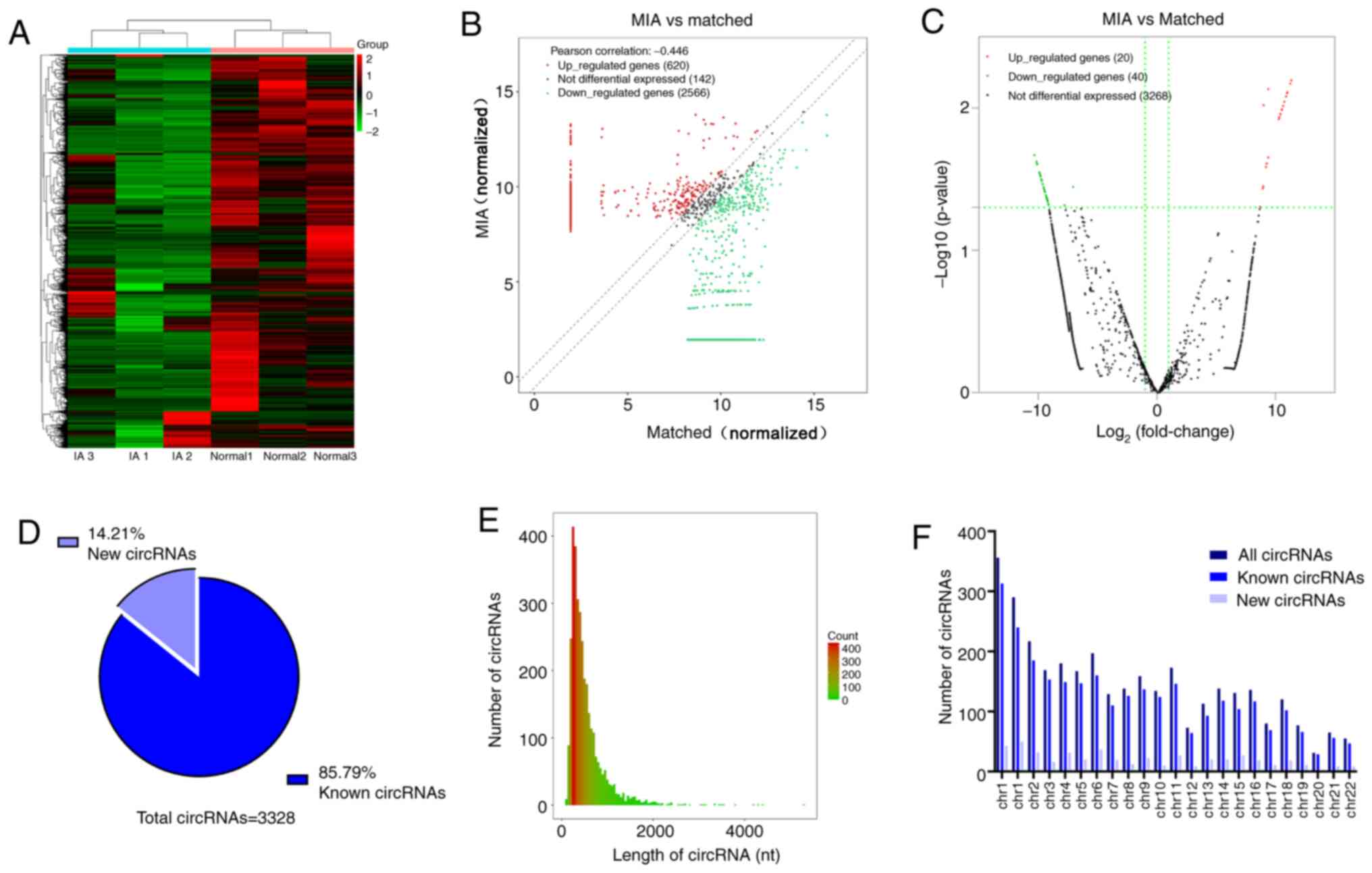
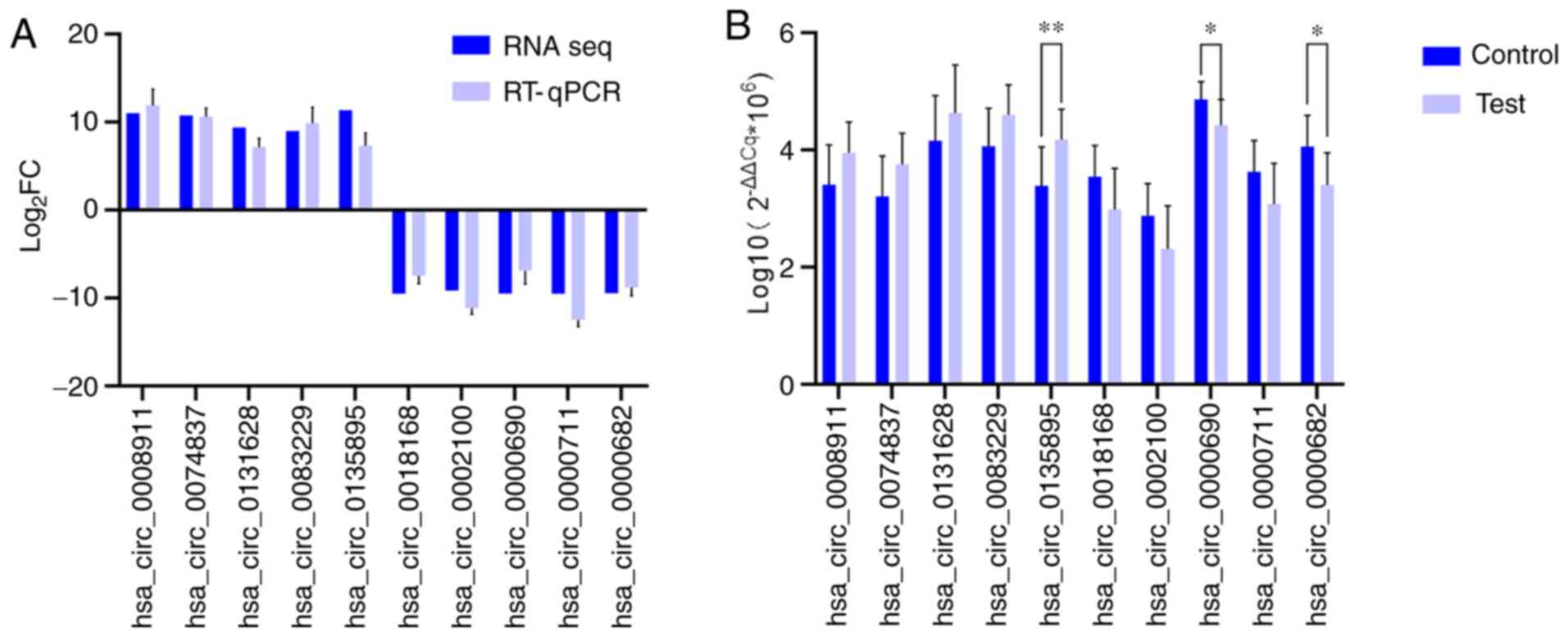
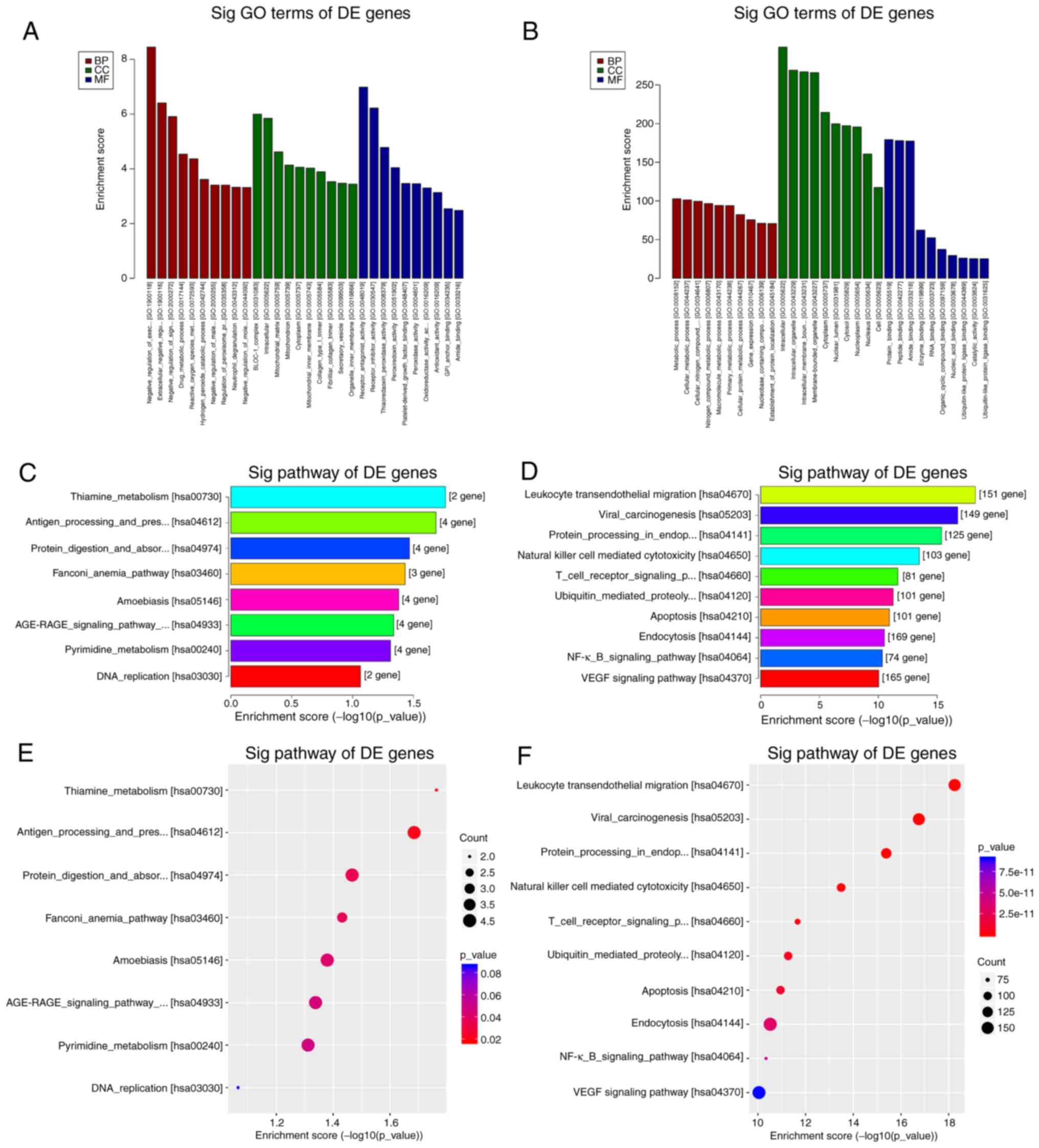
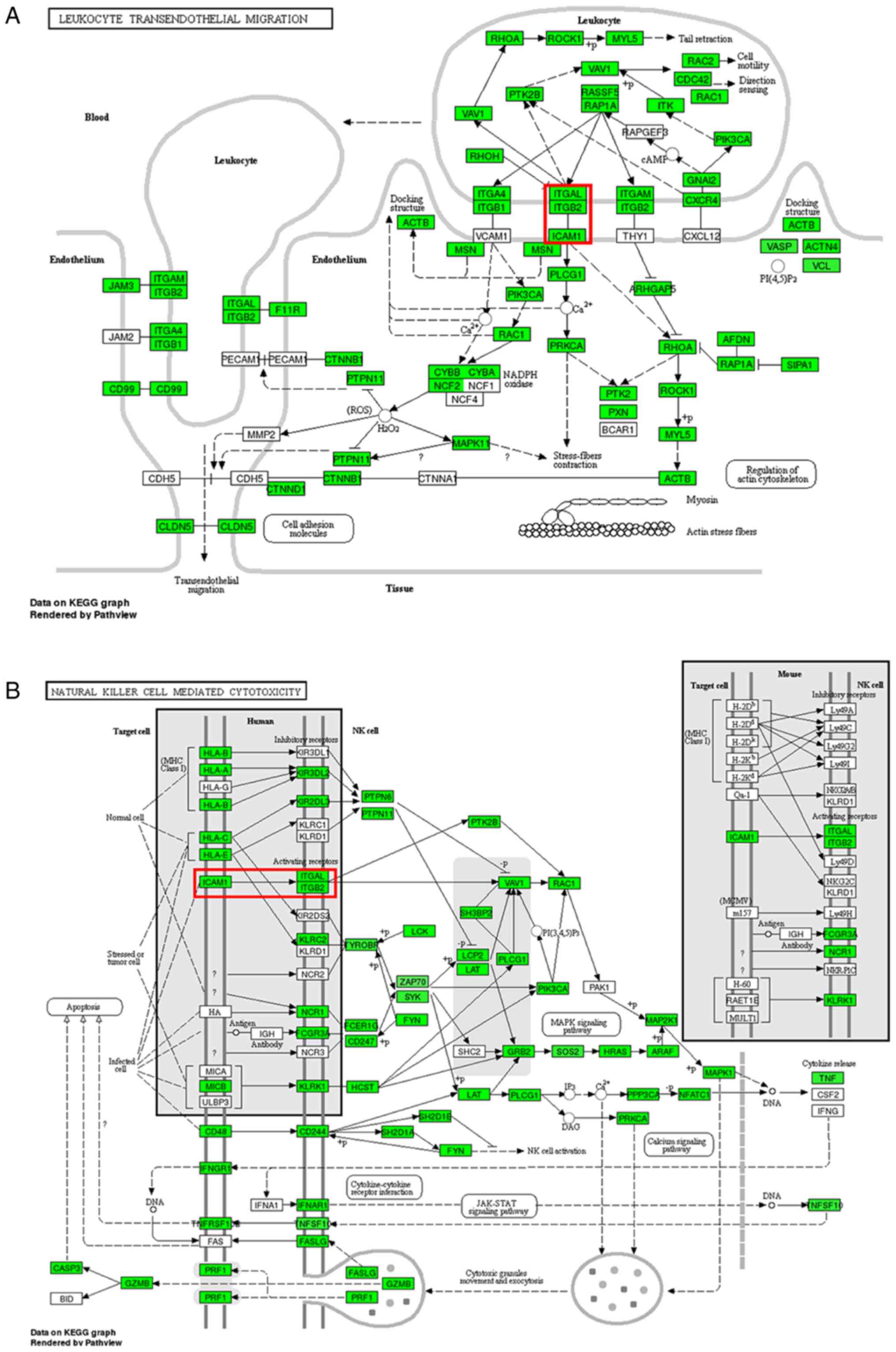
|
1
|
Nieuwkamp DJ, Setz LE, Algra A, Linn FH,
de Rooij NK and Rinkel GJ: Changes in case fatality of aneurysmal
subarachnoid haemorrhage over time, according to age, sex, and
region: A meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 8:635–642. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Brown RD Jr, Huston J, Hornung R, Foroud
T, Kallmes DF, Kleindorfer D, Meissner I, Woo D, Sauerbeck L and
Broderick J: Screening for brain aneurysm in the Familial
Intracranial Aneurysm study: Frequency and predictors of lesion
detection. J Neurosurg. 108:1132–1138. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bo L, Wei B, Wang Z, Kong D, Gao Z and
Miao Z: Screening of Critical Genes and MicroRNAs in Blood Samples
of Patients with Ruptured Intracranial Aneurysms by Bioinformatic
Analysis of Gene Expression Data. Med Sci Monit. 23:4518–4525.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wei L, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Yang C, Guan H,
