|
1
|
Kapoor M, Pringle K, Kumar A, Dearth S,
Liu L, Lovchik J, Perez O, Pontones P, Richards S, Yeadon-Fagbohun
J, et al: Clinical and laboratory findings of the first imported
case of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus to the United
States. Clin Infect Dis. 59:1511–1518. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhong NS, Zheng BJ, Li YM, Poon Xie ZH,
Chan KH, Li PH, Tan SY, Chang Q, Xie JP, et al: Epidemiology and
cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Guangdong,
People's Republic of China, in February, 2003. Lancet.
362:1353–1358. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Plipat T, Buathong R, Wacharapluesadee S,
Siriarayapon P, Pittayawonganon C, Sangsajja C, Kaewpom T,
Petcharat S, Ponpinit T, Jumpasri J, et al: Imported case of Middle
East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection from
Oman to Thailand, June 2015. Euro Surveill.
22(30598)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Vijayanand P, Wilkins E and Woodhead M:
Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS): A review. Clin Med.
4:152–160. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Muthumani K, Falzarano D, Reuschel EL,
Tingey C, Flingai S, Villarreal DO, Wise M, Patel A, Izmirly A,
Aljuaid A, et al: A synthetic consensus anti-spike protein DNA
vaccine induces protective immunity against Middle East respiratory
syndrome coronavirus in nonhuman primates. Sci Transl Med.
7(301ra132)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Paules CI, Marston HD and Fauci AS:
Coronavirus infections-More Than Just the common cold. JAMA.
323:707–708. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fehr AR and Perlman S: Coronaviruses: An
overview of their replication and pathogenesis. Methods Mol Biol.
1282:1–23. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang SF, Tuo JL, Huang XB, Zhu X, Zhang
DM, Zhou K, Yuan L, Luo HJ, Zheng BJ, Yuen KY, et al: Epidemiology
characteristics of human coronaviruses in patients with respiratory
infection symptoms and phylogenetic analysis of HCoV-OC43 during
2010-2015 in Guangzhou. PLoS One. 13(e0191789)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Berry M, Gamieldien J and Fielding BC:
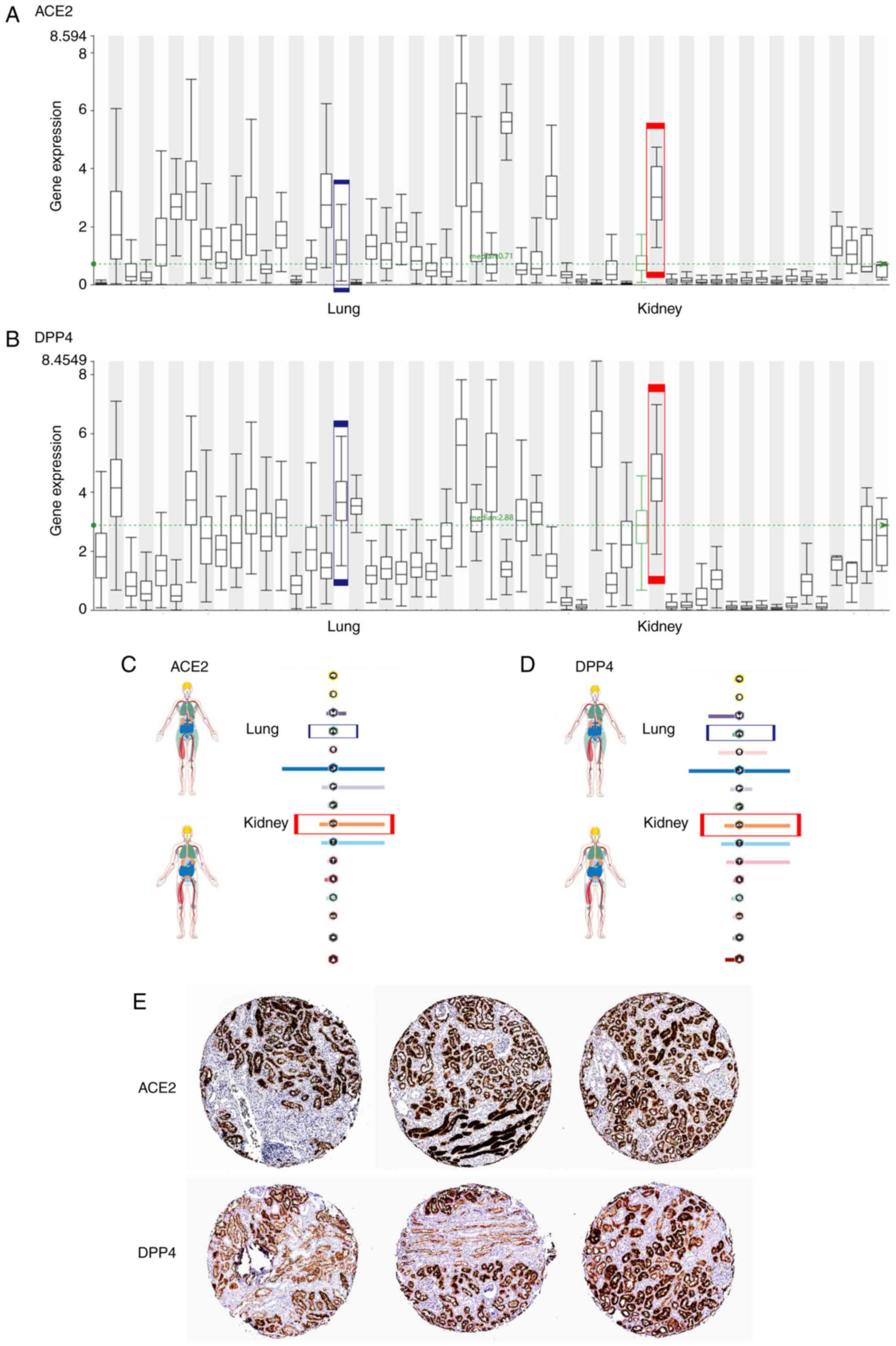
Identification of new respiratory viruses in the new millennium.
