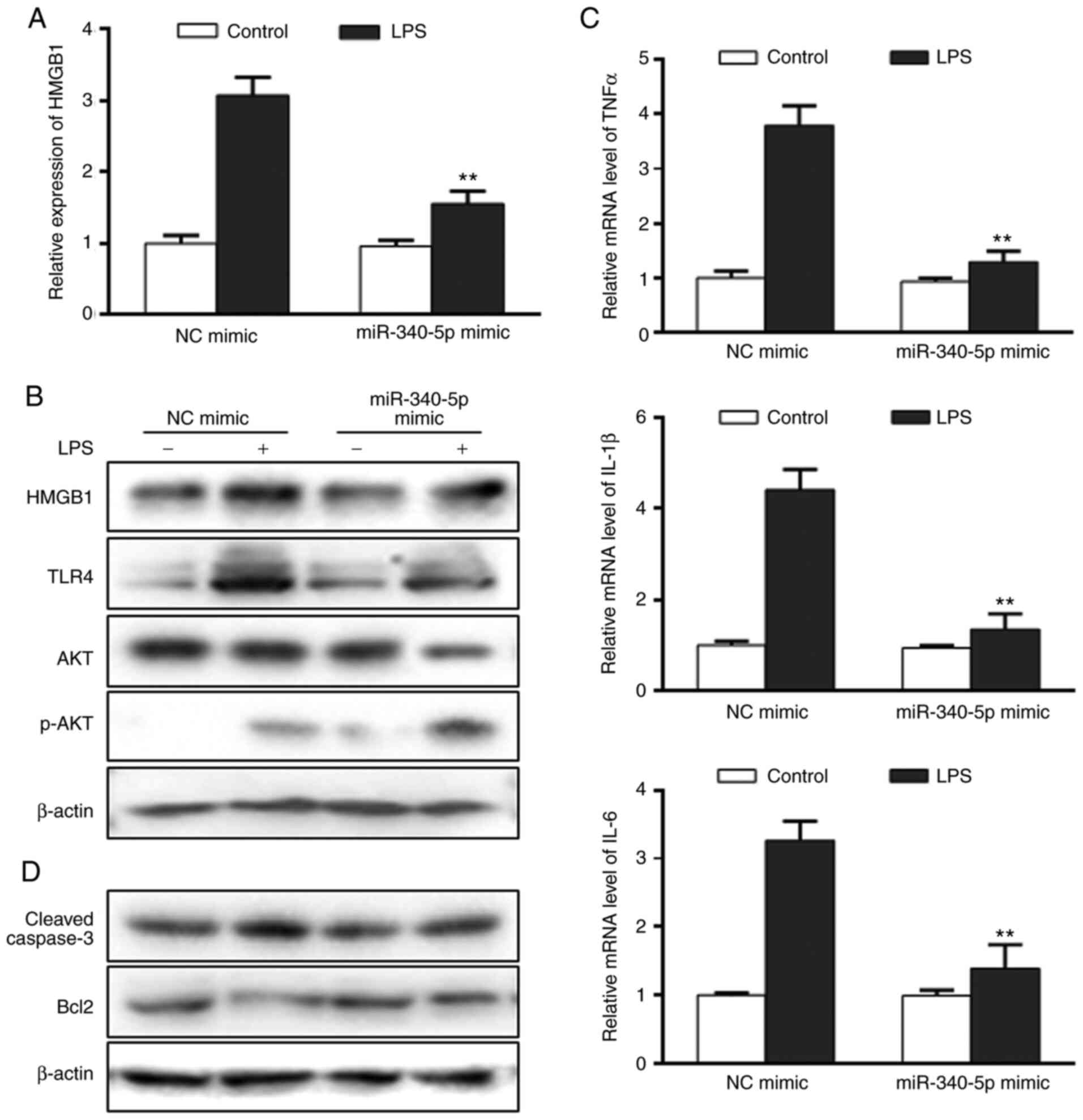
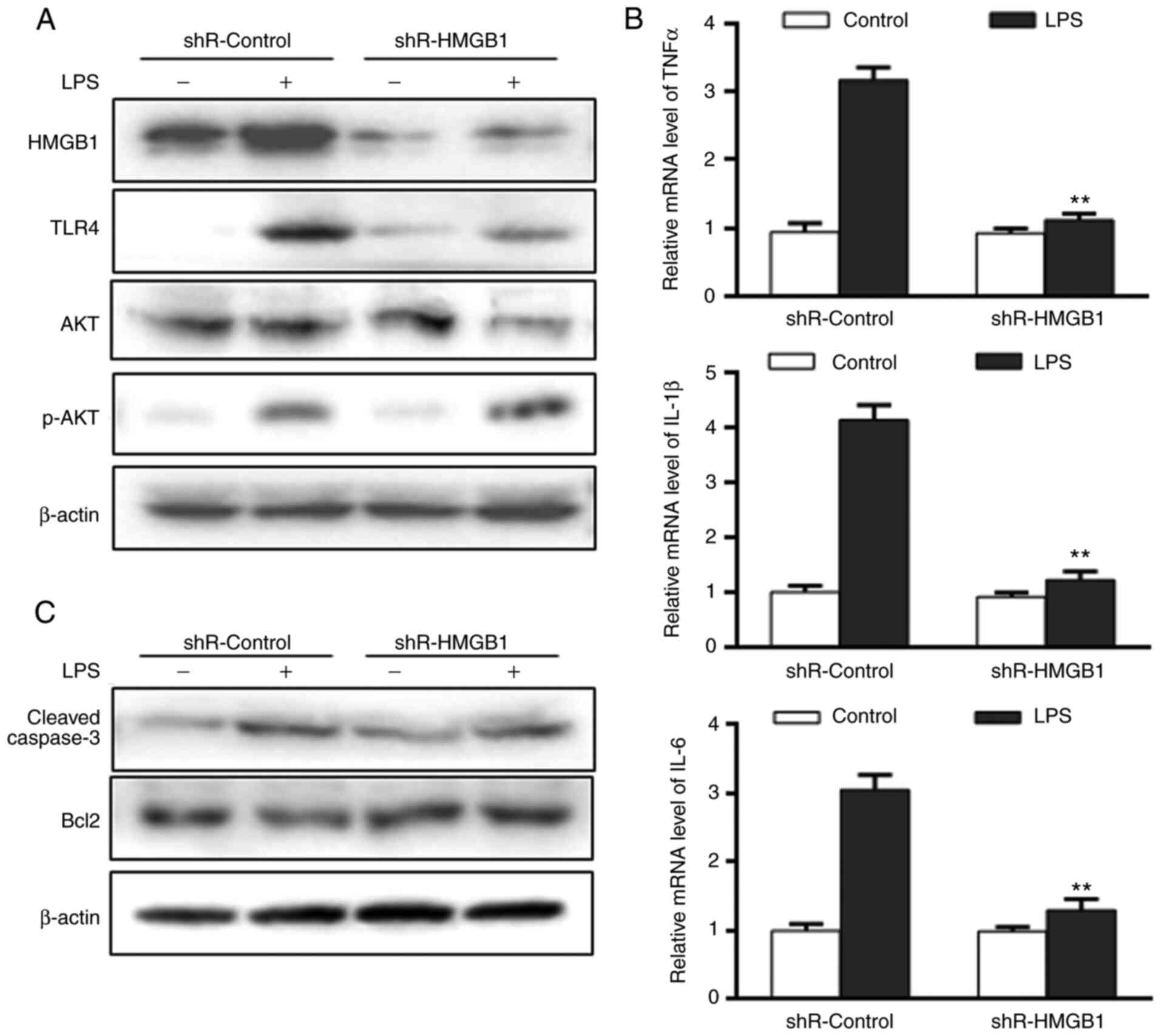
|
1
|
Ji L, Lv JC, Song ZF, Jiang MT, Li L and
Sun B: Risk factors of infected pancreatic necrosis secondary to
severe acute pancreatitis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int.
15:428–433. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Singh P and Garg PK: Pathophysiological
mechanisms in acute pancreatitis: Current understanding. Indian J
Gastroenterol. 35:153–166. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bhatia M, Wong FL, Cao Y, Lau HY, Huang J,
Puneet P and Chevali L: Pathophysiology of acute pancreatitis.
Pancreatology. 5:132–144. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Pandol SJ, Saluja AK, Imrie CW and Banks
PA: Acute pancreatitis: Bench to the bedside. Gastroenterology.
