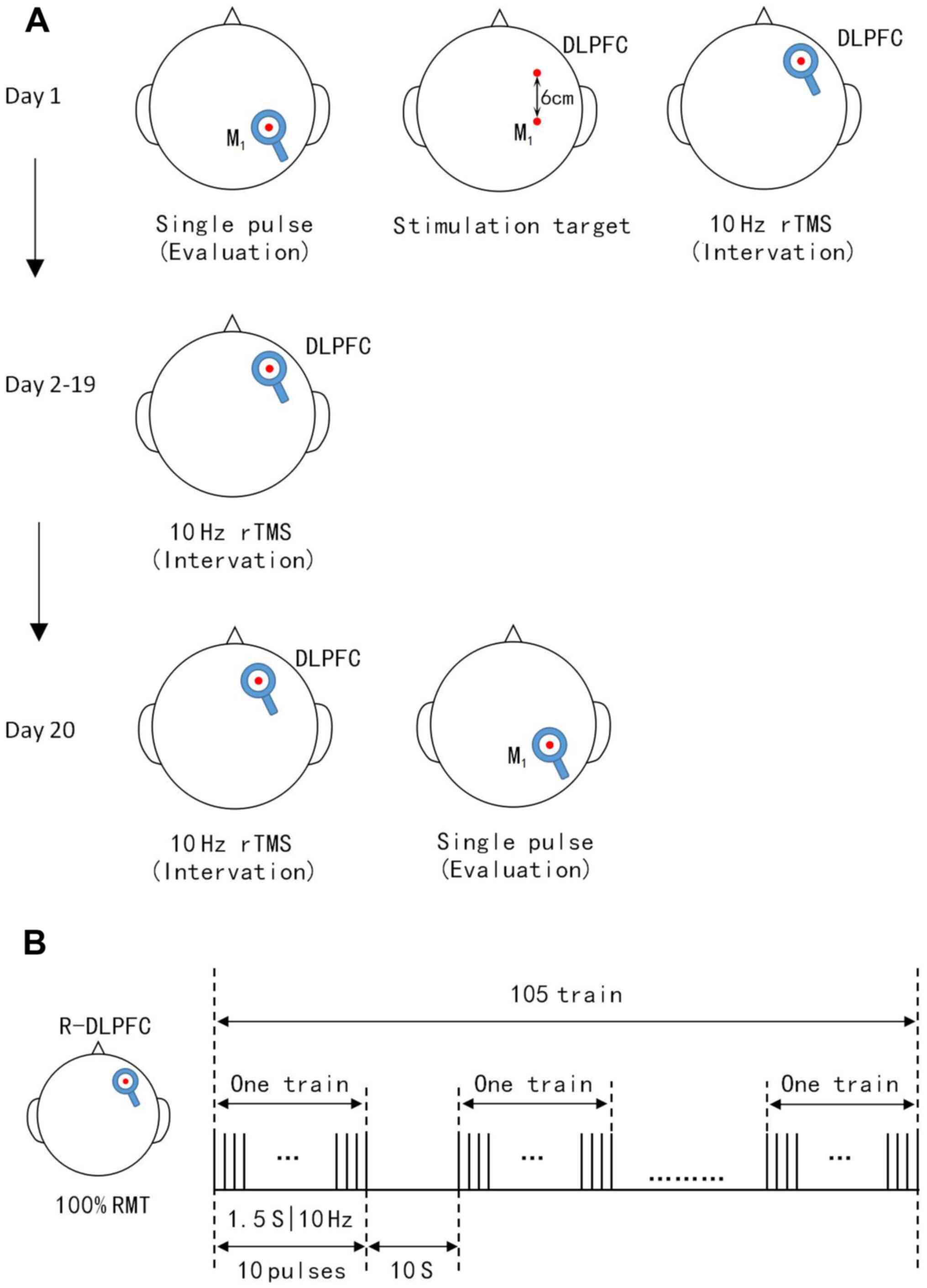
|
1
|
Giacino JT, Fins JJ, Laureys S and Schiff
ND: Disorders of consciousness after acquired brain injury: The
state of the science. Nat Rev Neurol. 10:99–114. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wu DY, Cai G, Yuan Y, Liu L, Li GQ, Song
WQ and Wang MB: Application of nonlinear dynamics analysis in
assessing unconsciousness: A preliminary study. Clin Neurophysiol.
