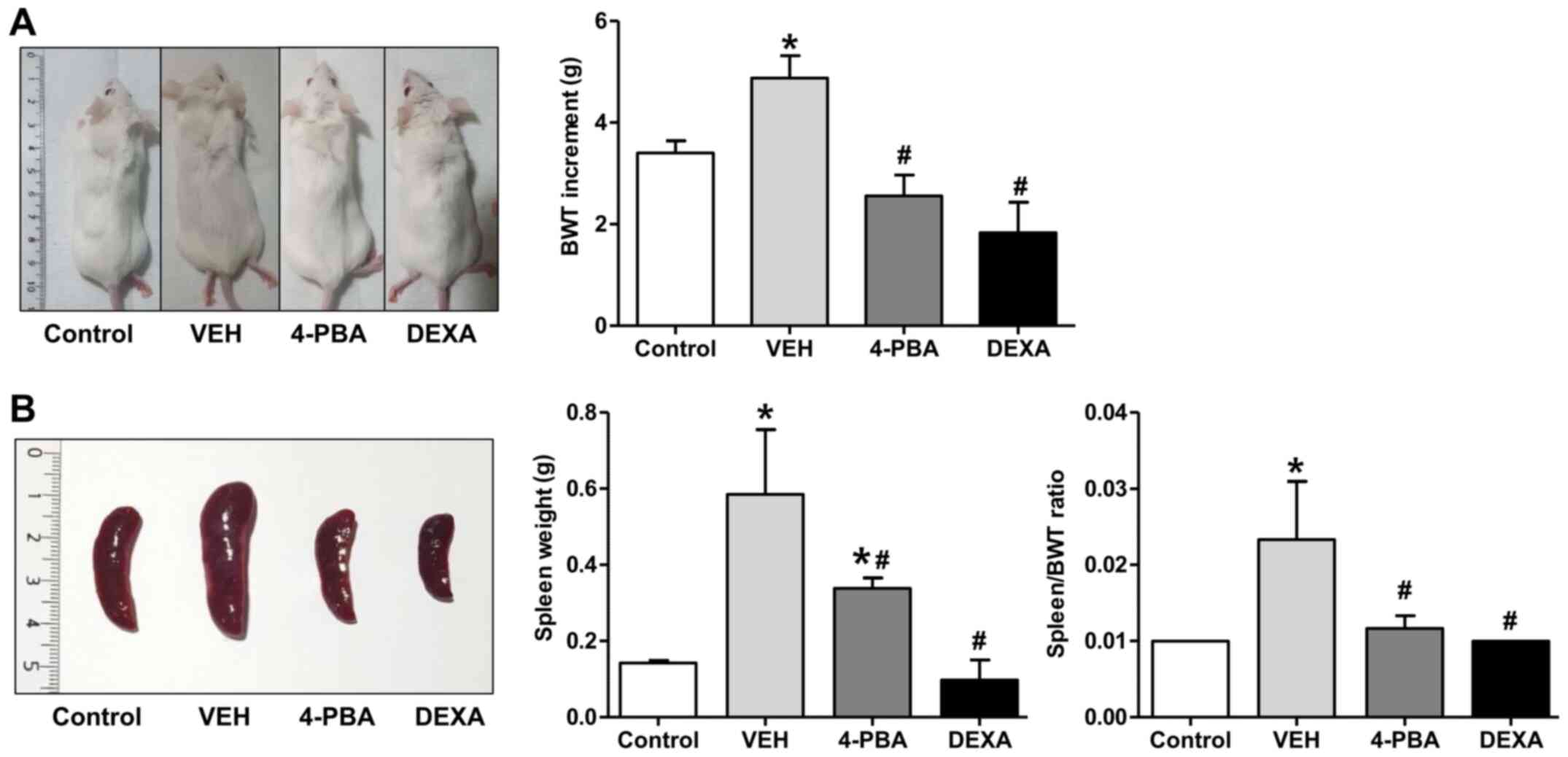
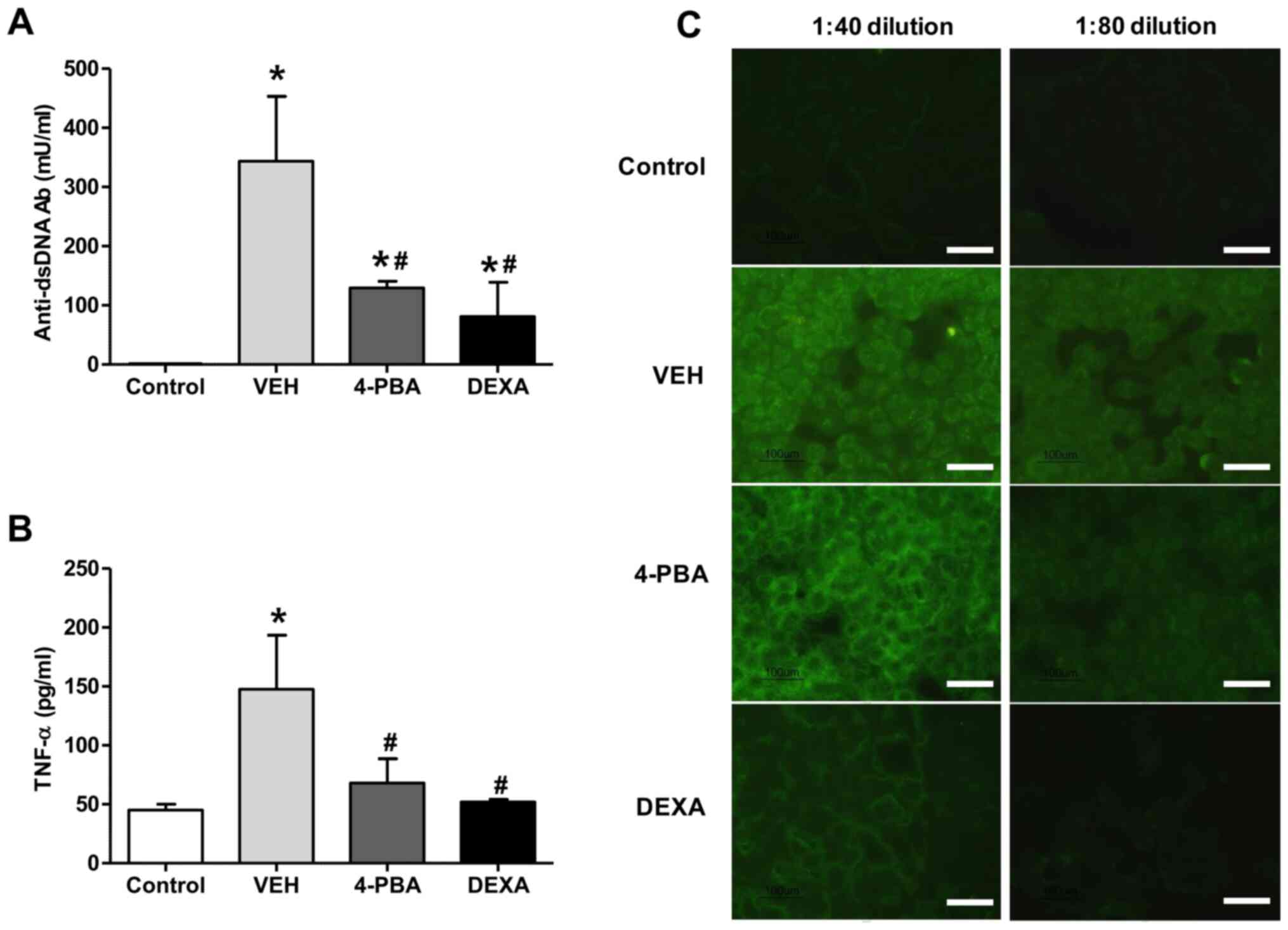
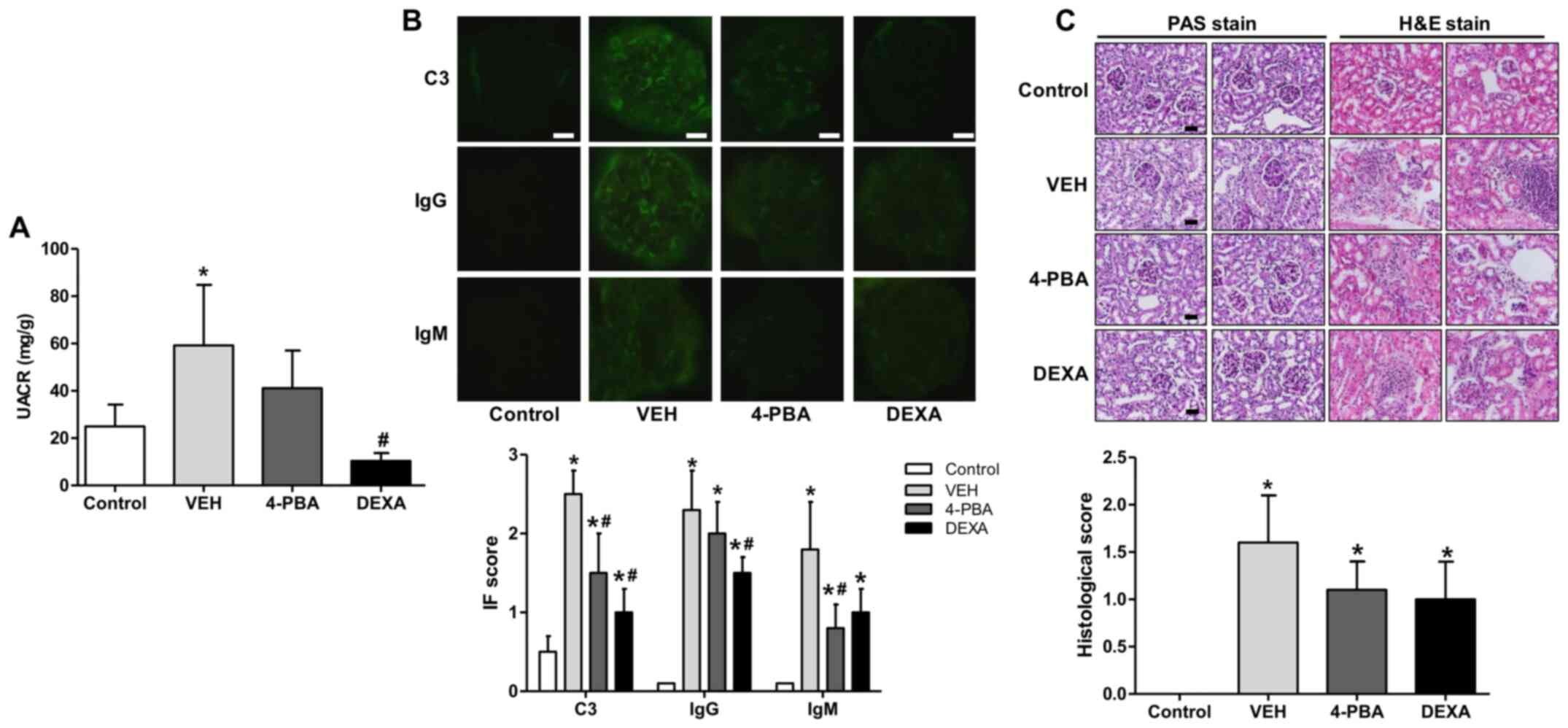
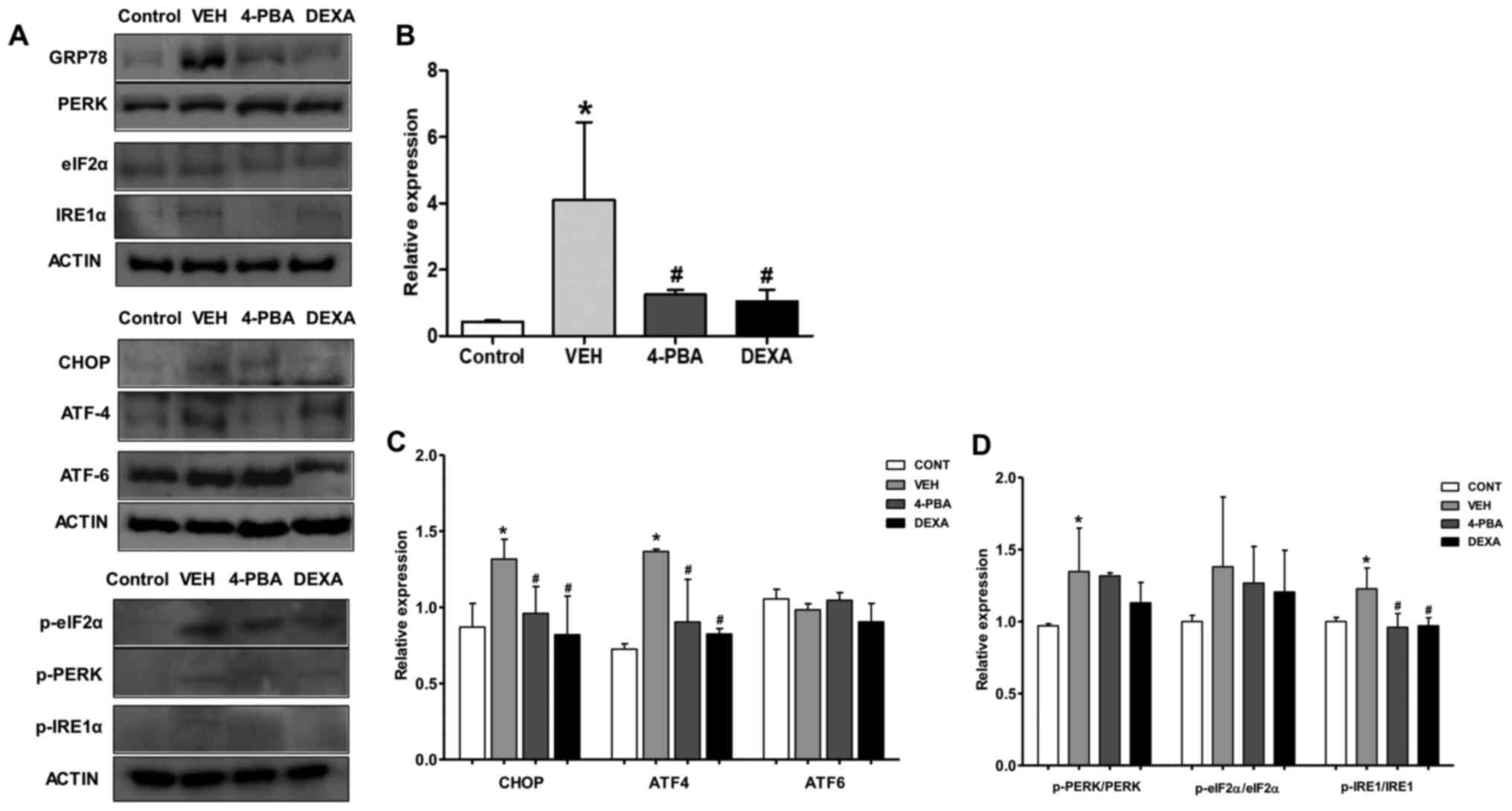
|
1
|
Tsokos GC: Systemic lupus erythematosus. N
Engl J Med. 365:2110–2121. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Kiriakidou M, Cotton D, Taichman D and
Williams S: Systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Intern Med.
159:ITC4–ITC1. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sakaguchi S: Regulatory T cells: Key
controllers of immunologic self-tolerance. Cell. 101:455–458.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Shevach EM: CD4+
CD25+ suppressor T cells: More questions than answers.
