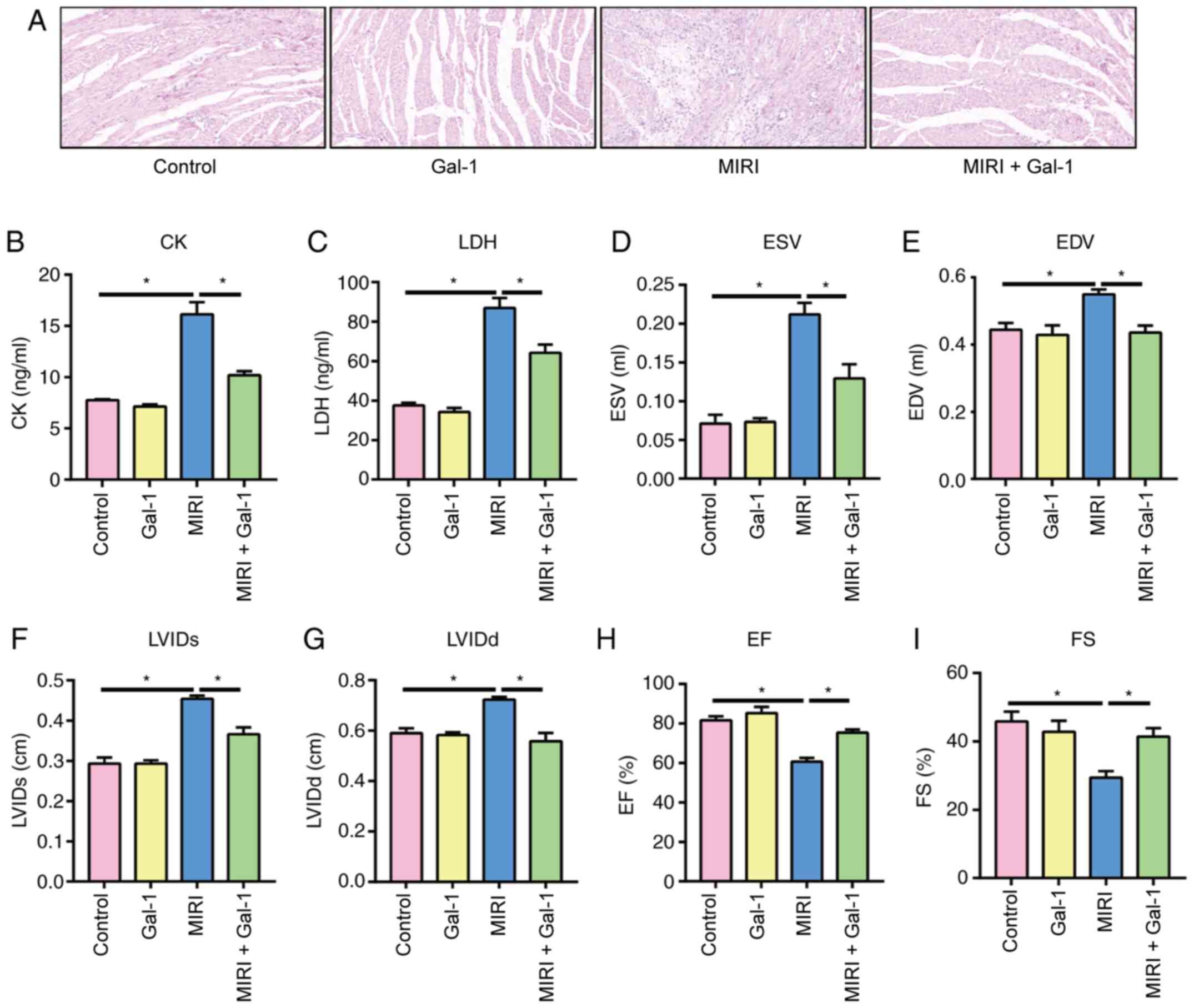
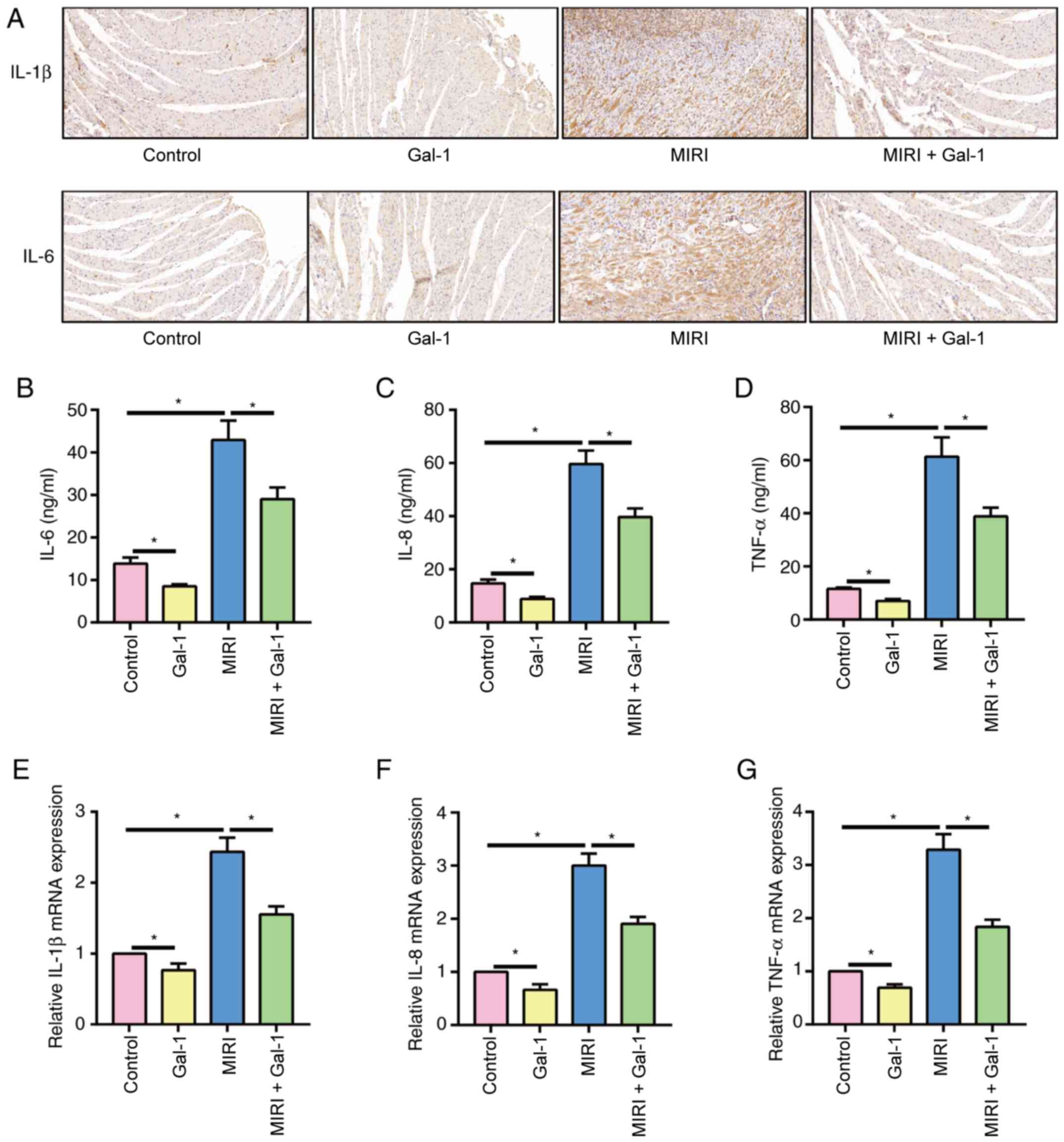
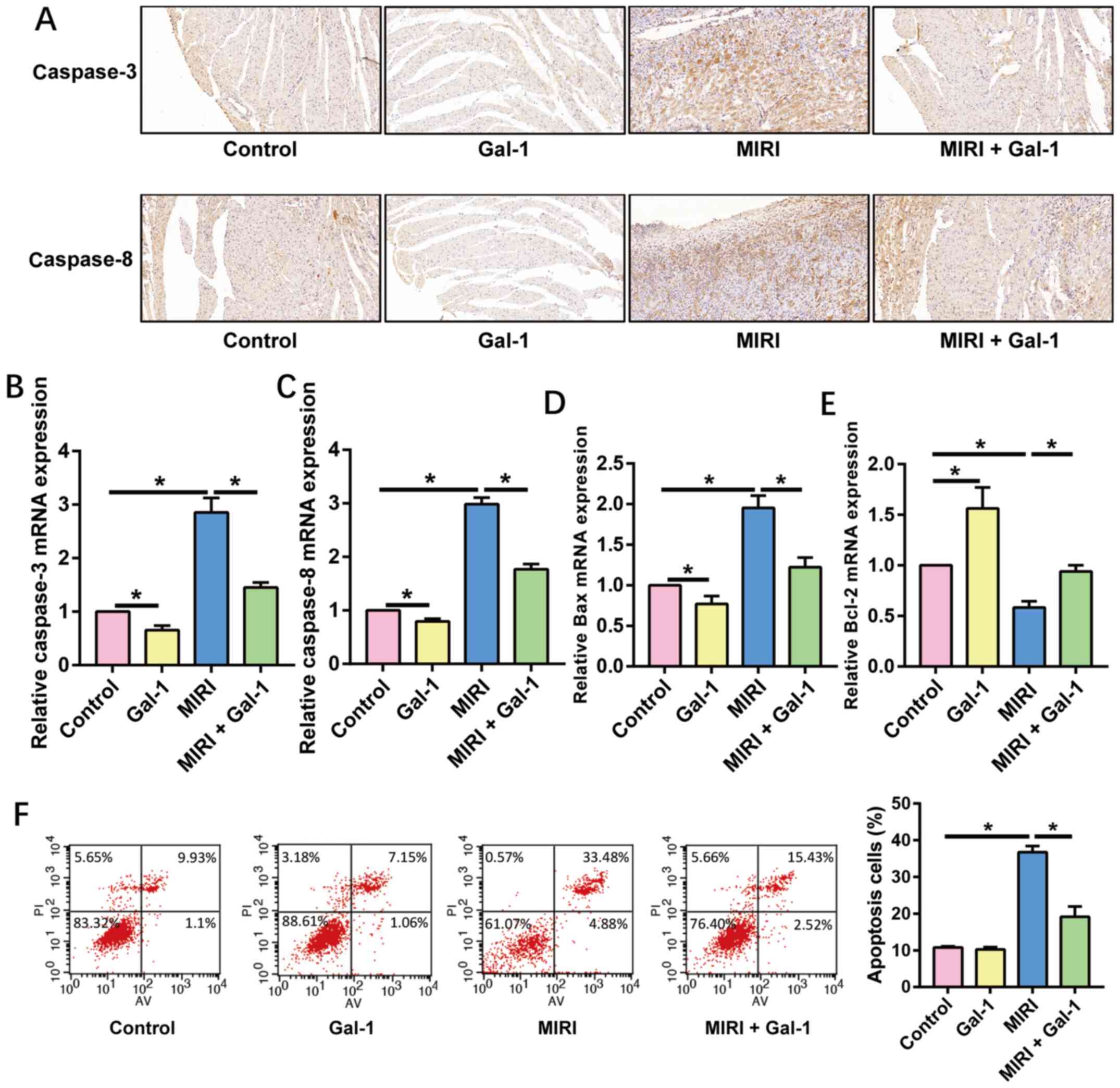
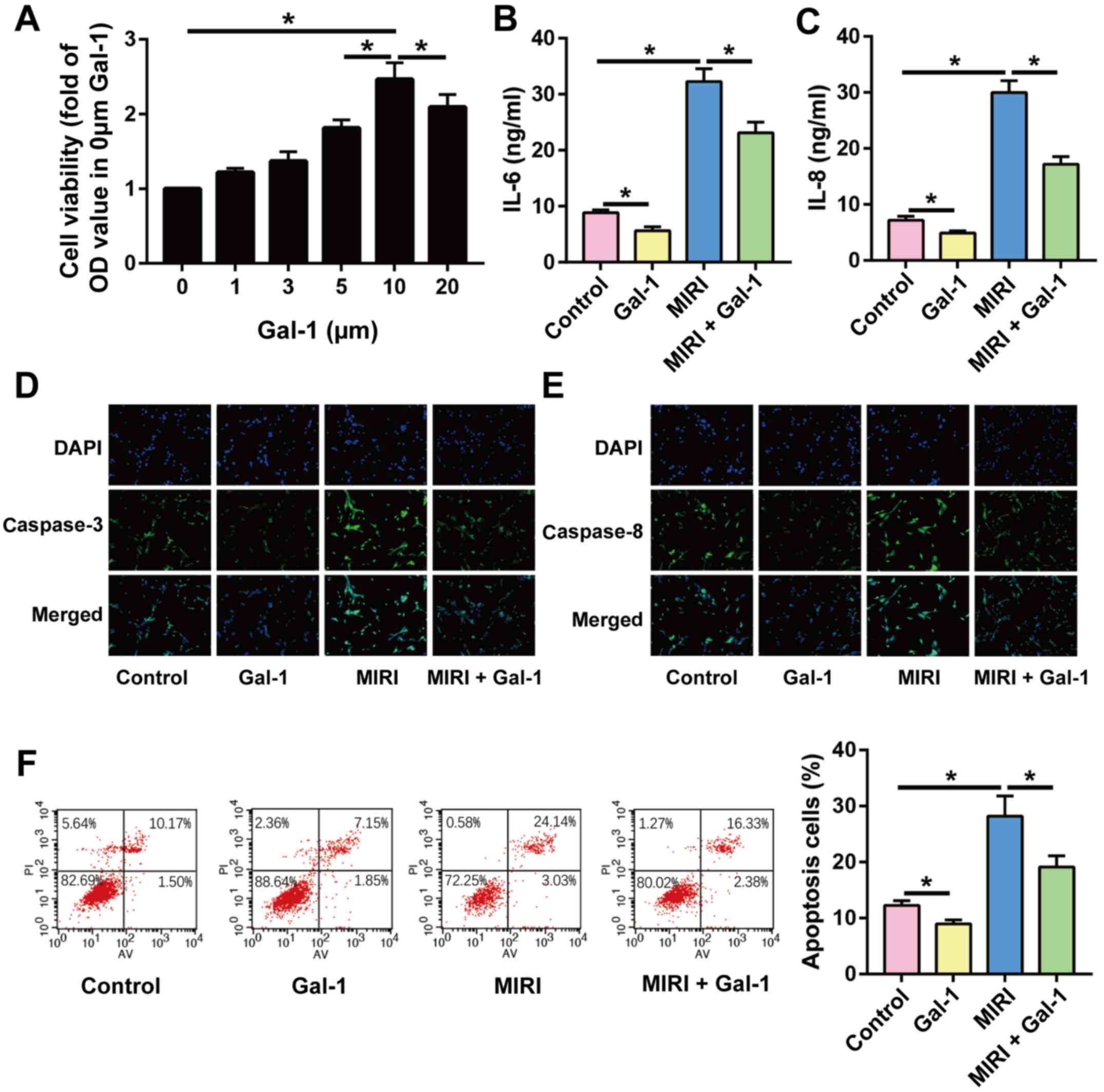
|
1
|
Popescu CP, Florescu SA, Hasbun R, Harxhi
A, Evendar R, Kahraman H, Neuberger A, Codreanu D, Zaharia MF,
Tosun S, et al: Prediction of unfavorable outcomes in West Nile
virus neuroinvasive infection-Result of a multinational ID-IRI
study. J Clin Virol. 122(104213)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Henry JJD, Delrosario L, Fang J, Wong SY,
Fang Q, Sievers R, Kotha S, Wang A, Farmer D, Janaswamy P, et al:
Development of injectable amniotic membrane matrix for