122:490–498. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Guerra A, Costantini EM, Maatta S, Ponzo D
and Ferreri F: Disorders of consciousness and electrophysiological
treatment strategies: A review of the literature and new
perspectives. Curr Pharm Des. 20:4248–4267. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shin SS, Dixon CE, Okonkwo DO and
Richardson RM: Neurostimulation for traumatic brain injury. J
Neurosurg. 121:1219–1231. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Rossini PM, Barker AT, Berardelli A,
Caramia MD, Caruso G, Cracco RQ, Dimitrijević MR, Hallett M,
Katayama Y, Lücking CH, et al: Noninvasive electrical and magnetic
stimulation of the brain, spinal cord and roots: Basic principles
and procedures for routine clinical application Report of an IFCN
committee. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 91:79–92.
1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Louise-Bender Pape T, Rosenow J, Lewis G,
Ahmed G, Walker M, Guernon A, Roth H and Patil V: Repetitive
transcranial magnetic stimulation-associated neurobehavioral gains
during coma recovery. Brain Stimul. 2:22–35. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Xia X, Bai Y, Zhou Y, Yang Y, Xu R, Gao X,
Li X and He J: Effects of 10 Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic
stimulation of the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in disorders
of consciousness. Front Neurol. 8(182)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Xie Y and Zhang T: Repetitive transcranial
Magnetic Stimulation improves Consciousness disturbance in stroke
patients: A quantitative electroencephalography spectral power
analysis. Neural Regen Res. 7:2465–2472. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Barker AT, Jalinous R and Freeston IL:
Non-invasive magnetic stimulation of human motor cortex. Lancet.
1:1106–1107. 1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Di Lazzaro V, Oliviero A, Pilato F,
Saturno E, Dileone M, Mazzone P, Insola A, Tonali PA and Rothwell
JC: The physiological basis of transcranial motor cortex
stimulation in conscious humans. Clin Neurophysiol. 115:255–266.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chervyakov AV, Chernyavsky AY, Sinitsyn DO
and Piradov MA: Possoble mechanisms underlying the therapeutic
effects of transcranial magnetic stimulation. Front Hum Neurosci.
9(303)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Maeda F, Keenan JP, Tormos JM, Topka H and
Pascual-Leone A: Modulation of corticospinal excitability by
repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Clin Neurophysiol.
111:800–805. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Klomjai W, Lackmy-Vallée A, Roche N,
Pradat-Diehl P, Marchand-Pauvert V and Katz R: Repetitive
transcranial magnetic stimulation and transcranial direct current
stimulation in motor rehabilitation after stroke: An update. Ann
Phys Rehabil Med. 58:220–224. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lefaucheur JP, André-Obadia N, Antal A,
Ayache SS, Baeken C, Benninger DH, Cantello RM, Cincotta M, de
Carvalho M, De Ridder D, et al: Evidence-based guidelines on the
therapeutic use of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation
(rTMS). Clin Neurophysiol. 125:2150–2206. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Rossini PM, Burke D, Chen R, Cohen LG,
Daskalakis Z, Di Iorio R, Di Lazzaro V, Ferreri F, Fitzgerald PB,
George MS, et al: Non-invasive electrical and magnetic stimulation
of the brain, spinal cord, roots and peripheral nerves: Basic
principles and procedures for routine clinical and research
application An updated report from an I.F.C.N. Committee. Clin
Neurophysiol. 126:1071–1107. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Phillips AL, Burr RL and Dunner DL: rTMS
effects in patients with co-morbid somatic pain and depressive mood
disorders. J Affect Disord. 241:411–416. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kozel FA: Clinical repetitive transcranial
magnetic stimulation for posttraumatic stress disorder, generalized
anxiety disorder, and bipolar disorder. Psychiatr Clin North Am.
41:433–446. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kimiskidis VK, Valentin A and Kälviäinen
R: Transcranial magnetic stimulation for thediagnosis and treatment
of epilepsy. Curr Opin Neurol. 27:236–241. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Randver R: Repetitive transcranial
magnetic stimulation of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex to
alleviate depression and cognitive impairment associated with
Parkinson's disease: A review and clinical implications. J Neurol
Sci. 393:88–99. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Nardone R, Tezzon F, Höller Y, Golaszewski
S, Trinka E and Brigo F: Transcranial magnetic stimulation
(TMS)/repetitive TMS in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's
disease. Acta Neurol Scand. 129:351–366. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Naro A, Russo M, Leo A, Bramanti P,
Quartarone A and Calabrò RS: A single session of repetitive
transcranial magnetic stimulation over the dorsolateral prefrontal
cortex in patients with unresponsive wakefulness syndrome:
Preliminary results. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 29:603–613.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu P, Gao J, Pan S, Meng F, Pan G, Li J
and Luo B: Effects of High-frequency repetitive transcranial
magnetic stimulation on cerebral hemodynamics inpatients with
disorders of consciousness: A Sham-controlled study. Eur Neurol.
