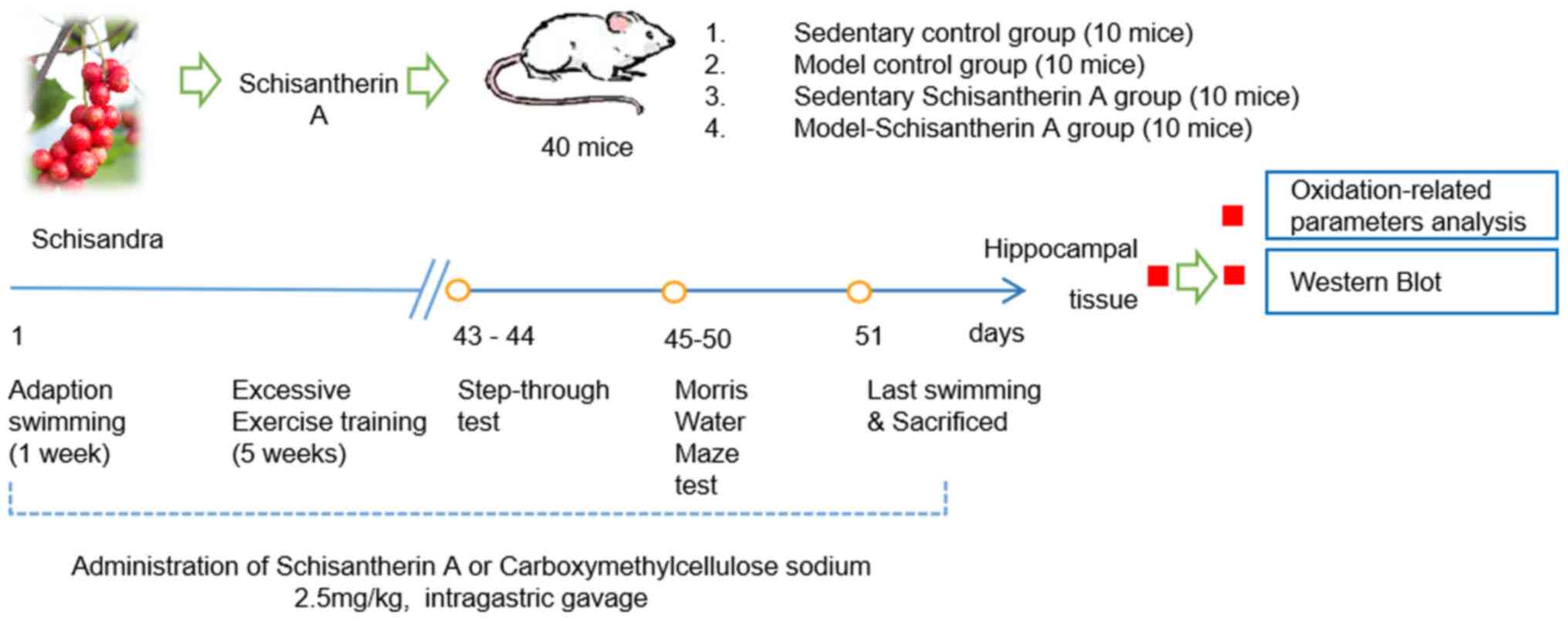
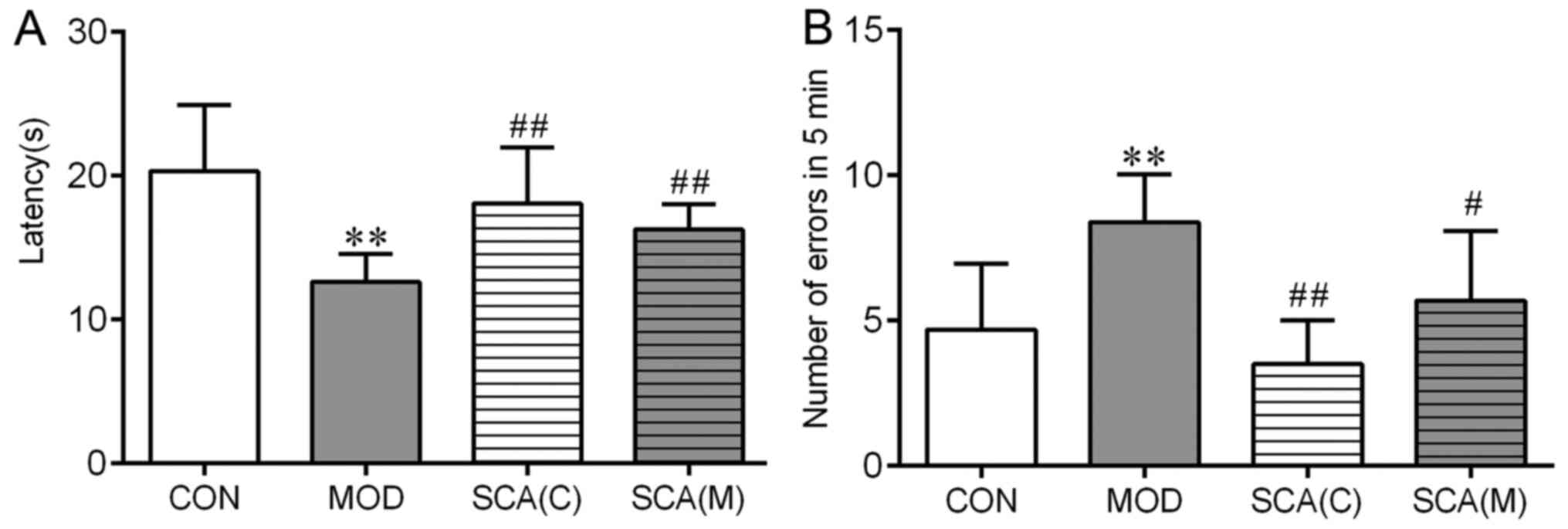
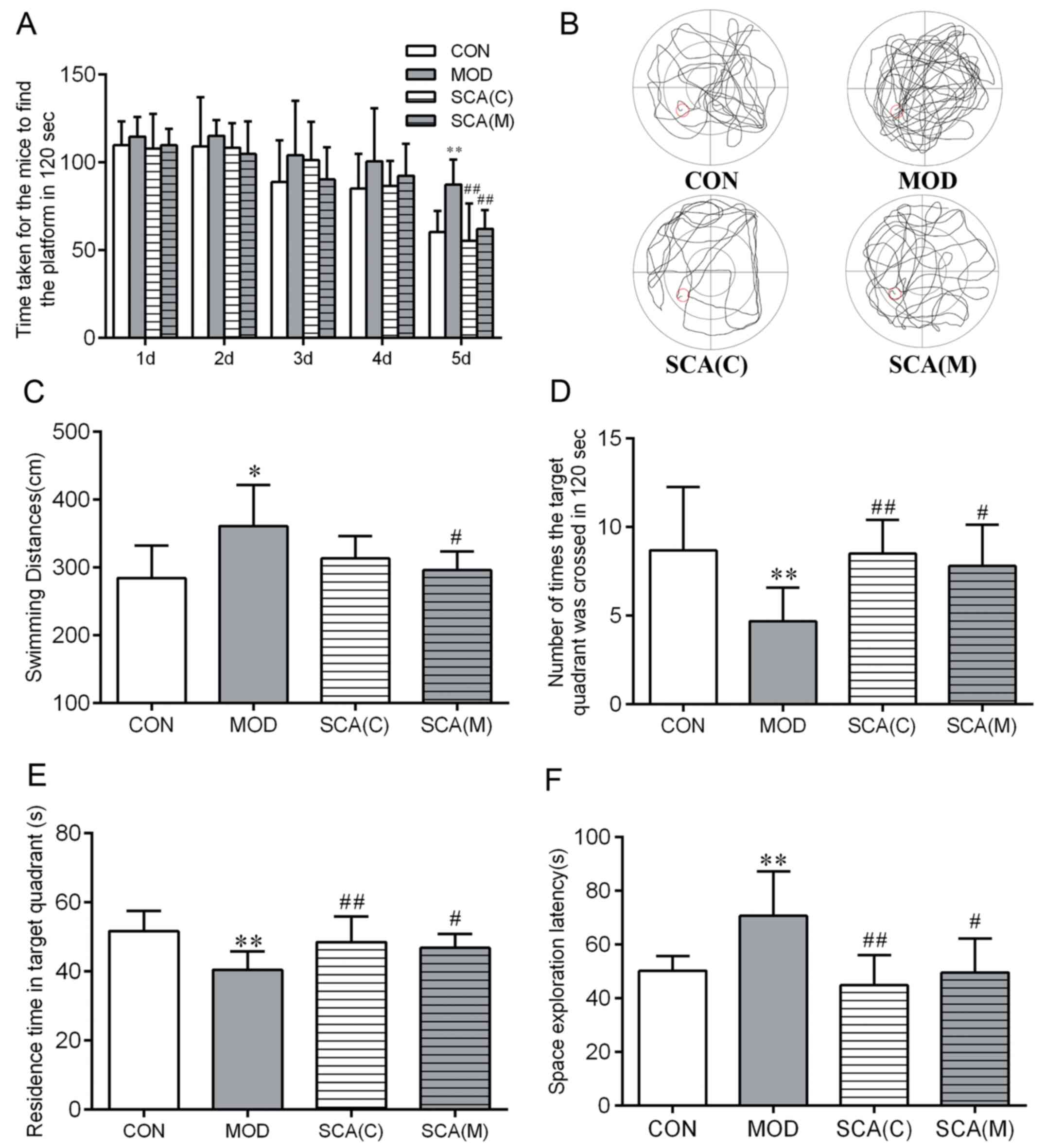
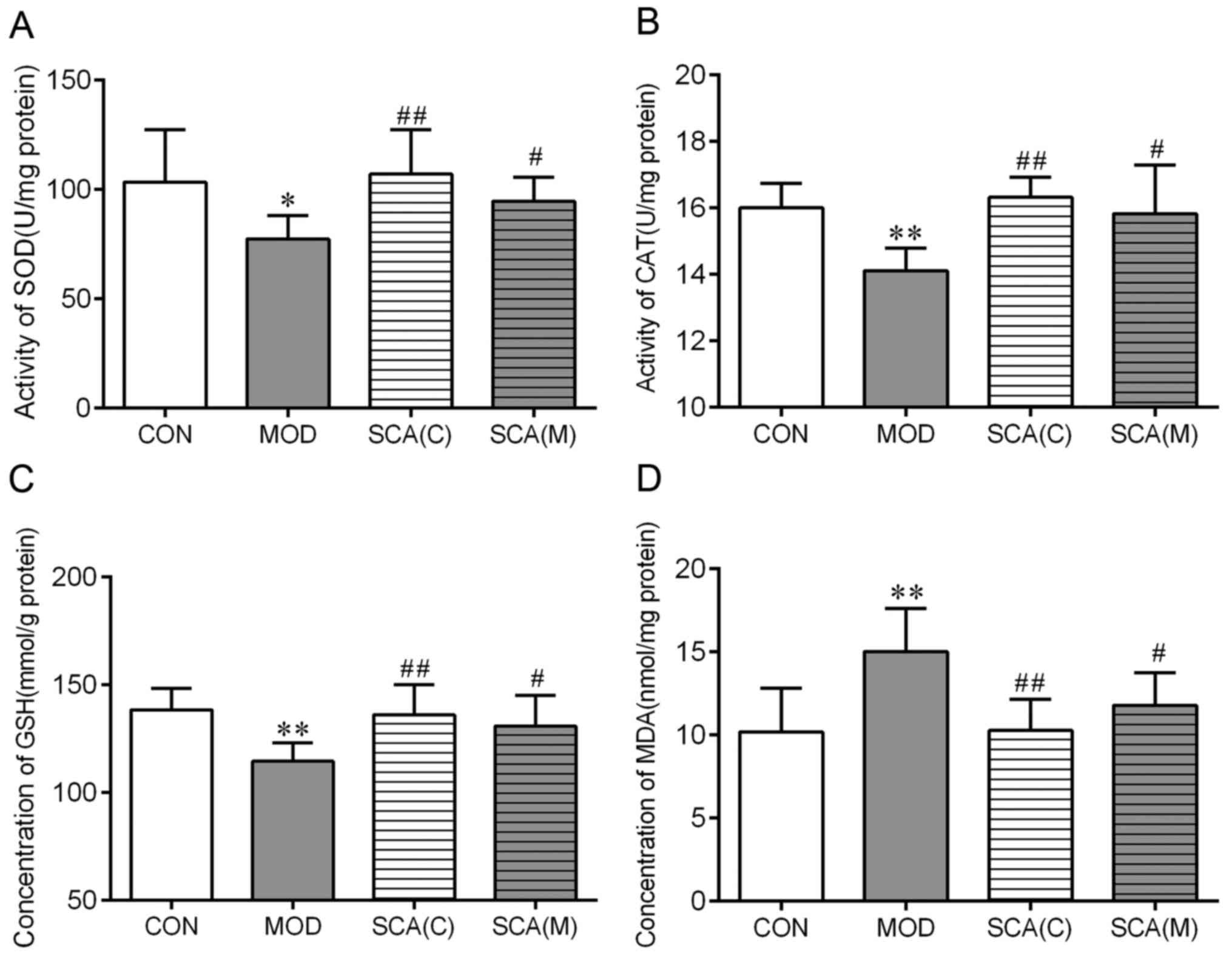
|
1
|
Feng S, Liu W, Zuo S, Xie T, Deng H, Zhang
Q and Zhong B: Impaired function of the intestinal barrier in a
novel sub-health rat model. Mol Med Rep. 13:3459–3465.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bi JL, Chen J, Sun XM, Nie XL, Liu YY, Luo
R and Zhao XS: The development and evaluation of a sub-health
self-rating scale for university students in China. BMC Public
Health. 19(330)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Xu X, Zeng Q, Ding H, Feng L and Deng L:
Correlation between women's sub-health and reproductive diseases