Nat Rev Immunol. 2:389–400. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M
and Toda M: Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T
cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a
single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune
diseases. J Immunol. 155:1151–1164. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Buckner JH: Mechanisms of impaired
regulation by CD4(+)CD25(+)FOXP3(+) regulatory T cells in human
autoimmune diseases. Nat Rev Immunol. 10:849–859. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mukai S, Ogawa Y, Urano F, Kudo-Saito C,
Kawakami Y and Tsubota K: Novel Treatment of Chronic
Graft-Versus-Host Disease in Mice Using the ER Stress Reducer
4-Phenylbutyric Acid. Sci Rep. 7(41939)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zeng M, Sang W, Chen S, Chen R, Zhang H,
Xue F, Li Z, Liu Y, Gong Y, Zhang H, et al: 4-PBA inhibits
LPS-induced inflammation through regulating ER stress and autophagy
in acute lung injury models. Toxicol Lett. 271:26–37.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Mohammed-Ali Z, Lu C, Marway MK, Carlisle
RE, Ask K, Lukic D, Krepinsky JC and Dickhout JG: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress inhibition attenuates hypertensive chronic kidney
disease through reduction in proteinuria. Sci Rep.
7(41572)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zheng P, Lin Y, Wang F, Luo R, Zhang T, Hu
S, Feng P, Liang X, Li C and Wang W: 4-PBA improves lithium-induced
nephrogenic diabetes insipidus by attenuating ER stress. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 311:F763–F776. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Braakman I and Hebert DN: Protein folding
in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
5(a013201)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Fagone P and Jackowski S: Membrane
phospholipid synthesis and endoplasmic reticulum function. J Lipid
Res. 50 (Suppl):S311–S316. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Clapham DE: Calcium signaling. Cell.