76:1–7. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bai Y, Xia X, Kang J, Yin X, Yang Y, He J
and Li X: Evaluating the effect of repetitive transcranial magnetic
stimulation on disorders of consciousness by using TMS-EEG. Front
Neurosci. 10(473)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Cincotta M, Giovannelli F, Chiaramonti R,
Bianco G, Godone M, Battista D, Cardinali C, Borgheresi A,
Sighinolfi A, D'Avanzo AM, et al: No effects of 20 Hz-rTMS of the
primary motor cortex in vegetative state: A randomised,
sham-controlled study. Cortex. 71:368–3676. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hosono Y, Urushihara R, Harada M, Morita
N, Murase N, Kunikane Y, Shimazu H, Asanuma K, Uguisu H and Kaji R:
Comparison of monophasic versus biphasic stimulation in rTMS over
premotor cortex: SEP and SPECT studies. Clin Neurophysiol.
119:2538–2545. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Johnson KA, Baig M, Ramsey D, Lisanby SH,
Avery D, McDonald WM, Li X, Bernhardt ER, Haynor DR, Holtzheimer PE
III, et al: Prefrontal rTMS for treating depression: Location and
intensity results from the OPT-TMS Multi-site clinical trial. Brain
Stimul. 6:108–117. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Laureys S, Owen AM and Schiff ND: Brain
function in coma, vegetative state, and related disorders. Lancet
Neurol. 3:537–546. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Terao Y and Ugawa Y: Basic mechanisms of
TMS. J Clin Neurophysiol. 19:322–343. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Piccione F, Cavinato M, Manganotti P,
Formaggio E, Storti SF, Battistin L, Cagnin A, Tonin P and Dam M:
Behavioral and neurophysiological effects of repetitive
transcranial magnetic stimulation on the minimally conscious state:
A case study. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 25:98–102.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Manganotti P, Formaggio E, Storti SF,
Fiaschi A, Battistin L, Tonin P, Piccione F and Cavinato M: Effect
of high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation on
brain excitability in severely Brain-injured patients in minimally
conscious or vegetative state. Brain Stimul. 6:913–921.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Wassermann EM and Lisanby SH: Therapeutic
application of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation: A
review. Clin Neurophysiol. 112:1367–1377. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cavinato M, Iaia V and Piccione F:
Repeated sessions of Sub-threshold 20-Hz rTMS. Potential cumulative
effects in a Brain-injured patient. Clin Neurophysiol.
123:1893–1895. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Thibaut A, Bodien YG, Laureys S and
Giacino JT: Minimally conscious state ‘plus’: Diagnostic criteria
and relation to functional recovery. J Neurol. 267:1245–1254.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Bruno MA, Majerus S, Boly M,
Vanhaudenhuyse A, Schnakers C, Gosseries O, Boveroux P, Kirsch M,
Demertzi A, Bernard C, et al: Functional neuroanatomy underlying
the clinical subcategorization of minimally conscious state
patients. J Neurol. 259:1087–1098. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Annen J, Filippini MM, Bonin E, Cassol H,
Aubinet C, Carrière M, Gosseries O, Thibaut A, Barra A, Wolff A, et
al: Diagnostic accuracy of the CRS-R index in patients with
disorders of consciousness. Brain Inj. 33:1409–1412.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Lammi MH, Smith VH, Tate RL and Taylor CM:
The minimally conscious state and recovery potential: A follow-up
study 2 to 5 years after traumatic brain injury. Arch Phys Med
Rehabil. 86:746–754. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bodien YG, Carlowicz CA, Chatelle C and
Giacino JT: Sensitivity and specificity of the coma recovery
Scale-revised total score in detection of conscious awareness. Arch
Phys Med Rehabil. 97:490–492.e1. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cakar E, Akyuz G, Durmus O, Bayman L,
Yagci I, Karadag-Saygi E and Gunduz OH: The relationships of
Motor-evoked potentials to hand dexterity, motor function, and
spasticity in chronic stroke patients: A transcranial magnetic
stimulation study. Acta Neurol Belg. 116:481–487. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|