postmyocardial infarction tissue repair. Adv Healthc Mater.
9(e1900544)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Murthy SB, Diaz I, Wu X, Merkler AE,
Iadecola C, Safford MM, Sheth KN, Navi BB and Kamel H: Risk of
arterial ischemic events after intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke.
51:137–142. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
GBD 2017 Disease and Injury Incidence and
Prevalence Collaborators. Global, regional, and national incidence,
prevalence, and years lived with disability for 354 diseases and
injuries for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: A systematic
analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet.
392:1789–1858. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jackson CA, Kerssens J, Fleetwood K, Smith
DJ, Mercer SW and Wild SH: Incidence of ischaemic heart disease and
stroke among people with psychiatric disorders: Retrospective
cohort study. Br J Psychiatry. 217:442–449. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gul-Kahraman K, Yilmaz-Bozoglan M and
Sahna E: Physiological and pharmacological effects of melatonin on
remote ischemic perconditioning after myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats: Role of Cybb, Fas, NfκB,
irisin signaling pathway. J Pineal Res. 67(e12589)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Merz SF, Korste S, Bornemann L, Michel L,
Stock P, Squire A, Soun C, Engel DR, Detzer J, Lörchner H, et al:
Contemporaneous 3D characterization of acute and chronic myocardial
I/R injury and response. Nat Commun. 10(2312)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Stiermaier T, Jensen JO, Rommel KP, de
Waha-Thiele S, Fuernau G, Desch S, Thiele H and Eitel I: Combined
intrahospital remote ischemic perconditioning and postconditioning
improves clinical outcome in ST-elevation myocardial infarction.
