|
1
|
Archer NM, Forbes PW, Dargie J, Manganella
J, Licameli GR, Kenna MA and Brugnara C: Association of blood type
with postsurgical mucosal bleeding in pediatric patients undergoing
tonsillectomy with or without adenoidectomy. JAMA Netw Open.
3(e201804)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Materia E, Di Domenicantonio R, Baglio G,
Marchisio P, Perletti L, Lispi L, Mele A and Guasticchi G:
Epidemiology of tonsillectomy and/or adenoidectomy in Italy.
Pediatr Med Chir. 26:179–186. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Roushdy MM, Abdel-Ghaffar HS, Mohammed MA
and Khalifa AH: Comparative study between the effect of Diclofenac
and Ketorolac in post-tonsillectomy pain management. Egypt J Neck
Surg Otorhinolaryngol. 6:43–53. 2020.
|
|
4
|
Di Luca M, Iannella G, Montevecchi F,
Magliulo G, De Vito A, Cocuzza S, Maniaci A, Meccariello G,
Cammaroto G, Sgarzani R, et al: Use of the transoral robotic
surgery to treat patients with recurrent lingual tonsillitis. Int J
Med Robot. 16(e2106)2020.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Soaper AL, Richardson ZL, Chen JL and
Gerber ME: Pediatric tonsillectomy: A short-term and long-term
comparison of intracapsular versus extracapsular techniques. Int J
Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 133(109970)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Joseph M, Reardon E and Goodman M: Lingual
tonsillectomy: A treatment for inflammatory lesions of the lingual
tonsil. Laryngoscope. 94:179–184. 1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Krishna P and Lee D: Post-tonsillectomy
bleeding: A meta-analysis. Laryngoscope. 111:1358–1361.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Broadman LM, Patel RI, Feldman BA, Sellman
GL, Milmoe G and Camilon F: The effects of peritonsillar
infiltration on the reduction of intraoperative blood loss and
post-tonsillectomy pain in children. Laryngoscope. 99:578–581.
1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Teker AM, Korkut AY, Gedikli O and Kahya
V: Prospective, controlled clinical trial of Ankaferd Blood Stopper
in children undergoing tonsillectomy. Int J Pediatr
Otorhinolaryngol. 73:1742–1745. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kargi E, Hoşnuter M, Babucçu O, Altunkaya
H and Altinyazar C: Effect of steroids on edema, ecchymosis, and
intraoperative bleeding in rhinoplasty. Ann Plast Surg. 51:570–574.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wohlgemuth PR and O'Brien GR:
Postoperative edema in maxillofacial surgery; prevention and
treatment with promethazine. Am J Surg. 94:537–541. 1957.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Xu F, Zeng W, Mao X and Fan GK: The
efficacy of melilotus extract in the management of postoperative
ecchymosis and edema after simultaneous rhinoplasty and
blepharoplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 32:599–603. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Davidoss NH, Eikelboom R, Friedland PL and
Santa Maria PL: Wound healing after tonsillectomy - a review of the
literature. J Laryngol Otol. 132:764–770. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Deutsch ES and Isaacson GC: Tonsils and
adenoids: An update. Pediatr Rev. 16:17–21. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Linden BE, Gross CW, Long TE and Lazar RH:
Morbidity in pediatric tonsillectomy. Laryngoscope. 100:120–124.
1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Odhagen E, Stalfors J and Sunnergren O:
Morbidity after pediatric tonsillotomy versus tonsillectomy: A
population-based cohort study. Laryngoscope. 129:2619–2626.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Nikandish R, Maghsoodi B, Khademi S,
Motazedian S and Kaboodkhani R: Peritonsillar infiltration with
bupivacaine and pethidine for relief of post-tonsillectomy pain: A
randomised double-blind study. Anaesthesia. 63:20–25.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sun J, Wu X, Meng Y and Jin L: Bupivacaine
versus normal saline for relief of post-adenotonsillectomy pain in
children: A meta-analysis. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol.
