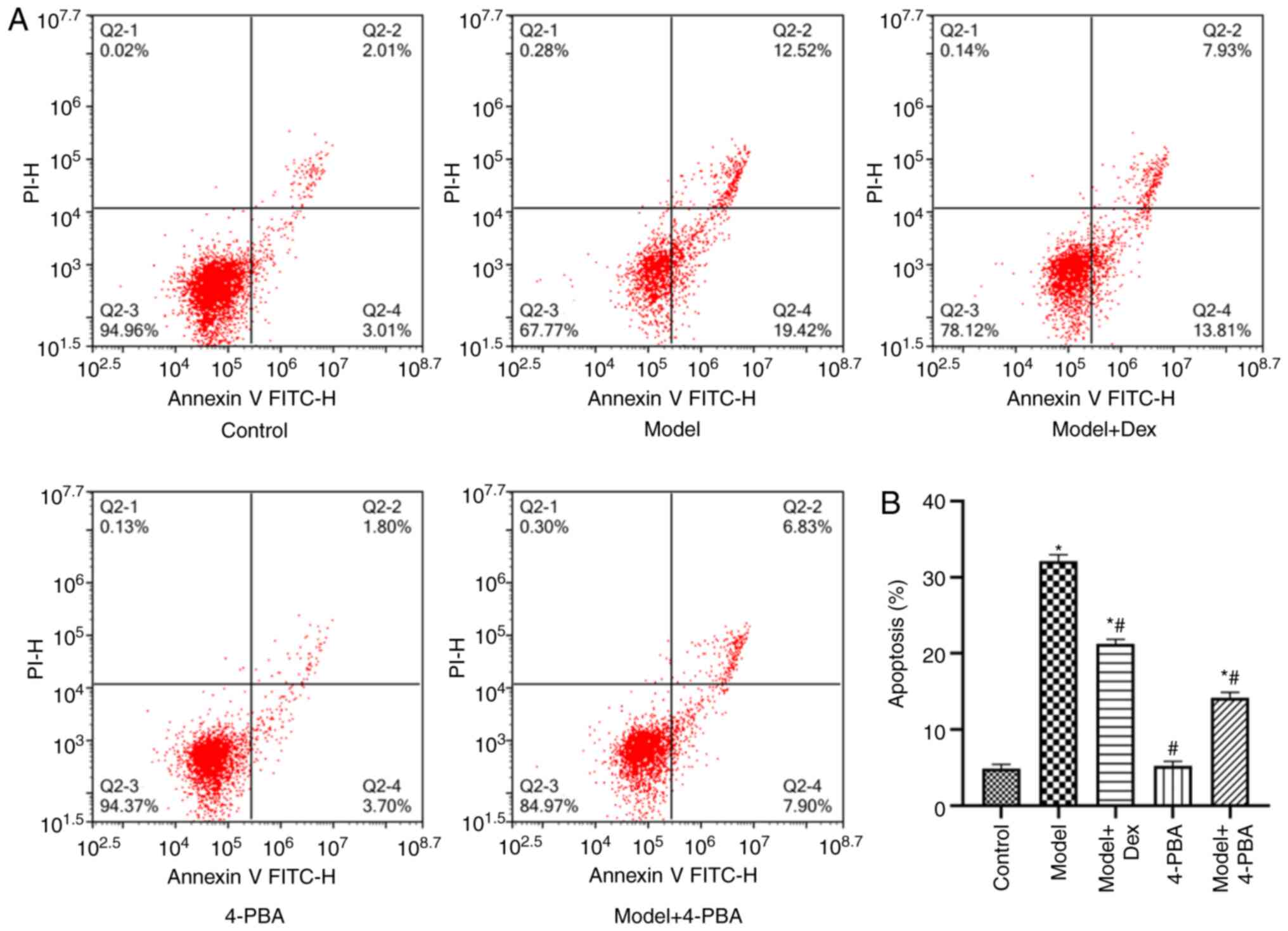
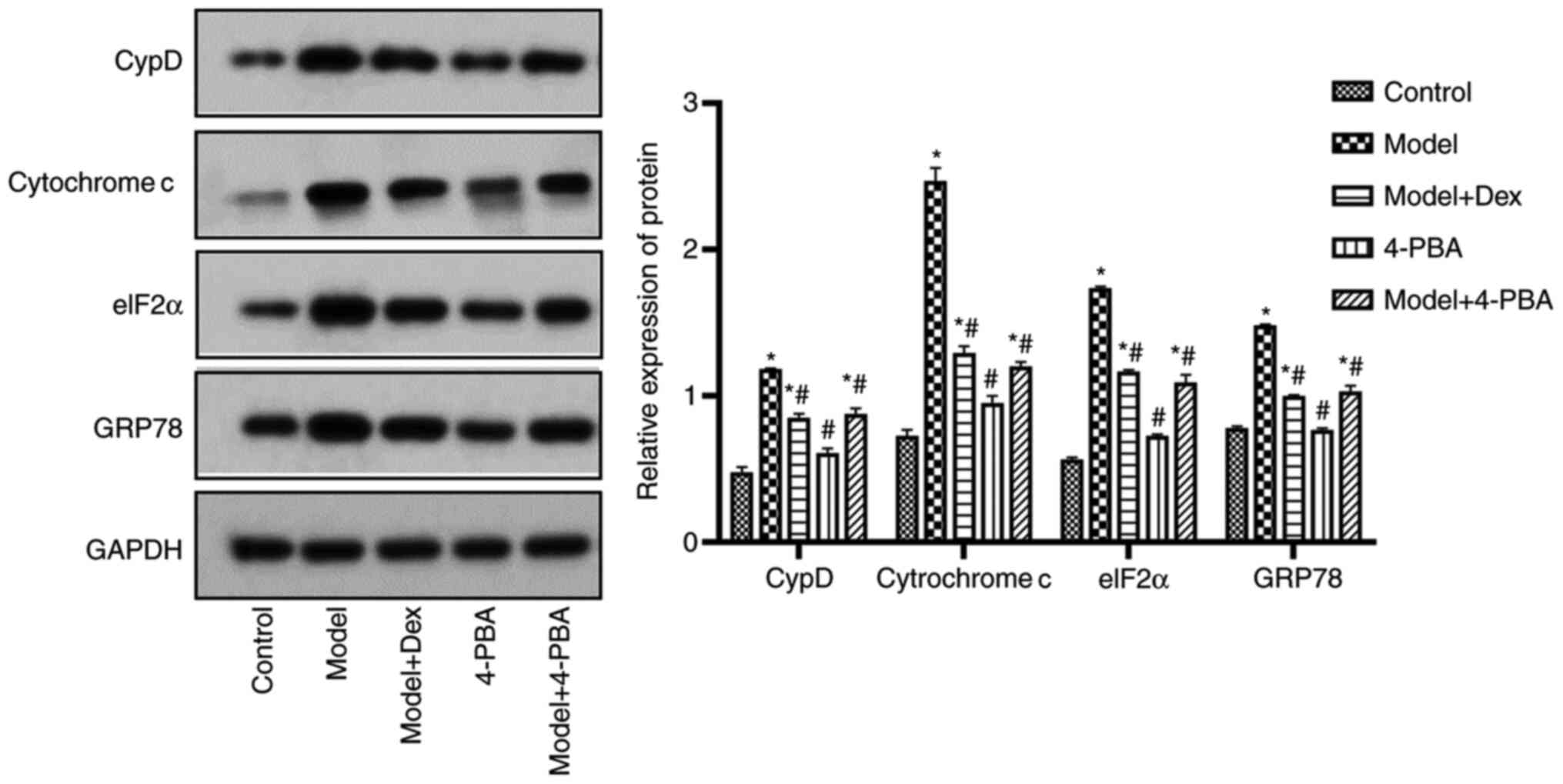
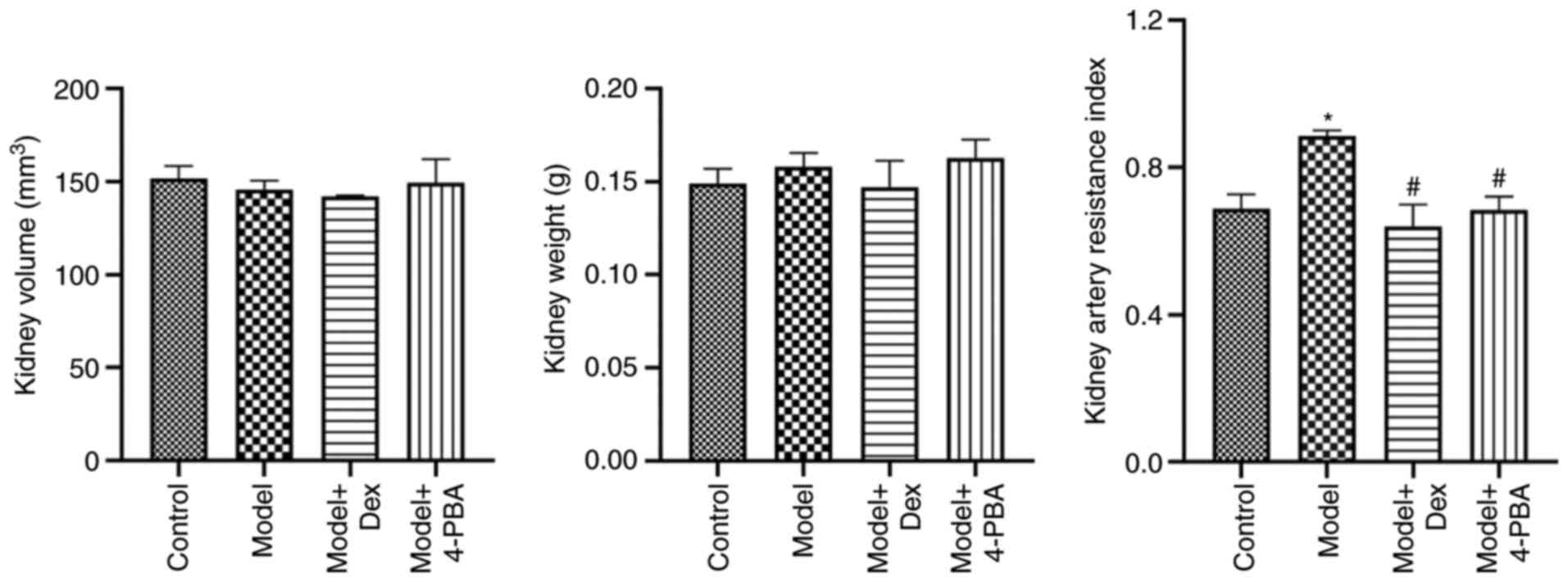
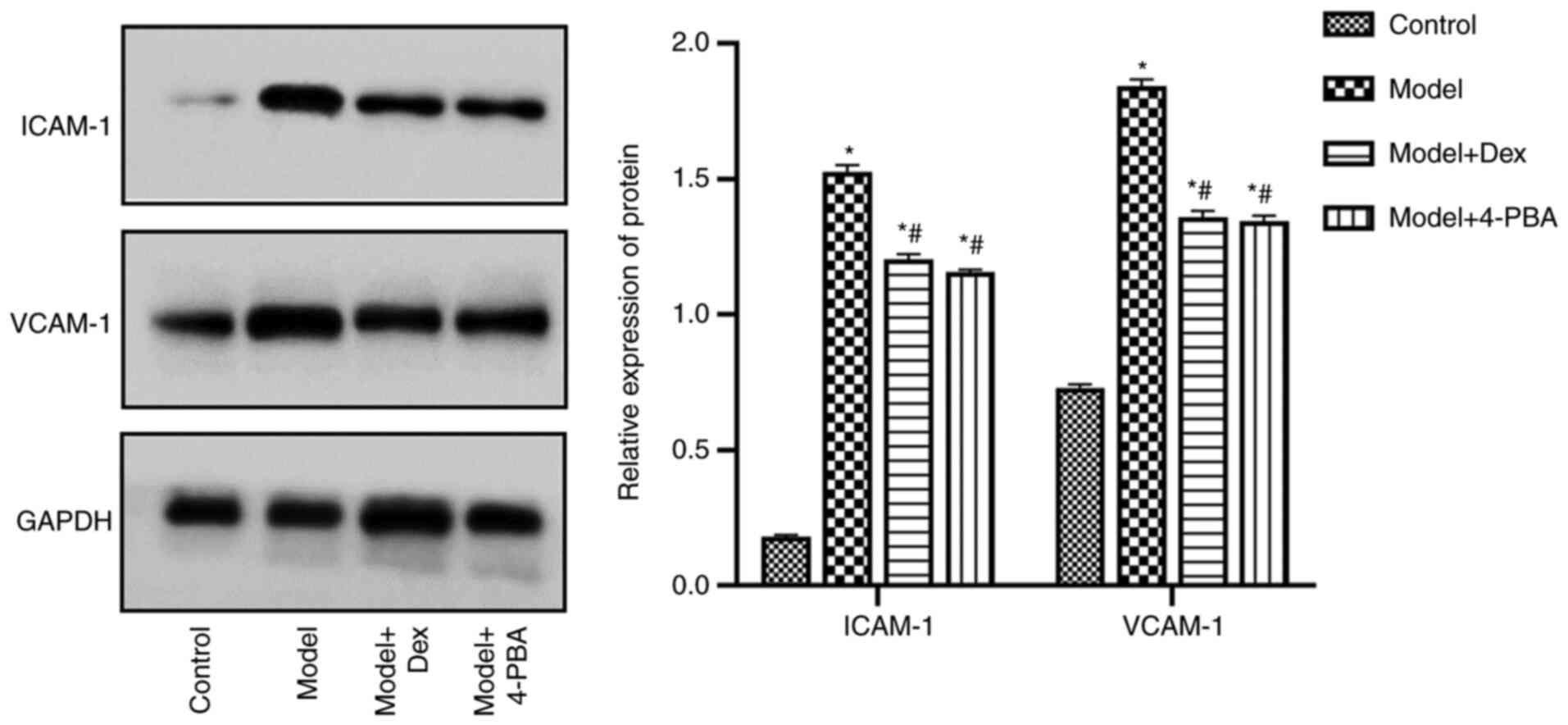
|
1
|
Kusch A, Hoff U, Bubalo G, Zhu Y, Fechner
M, Schmidt-Ullrich R, Marko L, Müller DN, Schmidt-Ott KM, Gürgen D,
et al: Novel signalling mechanisms and targets in renal ischaemia
and reperfusion injury. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 208:25–40.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
de Vries DK, Khairoun M, Lindeman JH,
Bajema IM, de Heer E, Roest M, van Zonneveld AJ, van Kooten C,
Rabelink TJ, Schaapherder AF and Reinders ME: Renal
ischemia-reperfusion induces release of angiopoietin-2 from human
grafts of living and deceased donors. Transplantation. 96:282–289.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Perico N, Cattaneo D, Sayegh MH and
Remuzzi G: Delayed graft function in kidney transplantation.
Lancet. 364:1814–1827. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kalyanaraman B: Teaching the basics of