Viruses. 7:996–1019. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chan PK and Chan MC: Tracing the
SARS-coronavirus. J Thorac Dis. 5 (Suppl 2):S118–S121.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zumla A, Hui DS and Perlman S: Middle East
respiratory syndrome. Lancet. 386:995–1007. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Skariyachan S, Challapilli SB, Packirisamy
S, Kumargowda ST and Sridhar VS: Recent aspects on the pathogenesis
mechanism, animal models and novel therapeutic interventions for
middle east respiratory syndrome coronavirus infections. Front
Microbiol. 10(569)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han
Y, Qiu Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Wei Y, et al: Epidemiological and clinical
characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in
Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet. 395:507–513.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Heymann DL, Mackenzie JS and Peiris M:
SARS legacy: Outbreak reporting is expected and respected. Lancet.
381:779–781. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Anderson LJ and Tong S: Update on SARS
research and other possibly zoonotic coronaviruses. Int J
Antimicrob Agents. 36 (Suppl 1):S21–S25. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Meo SA, Alhowikan AM, Al-Khlaiwi T, Meo
IM, Halepoto DM, Iqbal M, Usmani AM, Hajjar W and Ahmed N: Novel
coronavirus 2019-nCoV: Prevalence, biological and clinical
characteristics comparison with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 24:2012–2019. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kuiken T, Fouchier RA, Schutten M,
Rimmelzwaan GF, van Amerongen G, van Riel D, Laman JD, de Jong T,
van Doornum G, Lim W, et al: Newly discovered coronavirus as the
primary cause of severe acute respiratory syndrome. Lancet.
362:263–270. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Fouchier RA, Kuiken T, Schutten M, van
Amerongen G, van Doornum GJ, van den Hoogen BG, Peiris M, Lim W,
Stöhr K and Osterhaus AD: Aetiology: Koch's postulates fulfilled
for SARS virus. Nature. 423(240)2003.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Peiris JS, Yuen KY, Osterhaus AD and Stöhr
K: The severe acute respiratory syndrome. N Engl J Med.