74:369–373. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Furutani K, Ikoma M, Ishii H, Baba H and
Kohno T: Bupivacaine inhibits glutamatergic transmission in spinal
dorsal horn neurons. Anesthesiology. 112:138–143. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Paganelli MA and Popescu GK: Actions of
bupivacaine, a widely used local anesthetic, on NMDA receptor
responses. J Neurosci. 35:831–842. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Block L, Jörneberg P, Björklund U,
Westerlund A, Biber B and Hansson E: Ultralow concentrations of
bupivacaine exert anti-inflammatory effects on
inflammation-reactive astrocytes. Eur J Neurosci. 38:3669–3678.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Cassuto J, Sinclair R and Bonderovic M:
Anti-inflammatory properties of local anesthetics and their present
and potential clinical implications. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand.
50:265–282. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Anderson LA, Engel GM, Bruckner JD,
Stoddard GJ and Peters CL: Reduced blood loss after total knee
arthroplasty with local injection of bupivacaine and epinephrine. J
Knee Surg. 22:130–136. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Metaxotos NG, Asplund O and Hayes M: The
efficacy of bupivacaine with adrenaline in reducing pain and
bleeding associated with breast reduction: A prospective trial. Br
J Plast Surg. 52:290–293. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kuthiala G and Chaudhary G: Ropivacaine: A
review of its pharmacology and clinical use. Indian J Anaesth.
55:104–110. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Polley LS, Columb MO, Naughton NN, Wagner
DS and van de Ven CJ: Relative analgesic potencies of ropivacaine
and bupivacaine for epidural analgesia in labor: Implications for
therapeutic indexes. Anesthesiology. 90:944–950. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Spivey WH, McNamara RM, MacKenzie RS, Bhat
S and Burdick WP: A clinical comparison of lidocaine and