redox biology to medical and graduate students: Oxidants,
antioxidants and disease mechanisms. Redox Biol. 1:244–257.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wang Y, He J, Pei X and Zhao W: Systematic
review and meta-analysis of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells therapy
for impaired renal function in small animal models. Nephrology
(Carlton). 18:201–208. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Song JY, Meng LQ and Li XM: Therapeutic
application and prospect of Astragalus membranaceus and Angelica
sinensis in treating renal microvascular lesions. Zhongguo Zhong Xi
Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 28:859–861. 2008.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
7
|
Afonso J and Reis F: Dexmedetomidine:
Current role in anesthesia and intensive care. Rev Bras Anestesiol.
62:118–133. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shukry M and Miller JA: Update on
dexmedetomidine: Use in nonintubated patients requiring sedation
for surgical procedures. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 6:111–121.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Patil RH, Naveen Kumar M, Kiran Kumar KM,
Nagesh R, Kavya K, Babu RL, Ramesh GT and Chidananda Sharma S:
Dexamethasone inhibits inflammatory response via down regulation of
AP-1 transcription factor in human lung epithelial cells. Gene.
645:85–94. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Luo T, Chen B and Wang X: 4-PBA prevents
pressure overload-induced myocardial hypertrophy and interstitial
fibrosis by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum stress. Chem Biol
Interact. 242:99–106. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang Z, Zheng S, Gu Y, Zhou L, Lin B and
Liu W: 4-PBA enhances autophagy by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum
stress in recombinant human beta nerve growth factor-induced PC12
cells after mechanical injury via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
World Neurosurg. 138:e659–e664. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zeng M, Sang W, Chen S, Chen R, Zhang H,
Xue F, Li Z, Liu Y, Gong Y, Zhang H and Kong X: 4-PBA inhibits
LPS-induced inflammation through regulating ER stress and autophagy
in acute lung injury models. Toxicol Lett. 271:26–37.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Bhardwaj R, Tandon C, Dhawan DK and Kaur
T: Effect of endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibition on
hyperoxaluria-induced oxidative stress: Influence on cellular ROS
sources. World J Urol. 35:1955–1965. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Association AVM: AVMA guidelines for the
euthanasia of animals. 2013.
|
|
15
|
Ng CK, Gill IS, Patil MB, Hung AJ, Berger
AK, de Castro Abreu AL, Nakamoto M, Eisenberg MS, Ukimura O,
Thangathurai D, et al: Anatomic renal artery branch microdissection
to facilitate zero-ischemia partial nephrectomy. Eur Urol.
