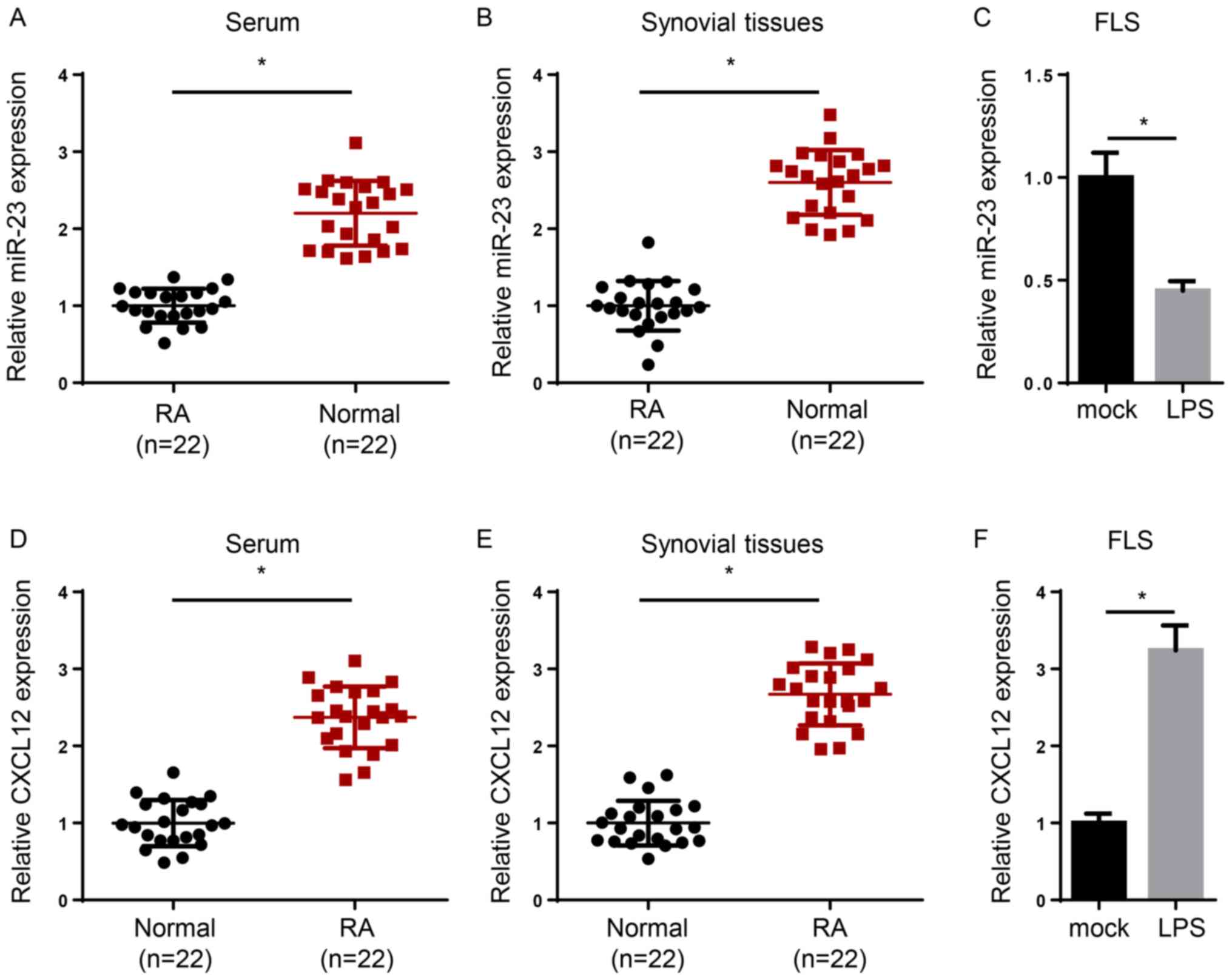
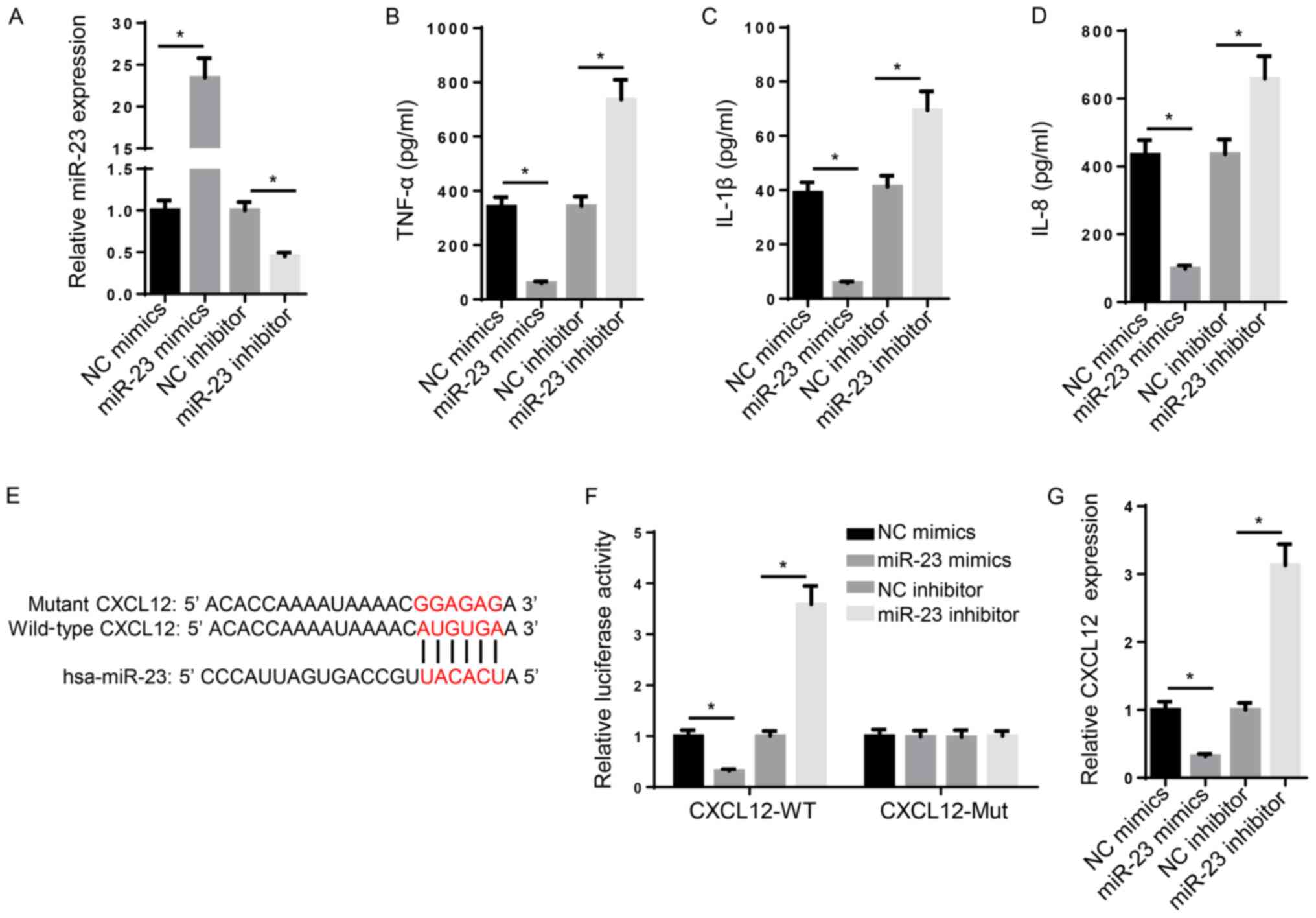