bupivacaine. Ann Emerg Med. 16:752–757. 1987.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
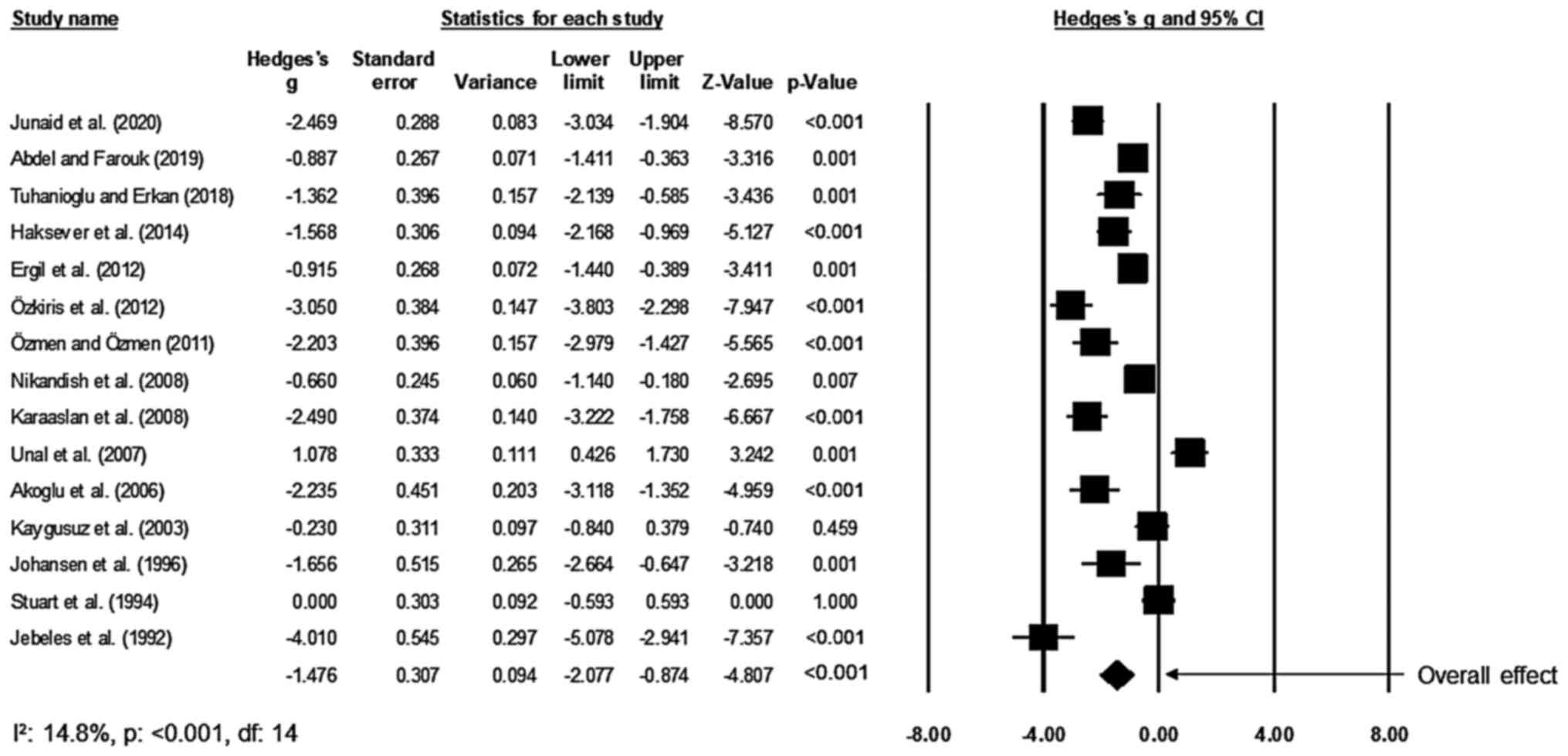
Abdel Raheem AG and Farouk ZM: Effect of
preincisional peritonsillar infiltration of bupivacaine on
post-tonsillectomy pain. Egypt J Neck Surg Otorhinolaryngol.
5:40–46. 2019.
|
|
29
|
Ergil J, Akkaya T, Gozaydin O, Gunsoy B,
Alicura S, Aladag E, Gumus H and Akin I: Vasoconstrictive and
analgesic efficacy of locally infiltrated levobupivacaine in
tonsillectomy patients. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol.
76:1429–1433. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Junaid M, Halim MS, Onali MA, Qadeer S,
Khan HU and Ali NS: Intraoperative use of analgesics in tonsillar
fossa and postoperative evaluation with visual analogue scale
scores-A prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind
clinical trial. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 24:e62–e67.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ozkiriş M, Kapusuz Z and Saydam L:
Comparison of ropivacaine, bupivacaine and lidocaine in the
management of post-tonsillectomy pain. Int J Pediatr
Otorhinolaryngol. 76:1831–1834. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Haksever M, Özmen S, Akduman D and Solmaz
F: Topical bupivacaine compared to bupivacaine infiltration for
post-tonsillectomy pain relief in children: A prospective
randomized controlled clinical study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol.
271:2555–2559. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Özmen OA and Özmen S: Topical bupivacaine
compared to lidocaine with epinephrine for post-tonsillectomy pain
relief in children: A randomized controlled study. Int J Pediatr
Otorhinolaryngol. 75:77–80. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Tuhanioglu B and Erkan SO: Tonsillectomy
pain control with IV dexamethasone, infiltrated dexamethasone and
infiltrated bupivacaine; a randomised, double-blind, placebo
controlled, prospective clinical trial. J Pak Med Assoc.