132:1127–1151. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jiang J, Yamato E and Miyazaki J:
Intravenous delivery of naked plasmid DNA for in vivo cytokine
expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 289:1088–1092.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Shimomura A, Shiino S, Kawauchi J,
Takizawa S, Sakamoto H, Matsuzaki J, Ono M, Takeshita F, Niida S,
Shimizu C, et al: Novel combination of serum microRNA for detecting
breast cancer in the early stage. Cancer Sci. 107:326–334.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Cech TR and Steitz JA: The noncoding RNA
revolution-trashing old rules to forge new ones. Cell. 157:77–94.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Khoshnam SE, Winlow W, Farbood Y,
Moghaddam HF and Farzaneh M: Emerging roles of microRNAs in
ischemic stroke: As possible therapeutic agents. J Stroke.
19:166–187. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Malumbres M: miRNAs and cancer: An
epigenetics view. Mol Aspects Med. 34:863–874. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Matts J, Jagadeeswaran G, Roe BA and
Sunkar R: Identification of microRNAs and their targets in
switchgrass, a model biofuel plant species. J Plant Physiol.
167:896–904. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Qu B and Shen N: miRNAs in the
pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Int J Mol Sci.
16:9557–9572. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang W, Dai LX, Zhang S, Yang Y, Yan N,
Fan P, Dai L, Tian HW, Cheng L, Zhang XM, et al: Regulation of
epidermal growth factor receptor signaling by plasmid-based
microRNA-7 inhibits human malignant gliomas growth and metastasis
in vivo. Neoplasma. 60:274–283. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Liu Y, Gao Y, Yang J, Shi C, Wang Y and Xu
Y: MicroRNA-381 reduces inflammation and infiltration of
macrophages in polymyositis via downregulating HMGB1. Int J Oncol.
53:1332–1342. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wei D, Miao Y, Yu L, Wang D and Wang Y:
Downregulation of microRNA-198 suppresses cell proliferation and
invasion in retinoblastoma by directly targeting PTEN. Mol Med Rep.
18:595–602. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang J, Ning X, Cui W, Bi M, Zhang D and
Zhang J: Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β-induced microRNA-216a
promotes acute pancreatitis via Akt and TGF-β pathway in mice. Dig
Dis Sci. 60:127–135. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Engel C, Brunkhorst FM, Bone HG,
Brunkhorst R, Gerlach H, Grond S, Gruendling M, Huhle G, Jaschinski
U, John S, et al: Epidemiology of sepsis in Germany: Results from a
national prospective multicenter study. Intensive Care Med.
33:606–618. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wu H, Li R, Pei LG, Wei ZH, Kang LN, Wang
L, Xie J and Xu B: Emerging role of high mobility group box-1 in
thrombosis-related diseases. Cell Physiol Biochem. 47:1319–1337.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Gao N, Yan C and Zhang G: Changes of serum
procalcitonin (PCT), C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-17
(IL-17), interleukin-6 (IL-6), high mobility group protein-B1
(HMGB1) and D-dimer in patients with severe acute pancreatitis
treated with continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) and its
clinical significance. Med Sci Monit. 24:5881–5886. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhao S, Yang J, Liu T, Zeng J, Mi L and
Xiang K: Dexamethasone inhibits NF-κBp65 and HMGB1 expression in
the pancreas of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Mol Med Rep.
18:5345–5352. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kang R, Zhang Q, Hou W, Yan Z, Chen R,
Bonaroti J, Bansal P, Billiar TR, Tsung A, Wang Q, et al:
Intracellular Hmgb1 inhibits inflammatory nucleosome release and
limits acute pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology. 146:1097–1107.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang ZW, Zhang QY, Zhou MT, Liu NX, Chen
TK, Zhu YF and Wu L: Antioxidant inhibits HMGB1 expression and
reduces pancreas injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Dig
Dis Sci. 55:2529–2536. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kang R, Lotze MT, Zeh HJ, Billiar TR and
Tang D: Cell death and DAMPs in acute pancreatitis. Mol Med.
20:466–477. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Saluja A, Dudeja V, Dawra R and Sah RP:
Early intra-acinar events in pathogenesis of pancreatitis.
Gastroenterology. 156:1979–1993. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Cheng L, Luo Z, Xiang K, Ren J, Huang Z,
Tang L and Tian F: Clinical significance of serum triglyceride
elevation at early stage of acute biliary pancreatitis. BMC
Gastroenterol. 15(19)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sit M, Aktas G, Yilmaz EE, Alcelik A,
Terzi EH and Tosun M: Effects of the inflammatory response on serum
omentin levels in early acute and chronic pancreatitis. Clin Ter.
