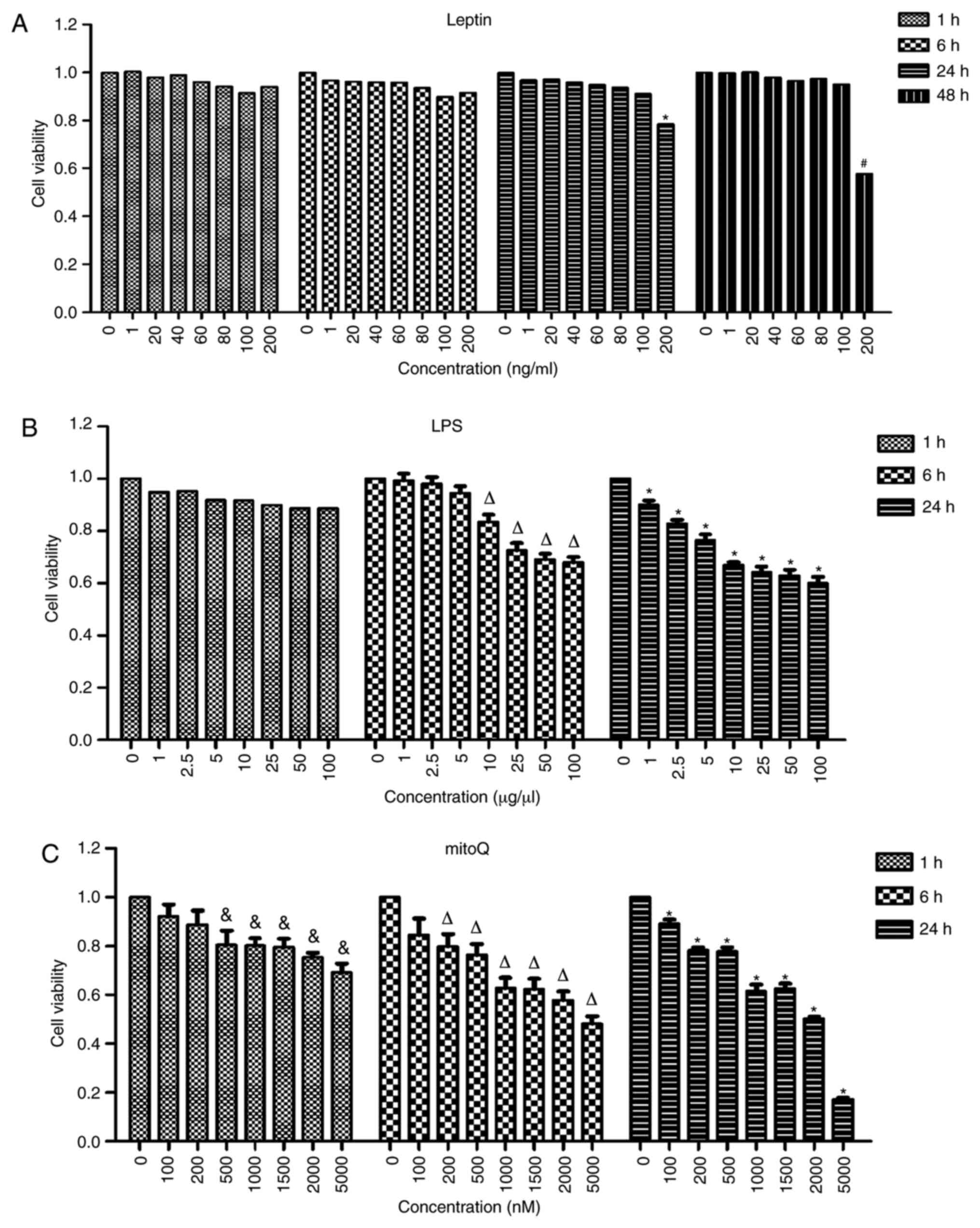
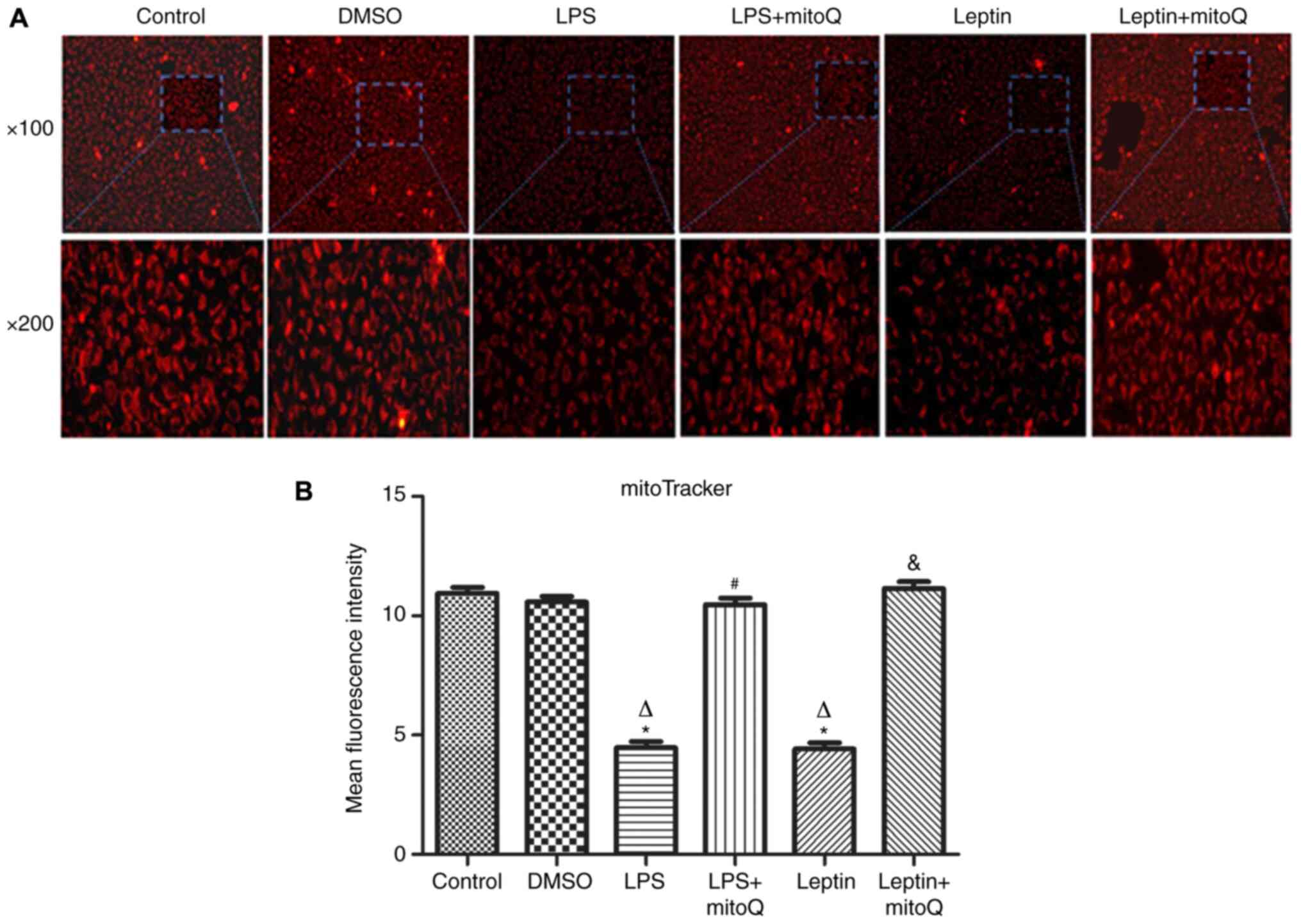
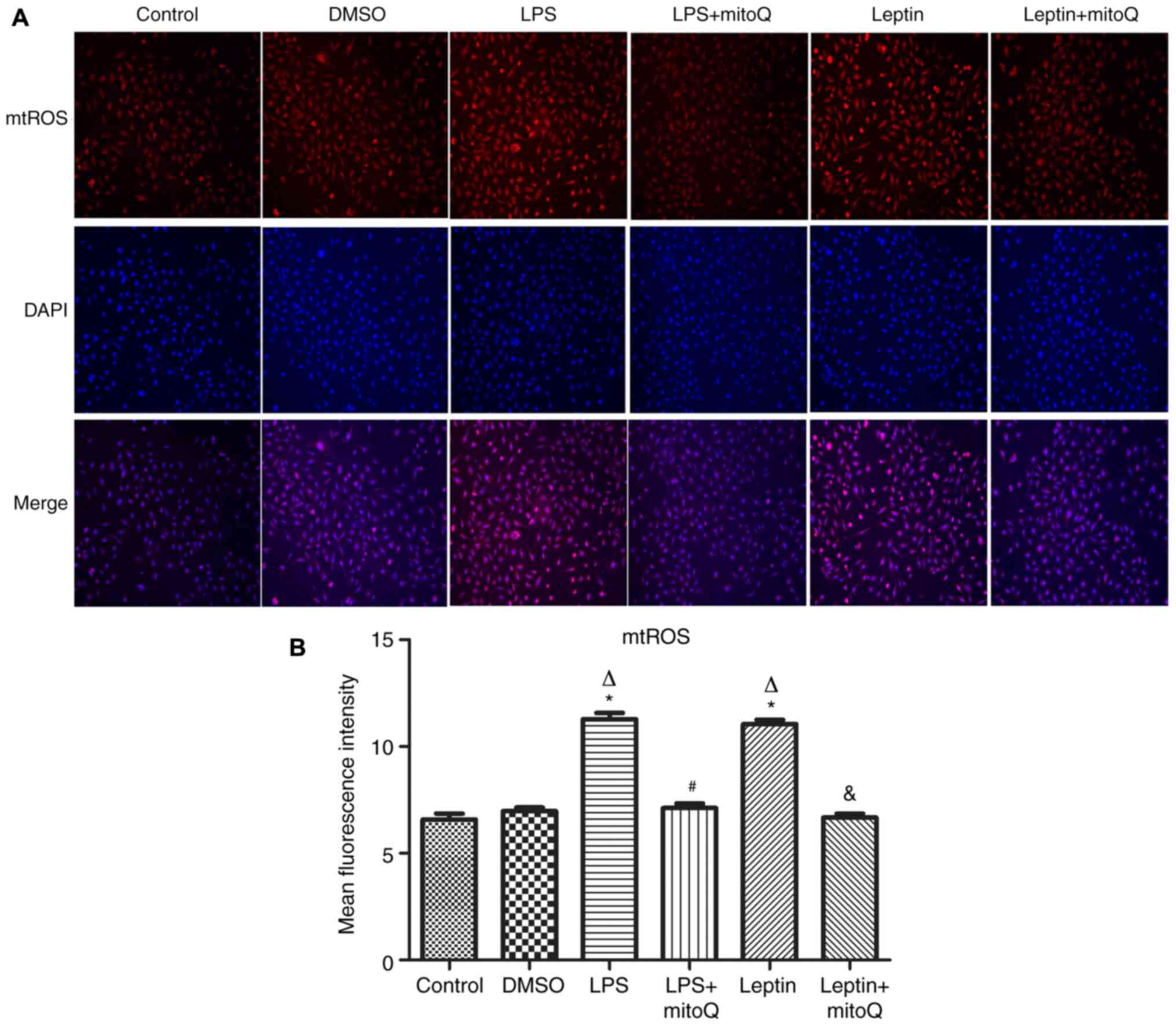
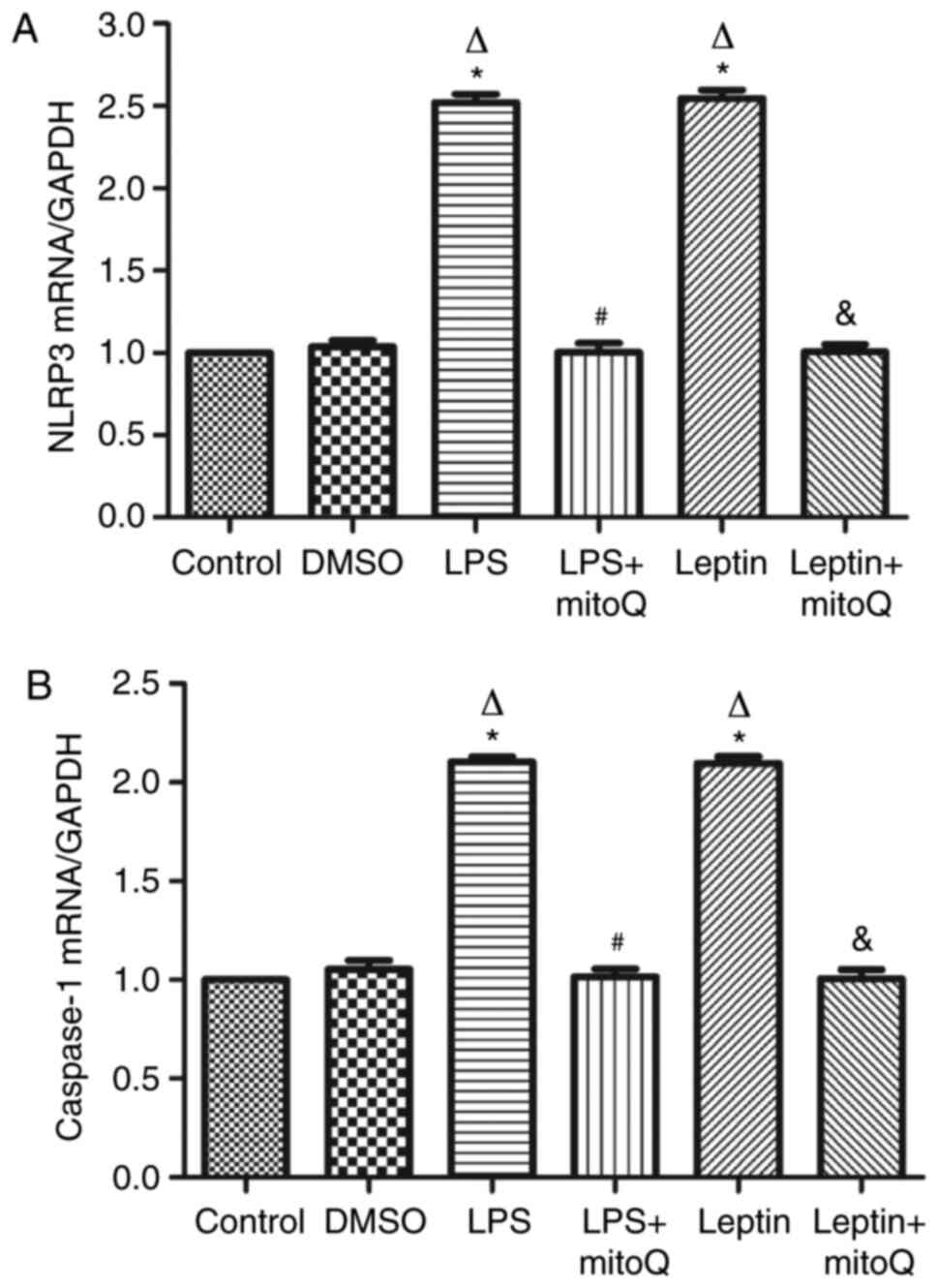
|
1
|
Figueroa-Muñoz JI, Chinn S and Rona RJ:
Association between obesity and asthma in 4-11 year old children in
the UK. Thorax. 56:133–137. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Beuther DA and Sutherland ER: Overweight,
obesity, and incident asthma: A meta-analysis of prospective
epidemiologic studies. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 175:661–666.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Quinto KB, Zuraw BL, Poon KY, Chen W,