with pregnancies and labors. J Tradit Chin Med. 34:465–469.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lenaert B, Boddez Y, Vlaeyen JWS and
Caroline MH: Learning to feel tired: A learning trajectory towards
chronic fatigue. Behav Res Ther. 100:54–66. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhao R, Hao W, Ma B and Chen Z:
Improvement effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on
sub-health mice. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 18:1245–1252.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lamou B, Taiwe GS, Hamadou A, Abene
Houlray J, Atour MM and Tan PV: Antioxidant and antifatigue
properties of the aqueous extract of Moringa oleifera in
rats subjected to forced swimming endurance test. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2016(3517824)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Duan FF, Guo Y, Li JW and Yuan K:
Antifatigue effect of luteolin-6-C-neohesperidoside on oxidative
stress injury induced by forced swimming of rats through modulation
of Nrf2/ARE signaling pathways. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017(3159358)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hsiao CY, Hsu YJ, Tung YT, Lee MC, Huang
CC and Hsieh CC: Effects of Antrodia camphorata and Panax
ginseng supplementation on anti-fatigue properties in mice. J
Vet Med Sci. 80:284–291. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Liu XL, Zhu CC, Qiao DC, Hou LJ and Kang
DF: Effect of exercise-induced fatigue on rat learning and memory
ability and expressions of CaN in the brain. Energy Procedia.
1:248–251. 2011.
|
|
10
|
van't Leven M, Zielhuis GA, van der Meer
JW, Verbeek AL and Bleijenberg G: Fatigue and chronic fatigue
syndrome-like complaints in the general population. Eur J Public
Health. 20:251–257. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Qi Y, Cheng X, Jing H, Yan T, Xiao F, Wu
B, Bi K and Jia Y: Effect of Alpinia oxyphylla-Schisandra
chinensis herb pair on inflammation and apoptosis in Alzheimer'
s disease mice model. J Ethnopharmacol. 237:28–38. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gao Y, Wu S, Cong R, Xiao J and Ma F:
Characterization of lignans in Schisandra chinensis oil with
a single analysis process by UPLC-Q/TOF-MS. Chem Phys Lipids.