68:1002–1008. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
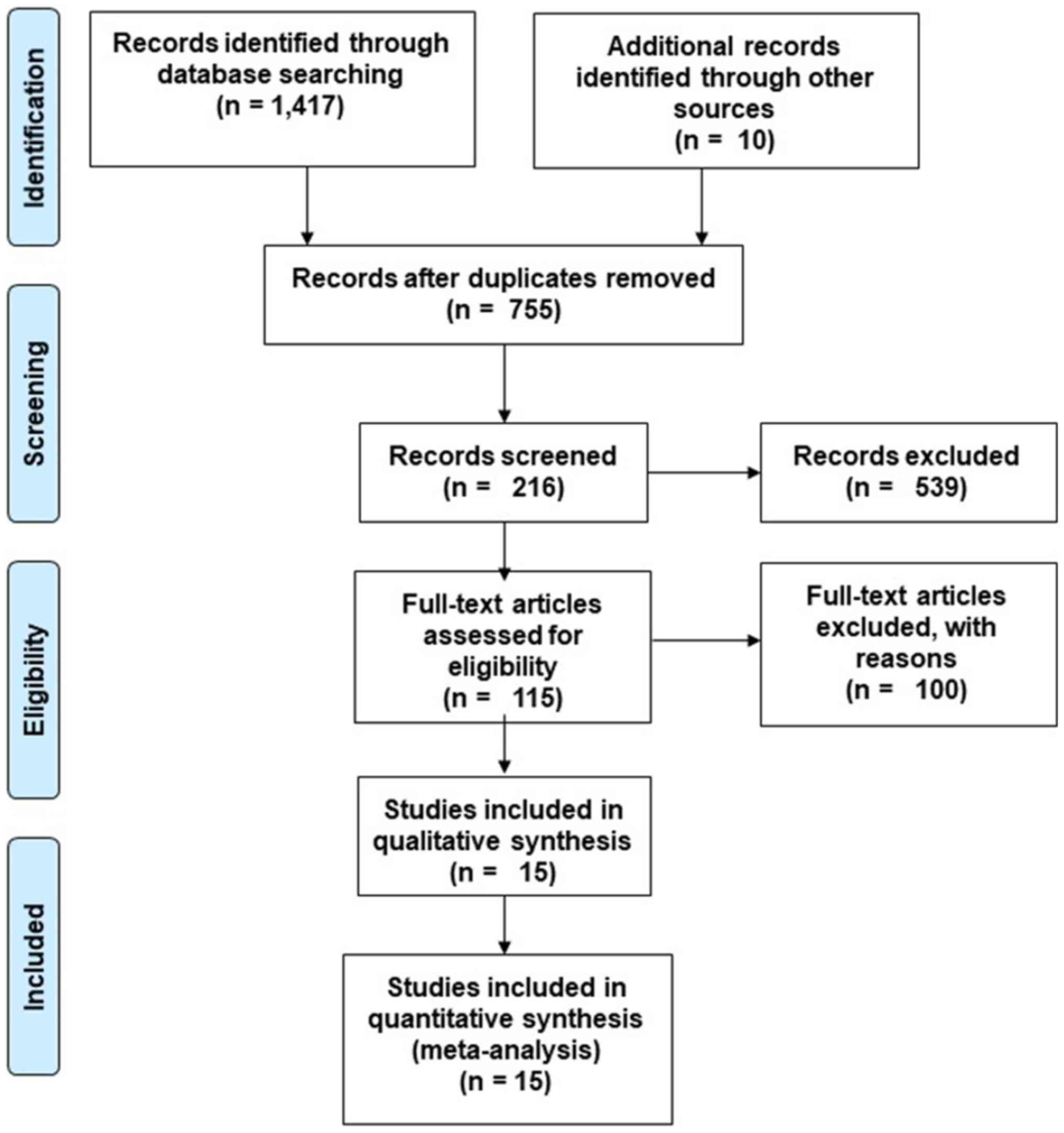
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J and Altman
DG: PRISMA Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews
and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Med.