Schatz M and Christiansen SC: The association of obesity and asthma
severity and control in children. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
128:964–969. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Papoutsakis C, Priftis KN, Drakouli M,
Prifti S, Konstantaki E, Chondronikola M, Antonogeorgos G and
Matziou V: Childhood overweight/obesity and asthma: Is there a
link? A systematic review of recent epidemiologic evidence. J Acad
Nutr Diet. 113:77–105. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jiang D, Wang L, Bai C and Chen O:
Association between abdominal obesity and asthma: A meta-analysis.
Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 15(16)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Barros R, Moreira P, Padrão P, Teixeira
VH, Carvalho P, Delgado L and Moreira A: Obesity increases the
prevalence and the incidence of asthma and worsens asthma severity.
Clin Nutr. 36:1068–1074. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Rastogi D: Quantifying the contribution of
obesity to incident childhood asthma: It's about time. Pediatrics.
142(e20182979)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Lang JE, Bunnell HT, Hossain MJ, Wysocki
T, Lima JJ, Finkel TH, Bacharier L, Dempsey A, Sarzynski L, Test M
and Forrest CB: Being overweight or obese and the development of
asthma. Pediatrics. 142(e20182119)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rzehak P, Wijga AH, Keil T, Eller E,
Bindslev-Jensen C, Smit HA, Weyler J, Dom S, Sunyer J, Mendez M, et
al: Body mass index trajectory classes and incident asthma in
childhood: Results from 8 European Birth Cohorts-a Global Allergy
and Asthma European Network initiative. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
131:1528–1536. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Mohan A, Grace J, Wang BR and Lugogo N:
The effects of obesity in asthma. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep.