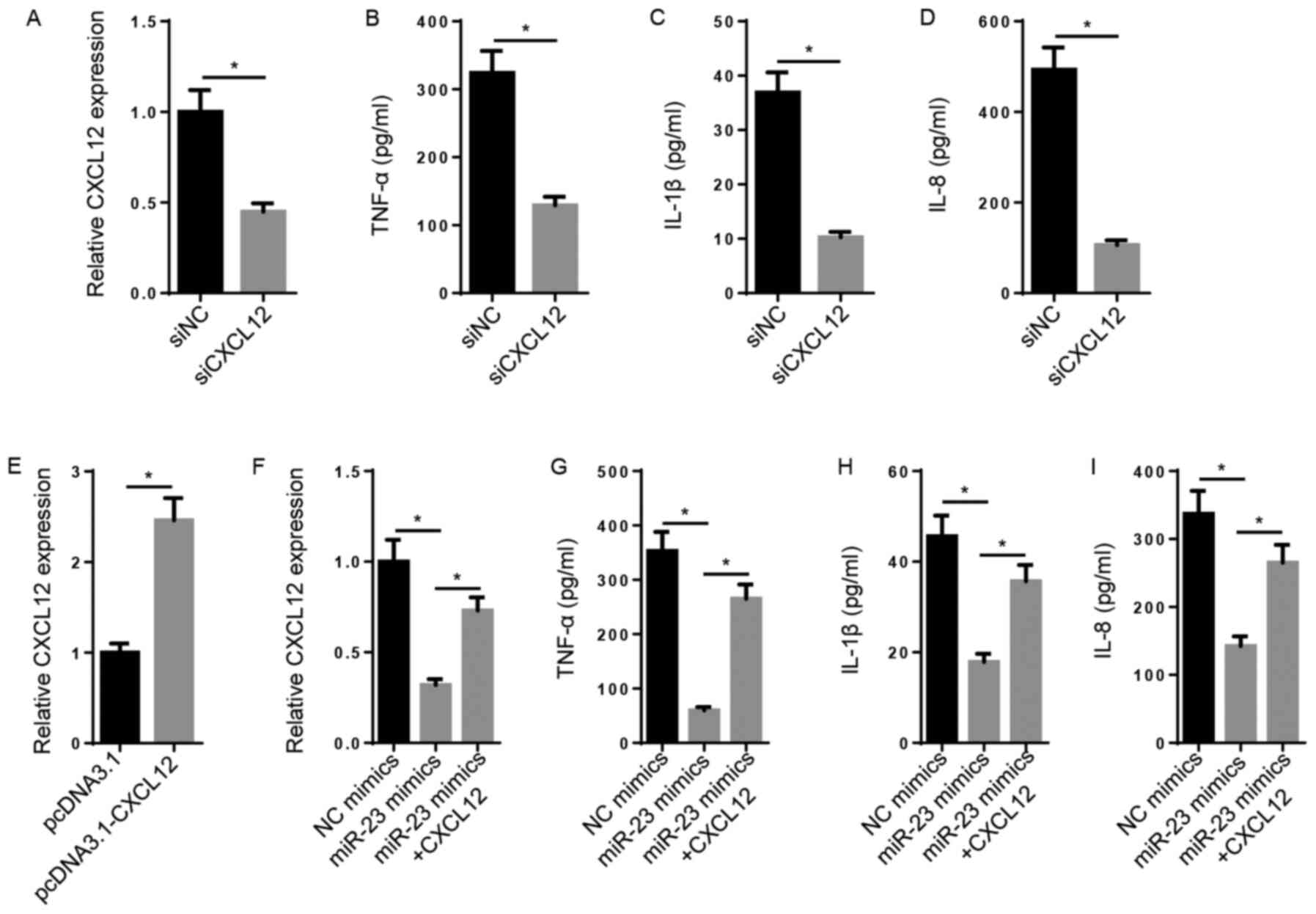
