|
1
|
Dou Z, Xu C, Donahue G, Shimi T, Pan JA,
Zhu J, Ivanov A, Capell BC, Drake AM, Shah PP, et al: Autophagy
mediates degradation of nuclear lamina. Nature. 527:105–109.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Singh R, Kaushik S, Wang Y, Xiang Y, Novak
I, Komatsu M, Tanaka K, Cuervo AM and Czaja MJ: Autophagy regulates
lipid metabolism. Nature. 458:1131–1135. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wan X, Huang W, Yang S, Zhang Y, Pu H, Fu
F, Huang Y, Wu H, Li T and Li Y: Identification of
androgen-responsive lncRNAs as diagnostic and prognostic markers
for prostate cancer. Oncotarget. 7:60503–60518. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhu X, Zhou M, Liu G, Huang X, He W, Gou X
and Jiang T: Autophagy activated by the c-Jun N-terminal
kinase-mediated pathway protects human prostate cancer PC3 cells
from celecoxib-induced apoptosis. Exp Ther Med. 13:2348–2354.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kim KY, Park KI, Kim SH, Yu SN, Park SG,
Kim YW, Seo YK, Ma JY and Ahn SC: Inhibition of autophagy promotes
salinomycin-induced apoptosis via reactive oxygen species-mediated
PI3K/AKT/mTOR and ERK/p38 MAPK-dependent signaling in human
prostate cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 18(1088)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Nie C, Zhou J, Qin X, Shi X, Zeng Q, Liu
J, Yan S and Zhang L: Diosgenininduced autophagy and apoptosis in a
human prostate cancer cell line. Mol Med Rep. 14:4349–4359.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wang L, Kim D, Wise J, Shi X, Zhang Z and
DiPaola RS: p62 as a therapeutic target for inhibition of autophagy
in prostate cancer. Prostate. 78:390–400. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chang MA, Morgado M, Warren CR, Hinton CV,
Farach-Carson MC and Delk NA: p62/SQSTM1 is required for cell
survival of apoptosis-resistant bone metastatic prostate cancer
cell lines. Prostate. 74:149–163. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Santanam U, Banach-Petrosky W, Abate-Shen
C, Shen MM, White E and DiPaola RS: Atg7 cooperates with Pten loss
to drive prostate cancer tumor growth. Genes Dev. 30:399–407.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Chandra P and Kumar D: Selective autophagy
gets more selective: Uncoupling of autophagy flux and xenophagy
flux in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages. Autophagy.
12:608–609. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bauckman KA, Owusu-Boaitey N and Mysorekar
IU: Selective autophagy: Xenophagy. Methods. 75:120–127.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mao K and Klionsky DJ: Xenophagy: A
battlefield between host and microbe, and a possible avenue for
cancer treatment. Autophagy. 13:223–224. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sui X, Liang X, Chen L, Guo C, Han W, Pan
H and Li X: Bacterial xenophagy and its possible role in cancer: A
potential antimicrobial strategy for cancer prevention and
treatment. Autophagy. 13:237–247. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhang L, Sung JJ, Yu J, Ng SC, Wong SH,
Cho CH, Ng SS, Chan FK and Wu WK: Xenophagy in Helicobacter
pylori- and Epstein-Barr virus-induced gastric cancer. J
Pathol. 233:103–112. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Verlhac P, Viret C and Faure M: Dual
function of CALCOCO2/NDP52 during xenophagy. Autophagy. 11:965–966.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Verlhac P, Viret C and Faure M: Handcuffs
for bacteria-NDP52 orchestrates xenophagy of intracellular
Salmonella. Microb Cell. 2:214–215. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
von Muhlinen N, Akutsu M, Ravenhill BJ,
Foeglein A, Bloor S, Rutherford TJ, Freund SM, Komander D and
Randow F: LC3C, bound selectively by a noncanonical LIR motif in
NDP52, is required for antibacterial autophagy. Mol Cell.