349:2431–2441. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Woodhead M, Ewig S and Torres A: Severe
acute respiratory syndrome (SARS). Eur Respir J. 21:739–740.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chu KH, Tsang WK, Tang CS, Lam MF, Lai FM,
To KF, Fung KS, Tang HL, Yan WW, Chan HW, et al: Acute renal
impairment in coronavirus-associated severe acute respiratory
syndrome. Kidney Int. 67:698–705. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lu HY, Xu XY, Lei Y, Wu YF, Chen BW, Xiao
F, Xie GQ and Han DM: Clinical features of probable severe acute
respiratory syndrome in Beijing. World J Gastroenterol.
11:2971–2974. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lee N, Hui D, Wu A, Chan P, Cameron P,
Joynt GM, Ahuja A, Yung MY, Leung CB, To KF, et al: A major
outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. N Engl
J Med. 348:1986–1994. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Hsu LY, Lee CC, Green JA, Ang B, Paton NI,
Lee L, Villacian JS, Lim PL, Earnest A and Leo YS: Severe acute
respiratory syndrome (SARS) in Singapore: Clinical features of
index patient and initial contacts. Emerg Infect Dis. 9:713–717.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jang TN, Yeh DY, Shen SH, Huang CH, Jiang
JS and Kao SJ: Severe acute respiratory syndrome in Taiwan:
Analysis of epidemiological characteristics in 29 cases. J Infect.
48:23–31. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cheng VC, Hung IF, Tang BS, Chu CM, Wong
MM, Chan KH, Wu AK, Tse DM, Chan KS, Zheng BJ, et al: Viral
replication in the nasopharynx is associated with diarrhea in
patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome. Clin Infect Dis.
38:467–475. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Gu J, Gong E, Zhang B, Zheng J, Gao Z,
Zhong Y, Zou W, Zhan J, Wang S, Xie Z, et al: Multiple organ
infection and the pathogenesis of SARS. J Exp Med. 202:415–424.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lang ZW, Zhang LJ, Zhang SJ, Meng X, Li
JQ, Song CZ, Sun L, Zhou YS and Dwyer DE: A clinicopathological
study of three cases of severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS).
Pathology. 35:526–531. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ding Y, He L, Zhang Q, Huang Z, Che X, Hou
J, Wang H, Shen H, Qiu L, Li Z, et al: Organ distribution of severe
acute respiratory syndrome (SARS) associated coronavirus (SARS-CoV)
in SARS patients: Implications for pathogenesis and virus
transmission pathways. J Pathol. 203:622–630. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Peiris JS, Chu CM, Cheng VC, Chan KS, Hung
IF, Poon LL, Law KI, Tang BS, Hon TY, Chan CS, et al: Clinical
progression and viral load in a community outbreak of
coronavirus-associated SARS pneumonia: A prospective study. Lancet.
361:1767–1772. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chan KH, Poon LL, Cheng VC, Guan Y, Hung
IF, Kong J, Yam LY, Seto WH, Yuen KY and Peiris JS: Detection of
SARS coronavirus in patients with suspected SARS. Emerg Infect Dis.
10:294–299. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cheng PK, Wong DA, Tong LK, Ip SM, Lo AC,
Lau CS, Yeung EY and Lim WW: Viral shedding patterns of coronavirus
in patients with probable severe acute respiratory syndrome.
Lancet. 363:1699–1700. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zaki AM, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM,
Osterhaus AD and Fouchier RA: Isolation of a novel coronavirus from
a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med. 367:1814–1820.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Cho H, Excler JL, Kim JH and Yoon IK:
Development of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus
vaccines-advances and challenges. Hum Vaccin Immunother.
14:304–313. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sun B, He H, Wang Z, Qu J, Li X, Ban C,
Wan J, Cao B, Tong Z and Wang C: Emergent severe acute respiratory
distress syndrome caused by adenovirus type 55 in immunocompetent
adults in 2013: A prospective observational study. Crit Care.