6(e1000097)2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
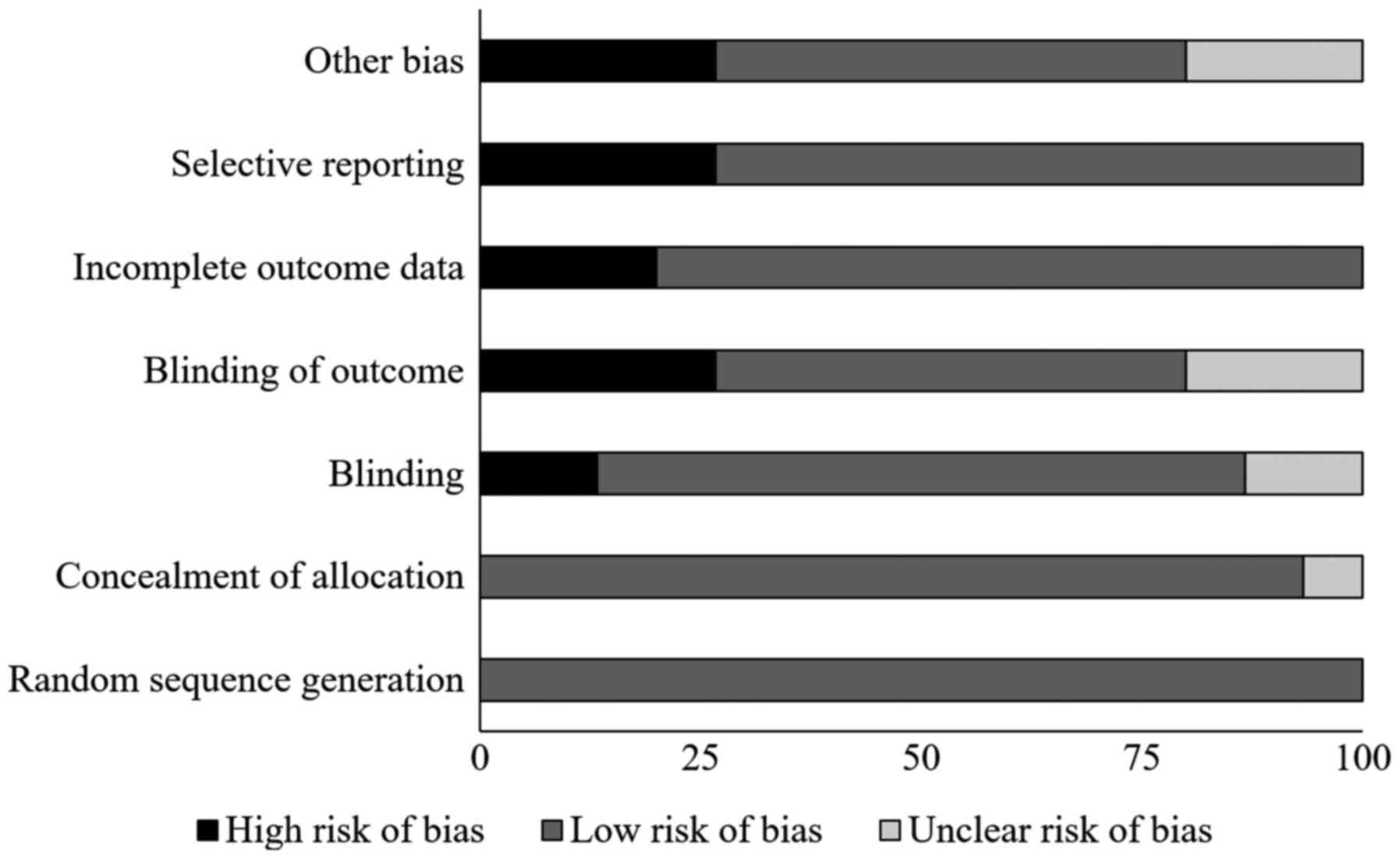
Jørgensen L, Paludan-Müller AS, Laursen
DR, Savović J, Boutron I, Sterne JA, Higgins JP and Hróbjartsson A:
Evaluation of the Cochrane tool for assessing risk of bias in
randomized clinical trials: Overview of published comments and
analysis of user practice in Cochrane and non-Cochrane reviews.
Syst Rev. 5(80)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Viswanathan M, Ansari MT, Berkman ND,
Chang S, Hartling L, McPheeters M, Santaguida PL, Shamliyan T,
Singh K, Tsertsvadze A, et al: Assessing the risk of bias of
individual studies in systematic reviews of health care
interventions. In: Methods Guide for Effectiveness and Comparative
Effectiveness Reviews. Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
(US), Rockville, MD, 2008.
|
|
38
|
Burns PB, Rohrich RJ and Chung KC: The
levels of evidence and their role in evidence-based medicine. Plast
Reconstr Surg. 128:305–310. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Bax L, Yu LM, Ikeda N and Moons KG: A
systematic comparison of software dedicated to meta-analysis of
causal studies. BMC Med Res Methodol. 7(40)2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Higgins JP, Thompson SG and Spiegelhalter
DJ: A re-evaluation of random-effects meta-analysis. J R Stat Soc
Ser A Stat Soc. 172:137–159. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Rosenthal R: Parametric measures of effect
size. In: The Handbook of Research Synthesis. Russell Sage
Foundation, New York, NY, pp231-244, 1994.