131:1047–1058. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bhandary B, Marahatta A, Kim HR and Chae
HJ: An involvement of oxidative stress in endoplasmic reticulum
stress and its associated diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 14:434–456.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lee AS: The ER chaperone and signaling
regulator GRP78/BiP as a monitor of endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Methods. 35:373–381. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lee WS, Sung MS, Lee EG, Yoo HG, Cheon YH,
Chae HJ and Yoo WH: A pathogenic role for ER stress-induced
autophagy and ER chaperone GRP78/BiP in T lymphocyte systemic lupus
erythematosus. J Leukoc Biol. 97:425–433. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ozcan U, Yilmaz E, Ozcan L, Furuhashi M,
Vaillancourt E, Smith RO, Görgün CZ and Hotamisligil GS: Chemical
chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a
mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science. 313:1137–1140.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kawasaki N, Asada R, Saito A, Kanemoto S
and Imaizumi K: Obesity-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress causes
chronic inflammation in adipose tissue. Sci Rep.
2(799)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yokogawa M, Takaishi M, Nakajima K,
Kamijima R, Fujimoto C, Kataoka S, Terada Y and Sano S:
Epicutaneous application of toll-like receptor 7 agonists leads to
systemic autoimmunity in wild-type mice: A new model of systemic
lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol. 66:694–706.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hasham MG, Baxan N, Stuckey DJ, Branca J,
Perkins B, Dent O, Duffy T, Hameed TS, Stella SE, Bellahcene M, et
al: Systemic autoimmunity induced by the TLR7/8 agonist Resiquimod
causes myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy in a new mouse model
of autoimmune heart disease. Dis Model Mech. 10:259–270.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yan JJ, Lee JG, Jang JY, Koo TY, Ahn C and
Yang J: IL-2/anti-IL-2 complexes ameliorate lupus nephritis by
expansion of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+
regulatory T cells. Kidney Int. 91:603–615. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lee YA, Kim HR, Lee JS, Jung HW, Kim HY,
Lee GM, Lee J, Sim JH, Oh SJ, Chung DH, et al: CD4+
FOXP3+ Regulatory T Cells Exhibit Impaired Ability to
Suppress Effector T Cell Proliferation in Patients with Turner
Syndrome. PLoS One. 10(e0144549)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yu F, Haas M, Glassock R and Zhao MH:
Redefining lupus nephritis: Clinical implications of
pathophysiologic subtypes. Nat Rev Nephrol. 13:483–495.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sakaguchi S: Naturally arising
CD4+ regulatory t cells for immunologic self-tolerance
and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol.
22:531–562. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Masteller EL, Tang Q and Bluestone JA:
Antigen-specific regulatory T cells - ex vivo expansion and
therapeutic potential. Semin Immunol. 18:103–110. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hasegawa H, Inoue A, Muraoka M, Yamanouchi
J, Miyazaki T and Yasukawa M: Therapy for pneumonitis and
sialadenitis by accumulation of CCR2-expressing
CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in MRL/lpr mice.
Arthritis Res Ther. 9(R15)2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Weigert O, von Spee C, Undeutsch R, Kloke
L, Humrich JY and Riemekasten G: CD4+Foxp3+
regulatory T cells prolong drug-induced disease remission in
(NZBxNZW) F1 lupus mice. Arthritis Res Ther. 15(R35)2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lamarche C and Levings MK: Guiding
regulatory T cells to the allograft. Curr Opin Organ Transplant.
23:106–113. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Ukena SN, Höpting M, Velaga S, Ivanyi P,
Grosse J, Baron U, Ganser A and Franzke A: Isolation strategies of
regulatory T cells for clinical trials: Phenotype, function,
stability, and expansion capacity. Exp Hematol. 39:1152–1160.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Donnelly C, Dykstra B, Mondal N, Huang J,
Kaskow BJ, Griffin R, Sackstein R and Baecher-Allan C: Optimizing
human Treg immunotherapy by Treg subset selection and E-selectin
ligand expression. Sci Rep. 8(420)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kim I, Xu W and Reed JC: Cell death and
endoplasmic reticulum stress: Disease relevance and therapeutic
opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:1013–1030. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|