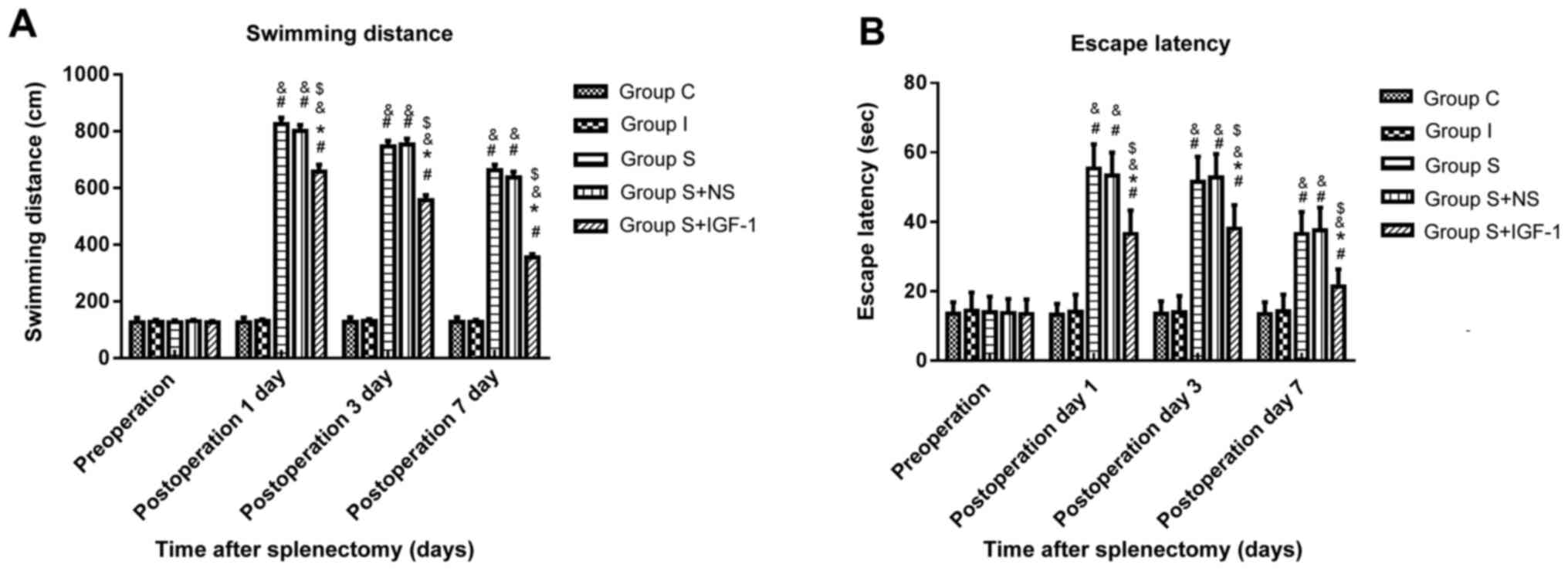
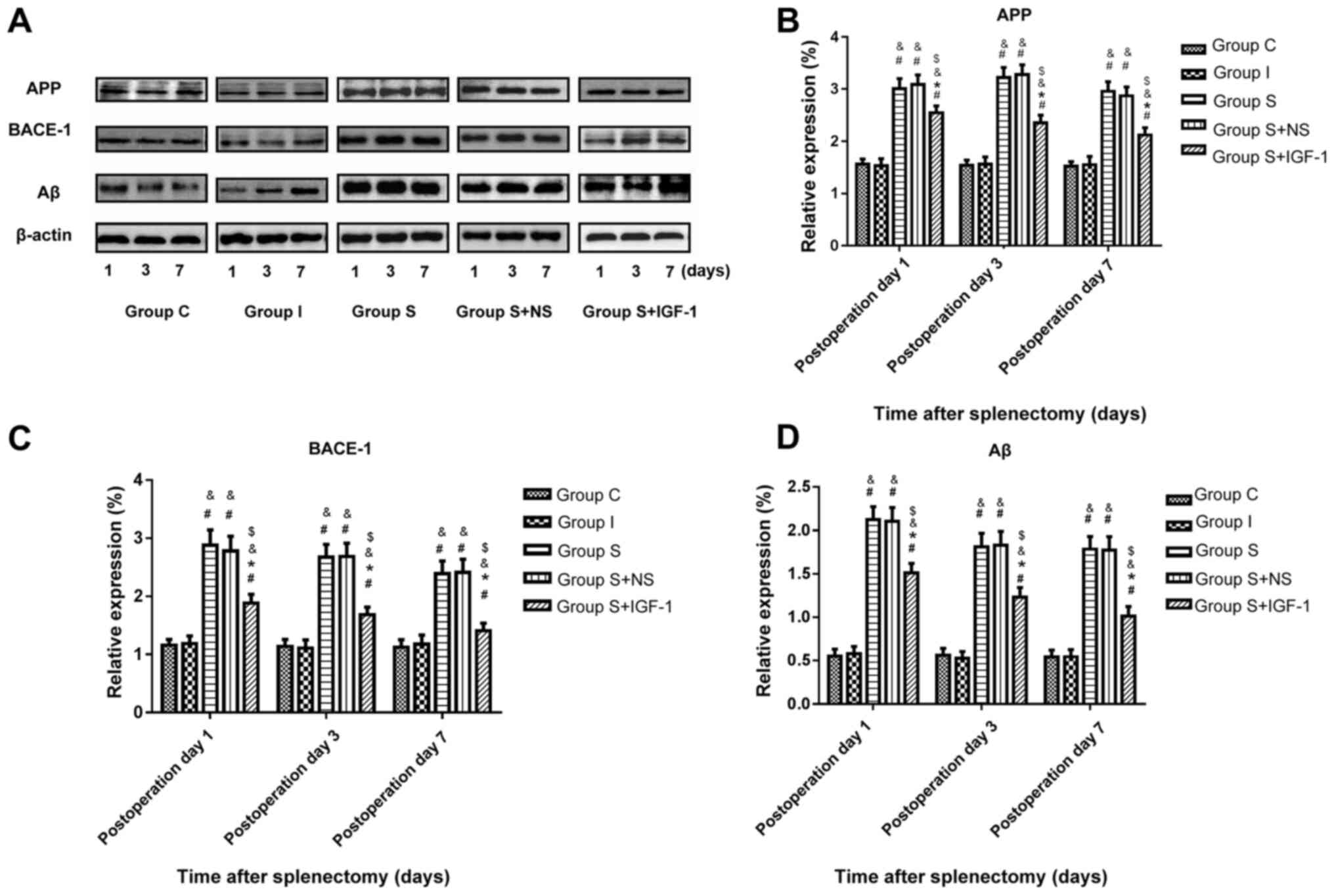
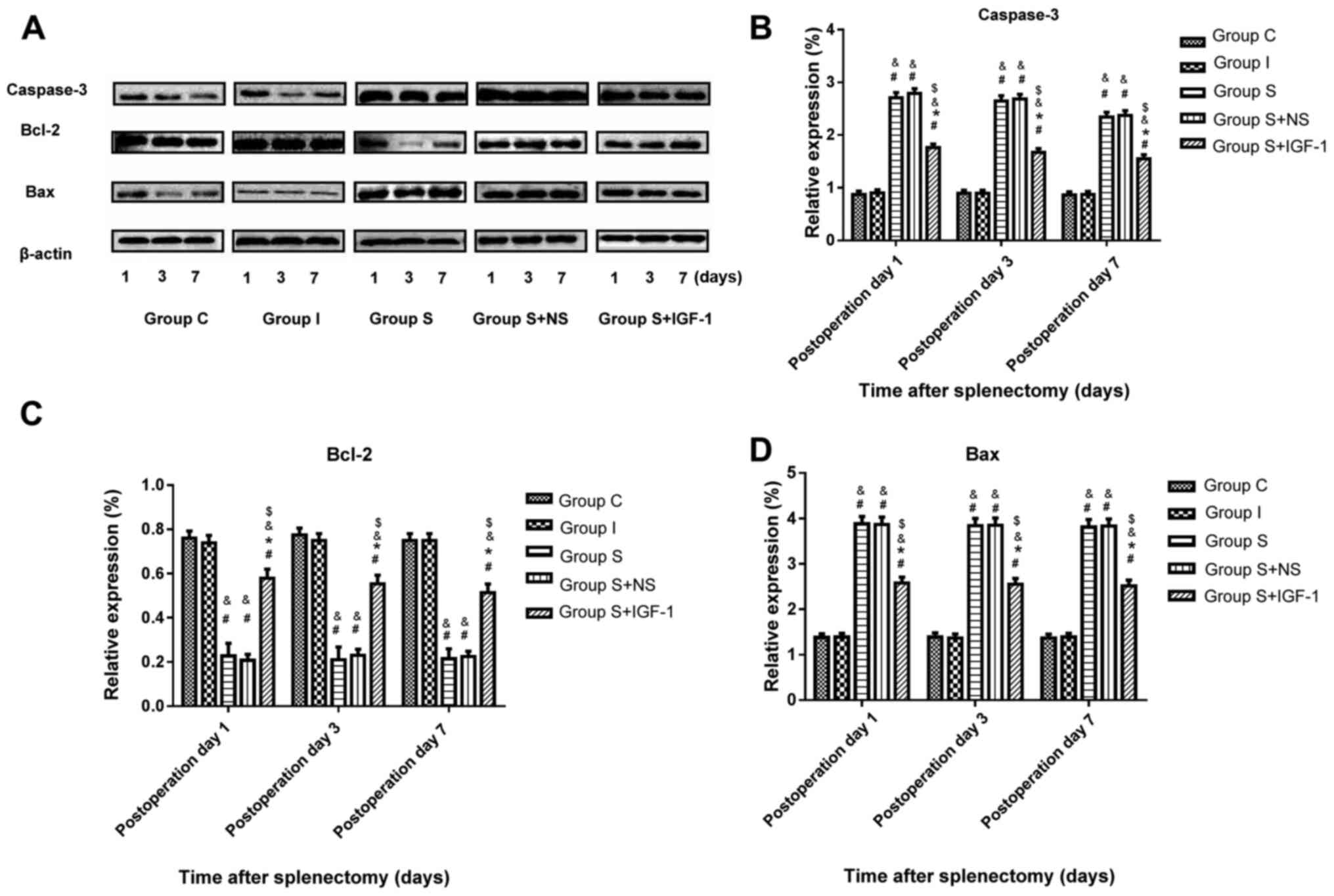
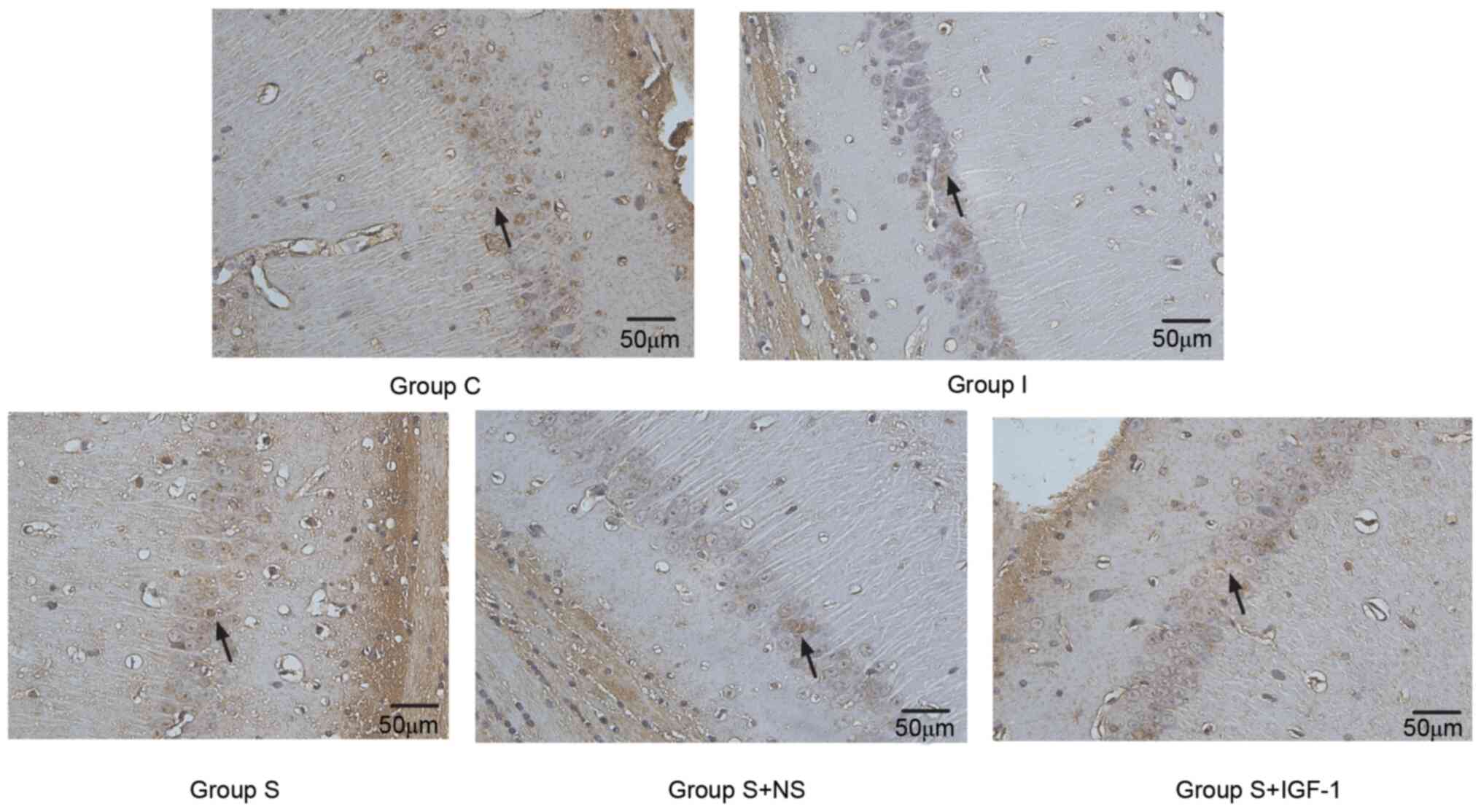
|
1
|
Safavynia SA and Goldstein PA: The role of
neuroinflammation in postoperative cognitive dysfunction: Moving
from hypothesis to treatment. Front Psychiatry.
9(752)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ramaiah R and Lam AM: Postoperative
cognitive dysfunction in the elderly. Anesthesiol Clin. 27:485–496.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Steinmetz J, Christensen KB, Lund T, Lohse
N and Rasmussen LS: ISPOCD Group. Long-term consequences of
postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Anesthesiology. 110:548–555.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wuri G, Wang DX, Zhou Y and Zhu SN:
