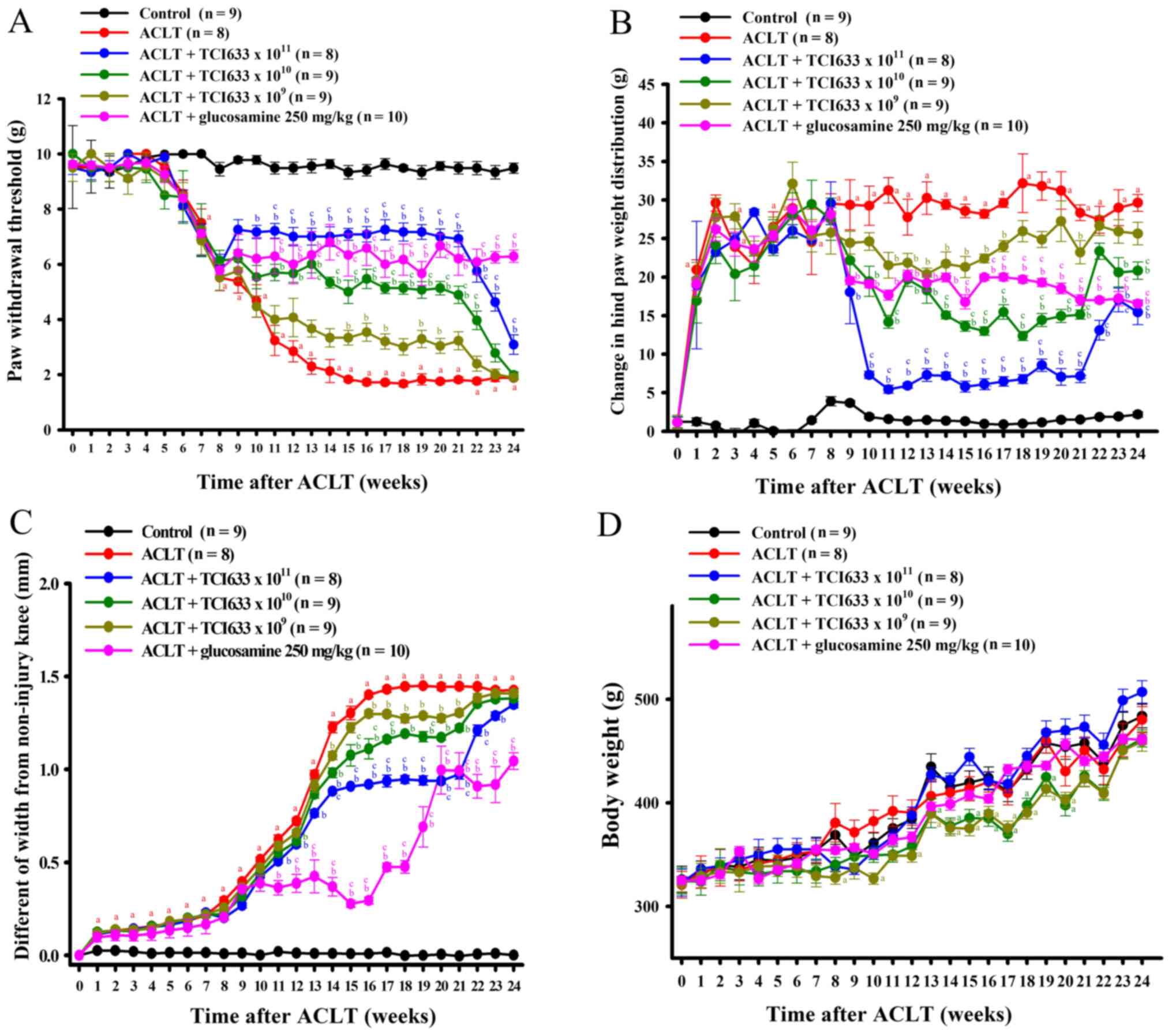
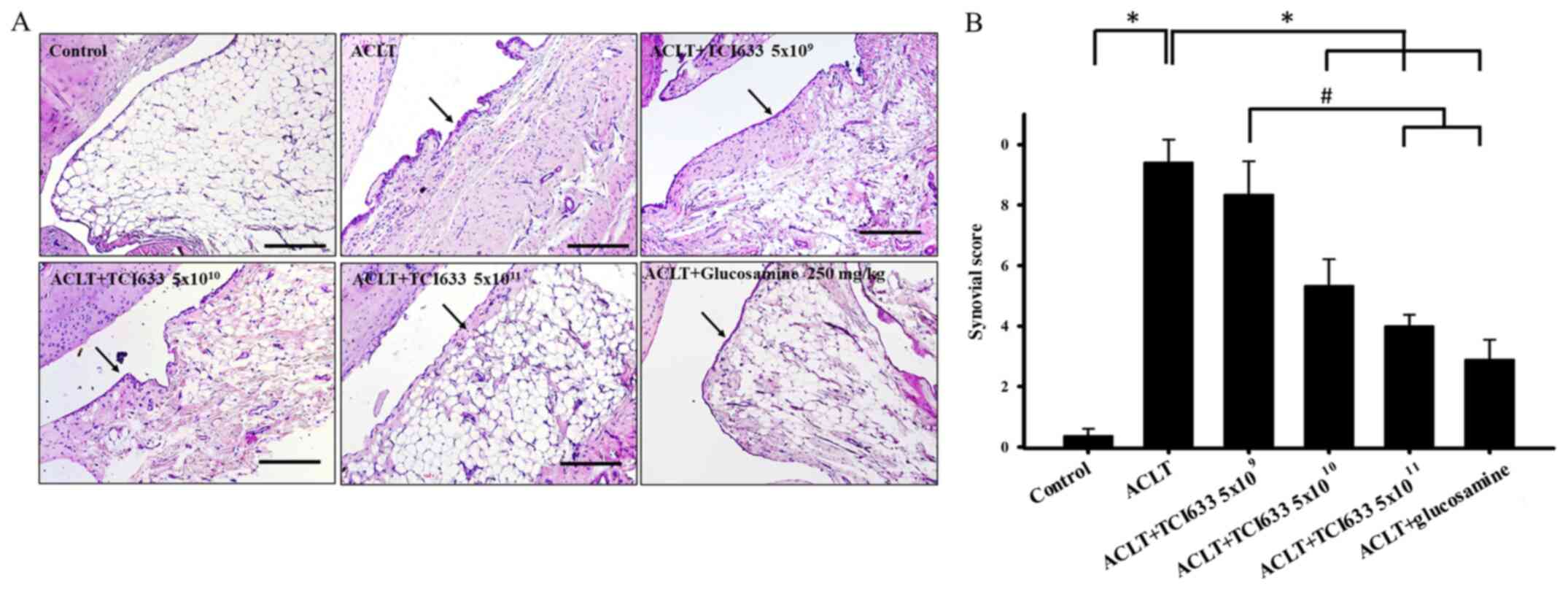