218:158–167. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang X, Yu J, Li W, Wang C, Li H, Ju W,
Chen J and Sun J: Characteristics and antioxidant activity of
lignans in Schisandra chinensis and Schisandra
sphenanthera from different locations. Chem Biodivers.
15(e1800030)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhang XY, Lin HJ, Li X, Jing S, Sun W,
Jiang WH, Wang CM, Sun JH, Li H and Chen JG: Schisantherin A
improves fatigue of mice by regulating the antioxidant pathway of
liver Nrf2/ARE. Food Sci. 41:1–10. 2020.
|
|
15
|
Liu C, Sun W, Li N, Gao J, Yu C, Wang C,
Sun J, Jing S, Chen J and Li H: Schisantherin A improves learning
and memory of mice with D-galactose-induced learning and memory
impairment through its antioxidation and regulation of
p19/p53/p21/Cyclin D1/CDK4/RB gene expressions. J Med Food.
21:678–688. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cheluvappa R, Scowen P and Eri R: Ethics
of animal research in human disease remediation, its institutional
teaching; and alternatives to animal experimentation. Pharmacol Res
Perspect. 5(e00332)2017.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Smith AJ, Clutton RE, Lilley E, Hansen KEA
and Brattelid T: PREPARE: Guidelines for planning animal research
and testing. Lab Anim. 52:135–141. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Yeh TS, Chuang HL, Huang WC, Chen YM,
Huang CC and Hsu MC: Astragalus membranaceus improves
exercise performance and ameliorates exercise-induced fatigue in
trained mice. Molecules. 19:2793–2807. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Falavigna G, Alves de Araújo J, Rogero MM,
Pires IS, Pedrosa RG, Martins E Jr, Alves de Castro I and Tirapegui
J: Effects of diets supplemented with branched-chain amino acids on
the performance and fatigue mechanisms of rats submitted to
prolonged physical exercise. Nutrients. 4:1767–1780.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liu C, Wen Y, Huang H, Lin W, Huang M, Lin
R and Ma Y: Over-expression of 5-HT6 receptor and activated
Jab-1/p-c-Jun play important roles in pilocarpine-induced seizures
and learning-memory impairment. J Mol Neurosci. 67:388–399.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhou J, Liu X, Chen T, Cheng G and Cai S:
Preventive effect of ethanol extract from Chinese sumac fruits
against tetrachloromethane-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Food
Funct. 11:7061–7072. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Huang CC, Hsu MC, Huang WC, Yang HR and
Hou CC: Triterpenoid-rich extract from Antrodia camphorata
improves physical fatigue and exercise performance in mice. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012(364741)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sowndhararajan K, Deepa P, Kim M, Park SJ
and Kim S: An overview of neuroprotective and cognitive enhancement
properties of lignans from. Schisandra chinensis. Biomed
Pharmacother. 97:958–968. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Rasouli O, Gotaas ME, Stensdotter AK,
Skovlund E, Landrø NI, Dåstøl P and Fors EA: Neuropsychological
dysfunction in chronic fatigue syndrome and the relation between
objective and subjective findings. Neuropsychology. 33:658–669.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Fan XL, Li F and Song YH: Effect of sihui
mixture on the learning and memory ability, mRNA expressions of
hippocampus NMDA subunit NR2A and NR2B, and EphB2 receptor in
fatigue rats. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 31:512–516.
2011.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Ramos D, Martins EG, Viana-Gomes D,
Casimiro-Lopes G and Salerno VP: Biomarkers of oxidative stress and
tissue damage released by muscle and liver after a single bout of
swimming exercise. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 38:507–511.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Baghcheghi Y, Salmani H, Beheshti F,
Shafei MN, Sadeghnia HR and Soukhtanloo M: Effects of PPAR-γ
agonist, pioglitazone on brain tissues oxidative damage and
learning and memory impairment in juvenile hypothyroid rats. Int J
Neurosci. 129:1024–1038. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Halder S, Kar R, Galav V, Mehta AK,
Bhattacharya SK, Mediratta PK and Banerjee BD: Cadmium exposure
during lactation causes learning and memory-impairment in F1
generation mice: Amelioration by quercetin. Drug Chem Toxicol.