Effects of surgical stress on long-term memory function in mice of
different ages. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 55:474–485.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Songjiang Z and Lixiang W: Amyloid-beta
associated with chitosan nano-carrier has favorable immunogenicity
and permeates the BBB. AAPS PharmSciTech. 10:900–905.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hoe HS, Lee HK and Pak DT: The upside of
APP at synapses. CNS Neurosci Ther. 18:47–56. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Poulsen SA, Watson AA, Fairlie DP and
Craik DJ: Solution structures in aqueous SDS micelles of two
amyloid beta peptides of A beta(1-28) mutated at the
alpha-secretase cleavage site (K16E, K16F). J Struct Biol.
130:142–152. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Garcez ML, Mina F, Bellettini-Santos T, da
Luz AP, Schiavo GL, Macieski JMC, Medeiros EB, Marques AO, Magnus
NQ and Budni J: The involvement of NLRP3 on the effects of
minocycline in an AD-like pathology induced by β-amyloid oligomers
administered to mice. Mol Neurobiol. 56:2606–2617. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ghahghaei A, Bathaie SZ, Kheirkhah H and
Bahraminejad E: The protective effect of crocin on the amyloid
fibril formation of Aβ42 peptide in vitro. Cell Mol Biol Lett.
18:328–339. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wu Z, Zhang M, Zhang Z, Dong W, Wang Q and
Ren J: Ratio of β-amyloid protein (Aβ) and Tau predicts the
postoperative cognitive dysfunction on patients undergoing total
hip/knee replacement surgery. Exp Ther Med. 15:878–884.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhang X, Dong H, Li N, Zhang S, Sun J,
Zhang S and Qian Y: Activated brain mast cells contribute to
postoperative cognitive dysfunction by evoking microglia activation
and neuronal apoptosis. J Neuroinflammation. 13(127)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Vassilakos G and Barton ER: Insulin-like
growth factor I regulation and its actions in skeletal muscle.
Compr Physiol. 9:413–438. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
D'Ercole AJ, Ye P and O'Kusky JR: Mutant
mouse models of insulin-like growth factor actions in the central
nervous system. Neuropeptides. 36:209–220. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Mishra N, Lata S, Deshmukh P, Kamat K,
Surolia A and Banerjee T: Insulin signaling pathway protects
neuronal cell lines by Sirt3 mediated IRS2 activation. Biofactors.