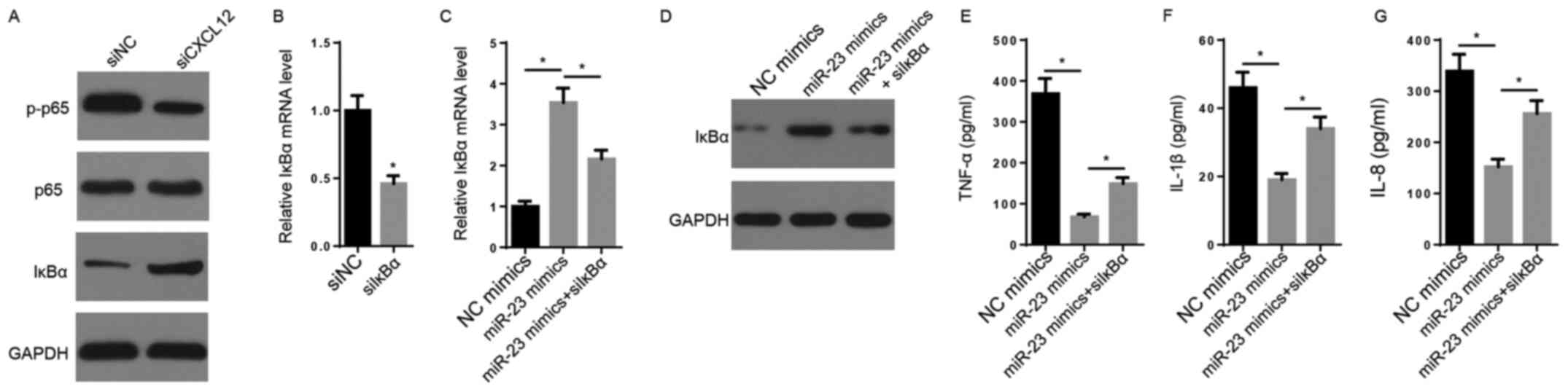
|
1
|
Šenolt L: Rheumatoid arthritis. Vnitr Lek.