48:329–342. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Verlhac P, Gregoire IP, Azocar O, Petkova
DS, Baguet J, Viret C and Faure M: Autophagy receptor NDP52
regulates pathogen-containing autophagosome maturation. Cell Host
Microbe. 17:515–525. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Thurston TL, Wandel MP, von Muhlinen N,
Foeglein A and Randow F: Galectin 8 targets damaged vesicles for
autophagy to defend cells against bacterial invasion. Nature.
482:414–418. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Leymarie O, Meyer L, Tafforeau L, Lotteau
V, Costa BD, Delmas B, Chevalier C and Le Goffic R: Influenza virus
protein PB1-F2 interacts with CALCOCO2 (NDP52) to modulate innate
immune response. J Gen Virol. 98:1196–1208. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cui F, Hu J, Fan Y, Tan J and Tang H:
Knockdown of spindle pole body component 25 homolog inhibits cell
proliferation and cycle progression in prostate cancer. Oncol Lett.
15:5712–5720. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Nabzdyk CS, Chun M, Pradhan NL, Yoshida S
and LoGerfo FW: Differential susceptibility of human primary aortic
and coronary artery vascular cells to RNA interference. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 425:261–265. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Dennis GJ, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang J,
Gao W, Lane HC and Lempicki RA: DAVID: Database for annotation,
visualization, and integrated discovery. Genome Biol.
4(P3)2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:D447–D452. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
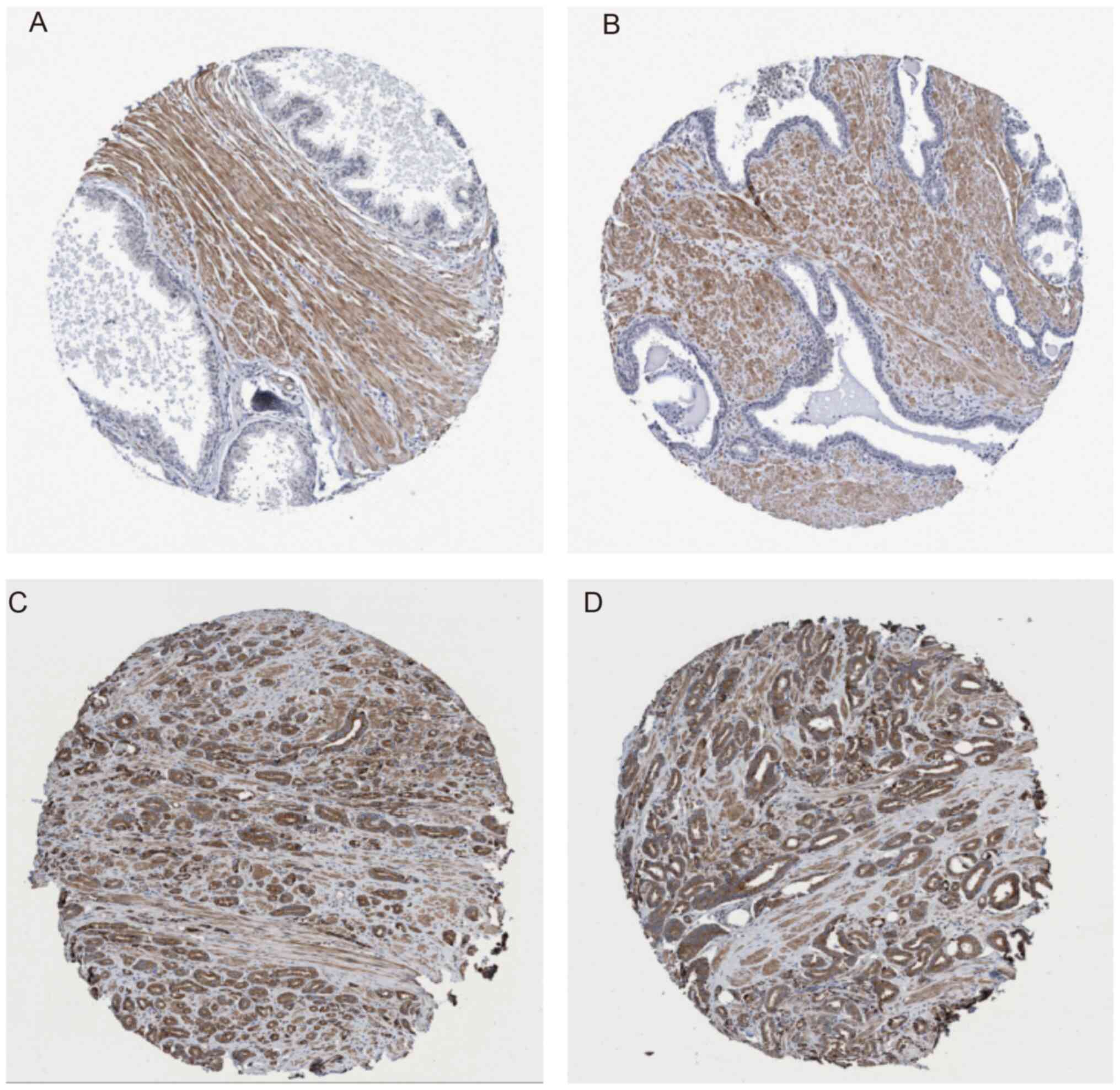
Uhlén M, Fagerberg L, Hallström BM,
Lindskog C, Oksvold P, Mardinoglu A, Sivertsson A, Kampf C,
Sjöstedt E, Asplund A, et al: Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the
human proteome. Science. 347(1260419)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
McFarland JM, Ho ZV, Kugener G, Dempster
JM, Montgomery PG, Bryan JG, Krill-Burger JM, Green TM, Vazquez F,
Boehm JS, et al: Improved estimation of cancer dependencies from