Chen Y and Sun Z: Identification of key genes, transcription
factors and microRNAs involved in intracranial aneurysm. Mol Med
Rep. 17:891–897. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Korostynski M, Morga R, Piechota M,
Hoinkis D, Golda S, Dziedzic T, Slowik A, Moskala M and Pera J:
Inflammatory Responses Induced by the Rupture of Intracranial
Aneurysms Are Modulated by miRNAs. Mol Neurobiol. 57:988–996.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Li H, Wang W, Zhang L, Lan Q, Wang J, Cao
Y and Zhao J: Identification of a Long Noncoding RNA-Associated
Competing Endogenous RNA Network in Intracranial Aneurysm. World
Neurosurg. 97:684–692.e4. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wu C, Song H, Wang Y, Gao L, Cai Y, Cheng
Q, Chen Y, Zheng Z, Liao Y, Lin J, et al: Long non-coding RNA
TCONS_00000200 as a non-invasive biomarker in patients with
intracranial aneurysm. Biosci Rep. 39(39)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kulcheski FR, Christoff AP and Margis R:
Circular RNAs are miRNA sponges and can be used as a new class of
biomarker. J Biotechnol. 238:42–51. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
't Hoen PA, Ariyurek Y, Thygesen HH,
Vreugdenhil E, Vossen RH, de Menezes RX, Boer JM, van Ommen GJ and
den Dunnen JT: Deep sequencing-based expression analysis shows
major advances in robustness, resolution and inter-lab portability
over five microarray platforms. Nucleic Acids Res.
36(e141)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Khan S and Kaihara KA: Single-Cell
RNA-Sequencing of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells with ddSEQ.
Methods Mol Biol. 1979:155–176. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jeck WR and Sharpless NE: Detecting and
characterizing circular RNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 32:453–461.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li HM, Dai YW, Yu JY, Duan P, Ma XL, Dong
WW, Li N and Li HG: Comprehensive circRNA/miRNA/mRNA analysis
reveals circRNAs protect against toxicity induced by BPA in GC-2
cells. Epigenomics. 11:935–949. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang Y, Wang Y, Li Y, Wang B, Miao Z, Liu