39:272–278. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Haddadi M, Jahromi SR, Sagar BK, Patil RK,
Shivanandappa T and Ramesh SR: Brain aging memory impairment and
oxidative stress: A study in Drosophila melanogaster. Behav
Brain Res. 259:60–69. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Schurman LD, Carper MC, Moncayo LV,
Ogasawara D, Richardson K, Yu L, Liu X, Poklis JL, Liu QS, Cravatt
BF and Lichtman AH: Diacylglycerol lipase-alpha regulates
hippocampal-dependent learning and memory processes in mice. J
Neurosci. 39:5949–5965. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tu WJ, Wang H, Li S, Liu Q and Sha H: The
anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant mechanisms of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE
signaling pathway in chronic diseases. Aging Dis. 10:637–651.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chen K, You J, Tang Y, Zhou Y, Liu P, Zou
D, Zhou Q, Zhang T, Zhu J and Mi M: Supplementation of superfine
powder prepared from Chaenomeles speciosa fruit increases
endurance capacity in rats via antioxidant and Nrf2/ARE signaling
pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2014(976438)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Taguchi K, Maher JM, Suzuki T, Kawatani Y,
Motohashi H and Yamamoto M: Genetic analysis of cytoprotective
functions supported by graded expression of Keap1. Mol Cell Biol.
30:3016–3026. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kopacz A, Kloska D, Forman HJ, Jozkowicz A
and Grochot-Przeczek A: Beyond repression of Nrf2: An update on
Keap1. Free Radic Biol Med. 157:63–74. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Baird L and Yamamoto M: The molecular
mechanisms regulating the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway. Mol Cell Biol.
40:e00099–20. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhong L, Zhao L, Yang F, Yang W, Sun Y and
Hu Q: Evaluation of anti-fatigue property of the extruded product
of cereal grains mixed with cordyceps militaris on mice. J Int Soc
Sports Nutr. 14(15)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Surhio MM, Wang YF, Fang S, Li J and Ye M:
Anti-fatigue activity of a lachnum polysaccharide and its
carboxymethylated derivative in mice. Bioorg Med Chem Lett.
27:4777–4780. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wang K, Chen Z, Huang J, Huang L, Luo N,
Liang X, Liang M and Xie W: Naringenin prevents ischaemic stroke
damage via anti-apoptotic and anti-oxidant effects. Clin Exp
Pharmacol Physiol. 44:862–871. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Jiang XM, Hu JH, Wang LL, Ma C, Wang X and
Liu XL: Ulinastatin alleviates neurological deficiencies evoked by
transient cerebral ischemia via improving autophagy, Nrf-2-ARE and
apoptosis signals in hippocampus. Physiol Res. 67:637–646.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yoo ES, Choo GS, Kim SH, Woo JS, Kim HJ,
Park YS, Kim BS, Kim SK, Park BK, Cho SD, et al: Antitumor and
apoptosis-inducing effects of piperine on human melanoma cells.
Anticancer Res. 39:1883–1892. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Niture SK and Jaiswal AK: Nrf2
up-regulates anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 and prevents cellular
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 287:9873–9886. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Zhang J, Su L, Ye Q, Zhang S, Kung H,
Jiang F, Jiang G, Miao J and Zhao B: Discovery of a novel Nrf2
inhibitor that induces apoptosis of human acute myeloid leukemia
cells. Oncotarget. 8:7625–7636. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ye J, Jiang R, Cui M, Zhu B, Sun L, Wang
Y, Zohaib A, Dong Q, Ruan X, Song Y, et al: Etanercept reduces
neuroinflammation and lethality in mouse model of Japanese
encephalitis. J Infect Dis. 210:875–889. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Gu Y, Yang Y, Cao X, Zhao Y, Gao X, Sun C,
Zhang F, Yuan Y, Xu Y, Zhang J, et al: Plin3 protects against
alcoholic liver injury by facilitating lipid export from the
endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biochem. 120:16075–16087.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|