44:224–236. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liao R, Yan F, Zeng Z, Farhan M, Little P,
Quirion R, Srivastava LK and Zheng W: Amiodarone-Induced Retinal
Neuronal Cell Apoptosis Attenuated by IGF-1 via Counter Regulation
of the PI3k/Akt/FoxO3a Pathway. Mol Neurobiol. 54:6931–6943.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nakao Y, Otani H, Yamamura T, Hattori R,
Osako M and Imamura H: Insulin-like growth factor 1 prevents
neuronal cell death and paraplegia in the rabbit model of spinal
cord ischemia. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 122:136–143.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lackey BR, Gray SL and Henricks DM:
Actions and interactions of the IGF system in Alzheimer's disease:
Review and hypotheses. Growth Horm IGF Res. 10:1–13.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sonntag WE1. Deak F, Ashpole N, Toth P,
Csiszar A, Freeman W and Ungvari Z: Insulin-like growth factor-1 in
CNS and cerebrovascular aging. Front Aging Neurosci.
5(27)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Angelini A, Bendini C, Neviani F,
Bergamini L, Manni B, Trenti T, Rovati R and Neri M: Insulin-like
growth factor-1 (IGF-1): Relation with cognitive functioning and
neuroimaging marker of brain damage in a sample of hypertensive
elderly subjects. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 49 (Suppl 1):5–12.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Guidance Suggestions for the Care and Use
of Laboratory Animals 9: 30, 2006.
|
|
21
|
Umholtz M and Nader ND: Anesthetic
immunomodulation of the neuroinflammation in postoperative
cognitive dysfunction. Immunol Invest. 46:805–815. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Newman S, Stygall J, Hirani S, Shaefi S,
Maze M and Warltier DC: Postoperative cognitive dysfunction after
noncardiac surgery: A systematic review. Anesthesiology.
106:572–590. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wan Y, Xu J, Ma D, Zeng Y, Cibelli M and
Maze M: Postoperative impairment of cognitive function in rats: A
possible role for cytokine-mediated inflammation in the
hippocampus. Anesthesiology. 106:436–443. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li M, Yong-Zhe L, Ya-Qun M, Sheng-Suo Z,
Li-Tao Z and Ning-Ling P: Ulinastatin alleviates neuroinflammation
but fails to improve cognitive function in aged rats following
partial hepatectomy. Neurochem Res. 38:1070–1077. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Cibelli M, Fidalgo AR, Terrando N, Ma D,
Monaco C, Feldmann M, Takata M, Lever IJ, Nanchahal J, Fanselow MS,
et al: Role of interleukin-1beta in postoperative cognitive
dysfunction. Ann Neurol. 68:360–368. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang B, Li S, Cao X, Dou X, Li J, Wang L,
Wang M and Bi Y: Blood-brain barrier disruption leads to
postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Curr Neurovasc Res.
14:359–367. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yu L, Sun L and Chen S: Protective effect
of senegenin on splenectomy-induced postoperative cognitive
dysfunction in elderly rats. Exp Ther Med. 7:821–826.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kamer AR, Galoyan SM, Haile M, Kline R,
Boutajangout A, Li YS and Bekker A: Meloxicam improves object
recognition memory and modulates glial activation after splenectomy
in mice. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 29:332–337. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Weitzner DS, Engler-Chiurazzi EB,
Kotilinek LA, Ashe KH and Reed MN: Morris water maze test:
Optimization for mouse strain and testing environment. J Vis Exp.
22(e52706)2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Jawa RS, Anillo S, Huntoon K, Baumann H
and Kulaylat M: Interleukin-6 in surgery, trauma, and critical care
part II: Clinical implications. J Intensive Care Med. 26:73–87.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Pang H, Huang T, Song J, Li D, Zhao Y and
Ma X: Inhibiting HMGB1 with glycyrrhizic acid protects brain injury
after DAI via its anti-inflammatory effect. Mediators Inflamm.
2016(4569521)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Lu SM, Gui B, Dong HQ, Zhang X, Zhang SS,
Hu LQ, Liu HL, Sun J and Qian YN: Prophylactic lithium alleviates
splenectomy-induced cognitive dysfunction possibly by inhibiting
hippocampal TLR4 activation in aged rats. Brain Res Bull.
114:31–41. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Canet J, Raeder J, Rasmussen LS, Enlund M,
Kuipers HM, Hanning CD, Jolles J, Korttila K, Siersma VD, Dodds C,
et al: ISPOCD2 investigators. Cognitive dysfunction after minor
surgery in the elderly. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 47:1204–1210.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Roher AE, Kokjohn TA, Clarke SG, Sierks
MR, Maarouf CL, Serrano GE, Sabbagh MS and Beach TG: APP/Aβ
structural diversity and Alzheimer's disease pathogenesis.