165:e148–e152. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Schneider L, Jabrailova B, Strobel O,
Hackert T and Werner J: Inflammatory profiling of early
experimental necrotizing pancreatitis. Life Sci. 126:76–80.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yang R, Tenhunen J and Tonnessen TI: HMGB1
and histones play a significant role in inducing systemic
inflammation and multiple organ dysfunctions in severe acute
pancreatitis. Int J Inflam. 2017(1817564)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Habtezion A: Inflammation in acute and
chronic pancreatitis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol. 31:395–399.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang S, Ni HM, Chao X, Wang H, Bridges B,
Kumer S, Schmitt T, Mareninova O, Gukovskaya A, De Lisle RC, et al:
Impaired TFEB-mediated lysosomal biogenesis promotes the
development of pancreatitis in mice and is associated with human
pancreatitis. Autophagy. 15:1954–1969. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Xin-Peng Z, Yong-Hua H, Yong L, Jing-Jing
W, Guang-Hua W, Ren-Jie W and Min Z: A high-mobility group box 1
that binds to DNA, enhances pro-inflammatory activity, and acts as
an anti-infection molecule in black rockfish, Sebastes schlegelii.
Fish Shellfish Immunol. 56:402–409. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kayagaki N, Wong MT, Stowe IB, Ramani SR,
Gonzalez LC, Akashi-Takamura S, Miyake K, Zhang J, Lee WP,
Muszyński A, et al: Noncanonical inflammasome activation by
intracellular LPS independent of TLR4. Science. 341:1246–1249.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Keppler-Noreuil KM, Parker VE, Darling TN
and Martinez-Agosto JA: Somatic overgrowth disorders of the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway & therapeutic strategies. Am J Med Genet
C Semin Med Genet. 172:402–421. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Estaras M, Ameur FZ, Roncero V,
Fernandez-Bermejo M, Blanco G, Lopez D, Mateos JM, Salido GM and
Gonzalez A: The melatonin receptor antagonist luzindole induces
Ca2+ mobilization, reactive oxygen species generation
and impairs trypsin secretion in mouse pancreatic acinar cells.
Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 1863(129407)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhao Q, Zhang H, Wu J, Lv X, Jin X and Hu
J: Melatonin inhibits the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced,
C/EBP homologous protein-mediated pathway in acute pancreatitis.
Mol Med Rep. 22:1647–1655. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Liu Y, Yang L, Chen KL, Zhou B, Yan H,
Zhou ZG and Li Y: Knockdown of GRP78 promotes apoptosis in
pancreatic acinar cells and attenuates the severity of cerulein and
LPS induced pancreatic inflammation. PLoS One.
9(e92389)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li Z, Xu C, Tao Y, Liang Y, Liang Q, Li J,
Li R and Ye H: Anisodamine alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced
pancreatic acinar cell injury through NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB
signaling pathway. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 40:58–66.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang H, Li YY and Wu XZ: Effect of
Tetrandrine on LPS-induced NF-kappaB activation in isolated
pancreatic acinar cells of rat. World J Gastroenterol.
12:4232–4236. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Bhatia M: Novel therapeutic targets for
acute pancreatitis and associated multiple organ dysfunction
syndrome. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 1:343–351.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Petrov MS, Shanbhag S, Chakraborty M,
Phillips AR and Windsor JA: Organ failure and infection of
pancreatic necrosis as determinants of mortality in patients with
acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology. 139:813–820. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Hong YP, Yu J, Su YR, Mei FC, Li M, Zhao
KL, Zhao L, Deng WH, Chen C and Wang WX: High-fat diet aggravates
acute pancreatitis via TLR4-mediated necroptosis and inflammation
in rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020(8172714)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Zhang X, Zhu C, Wu D and Jiang X: Possible
role of toll-like receptor 4 in acute pancreatitis. Pancreas.
39:819–824. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Abliz A, Deng W, Sun R, Guo W, Zhao L and
Wang W: Wortmannin, PI3K/Akt signaling pathway inhibitor,
attenuates thyroid injury associated with severe acute pancreatitis
in rats. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:13821–13833. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xu P, Wang J, Yang ZW, Lou XL and Chen C:
Regulatory roles of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in rats with
severe acute pancreatitis. PLoS One. 8(e81767)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Liu Y, Liao R, Qiang Z and Zhang C:
Pro-inflammatory cytokine-driven PI3K/Akt/Sp1 signalling and
H2S production facilitates the pathogenesis of severe
acute pancreatitis. Biosci Rep. 37(BSR20160483)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Fan J, Li Y, Levy RM, Fan JJ, Hackam DJ,
Vodovotz Y, Yang H, Tracey KJ, Billiar TR and Wilson MA:
Hemorrhagic shock induces NAD(P)H oxidase activation in
neutrophils: Role of HMGB1-TLR4 signaling. J Immunol.