Circ Res. 124:1482–1491. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tsai YT, Liang CH, Yu JH, Huang KC, Tung
CH, Wu JE, Wu YY, Chang CH, Hong TM and Chen YL: A DNA aptamer
targeting galectin-1 as a novel immunotherapeutic strategy for lung
cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 18:991–998. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kuroi K, Kamijo M, Ueki M, Niwa Y,
Hiramatsu H and Nakabayashi T: Time-resolved FTIR study on the
structural switching of human galectin-1 by light-induced disulfide
bond formation. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 22:1137–1144. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Huang XT, Liu W, Zhou Y, Sun M, Yang HH,
Zhang CY and Tang SY: Galectin-1 ameliorates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via AMPK-Nrf2 pathway
in mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 146:2222–233. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Carlos CP, Silva AA, Gil CD and Oliani SM:
Pharmacological treatment with galectin-1 protects against renal
ischaemia-reperfusion injury. Sci Rep. 8(9568)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lameijer H, Schutte JM, Schuitemaker NW,
van Roosmalen JJ and Pieper PG: Dutch Maternal Mortality and
Morbidity Committee. Maternal mortality due to cardiovascular
disease in the Netherlands: A 21-year experience. Neth Heart J.
28:27–36. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Seropian IM, González GE, Maller SM,
Berrocal DH, Abbate A and Rabinovich GA: Galectin-1 as an emerging
mediator of cardiovascular inflammation: Mechanisms and therapeutic
opportunities. Mediators Inflamm. 2018(8696543)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Fan J, Fan W, Lei J, Zhou Y, Xu H, Kapoor
I, Zhu G and Wang J: Galectin-1 attenuates cardiomyocyte
hypertrophy through splice-variant specific modulation of Ca1.2
calcium channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1865:218–229.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Seropian IM, Cerliani JP, Toldo S, Van
Tassell BW, Ilarregui JM, González GE, Matoso M, Salloum FN,
Melchior R, Gelpi RJ, et al: Galectin-1 controls cardiac
inflammation and ventricular remodeling during acute myocardial
infarction. Am J Pathol. 182:29–40. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Han B, Li S, Lv Y, Yang D, Li J, Yang Q,
Wu P, Lv Z and Zhang Z: Dietary melatonin attenuates
chromium-induced lung injury via activating the Sirt1/Pgc-1α/Nrf2
pathway. Food Funct. 10:5555–5565. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yang Q, Han B, Xue J, Lv Y, Li S, Liu Y,
Wu P, Wang X and Zhang Z: Hexavalent chromium induces mitochondrial
dynamics disorder in rat liver by inhibiting AMPK/PGC-1α signaling
pathway. Environ Pollut. 265(114855)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Romson JL, Hook BG, Kunkel SL, Abrams GD,
Schork MA and Lucchesi BR: Reduction of the extent of ischemic
myocardial injury by neutrophil depletion in the dog. Circulation.
67:1016–1023. 1983.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Frey UH, Klaassen M, Ochsenfarth C, Murke
F, Thielmann M, Kottenberg E, Kleinbongard P, Klenke S, Engler A,
Heusch G, et al: Remote ischaemic preconditioning increases serum
extracellular vesicle concentrations with altered micro-RNA
signature in CABG patients. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 63:483–492.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li HL, Karwatowska-Prokopczuk E, Mutomba
M, Wu J, Karanewsky D, Valentino K, Engler RL and Gottlieb RA:
Pharmacology of caspase inhibitors in rabbit cardiomyocytes
subjected to metabolic inhibition and recovery. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 3:113–123. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Abassi Z, Armaly Z and Heyman SN:
Glycocalyx degradation in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Pathol.
190:752–767. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gottlieb RA and Engler RL: Apoptosis in
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 874:412–426.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Amar DN, Epshtein M and Korin N:
Endothelial cell activation in an embolic ischemia-reperfusion
injury microfluidic model. Micromachines (Basel).
10(857)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gonzalez AL, Ciocci PA, Fantinelli JC,
Rojano B, Schinella GR and Mosca SM: Isoespintanol, a monoterpene
isolated from oxandra cf xylopioides, ameliorates the myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury by AKT/PKCepsilon/eNOS-dependent
pathways. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 393:629–638.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li S, Baiyun R, Lv Z, Li J, Han D, Zhao W,
Yu L, Deng N, Liu Z and Zhang Z: Exploring the kidney hazard of
exposure to mercuric chloride in mice:Disorder of mitochondrial
dynamics induces oxidative stress and results in apoptosis.