18(456)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Al Ghamdi M, Alghamdi KM, Ghandoora Y,
Alzahrani A, Salah F, Alsulami A, Bawayan MF, Vaidya D, Perl TM and
Sood G: Treatment outcomes for patients with Middle Eastern
respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS CoV) infection at a
coronavirus referral center in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. BMC
Infect Dis. 16(174)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sherbini N, Iskandrani A, Kharaba A,
Khalid G, Abduljawad M and Al-Jahdali H: Middle East respiratory
syndrome coronavirus in Al-Madinah City, Saudi Arabia: Demographic,
clinical and survival data. J Epidemiol Glob Health. 7:29–36.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Eckerle I, Muller MA, Kallies S, Gotthardt
DN and Drosten C: In-vitro renal epithelial cell infection reveals
a viral kidney tropism as a potential mechanism for acute renal
failure during Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS) Coronavirus
infection. Virol J. 10(359)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Poissy J, Goffard A, Parmentier-Decrucq E,
Favory R, Kauv M, Kipnis E, Mathieu D, van der Werf S and Guery B:
MERS-CoV Biology Group. Kinetics and pattern of viral excretion in
biological specimens of two MERS-CoV cases. J Clin Virol.
61:275–278. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Nassar MS, Bakhrebah MA, Meo SA, Alsuabeyl
MS and Zaher WA: Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus
(MERS-CoV) infection: Epidemiology, pathogenesis and clinical
characteristics. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 22:4956–4961.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Cha RH, Joh JS, Jeong I, Lee JY, Shin HS,
Kim G and Kim Y: Critical Care Team of National Medical Center.
Renal Complications and their prognosis in Korean patients with
Middle East respiratory syndrome-coronavirus from the central
MERS-CoV designated hospital. J Korean Med Sci. 30:1807–1814.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Alsaad KO, Hajeer AH, Al Balwi M, Al
Moaiqel M, Al Oudah N, Al Ajlan A, AlJohani S, Alsolamy S, Gmati
GE, Balkhy H, et al: 2. Histopathology. 72:516–524. 2018.
|
|
43
|
Ng DL, Al Hosani F, Keating MK, Gerber SI,
Jones TL, Metcalfe MG, Tong S, Tao Y, Alami NN, Haynes LM, et al:
Clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and Ultrastructural
findings of a fatal case of Middle East respiratory syndrome
coronavirus infection in the United Arab Emirates, April 2014. Am J
Pathol. 186:652–658. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Munster VJ, Koopmans M, van Doremalen N,
van Riel D and de Wit E: A novel coronavirus emerging in china-key
questions for impact assessment. N Engl J Med. 382:692–694.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhu N, Zhang D, Wang W, Li X, Yang B, Song
J, Zhao X, Huang B, Shi W, Lu R, et al: A Novel coronavirus from
patients with pneumonia in China, 2019. N Engl J Med. 382:727–733.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Perlman S: Another decade, another
coronavirus. N Engl J Med. 382:760–762. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Hui DS, I Azhar E, Madani TA, Ntoumi F,
Kock R, Dar O, Ippolito G, Mchugh TD, Memish ZA, Drosten C, et al:
The continuing 2019-nCoV epidemic threat of novel coronaviruses to
global health-The latest 2019 novel coronavirus outbreak in Wuhan,
China. Int J Infect Dis. 91:264–266. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Lu R, Zhao X, Li J, Niu P, Yang B, Wu H,
Wang W, Song H, Huang B, Zhu N, et al: Genomic characterisation and
epidemiology of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implications for virus
origins and receptor binding. Lancet. 395:565–574. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Chan JF, Kok KH, Zhu Z, Chu H, To KK, Yuan
S and Yuen KY: Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel
human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical
pneumonia after visiting Wuhan. Emerg Microbes Infect. 9:221–236.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zhou P, Yang XL, Wang XG, Hu B, Zhang L,
Zhang W, Si HR, Zhu Y, Li B, Huang CL, et al: A pneumonia outbreak
associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature.