Neurochem Int. 110:1–13. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhu D, Yang N, Liu YY, Zheng J, Ji C and
Zuo PP: M2 Macrophage transplantation ameliorates cognitive
dysfunction in amyloid-β-treated rats through regulation of
microglial polarization. J Alzheimers Dis. 52:483–495.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Masters CL and Selkoe DJ: Biochemistry of
amyloid β-protein and amyloid deposits in Alzheimer disease. Cold
Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2(a006262)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Kulic L, McAfoose J, Welt T, Tackenberg C,
Späni C, Wirth F, Finder V, Konietzko U, Giese M, Eckert A, et al:
Early accumulation of intracellular fibrillar oligomers and late
congophilic amyloid angiopathy in mice expressing the Osaka
intra-Aβ APP mutation. Transl Psychiatry. 2(e183)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xie Z and Tanzi RE: XieZ. Alzheimer's
disease and post-operative cognitive dysfunction. Exp Gerontol.
41:346–359. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Qian XL, Zhang W, Liu MZ, Zhou YB, Zhang
JM, Han L, Peng YM, Jiang JH and Wang QD: Dexmedetomidine improves
early postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged mice. Eur J
Pharmacol. 746:206–212. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Teng JA, Wu SG, Chen JX, Li Q, Peng F, Zhu
Z, Qin J and He ZY: The activation of ERK1/2 and JNK MAPK signaling
by insulin/IGF-1 is responsible for the development of colon cancer
with type 2 diabetes mellitus. PLoS One.
11(e0149822)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Araki W, Kume H, Oda A, Tamaoka A and
Kametani F: IGF-1 promotes beta-amyloid production by a
secretase-independent mechanism. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
380:111–114. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Zhou Q, Wang M, Du Y, Zhang W, Bai M,
Zhang Z, Li Z and Miao J: Inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase
activation reverses alzheimer disease phenotypes in APPswe/PS1d E9
mice. Ann Neurol. 77:637–654. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhang Q, Li Y, Bao Y, Yin C, Xin X, Guo Y,
Gao F, Huo S, Wang X and Wang Q: Pretreatment with nimodipine
reduces incidence of POCD by decreasing calcineurin mediated
hippocampal neuroapoptosis in aged rats. BMC Anesthesiol.
18(42)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lin HH, Chen JH, Huang CC and Wang CJ:
Apoptotic effect of 3,4-dihydroxybenzoic acid on human gastric
carcinoma cells involving JNK/p38 MAPK signaling activation. Int J
Cancer. 120:2306–2316. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Scorrano L and Korsmeyer SJ: Mechanisms of
cytochrome c release by proapoptotic BCL-2 family members. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 304:437–444. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Kopeina GS, Prokhorova EA, Lavrik IN and
Zhivotovsky B: Alterations in the nucleocytoplasmic transport in
apoptosis: Caspases lead the way. Cell Prolif.
51(e12467)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Shi Y: Mechanisms of caspase activation
and inhibition during apoptosis. Mol Cell. 9:459–470.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Peña-Blanco A and García-Sáez AJ: Bax, Bak
and beyond - mitochondrial performance in apoptosis. FEBS J.
285:416–431. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Festjens N, van Gurp M, van Loo G, Saelens
X and Vandenabeele P: Bcl-2 family members as sentinels of cellular
integrity and role of mitochondrial intermembrane space proteins in
apoptotic cell death. Acta Haematol. 111:7–27. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Yang L, Wang H, Liu L and Xie A: The role
of insulin/IGF-1/PI3K/Akt/GSK3β signaling in Parkinson's disease
dementia. Front Neurosci. 12(73)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Ueki K, Fruman DA, Brachmann SM, Tseng YH,
Cantley LC and Kahn CR: Molecular balance between the regulatory
and catalytic subunits of phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulates cell
signaling and survival. Mol Cell Biol. 22:965–977. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Dufour C, Holy X and Marie PJ:
Transforming growth factor-beta prevents osteoblast apoptosis
induced by skeletal unloading via PI3K/Akt, Bcl-2, and phospho-Bad
signaling. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 294:E794–E801.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Peruzzi F, Prisco M, Dews M, Salomoni P,
Grassilli E, Romano G, Calabretta B and Baserga R: Multiple
signaling pathways of the insulin-like growth factor 1receptor in
protection from apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol. 19:7203–7215.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Wymann MP and Pirola L: Structure and
function of phosphoinositide 3-kinases. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1436:127–150. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|