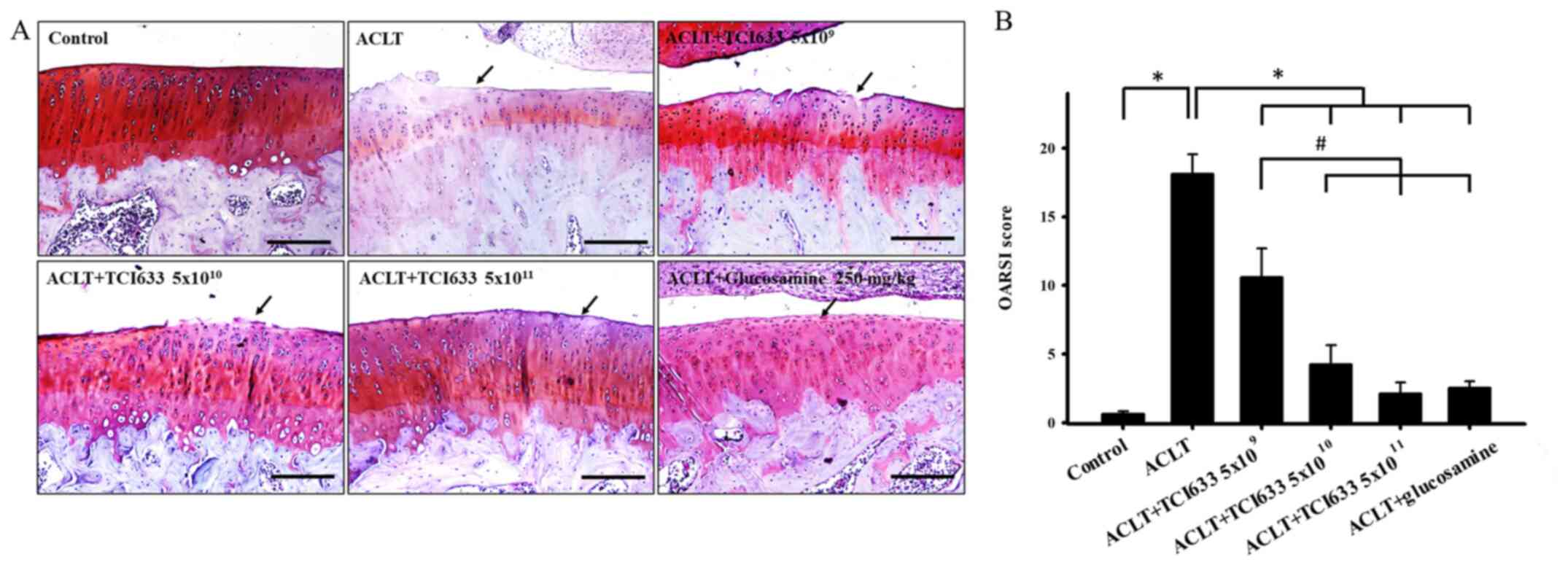
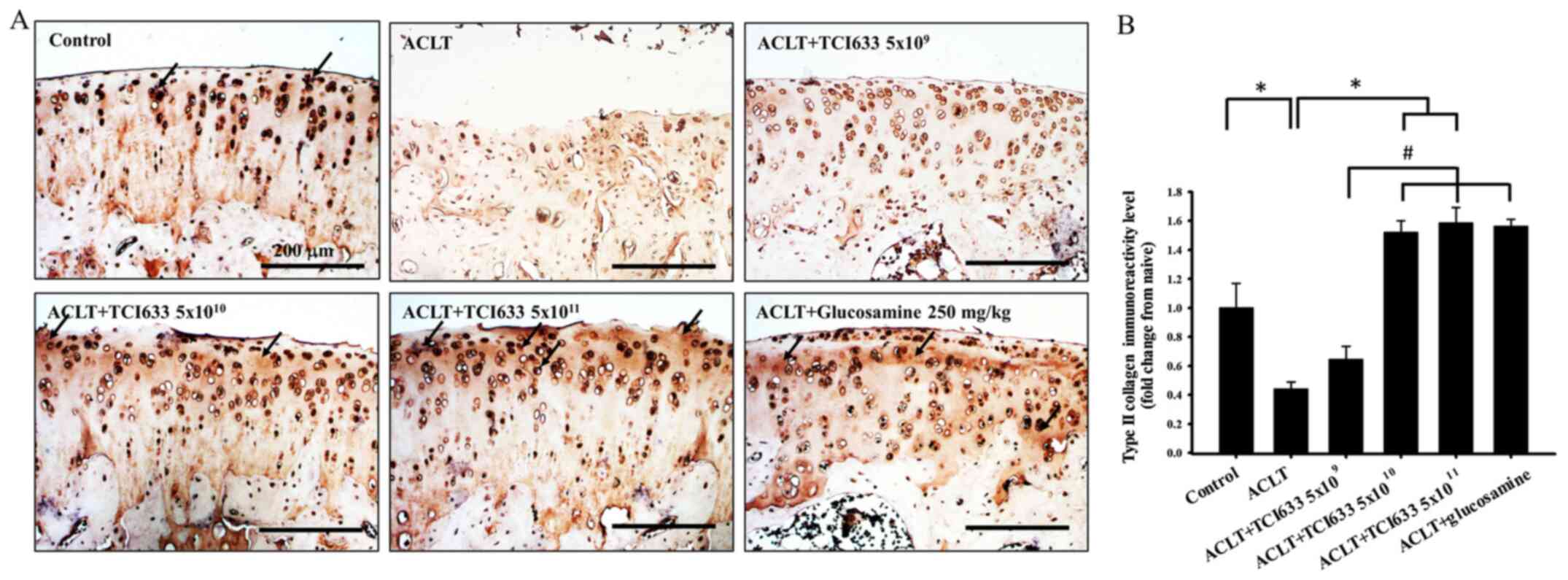
|
1
|
Litwic A, Edwards MH, Dennison EM and
Cooper C: Epidemiology and burden of osteoarthritis. Br Med Bull.