579:270–273. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J,
Wang B, Xiang H, Cheng Z, Xiong Y, et al: Clinical characteristics
of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected
pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 323:1061–1069. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He
JX, Liu L, Shan H, Lei CL, Hui DSC, et al: Clinical characteristics
of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 382:1708–1720.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J, Shu H, Xia J, Liu H,
Wu Y, Zhang L, Yu Z, Fang M, et al: Clinical course and outcomes of
critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China:
A single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet
Respir Med. 8:475–481. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu
Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, et al: Clinical features of patients
infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet.
395:497–506. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Xu XW, Wu XX, Jiang XG, Xu KJ, Ying LJ, Ma
CL, Li SB, Wang HY, Zhang S, Gao HN, et al: Clinical findings in a
group of patients infected with the 2019 novel coronavirus
(SARS-Cov-2) outside of Wuhan, China: Retrospective case series.
BMJ. 368(m606)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Cai Q, Huang D, Ou P, Yu H, Zhu Z, Xia Z,
Su Y, Ma Z, Zhang Y, Li Z, et al: COVID-19 in a designated
infectious diseases hospital outside Hubei Province, China.
Allergy. 75:1742–1752. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Cheng Y, Luo R, Wang K, Zhang M, Wang Z,
Dong L, Li J, Yao Y, Ge S and Xu G: Kidney disease is associated
with in-hospital death of patients with COVID-19. Kidney Int.
97:829–838. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Su H, Yang M, Wan C, Yi LX, Tang F, Zhu
HY, Yi F, Yang HC, Fogo AB, Nie X and Zhang C: Renal
histopathological analysis of 26 postmortem findings of patients
with COVID-19 in China. Kidney Int. 98:219–227. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Pei G, Zhang Z, Peng J, Liu L, Zhang C, Yu
C, Ma Z, Huang Y, Liu W, Yao Y, et al: Renal involvement and Early
prognosis in patients with COVID-19 pneumonia. J Am Soc Nephrol.
31:1157–1165. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Chen YT, Shao SC, Lai EC, Hung MJ and Chen
YC: Mortality rate of acute kidney injury in SARS, MERS, and
COVID-19 infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit
Care. 24(439)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Guery B, Poissy J, el Mansouf L, Séjourné
C, Ettahar N, Lemaire X, Vuotto F, Goffard A, Behillil S, Enouf V,
et al: Clinical features and viral diagnosis of two cases of
infection with Middle East Respiratory Syndrome coronavirus: A
report of nosocomial transmission. Lancet. 381:2265–2272.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Chan VW, Chiu PK, Yee CH, Yuan Y, Ng CF
and Teoh JY: A systematic review on COVID-19: Urological
manifestations, viral RNA detection and special considerations in
urological conditions. World J Urol: May 27, 2020 (Epub ahead of
print). doi: 10.1007/s00345-020-03246-4.
|
|
63
|
Müller MA, Raj VS, Muth D, Meyer B,
Kallies S, Smits SL, Wollny R, Bestebroer TM, Specht S, Suliman T,
et al: Human coronavirus EMC does not require the SARS-coronavirus
receptor and maintains broad replicative capability in mammalian
cell lines. mBio. 3:e00515–12. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Monteil V, Kwon H, Prado P, Hagelkrüys A,
Wimmer RA, Stahl M, Leopoldi A, Garreta E, Hurtado Del Pozo C,
Prosper F, et al: Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 infections in engineered
human tissues using clinical-grade soluble human ACE2. Cell.
181:905–913.e7. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Hamming I, Timens W, Bulthuis ML, Lely AT,
Navis G and van Goor H: Tissue distribution of ACE2 protein, the
functional receptor for SARS coronavirus. A first step in
understanding SARS pathogenesis. J Pathol. 203:631–637.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Rakušan D, Bürgelová M, Vaněčková I,
Vaňourková Z, Husková Z, Skaroupková P, Mrázová I, Opočenský M,
Kramer HJ, Netuka I, et al: Knockout of angiotensin 1-7 receptor
Mas worsens the course of two-kidney, one-clip Goldblatt
hypertension: Roles of nitric oxide deficiency and enhanced
vascular responsiveness to angiotensin II. Kidney Blood Press Res.