Chemosphere. 234:822–829. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liu B, Yu H, Baiyun R, Lu J, Li S, Bing Q,
Zhang X and Zhang Z: Protective effects of dietary luteolin against
mercuric chloride-induced lung injury in mice: Involvement of
AKT/Nrf2 and NF-κB pathways. Food Chem Toxicol. 113:296–302.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Baiyun R, Li S, Liu B, Lu J, Lv Y, Xu J,
Wu J, Li J, Lv Z and Zhang Z: Luteolin-mediated PI3K/AKT/Nrf2
signaling pathway ameliorates inorganic mercury-induced cardiac
injury. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 161:655–661. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhu J, Wang YF, Chai XM, Qian K, Zhang LW,
Peng P, Chen PM, Cao JF, Qin ZH, Sheng R and Xie H: Exogenous NADPH
ameliorates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats through
activating AMPK/mTOR pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 41:535–545.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xu XZ, Luo B, Xiao Y and Zheng WQ: Effects
of lncRNA MALAT1-mediated beta-catenin signaling pathway on
myocardial cell apoptosis in rats with myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
23:9557–9565. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lazou A, Iliodromitis EK, Cieslak D,
Voskarides K, Mousikos S, Bofilis E and Kremastinos DT: Ischemic
but not mechanical preconditioning attenuates ischemia/reperfusion
induced myocardial apoptosis in anaesthetized rabbits: The role of
Bcl-2 family proteins and ERK1/2. Apoptosis. 11:2195–2204.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wang N, Minatoguchi S, Chen X, Uno Y, Arai
M, Lu C, Takemura G, Fujiwara T and Fujiwara H: Antidiabetic drug
miglitol inhibits myocardial apoptosis involving decreased hydroxyl
radical production and Bax expression in an ischaemia/reperfusion
rabbit heart. Br J Pharmacol. 142:983–990. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhou BZ, Zhang DH, Yu WM and Ning JZ:
Protective effect of cyclosporine A in the treatment of severe
hydronephrosis in a rabbit renal pelvic perfusion model. Turk J Med
Sci. 49:1590–1598. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sheng X, Chen M, Huang B, Liu J, Zhou L,
Bao M and Li S: Cardioprotective effects of low-level carotid
baroreceptor stimulation against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion
injury in canine model. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 45:131–140.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ho MY, Wen MS, Yeh JK, Hsieh IC, Chen CC,
Hsieh MJ, Tsai ML, Yang CH, Wu VC, Hung KC, et al: Excessive irisin
increases oxidative stress and apoptosis in murine heart. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 503:2493–2498. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Abhari BA, McCarthy N, Agostinis P and
Fulda S: NF-κB contributes to Smac mimetic-conferred protection
from tunicamycin-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis. 24:269–277.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Toldo S, Mauro AG, Cutter Z and Abbate A:
Inflammasome, pyroptosis, and cytokines in myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
315:H1553–H1568. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Nichols TC: NF-kappaB and reperfusion
injury. Drug News Perspect. 17:99–104. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Qian Q, Cao X, Wang B, Qu Y, Qian Q, Sun Z
and Feng F: TNF-α-TNFR signal pathway inhibits autophagy and
promotes apoptosis of alveolar macrophages in coal worker's
pneumoconiosis. J Cell Physiol. 234:5953–5963. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Chen H, Zhang RQ, Wei XG, Ren XM and Gao
XQ: Mechanism of TLR-4/NF-κB pathway in myocardial ischemia
reperfusion injury of mouse. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 9:503–507.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Groot HE, Ali LA, van der Horst IC,
Schurer RA, van der Werf HW, Lipsic E, van Veldhuisen DJ, Karper JC
and van der Harst P: Plasma interleukin 6 levels are associated
with cardiac function after ST-elevation myocardial infarction.
Clin Res Cardiol. 108:612–621. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Moreira DM, da Silva RL, Vieira JL, Fattah
T, Lueneberg ME and Gottschall CA: Role of vascular inflammation in
coronary artery disease: Potential of anti-inflammatory drugs in
the prevention of atherothrombosis. Inflammation and
anti-inflammatory drugs in coronary artery disease. Am J Cardiovasc
Drugs. 15:1–11. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|