19(49)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Muc M, Mota-Pinto A and Padez C:
Association between obesity and asthma-epidemiology,
pathophysiology and clinical profile. Nutr Res Rev. 29:194–201.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Trayhurn P, Bing C and Wood IS: Adipose
tissue and adipokines-energy regulation from the human perspective.
J Nutr. 136 (Suppl 7):S1935–S1939. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
López-Jaramillo P, Gómez-Arbeláez D,
López-López J, López-López C, Martínez-Ortega J, Gómez-Rodríguez A
and Triana-Cubillos S: The role of leptin/adiponectin ratio in
metabolic syndrome and diabetes. Horm Mol Biol Clin Investig.
18:37–45. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Balistreri CR, Caruso C and Candore G: The
role of adipose tissue and adipokines in obesity-related
inflammatory diseases. Mediators Inflamm.
2010(802078)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang M, Cheng H, Zhao X, Hou D, Yan Y,
Cianflone K, Li M and Mi J: Leptin and leptin-to-adiponectin ratio
predict adiposity gain in nonobese children over a six-year period.
Child Obes. 13:213–221. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li Z, Leynaert B, Dumas O, Diaz Gil O,
Garcia-Aymerich J, Fito Colomer M, Le Moual N, Pison C, Romieu I,
Siroux V, et al: Role of leptin in the association between body
adiposity and persistent asthma: A longitudinal study. Obesity
(Silver Spring). 27:894–898. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Holguin F, Rojas M, Brown LA and
Fitzpatrick AM: Airway and plasma leptin and adiponectin in lean
and obese asthmatics and controls. J Asthma. 48:217–223.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Bodini A, Tenero L, Sandri M, Maffeis C,
Piazza M, Zanoni L, Peroni D, Boner A and Piacentini G: Serum and
exhaled breath condensate leptin levels in asthmatic and obesity
children: A pilot study. J Breath Res. 11(46005)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Davis BK, Wen H and Ting JP: The
inflammasome NLRs in immunity, inflammation, and associated
diseases. Annu Rev Immunol. 29:707–735. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Birrell MA and Eltom S: The role of the
NLRP3 inflammasome in the pathogenesis of airway disease. Pharmacol
Ther. 130:364–370. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Theofani E, Semitekolou M, Morianos I,
Samitas K and Xanthou G: Targeting NLRP3 inflammasome activation in
severe asthma. J Clin Med. 8(1615)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kim HY, Lee HJ, Chang YJ, Pichavant M,
Shore SA, Fitzgerald KA, Iwakura Y, Israel E, Bolger K, Faul J, et
al: Interleukin-17-producing innate lymphoid cells and the NLRP3
inflammasome facilitate obesity-associated airway hyperreactivity.
Nat Med. 20:54–61. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xu M, Wang L, Wang M, Wang H, Zhang H,
Chen Y, Wang X, Gong J, Zhang JJ, Adcock IM, et al: Mitochondrial
ROS and NLRP3 inflammasome in acute ozone-induced murine model of
airway inflammation and bronchial hyperresponsiveness. Free Radic
Res. 53:780–790. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Fu S, Liu L, Han L and Yu Y: Leptin
promotes IL18 secretion by activating the NLRP3 inflammasome in RAW
264.7 cells. Mol Med Rep. 16:9770–9776. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Raut PK, Kim SH, Choi DY, Jeong GS and
Park PH: Growth of breast cancer cells by leptin is mediated via
activation of the inflammasome: Critical roles of estrogen receptor
signaling and reactive oxygen species production. Biochem
Pharmacol. 161:73–88. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Löllmann B, Grüninger S, Stricker-Krongrad
A and Chiesi M: Detection and quantification of the leptin receptor
splice variants Ob-Ra, b, and, e in different mouse tissues.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 238:648–652. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Murphy MP: Understanding and preventing
mitochondrial oxidative damage. Biochem Soc Trans. 44:1219–1226.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Adlam VJ, Harrison JC, Porteous CM, James
AM, Smith RA, Murphy MP and Sammut IA: Targeting an antioxidant to
mitochondria decreases cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury. FASEB
J. 19:1088–1095. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Graham D, Huynh NN, Hamilton CA, Beattie
E, Smith RA, Cochemé HM, Murphy MP and Dominiczak AF:
Mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ10 improves endothelial
function and attenuates cardiac hypertrophy. Hypertension.