64:98–106. 2018.PubMed/NCBI(In Czech).
|
|
2
|
Wasserman A: Rheumatoid arthritis: Common
questions about diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician.
97:455–462. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Katz P: Causes and consequences of fatigue
in rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 29:269–276.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Baum R and Gravallese EM: Bone as a target
organ in rheumatic disease: Impact on osteoclasts and osteoblasts.
Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 51:1–15. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Burmester GR and Pope JE: Novel treatment
strategies in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 389:2338–2348.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mellado M, Martínez-Muñoz L, Cascio G,
Lucas P, Pablos JL and Rodríguez-Frade JG: T cell migration in
rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol. 6(384)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hoxha M: A systematic review on the role
of eicosanoid pathways in rheumatoid arthritis. Adv Med Sci.
63:22–29. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bustamante MF, Garcia-Carbonell R,
Whisenant KD and Guma M: Fibroblast-like synoviocyte metabolism in
the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther.
19(110)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Doody KM, Bottini N and Firestein GS:
Epigenetic alterations in rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like
synoviocytes. Epigenomics. 9:479–492. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li S, Zhang T, Xu W, Ding J, Yin F, Xu J,
Sun W, Wang H, Sun M, Cai Z and Hua Y: Sarcoma-targeting
peptide-decorated polypeptide nanogel intracellularly delivers
shikonin for upregulated osteosarcoma necroptosis and diminished
pulmonary metastasis. Theranostics. 8:1361–1375. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lu TX and Rothenberg ME: MicroRNA. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 141:1202–1207. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Vishnoi A and Rani S: MiRNA biogenesis and
regulation of diseases: An overview. Methods Mol Biol. 1509:1–10.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Rupaimoole R and Slack FJ: MicroRNA
therapeutics: Towards a new era for the management of cancer and
other diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 16:203–222. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bijkerk R, van Solingen C, de Boer HC, van
der Pol P, Khairoun M, de Bruin RG, van Oeveren-Rietdijk AM,
Lievers E, Schlagwein N, van Gijlswijk DJ, et al: Hematopoietic
microRNA-126 protects against renal ischemia/reperfusion injury by
promoting vascular integrity. J Am Soc Nephrol. 25:1710–1722.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liu X, Zhang C, Wang C, Sun J, Wang D,
Zhao Y and Xu X: miR-210 promotes human osteosarcoma cell migration
and invasion by targeting FGFRL1. Oncol Lett. 16:2229–2236.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ying Y, Mao Y and Yao M: NLRP3
inflammasome activation by microRNA-495 promoter methylation may
contribute to the progression of acute lung injury. Mol Ther
Nucleic Acids. 18:801–814. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li L, Hou A, Gao X, Zhang J, Zhang L, Wang
J, Li H and Song Y: Lentivirus-mediated miR-23a overexpression
induces trophoblast cell apoptosis through inhibiting X-linked
inhibitor of apoptosis. Biomed Pharmacother. 94:412–417.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lin ST, Huang Y, Zhang L, Heng MY, Ptácek
LJ and Fu YH: MicroRNA-23a promotes myelination in the central
nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:17468–17473.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Castro-Villegas C, Pérez-Sánchez C,
Escudero A, Filipescu I, Verdu M, Ruiz-Limón P, Aguirre MA,
Jiménez-Gomez Y, Font P, Rodriguez-Ariza A, et al: Circulating
miRNAs as potential biomarkers of therapy effectiveness in
rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with anti-TNFα. Arthritis Res
Ther. 17(49)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Janssens R, Struyf S and Proost P: The
unique structural and functional features of CXCL12. Cell Mol
Immunol. 15:299–311. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yang L, Wang M, Guo YY, Sun T, Li YJ, Yang
Q, Zhang K, Liu SB, Zhao MG and Wu YM: Systemic inflammation
induces anxiety disorder through CXCL12/CXCR4 pathway. Brain Behav
Immun. 56:352–362. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Xu J, Wang H, Hu Y, Zhang YS, Wen L, Yin
F, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Li S, Miao Y, et al: Inhibition of CaMKIIα
activity enhances antitumor effect of fullerene C60 nanocrystals by
suppression of autophagic degradation. Adv Sci (Weinh).
6(1801233)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Nicastro M, Vescovini R, Maritati F,
Palmisano A, Urban ML, Incerti M, Fenaroli P, Peyronel F, Benigno
GD, Mangieri D, et al: Fibrocytes in chronic periaortitis: A novel
mechanism linking inflammation and fibrosis. Arthritis Rheumatol.