61:67–74. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ye F, Li X, Liu Y, Jiang A, Li X, Yang L,
Chang W, Yuan J and Chen J: CypD deficiency confers neuroprotection
against mitochondrial abnormality caused by lead in SH-SY5Y cell.
Toxicol Lett. 323:25–34. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ramachandran A, Lebofsky M, Baines CP,
Lemasters JJ and Jaeschke H: Cyclophilin D deficiency protects
against acetaminophen-induced oxidant stress and liver injury. Free
Radic Res. 45:156–164. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu K, Shu D, Song N, Gai Z, Yuan Y, Li J,
Li M, Guo S, Peng J and Hong H: The role of cytochrome c on
apoptosis induced by Anagrapha falcifera multiple nuclear
polyhedrosis virus in insect Spodoptera litura cells. PLoS One.
7(e40877)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
McManus MJ and Franklin JL: Dissociation
of JNK activation from elevated levels of reactive oxygen species,
cytochrome c release, and cell death in NGF-Deprived sympathetic
neurons. Mol Neurobiol. 55:382–389. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Palam LR, Baird TD and Wek RC:
Phosphorylation of eIF2 facilitates ribosomal bypass of an
inhibitory upstream ORF to enhance CHOP translation. J Biol Chem.
286:10939–10949. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dias-Teixeira KL, Calegari-Silva TC,
Medina JM, Vivarini ÁC, Cavalcanti Á, Teteo N, Santana AKM, Real F,
Gomes CM, Pereira RMS, et al: Emerging role for the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4
in human cutaneous leishmaniasis. Sci Rep. 7(17074)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Page AB, Owen CR, Kumar R, Miller JM,
Rafols JA, White BC, DeGracia DJ and Krause GS: Persistent
eIF2alpha(P) is colocalized with cytoplasmic cytochrome c in
vulnerable hippocampal neurons after 4 hours of reperfusion
following 10-minute complete brain ischemia. Acta Neuropathol.
106:8–16. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chesnokova E, Bal N and Kolosov P: Kinases
of eIF2a switch translation of mRNA subset during neuronal
plasticity. Int J Mol Sci. 18(2213)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Teng J, Liu M, Su Y, Li K, Sui N, Wang S,
Li L, Sun Y and Wang Y: Down-regulation of GRP78 alleviates
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury. Int Urol Nephrol.
50:2099–2107. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Aksoy MO, Kim V, Cornwell WD, Rogers TJ,
Kosmider B, Bahmed K, Barrero C, Merali S, Shetty N and Kelsen SG:
Secretion of the endoplasmic reticulum stress protein, GRP78, into
the BALF is increased in cigarette smokers. Respir Res.
18(78)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Small DL, Morley P and Buchan AM: Biology
of ischemic cerebral cell death. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 42:185–207.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chaves KC, Peron JP, Chammas R, Turaça LT,
Pesquero JB, Braga MS, Foguer K, Schor N and Bellini MH: Endostatin
gene therapy stimulates upregulation of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 in a
metastatic renal cell carcinoma model. Cancer Gene Ther.
19:558–565. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Xing H, Sun S, Mei Y and Herman D: The
protective effect of rosuvastatin on ischemic brain injury and its
mechanism. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 26:667–669.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shen A, Yang J, Gu Y, Zhou D, Sun L, Qin
Y, Chen J, Wang P, Xiao F, Zhang L and Cheng C:
Lipopolysaccharide-evoked activation of p38 and JNK leads to an
increase in ICAM-1 expression in Schwann cells of sciatic nerves.
FEBS J. 275:4343–4353. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Cardon AD, Bailey MR and Bennett BT: The
animal welfare Act: From enactment to enforcement. J Am Assoc Lab
Anim Sci. 51:301–305. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|