|
|
42
|
Higgins JP and Thompson SG: Quantifying
heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. 21:1539–1558.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Petitti DB: Approaches to heterogeneity in
meta-analysis. Stat Med. 20:3625–3633. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
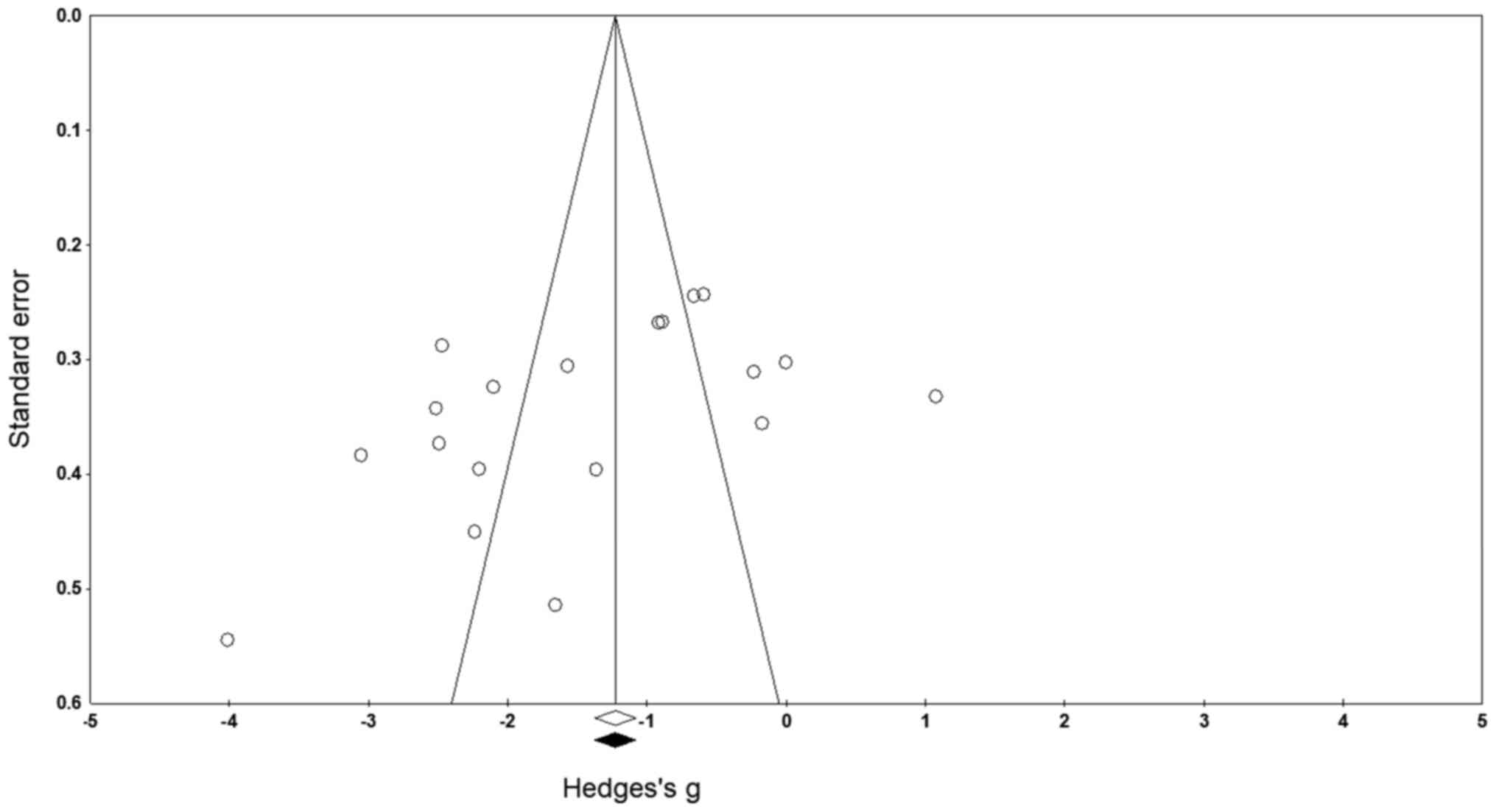
Duval S and Tweedie R: Trim and fill: A
simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for
publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. 56:455–463.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Karaaslan K, Yilmaz F, Gulcu N, Sarpkaya
A, Colak C and Kocoglu H: The effects of levobupivacaine versus
levobupivacaine plus magnesium infiltration on postoperative
analgesia and laryngospasm in pediatric tonsillectomy patients. Int
J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 72:675–681. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Akoglu E, Akkurt BC, Inanoglu K, Okuyucu S
and Dagli S: Ropivacaine compared to bupivacaine for
post-tonsillectomy pain relief in children: A randomized controlled
study. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 70:1169–1173.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Jebeles JA, Reilly JS, Gutierrez JF,
Bradley EL Jr and Kissin I: The effect of pre-incisional
infiltration of tonsils with bupivacaine on the pain following
tonsillectomy under general anesthesia. Pain. 47:305–308.