105:185–199. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cross M, Smith E, Hoy D, Nolte S, Ackerman
I, Fransen M, Bridgett L, Williams S, Guillemin F, Hill CL, et al:
The global burden of hip and knee osteoarthritis: Estimates from
the global burden of disease 2010 study. Ann Rheum Dis.
73:1323–1330. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Neogi T: The epidemiology and impact of
pain in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 21:1145–1153.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Castrogiovanni P, Di Rosa M, Ravalli S,
Castorina A, Guglielmino C, Imbesi R, Vecchio M, Drago F,
Szychlinska MA and Musumeci G: Moderate physical activity as a
prevention method for knee osteoarthritis and the tole of
dynoviocytes as niological key. Int J Mol Sci.
20(20)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Naito K, Watari T, Furuhata A, Yomogida S,
Sakamoto K, Kurosawa H, Kaneko K and Nagaoka I: Evaluation of the
effect of glucosamine on an experimental rat osteoarthritis model.
Life Sci. 86:538–543. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Cohen-Solal M, Funck-Brentano T and Hay E:
Animal models of osteoarthritis for the understanding of the bone
contribution. Bonekey Rep. 2(422)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Carmona FD, González-Gay MA and Martín J:
Genetic component of giant cell arteritis. Rheumatology (Oxford).
53:6–18. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tsai WY, Wu JL, Liu CC, Cherng CH, Tsai
RY, Jean YH and Wong CS: Early intraarticular injection of
hyaluronic acid attenuates osteoarthritis progression in anterior
cruciate ligament-transected rats. Connect Tissue Res. 54:49–54.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wen ZH, Tang CC, Chang YC, Huang SY, Chen
CH, Wu SC, Hsieh SP, Hsieh CS, Wang KY, Lin SY, et al:
Intra-articular injection of the selective cyclooxygenase-2
inhibitor meloxicam (Mobic) reduces experimental osteoarthritis and
nociception in rats. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 21:1976–1986.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wen ZH, Tang CC, Chang YC, Huang SY, Lin
YY, Hsieh SP, Lee HP, Lin SC, Chen WF and Jean YH: Calcitonin
attenuates cartilage degeneration and nociception in an
experimental rat model of osteoarthritis: Role of TGF-β in
chondrocytes. Sci Rep. 6(28862)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhen G, Wen C, Jia X, Li Y, Crane JL,
Mears SC, Askin FB, Frassica FJ, Chang W, Yao J, et al: Inhibition
of TGF-β signaling in mesenchymal stem cells of subchondral bone
attenuates osteoarthritis. Nat Med. 19:704–712. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Giunta S, Castorina A, Marzagalli R,
Szychlinska MA, Pichler K, Mobasheri A and Musumeci G: Ameliorative
effects of PACAP against cartilage degeneration. Morphological,
immunohistochemical and biochemical evidence from in vivo and in
vitro models of rat osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 16:5922–5944.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Benito MJ, Veale DJ, FitzGerald O, van den
Berg WB and Bresnihan B: Synovial tissue inflammation in early and
late osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 64:1263–1267. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Rengel Y, Ospelt C and Gay S: Proteinases
in the joint: Clinical relevance of proteinases in joint
destruction. Arthritis Res Ther. 9(221)2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Eyre D: Collagen of articular cartilage.
Arthritis Res. 4:30–35. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Poole AR, Kobayashi M, Yasuda T, Laverty
S, Mwale F, Kojima T, Sakai T, Wahl C, El-Maadawy S, Webb G, et al:
Type II collagen degradation and its regulation in articular
cartilage in osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 61 (Suppl 2):ii78–ii81.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hwang HS and Kim HA: Chondrocyte apoptosis
in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci.