X and Ma Y: Decreased expression of circ_0020397 in intracranial
aneurysms may be contributing to decreased vascular smooth muscle
cell proliferation via increased expression of miR-138 and
subsequent decreased KDR expression. Cell Adhes Migr. 13:220–228.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
eLife. 4(4)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Glažar P, Papavasileiou P and Rajewsky N:
circBase: A database for circular RNAs. RNA. 20:1666–1670.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chou CH, Shrestha S, Yang CD, Chang NW,
Lin YL, Liao KW, Huang WC, Sun TH, Tu SJ, Lee WH, et al: miRTarBase
update 2018: A resource for experimentally validated
microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 46D:D296–D302.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Maass PG, Glažar P, Memczak S, Dittmar G,
Hollfinger I, Schreyer L, Sauer AV, Toka O, Aiuti A, Luft FC, et
al: A map of human circular RNAs in clinically relevant tissues. J
Mol Med (Berl). 95:1179–1189. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Caranci F, Briganti F, Cirillo L, Leonardi
M and Muto M: Epidemiology and genetics of intracranial aneurysms.
Eur J Radiol. 82:1598–1605. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Alg VS, Sofat R, Houlden H and Werring DJ:
Genetic risk factors for intracranial aneurysms: A meta-analysis in
more than 116,000 individuals. Neurology. 80:2154–2165.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Hussain I, Duffis EJ, Gandhi CD and
Prestigiacomo CJ: Genome-wide association studies of intracranial
aneurysms: An update. Stroke. 44:2670–2675. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Shao Y and Chen Y: Roles of Circular RNAs
in Neurologic Disease. Front Mol Neurosci. 9(25)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
van Rossum D, Verheijen BM and Pasterkamp
RJ: Circular RNAs: Novel Regulators of Neuronal Development. Front
Mol Neurosci. 9(74)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hao Z, Li Y, Yu N, Zhao Y, Hu S, Liu Z and
Li M: Analysis of differentially expressed circular RNAs in
endothelial cells under impinging flow. Mol Cell Probes.