33:476–488. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Li W, Moore MJ, Vasilieva N, Sui J, Wong
SK, Berne MA, Somasundaran M, Sullivan JL, Luzuriaga K, Greenough
TC, et al: Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 is a functional receptor
for the SARS coronavirus. Nature. 426:450–454. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Raj VS, Mou H, Smits SL, Dekkers DH,
Müller MA, Dijkman R, Muth D, Demmers JA, Zaki A, Fouchier RA, et
al: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a functional receptor for the
emerging human coronavirus-EMC. Nature. 495:251–254.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Li F and Du L: MERS coronavirus: An
emerging zoonotic virus. Viruses. 11(663)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Abdel-Moneim AS: Middle East respiratory
syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV): Evidence and speculations. Arch
Virol. 159:1575–1584. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Kenny AJ, Booth AG, George SG, Ingram J,
Kershaw D, Wood EJ and Young AR: Dipeptidyl peptidase IV, a kidney
brush-border serine peptidase. Biochem J. 157:169–182.
1976.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Lian Q, Wang S, Zhang G, Wang D, Luo G,
Tang J, Chen L and Gu J: HCCDB: A database of hepatocellular
carcinoma expression atlas. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics.
16:269–275. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Ponten F, Jirstrom K and Uhlen M: The
human protein atlas-a tool for pathology. J Pathol. 216:387–393.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Uhlen M, Fagerberg L, Hallstrom BM,
Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A, Sivertsson Å, Kampf C,
Sjöstedt E, Asplund A, et al: Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the
human proteome. Science. 347(1260419)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Xu H, Zhong L, Deng J, Peng J, Dan H, Zeng
X, Li T and Chen Q: High expression of ACE2 receptor of 2019-nCoV
on the epithelial cells of oral mucosa. Int J Oral Sci.
12(8)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S,
Krüger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, Schiergens TS, Herrler G, Wu NH,
Nitsche A, et al: SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2
and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell.
181:271–280.e8. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Harmer D, Gilbert M, Borman R and Clark
KL: Quantitative mRNA expression profiling of ACE 2, a novel
homologue of angiotensin converting enzyme. FEBS Lett. 532:107–110.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Lely AT, Hamming I, van Goor H and Navis
GJ: Renal ACE2 expression in human kidney disease. J Pathol.
204:587–593. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Pala L, Mannucci E, Pezzatini A, Ciani S,
Sardi J, Raimondi L, Ognibene A, Cappadona A, Vannelli BG and
Rotella CM: Dipeptidyl peptidase-IV expression and activity in
human glomerular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
310:28–31. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Kuba K, Imai Y, Rao S, Gao H, Guo F, Guan
B, Huan Y, Yang P, Zhang Y, Deng W, et al: A crucial role of
angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in SARS coronavirus-induced
lung injury. Nat Med. 11:875–879. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Ge XY, Li JL, Yang XL, Chmura AA, Zhu G,
Epstein JH, Mazet JK, Hu B, Zhang W, Peng C, et al: Isolation and
characterization of a bat SARS-like coronavirus that uses the ACE2
receptor. Nature. 503:535–538. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Strawn WB, Richmond RS, Ann Tallant E,
Gallagher PE and Ferrario CM: Renin-angiotensin system expression
in rat bone marrow haematopoietic and stromal cells. Br J Haematol.
126:120–126. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Batlle D, Wysocki J and Satchell K:
Soluble angiotensin-converting enzyme 2: A potential approach for
coronavirus infection therapy? Clin Sci. 134:543–545.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Yang XH, Deng W, Tong Z, Liu YX, Zhang LF,
Zhu H, Gao H, Huang L, Liu YL, Ma CM, et al: Mice transgenic for
human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 provide a model for SARS
coronavirus infection. Comp Med. 57:450–459. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Wrapp D, Wang N, Corbett KS, Goldsmith JA,
Hsieh CL, Abiona O, Graham BS and McLellan JS: Cryo-EM structure of
the 2019-nCoV spike in the prefusion conformation. Science.