16:26035–26054. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wu L and Liu Z: The molecular mechanisms
of preventing apoptosis of cartilage chondrocyte to target
osteoarthritis. Future Med Chem. 9:537–540. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Musumeci G, Castrogiovanni P, Loreto C,
Castorina S, Pichler K and Weinberg AM: Post-traumatic caspase-3
expression in the adjacent areas of growth plate injury site: A
morphological study. Int J Mol Sci. 14:15767–15784. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Musumeci G, Loreto C, Carnazza ML and
Martinez G: Characterization of apoptosis in articular cartilage
derived from the knee joints of patients with osteoarthritis. Knee
Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 19:307–313. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Lespasio MJ, Piuzzi NS, Husni ME, Muschler
GF, Guarino A and Mont MA: Knee Osteoarthritis: A Primer. Perm J.
21:16–183. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sinusas K: Osteoarthritis: Diagnosis and
treatment. Am Fam Physician. 85:49–56. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma VY, Chan L and Carruthers KJ:
Incidence, prevalence, costs, and impact on disability of common
conditions requiring rehabilitation in the United States: Stroke,
spinal cord injury, traumatic brain injury, multiple sclerosis,
osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, limb loss, and back pain.
Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 95:986–995.e1. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lin YH, Su HL and Yu CH: Method of
enhancing hyaluronic acid secretion using probiotic strain. US
Patent US9289455B2. Filed March 26, 2015; issued October 15,
2015.
|
|
25
|
Ogita T, Nakashima M, Morita H, Saito Y,
Suzuki T and Tanabe S: Streptococcus thermophilus ST28
ameliorates colitis in mice partially by suppression of
inflammatory Th17 cells. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2011(378417)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ai C, Zhang Q, Ren C, Wang G, Liu X, Tian
F, Zhao J, Zhang H, Chen YQ and Chen W: Genetically engineered
Lactococcus lactis protect against house dust mite allergy
in a BALB/c mouse model. PLoS One. 9(e109461)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lin YH, Chen IH, Shih HH and Lee CY:
Method for preventing and/or treating osteoporosis by using
Streptococcus thermophilus TC1633 strain and its
metabolites. US Patent US10149871B2. Filed June 21, 2017; issued
December 21, 2017.
|
|
28
|
Balazs EA and Denlinger JL:
Viscosupplementation: A new concept in the treatment of
osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol Suppl. 39:3–9. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shimizu C, Yoshioka M, Coutts RD, Harwood
FL, Kubo T, Hirasawa Y and Amiel D: Long-term effects of hyaluronan
on experimental osteoarthritis in the rabbit knee. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 6:1–9. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Abatangelo G, Botti P, Del Bue M, Gei G,
Samson JC, Cortivo R, De Galateo A and Martelli M: Intraarticular
sodium hyaluronate injections in the Pond-Nuki experimental model
of osteoarthritis in dogs. I. Biochemical results. Clin Orthop
Relat Res. 241:278–285. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yoshimi T, Kikuchi T, Obara T, Yamaguchi
T, Sakakibara Y, Itoh H, Iwata H and Miura T: Effects of
high-molecular-weight sodium hyaluronate on experimental
osteoarthrosis induced by the resection of rabbit anterior cruciate
ligament. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 298:296–304. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Altman RD and Moskowitz R: Hyalgan Study
Group. Intraarticular sodium hyaluronate (Hyalgan) in the treatment
of patients with osteoarthritis of the knee: A randomized clinical
trial. J Rheumatol. 25:2203–2212. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Amiel D, Toyoguchi T, Kobayashi K, Bowden
K, Amiel ME and Healey RM: Long-term effect of sodium hyaluronate
(Hyalgan) on osteoarthritis progression in a rabbit model.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 11:636–643. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Tamoto K, Tada M, Shimada S, Nochi H and
Mori Y: Effects of high-molecular-weight hyaluronates on the
functions of guinea pig polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Semin
Arthritis Rheum. 22 (Suppl 1):4–8. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sheehan KM, DeLott LB, Day SM and DeHeer
DH: Hyalgan has a dose-dependent differential effect on macrophage
proliferation and cell death. J Orthop Res. 21:744–751.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ghosh P, Read R, Numata Y, Smith S,
Armstrong S and Wilson D: The effects of intraarticular
administration of hyaluronan in a model of early osteoarthritis in
sheep. II. Cartilage composition and proteoglycan metabolism. Semin
Arthritis Rheum. 22 (Suppl 1):31–42. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yang PY, Tang CC, Chang YC, Huang SY,
Hsieh SP, Fan SS, Lee HP, Lin SC, Chen WF, Wen ZH, et al: Effects
of tibolone on osteoarthritis in ovariectomized rats: Association
with nociceptive pain behaviour. Eur J Pain. 18:680–690.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wen ZH, Tang CC, Chang YC, Huang SY, Hsieh
SP, Lee CH, Huang GS, Ng HF, Neoh CA, Hsieh CS, et al: Glucosamine
sulfate reduces experimental osteoarthritis and nociception in
rats: Association with changes of mitogen-activated protein kinase
in chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 18:1192–1202.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Fernihough J, Gentry C, Malcangio M, Fox
A, Rediske J, Pellas T, Kidd B, Bevan S and Winter J: Pain related
behaviour in two models of osteoarthritis in the rat knee. Pain.