54:322–328. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lowes DA, Thottakam BM, Webster NR, Murphy
MP and Galley HF: The mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ
protects against organ damage in a lipopolysaccharide-peptidoglycan
model of sepsis. Free Radic Biol Med. 45:1559–1565. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Mercer JR, Yu E, Figg N, Cheng KK, Prime
TA, Griffin JL, Masoodi M, Vidal-Puig A, Murphy MP and Bennett MR:
The mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ decreases features of
the metabolic syndrome in ATM+/-/ApoE-/-
mice. Free Radic Biol Med. 52:841–849. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Dashdorj A, Jyothi KR, Lim S, Jo A, Nguyen
MN, Ha J, Yoon KS, Kim HJ, Park JH, Murphy MP and Kim SS:
Mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ ameliorates experimental
mouse colitis by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated
inflammatory cytokines. BMC Med. 11(178)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Han Y, Xu X, Tang C, Gao P, Chen X, Xiong
X, Yang M, Yang S, Zhu X, Yuan S, et al: Reactive oxygen species
promote tubular injury in diabetic nephropathy: The role of the
mitochondrial ros-txnip-nlrp3 biological axis. Redox Biol.
16:32–46. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang Y, Proenca R, Maffei M, Barone M,
Leopold L and Friedman JM: Positional cloning of the mouse obese
gene and its human homologue. Nature. 372:425–432. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Maffei M, Halaas J, Ravussin E, Pratley
RE, Lee GH, Zhang Y, Fei H, Kim S, Lallone R, Ranganathan S, et al:
Leptin levels in human and rodent: Measurement of plasma leptin and
ob RNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat Med. 1:1155–1161.
1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sood A, Seagrave JC, Herbert G, Harkins M,
Qualls C and Schuyler M: Asthma is associated with lower
adiponectin concentrations in sputum than controls. Am Thorac Soc
Int Confer. 185(A6502)2012.
|
|
38
|
Bruno A, Chanez P, Chiappara G, Siena L,
Giammanco S, Gjomarkaj M, Bonsignore G, Bousquet J and Vignola AM:
Does leptin play a cytokine-like role within the airways of COPD
patients? Eur Respir J. 26:398–405. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Chong L, Liu L, Zhu L, Li H, Shao Y, Zhang
H and Yu G: Expression levels of predominant adipokines and
activations of STAT3, STAT6 in an experimental mice model of obese
asthma. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 18:62–71. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Xiao Y, Xu W and Su W: NLRP3 inflammasome:
A likely target for the treatment of allergic diseases. Clin Exp
Allergy. 48:1080–1091. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Kim RY, Pinkerton JW, Essilfie AT,
Robertson AAB, Baines KJ, Brown AC, Mayall JR, Ali MK, Starkey MR,
Hansbro NG, et al: Role for NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated,
IL-1β-dependent responses in severe, steroid-resistant asthma. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 196:283–297. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kim SR, Kim DI, Kim SH, Lee H, Lee KS, Cho
SH and Lee YC: NLRP3 inflammasome activation by mitochondrial ROS
in bronchial epithelial cells is required for allergic
inflammation. Cell Death Dis. 5(e1498)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Snow BJ, Rolfe FL, Lockhart MM, Frampton
CM, O'Sullivan JD, Fung V, Smith RA, Murphy MP and Taylor KM:
Protect Study Group. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study to
assess the mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ as a
disease-modifying therapy in Parkinson's disease. Move Disord.
25:1670–1674. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Gane EJ, Weilert F, Orr DW, Keogh GF,
Gibson M, Lockhart MM, Frampton CM, Taylor KM, Smith RA and Murphy
MP: The mitochondria-targeted anti-oxidant mitoquinone decreases
liver damage in a phase II study of hepatitis C patients. Liver
Int. 30:1019–1026. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wiegman CH, Michaeloudes C, Haji G, Narang
P, Clarke CJ, Russell KE, Bao W, Pavlidis S, Barnes PJ, Kanerva J,
et al: Oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction drives
inflammation and airway smooth muscle remodeling in patients with
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
136:769–780. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|