367:1260–1263. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Shang J, Ye G, Shi K, Wan Y, Luo C, Aihara
H, Geng Q, Auerbach A and Li F: Structural basis of receptor
recognition by SARS-CoV-2. Nature. 581:221–224. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Lan J, Ge J, Yu J, Shan S, Zhou H, Fan S,
Zhang Q, Shi X, Wang Q, Zhang L and Wang X: Structure of the
SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain bound to the ACE2
receptor. Nature. 581:215–220. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Pan XW, Xu D, Zhang H, Zhou W, Wang LH and
Cui XG: Identification of a potential mechanism of acute kidney
injury during the COVID-19 outbreak: A study based on single-cell
transcriptome analysis. Intensive Care Med. 46:1114–1116.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Farkash EA, Wilson AM and Jentzen JM:
Ultrastructural evidence for direct renal infection with
SARS-CoV-2. J Am Soc Nephrol. 31:1683–1687. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Iwata-Yoshikawa N, Okamura T, Shimizu Y,
Kotani O, Sato H, Sekimukai H, Fukushi S, Suzuki T, Sato Y, Takeda
M, et al: Acute respiratory infection in human Dipeptidyl Peptidase
4-transgenic mice infected with Middle East respiratory syndrome
coronavirus. J Virol. 93:e01818–18. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Lu G, Hu Y, Wang Q, Qi J, Gao F, Li Y,
Zhang Y, Zhang W, Yuan Y, Bao J, et al: Molecular basis of binding
between novel human coronavirus MERS-CoV and its receptor CD26.
Nature. 500:227–231. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Deeks SG, Tracy R and Douek DC: Systemic
effects of inflammation on health during chronic HIV infection.
Immunity. 39:633–645. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Wang W, Li G, De Wu Luo Z, Pan P, Tian M,
Wang Y, Xiao F, Li A, Wu K, et al: Zika virus infection induces
host inflammatory responses by facilitating NLRP3 inflammasome
assembly and interleukin-1β secretion. Nat Commun.
9(106)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Wong CK, Lam CW, Wu AK, Ip WK, Lee NL,
Chan IH, Lit LC, Hui DS, Chan MH, Chung SS and Sung JJ: Plasma
inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in severe acute respiratory
syndrome. Clin Exp Immunol. 136:95–103. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Mahallawi WH, Khabour OF, Zhang Q,
Makhdoum HM and Suliman BA: MERS-CoV infection in humans is
associated with a pro-inflammatory Th1 and Th17 cytokine profile.
Cytokine. 104:8–13. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Al-Jasser FS, Nouh RM and Youssef RM:
Epidemiology and predictors of survival of MERS-CoV infections in
Riyadh region, 2014-2015. J Infect Public Health. 12:171–177.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Reichsoellner M, Raggam RB, Wagner J,
Krause R and Hoenigl M: Clinical evaluation of multiple
inflammation biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis for patients
with systemic inflammatory response syndrome. J Clin Microbiol.
52:4063–4066. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Hui DSC and Zumla A: Severe acute
respiratory syndrome: Historical, epidemiologic, and clinical
features. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 33:869–889. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Tisoncik JR, Korth MJ, Simmons CP, Farrar
J, Martin TR and Katze MG: Into the eye of the cytokine storm.
Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 76:16–32. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Fani F, Regolisti G, Delsante M,
Cantaluppi V, Castellano G, Gesualdo L, Villa G and Fiaccadori E:
Recent advances in the pathogenetic mechanisms of sepsis-associated
acute kidney injury. J Nephrol. 31:351–359. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Martinez-Garcia JJ, Leon-Sicairos NM,
Canizalez-Roman A and García-Arellano BA: Fluid balance and acute
kidney injury in septic shock. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex. 74:282–288.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Spanish).
|
|
102
|
Jia X, Liu B, Bao L, Lv Q, Li F, Li H, An
Y, Zhang X, Cao B and Wang C: Delayed oseltamivir plus sirolimus
treatment attenuates H1N1 virus-induced severe lung injury
correlated with repressed NLRP3 inflammasome activation and
inflammatory cell infiltration. PLoS Pathog.