71:1913–1922. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Karouzakis E, Rengel Y, Jüngel A, Kolling
C, Gay RE, Michel BA, Tak PP, Gay S, Neidhart M and Ospelt C: DNA
methylation regulates the expression of CXCL12 in rheumatoid
arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Genes Immun. 12:643–652.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Sun SC: The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in
immunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 17:545–558.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Afonina IS, Zhong Z, Karin M and Beyaert
R: Limiting inflammation-the negative regulation of NF-κB and the
NLRP3 inflammasome. Nat Immunol. 18:861–869. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Novack DV: Role of NF-κB in the skeleton.
Cell Res. 21:169–182. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Moran-Moguel MC, Petarra-Del Rio S,
Mayorquin-Galvan EE and Zavala-Cerna MG: Rheumatoid arthritis and
miRNAs: A critical review through a functional view. J Immunol Res.
2018(2474529)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hegemann N, Wondimu A, Ullrich K and
Schmidt MF: Synovial MMP-3 and TIMP-1 levels and their correlation
with cytokine expression in canine rheumatoid arthritis. Vet
Immunol Immunopathol. 91:199–204. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Huang Y: The novel regulatory role of
lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Mol Med.
22:5768–5775. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Liao YX, Zhou CH, Zeng H, Zuo DQ, Wang ZY,
Yin F, Hua YQ and Cai ZD: The role of the CXCL12-CXCR4/CXCR7 axis
in the progression and metastasis of bone sarcomas (review). Int J
Mol Med. 32:1239–1246. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Coskun Benlidayi I: Sleep impairment: An
obstacle to achieve optimal quality of life in rheumatoid
arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 38:2183–2192. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wasserman AM: Diagnosis and management of
rheumatoid arthritis. Am Fam Physician. 84:1245–1252.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chinese Rheumatology Association. 2018
Chinese guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid
arthritis. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 57:242–251. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
36
|
Salehi E, Eftekhari R, Oraei M, Gharib A
and Bidad K: MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol.
34:615–628. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Song YJ, Li G, He JH, Guo Y and Yang L:
Bioinformatics-based identification of microRNA-regulated and
rheumatoid arthritis-associated genes. PLoS One.
10(e0137551)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Guo T, Ding H, Jiang H, Bao N, Zhou L and
Zhao J: miR-338-5p regulates the viability, proliferation,
apoptosis and migration of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like
synoviocytes by targeting NFAT5. Cell Physiol Biochem. 49:899–910.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Philippe L, Alsaleh G, Pichot A, Ostermann
E, Zuber G, Frisch B, Sibilia J, Pfeffer S, Bahram S, Wachsmann D
and Georgel P: MiR-20a regulates ASK1 expression and TLR4-dependent
cytokine release in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Ann
Rheum Dis. 72:1071–1079. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Cecchinato V, D'Agostino G, Raeli L,
Nerviani A, Schiraldi M, Danelon G, Manzo A, Thelen M, Ciurea A,
Bianchi ME, et al: Redox-mediated mechanisms fuel monocyte
responses to CXCL12/HMGB1 in active rheumatoid arthritis. Front
Immunol. 9(2118)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Wu S, Zheng Q, Xing X, Dong Y, Wang Y, You
Y, Chen R, Hu C, Chen J, Gao D, et al: Matrix stiffness-upregulated
LOXL2 promotes fibronectin production, MMP9 and CXCL12 expression
and BMDCs recruitment to assist pre-metastatic niche formation. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37(99)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Castejón ML, Rosillo MA, Montoya T,
González-Benjumea A, Fernández-Bolaños JG and Alarcón-de-la-Lastra
C: Oleuropein down-regulated IL-1β-induced inflammation and
oxidative stress in human synovial fibroblast cell line SW982. Food
Funct. 8:1890–1898. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhang N, Liu Z, Luo H, Wu W, Nie K, Cai L,
Tan S, Chen X, Huang Y, Liu J, et al: FM0807 decelerates
experimental arthritis progression by inhibiting inflammatory
responses and joint destruction via modulating NF-κB and MAPK
pathways. Biosci Rep. 39(BSR20182263)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yao Z, Xing L and Boyce BF: NF-κB p100
limits TNF-induced bone resorption in mice by a TRAF3-dependent
mechanism. J Clin Invest. 119:3024–3034. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Noort AR, Tak PP and Tas SW: Non-canonical
NF-κB signaling in rheumatoid arthritis: Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde?
Arthritis Res Ther. 17(15)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|