large-scale RNAi screens using model-based normalization and data
integration. Nat Commun. 9(4610)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Nakayama N, Nakayama K, Shamima Y,
Ishikawa M, Katagiri A, Iida K and Miyazaki K: Gene amplification
CCNE1 is related to poor survival and potential therapeutic target
in ovarian cancer. Cancer. 116:2621–2634. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu Y, Zhang X, Han C, Wan G, Huang X,
Ivan C, Jiang D, Rodriguez-Aguayo C, Lopez-Berestein G, Rao PH, et
al: TP53 loss creates therapeutic vulnerability in colorectal
cancer. Nature. 520:697–701. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. The
molecular taxonomy of primary prostate cancer. Cell. 163:1011–1025.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhong Z, Sanchez-Lopez E and Karin M:
Autophagy, inflammation, and immunity: A Troika governing cancer
and its treatment. Cell. 166:288–298. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Liu C, Xu P, Chen D, Fan X, Xu Y, Li M,
Yang X and Wang C: Roles of autophagy-related genes Beclin-1 and
LC3 in the development and progression of prostate cancer and
benign prostatic hyperplasia. Biomed Rep. 1:855–860.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Jiang X, Huang Y, Liang X, Jiang F, He Y,
Li T, Xu G, Zhao H, Yang W, Jiang G, et al: Metastatic prostate
cancer-associated P62 inhibits autophagy flux and promotes
epithelial to mesenchymal transition by sustaining the level of
HDAC6. Prostate. 78:426–434. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Evan GI and Vousden KH: Proliferation,
cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 411:342–348.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Fuertes MB, Woo SR, Burnett B, Fu YX and
Gajewski TF: Type I interferon response and innate immune sensing
of cancer. Trends Immunol. 34:67–73. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xia Y, Shen S and Verma IM: NF-κB, an
active player in human cancers. Cancer Immunol Res. 2:823–830.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|