14(e1007428)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Lorz C, Justo P, Sanz A, Subirá D, Egido J
and Ortiz A: Paracetamol-induced renal tubular injury: A role for
ER stress. J Am Soc Nephrol. 15:380–389. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Khwaja A: KDIGO clinical practice
guidelines for acute kidney injury. Nephron. Clin Pract.
120:c179–c184. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Al-Dorzi HM, Aldawood AS, Khan R, Baharoon
S, Alchin JD, Matroud AA, Al Johany SM, Balkhy HH and Arabi YM: The
critical care response to a hospital outbreak of Middle East
respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection: An
observational study. Ann Intensive Care. 6(101)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Li Y, Cao C, Huang L, Xiong H, Mao H, Yin
Q and Luo X: ‘Awake’ extracorporeal membrane oxygenation combined
with continuous renal replacement therapy for the treatment of
severe chemical gas inhalation lung injury. J Burn Care Res.
41:908–912. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Ostermann M, Connor M Jr and Kashani K:
Continuous renal replacement therapy during extracorporeal membrane
oxygenation: Why, when and how? Curr Opin Crit Care. 24:493–503.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Xiong F, Tang H, Liu L, Tu C, Tian JB, Lei
CT, Liu J, Dong JW, Chen WL, Wang XH, et al: Clinical
characteristics of and medical interventions for COVID-19 in
hemodialysis patients in Wuhan, China. J Am Soc Nephrol.
31:1387–1397. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Ronco C, Tetta C, Mariano F, Wratten ML,
Bonello M, Bordoni V, Cardona X, Inguaggiato P, Pilotto L, d'Intini
V and Bellomo R: Interpreting the mechanisms of continuous renal
replacement therapy in sepsis: The peak concentration hypothesis.
Artif Organs. 27:792–801. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Ma J, Xia P, Zhou Y, Liu Z, Zhou X, Wang
J, Li T, Yan X, Chen L, Zhang S, et al: Potential effect of blood
purification therapy in reducing cytokine storm as a late
complication of critically ill COVID-19. Clin Immunol.
214(108408)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Tang B, Li S, Xiong Y, Tian M, Yu J, Xu L,
Zhang L, Li Z, Ma J, Wen F, et al: COVID-19 pneumonia in a
hemodialysis patient. Kidney Med. 2:354–358. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Xu X, Han M, Li T, Sun W, Wang D, Fu B,
Zhou Y, Zheng X, Yang Y, Li X, et al: Effective treatment of severe
COVID-19 patients with tocilizumab. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
117:10970–10975. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Fu B, Xu X and Wei H: Why tocilizumab
could be an effective treatment for severe COVID-19? J Transl Med.
18(164)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Yang XH, Sun RH, Zhao MY, Chen EZ, Liu J,
Wang HL, Yang RL and Chen DC: Expert recommendations on blood
purification treatment protocol for patients with severe COVID-19:
Recommendation and consensus. Chronic Dis Transl Med. 6:106–114.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Zhang Y, Yu L, Tang L, Zhu M, Jin Y, Wang
Z and Li L: A promising anti-cytokine-storm targeted therapy for
COVID-19: The artificial-liver blood-purification system.
Engineering (Beijing): Mar 20, 2020 (Epub ahead of print). doi:
10.1016/j.eng.2020.03.006.
|
|
116
|
Stone JH, Frigault MJ, Serling-Boyd NJ,
Fernandes AD, Harvey L, Foulkes AS, Horick NK, Healy BC, Shah R,
Bensaci AM, et al: Efficacy of tocilizumab in patients hospitalized
with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 383:2333–2344. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
RECOVERY Collaborative Group. Horby P, Lim
WS, Emberson JR, Mafham M, Bell JL, Linsell L, Staplin N,
Brightling C, Ustianowski A, et al: Dexamethasone in hospitalized
patients with Covid-19-preliminary report. N Engl J Med: Jul 17,
2020 (Epub ahead of print). doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2021436.
|