51(101539)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Huang Q, Huang QY, Sun Y and Wu S:
High-Throughput Data Reveals Novel Circular RNAs via Competitive
Endogenous RNA Networks Associated with Human Intracranial
Aneurysms. Med Sci Monit. 25:4819–4830. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Signorelli F, Sela S, Gesualdo L, Chevrel
S, Tollet F, Pailler-Mattei C, Tacconi L, Turjman F, Vacca A and
Schul DB: Hemodynamic Stress, Inflammation, and Intracranial
Aneurysm Development and Rupture: A Systematic Review. World
Neurosurg. 115:234–244. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chidlow JH Jr, Glawe JD, Alexander JS and
Kevil CG: VEGF164 differentially regulates neutrophil and T cell
adhesion through ItgaL- and ItgaM-dependent mechanisms. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 299:G1361–G1367.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Hoh BL, Rojas K, Lin L, Fazal HZ, Hourani
S, Nowicki KW, Schneider MB and Hosaka K: Estrogen Deficiency
Promotes Cerebral Aneurysm Rupture by Upregulation of Th17 Cells
and Interleukin-17A Which Downregulates E-Cadherin. J Am Heart
Assoc. 7(7)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sawyer DM, Pace LA, Pascale CL, Kutchin
AC, O'Neill BE, Starke RM and Dumont AS: Lymphocytes influence
intracranial aneurysm formation and rupture: Role of extracellular
matrix remodeling and phenotypic modulation of vascular smooth
muscle cells. J Neuroinflammation. 13(185)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Dai D and Xu Z: Expression
of NF-kappaB, MCP-1 and MMP-9 in a Cerebral Aneurysm Rabbit Model.
Can J Neurol Sci. 41:200–205. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Dou C, Cao Z, Yang B, Ding N, Hou T, Luo
F, Kang F, Li J, Yang X, Jiang H, et al: Changing expression
profiles of lncRNAs, mRNAs, circRNAs and miRNAs during
osteoclastogenesis. Sci Rep. 6(21499)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Faveeuw C, Di Mauro ME, Price AA and Ager
A: Roles of alpha(4) integrins/VCAM-1 and LFA-1/ICAM-1 in the
binding and transendothelial migration of T lymphocytes and T
lymphoblasts across high endothelial venules. Int Immunol.
12:241–251. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Hinterseher I, Schworer CM, Lillvis JH,
Stahl E, Erdman R, Gatalica Z, Tromp G and Kuivaniemi H:
Immunohistochemical analysis of the natural killer cell
cytotoxicity pathway in human abdominal aortic aneurysms. Int J Mol
Sci. 16:11196–11212. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yang H, Graham LC, Reagan AM, Grabowska
WA, Schott WH and Howell GR: Transcriptome profiling of brain
myeloid cells revealed activation of Itgal, Trem1, and Spp1 in
western diet-induced obesity. J Neuroinflammation.
16(169)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhu Z, Li Y, Liu W, He J, Zhang L, Li H,
Li P and Lv L: Comprehensive circRNA expression profile and
construction of circRNA-associated ceRNA network in fur skin. Exp
Dermatol. 27:251–257. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wu J, Liu S, Xiang Y, Qu X, Xie Y and
Zhang X: Bioinformatic Analysis of Circular RNA-Associated ceRNA
Network Associated with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BioMed Res Int.
2019(8308694)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Cao M, Zhang L, Wang JH, Zeng H, Peng Y,
Zou J, Shi J, Zhang L, Li Y, Yoshida S, et al: Identifying
circRNA-associated-ceRNA networks in retinal neovascularization in
mice. Int J Med Sci. 16:1356–1365. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li X, Ding J, Wang X, Cheng Z and Zhu Q:
NUDT21 regulates circRNA cyclization and ceRNA crosstalk in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 39:891–904. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Li C, Li M and Xue Y: Downregulation of
CircRNA CDR1as specifically triggered low-dose Diosbulbin-B induced
gastric cancer cell death by regulating miR-7-5p/REGγ axis. Biomed
Pharmacother. 120(109462)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|