1991.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Johansen M, Harbo G and Illum P:
Preincisional infiltration with bupivacaine in tonsillectomy. Arch
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 122:261–263. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Kaygusuz I and Susaman N: The effects of
dexamethasone, bupivacaine and topical lidocaine spray on pain
after tonsillectomy. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 67:737–742.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Stuart JC, MacGregor FB, Cairns CS and
Chandrachud HR: Peritonsillar infiltration with bupivacaine for
paediatric tonsillectomy. Anaesth Intensive Care. 22:679–682.
1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Unal Y, Pampal K, Korkmaz S, Arslan M,
Zengin A and Kurtipek O: Comparison of bupivacaine and ropivacaine
on postoperative pain after tonsillectomy in paediatric patients.
Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 71:83–87. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Sedgwick P: Meta-analyses: How to read a
funnel plot. BMJ. 346(f1342)2013.
|
|
53
|
Terrin N, Schmid CH and Lau J: In an
empirical evaluation of the funnel plot, researchers could not
visually identify publication bias. J Clin Epidemiol. 58:894–901.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Bangera A: Anaesthesia for
adenotonsillectomy: An update. Indian J Anaesth. 61:103–109.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Verma R and Verma RR and Verma RR:
Tonsillectomy-comparative study of various techniques and changing
trend. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 69:549–558.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Babst CR and Gilling BN: Bupivacaine: A
review. Anesth Prog. 25:87–91. 1978.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Iida H, Watanabe Y, Dohi S and Ishiyama T:
Direct effects of ropivacaine and bupivacaine on spinal pial
vessels in canine. Assessment with closed spinal window technique.
Anesthesiology. 87:75–81. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Newton DJ, McLeod GA, Khan F and Belch JJ:
Vasoactive characteristics of bupivacaine and levobupivacaine with
and without adjuvant epinephrine in peripheral human skin. Br J
Anaesth. 94:662–667. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Prasad KC and Prasad SC: Assessment of
operative blood loss and the factors affecting it in tonsillectomy
and adenotonsillectomy. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg.
63:343–348. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Yu CN, Chow TK, Kwan AS, Wong SL and Fung
SC: Intra-operative blood loss and operating time in orthognathic
surgery using induced hypotensive general anaesthesia: Prospective
study. Hong Kong Med J. 6:307–311. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Nosulia EV: Peculiarities of blood supply
of palatal tonsils and the potential risk of hemorrhage during
tonsillectomy: The literature review and case report. Vestn
Otorinolaringol. 1:75–78. 2014.PubMed/NCBI(In Russian).
|
|
62
|
Liu JH, Anderson KE, Willging JP, Myer CM
III, Shott SR, Bratcher GO and Cotton RT: Posttonsillectomy
hemorrhage: What is it and what should be recorded? Arch
Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 127:1271–1275. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Mutz I and Simon H: Hemorrhagic
complications after tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. Experiences
with 7,743 operations in 14 years. Wien Klin Wochenschr.
105:520–522. 1993.PubMed/NCBI(In German).
|
|
64
|
PLoS Medicine Editors. Best practice in
systematic reviews: The importance of protocols and registration.
PLoS Med. 8(e1001009)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|