112:83–93. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM
and Yaksh TL: Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the
rat paw. J Neurosci Methods. 53:55–63. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Pritzker KP, Gay S, Jimenez SA, Ostergaard
K, Pelletier JP, Revell PA, Salter D and van den Berg WB:
Osteoarthritis cartilage histopathology: Grading and staging.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 14:13–29. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Lee CH, Wen ZH, Chang YC, Huang SY, Tang
CC, Chen WF, Hsieh SP, Hsieh CS and Jean YH: Intra-articular
magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) reduces experimental
osteoarthritis and nociception: Association with attenuation of
N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunit 1 phosphorylation and
apoptosis in rat chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
17:1485–1493. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Bartley EJ, Palit S and Staud R:
Predictors of osteoarthritis pain: The importance of resilience.
Curr Rheumatol Rep. 19(57)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kao JH, Lin SH, Lai CF, Lin YC, Kong ZL
and Wong CS: Shea nut oil triterpene concentrate attenuates knee
osteoarthritis development in rats: Evidence from knee joint
histology. PLoS One. 11(e0162022)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Monticone M, Frizziero A, Rovere G,
Vittadini F, Uliano D, LA Bruna S, Gatto R, Nava C, Leggero V and
Masiero S: Hyaluronic acid intra-articular injection and exercise
therapy: Effects on pain and disability in subjects affected by
lower limb joints osteoarthritis. A systematic review by the
Italian Society of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine (SIMFER).
Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 52:389–399. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Hashizume M, Koike N, Yoshida H, Suzuki M
and Mihara M: High molecular weight hyaluronic acid relieved joint
pain and prevented the progression of cartilage degeneration in a
rabbit osteoarthritis model after onset of arthritis. Mod
Rheumatol. 20:432–438. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Stoop R, Buma P, van der Kraan PM,
Hollander AP, Billinghurst RC, Meijers TH, Poole AR and van den
Berg WB: Type II collagen degradation in articular cartilage
fibrillation after anterior cruciate ligament transection in rats.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 9:08–315. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Bakilan F, Armagan O, Ozgen M, Tascioglu
F, Bolluk O and Alatas O: Effects of native type II collagen
treatment on knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial.
Eurasian J Med. 48:95–101. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zhang Z, Wei X, Gao J, Zhao Y, Zhao Y, Guo
L, Chen C, Duan Z, Li P and Wei L: Intra-articular injection of
cross-linked Hyaluronic acid-dexamethasone hydrogel attenuates
osteoarthritis: An experimental study in a rat model of
osteoarthritis. Int J Mol Sci. 17(411)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Dejica VM, Mort JS, Laverty S, Percival
MD, Antoniou J, Zukor DJ and Poole AR: Cleavage of type II collagen
by cathepsin K in human osteoarthritic cartilage. Am J Pathol.
173:161–169. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Aigner T and Kim HA: Apoptosis and
cellular vitality: Issues in osteoarthritic cartilage degeneration.
Arthritis Rheum. 46:1986–1996. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Lotz M, Hashimoto S and Kühn K: Mechanisms
of chondrocyte apoptosis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 7:389–391.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Barreto RB, Sadigursky D, de Rezende MU
and Hernandez AJ: Effect of hyaluronic acid on chondrocyte
apoptosis. Acta Ortop Bras. 23:90–93. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|