178:6573–6580. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kokkola R, Andersson A, Mullins G, Ostberg
T, Treutiger CJ, Arnold B, Nawroth P, Andersson U, Harris RA and
Harris HE: RAGE is the major receptor for the proinflammatory
activity of HMGB1 in rodent macrophages. Scand J Immunol. 61:1–9.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Tian X, Sun L, Feng D, Sun Q, Dou Y, Liu
C, Zhou F, Li H, Shen H, Wang Z and Chen G: HMGB1 promotes
neurovascular remodeling via Rage in the late phase of subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Brain Res. 1670:135–145. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Akira S, Takeda K and Kaisho T: Toll-like
receptors: Critical proteins linking innate and acquired immunity.
Nat Immunol. 2:675–680. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Xu GF, Guo M, Tian ZQ, Wu GZ, Zou XP and
Zhang WJ: Increased of serum high-mobility group box chromosomal
protein 1 correlated with intestinal mucosal barrier injury in
patients with severe acute pancreatitis. World J Emerg Surg.
9(61)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Kylänpää ML, Repo H and Puolakkainen PA:
Inflammation and immunosuppression in severe acute pancreatitis.
World J Gastroenterol. 16:2867–2872. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Sun J, Shi S, Wang Q, Yu K and Wang R:
Continuous hemodiafiltration therapy reduces damage of multi-organs
by ameliorating of HMGB1/TLR4/NFκB in a dog sepsis model. Int J
Clin Exp Pathol. 8:1555–1564. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Todorova J and Pasheva E: High mobility
group B1 protein interacts with its receptor RAGE in tumor cells
but not in normal tissues. Oncol Lett. 3:214–218. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Schiraldi M, Raucci A, Muñoz LM, Livoti E,
Celona B, Venereau E, Apuzzo T, De Marchis F, Pedotti M, Bachi A,
et al: HMGB1 promotes recruitment of inflammatory cells to damaged
tissues by forming a complex with CXCL12 and signaling via CXCR4. J
Exp Med. 209:551–563. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Diener KR, Al-Dasooqi N, Lousberg EL and
Hayball JD: The multifunctional alarmin HMGB1 with roles in the
pathophysiology of sepsis and cancer. Immunol Cell Biol.
91:443–450. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Biscetti F, Ghirlanda G and Flex A:
Therapeutic potential of high mobility group box-1 in ischemic
injury and tissue regeneration. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 9:677–681.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Kanakoudi-Tsakalidou F, Farmaki E,
Tzimouli V, Taparkou A, Paterakis G, Trachana M, Pratsidou-Gertsi
P, Nalbanti P and Papachristou F: Simultaneous changes in serum
HMGB1 and IFN-α levels and in LAIR-1 expression on plasmatoid
dendritic cells of patients with juvenile SLE. New therapeutic
options? Lupus. 23:305–312. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Gu H, Werner J, Bergmann F, Whitcomb DC,
Büchler MW and Fortunato F: Necro-inflammatory response of
pancreatic acinar cells in the pathogenesis of acute alcoholic
pancreatitis. Cell Death Dis. 4(e816)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Samanta S, Balasubramanian S, Rajasingh S,
Patel U, Dhanasekaran A, Dawn B and Rajasingh J: MicroRNA: A new
therapeutic strategy for cardiovascular diseases. Trends Cardiovasc
Med. 26:407–419. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Wang AY, Ehrhardt A, Xu H and Kay MA:
Adenovirus transduction is required for the correction of diabetes
using Pdx-1 or Neurogenin-3 in the liver. Mol Ther. 15:255–263.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Wang AY, Peng PD, Ehrhardt A, Storm TA and
Kay MA: Comparison of adenoviral and adeno-associated viral vectors
for pancreatic gene delivery in vivo. Hum Gene Ther. 15:405–413.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Li D, Zhou J, Yang B and Yu Y:
MicroRNA-340-5p inhibits hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis
and oxidative stress in cardiomyocytes by regulating the Act1/NF-κB
pathway. J Cell Biochem. 120:14618–14627. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Zheng Y, Zhao P, Lian Y, Li S, Chen Y and
Li L: MiR-340-5p alleviates oxygen-glucose
deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuronal injury via PI3K/Akt
activation by targeting PDCD4. Neurochem Int.
134(104650)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|