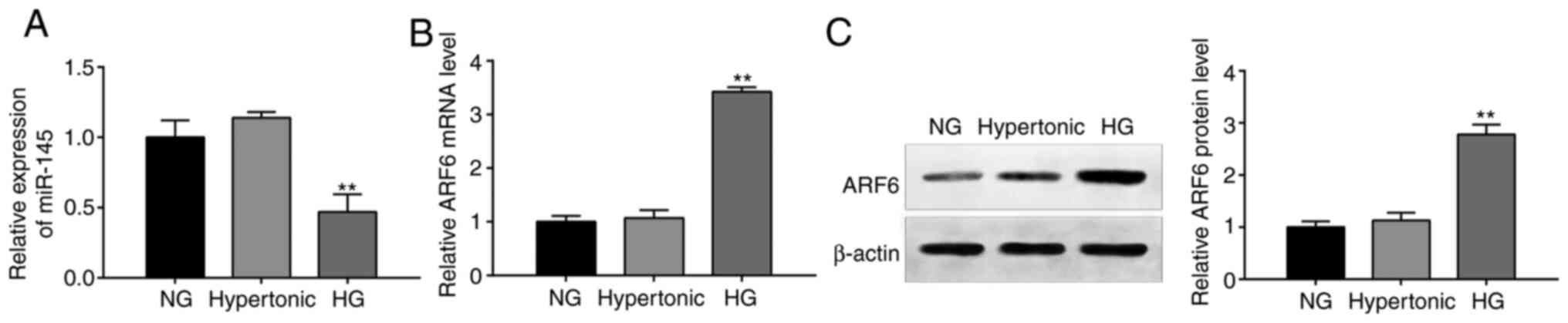
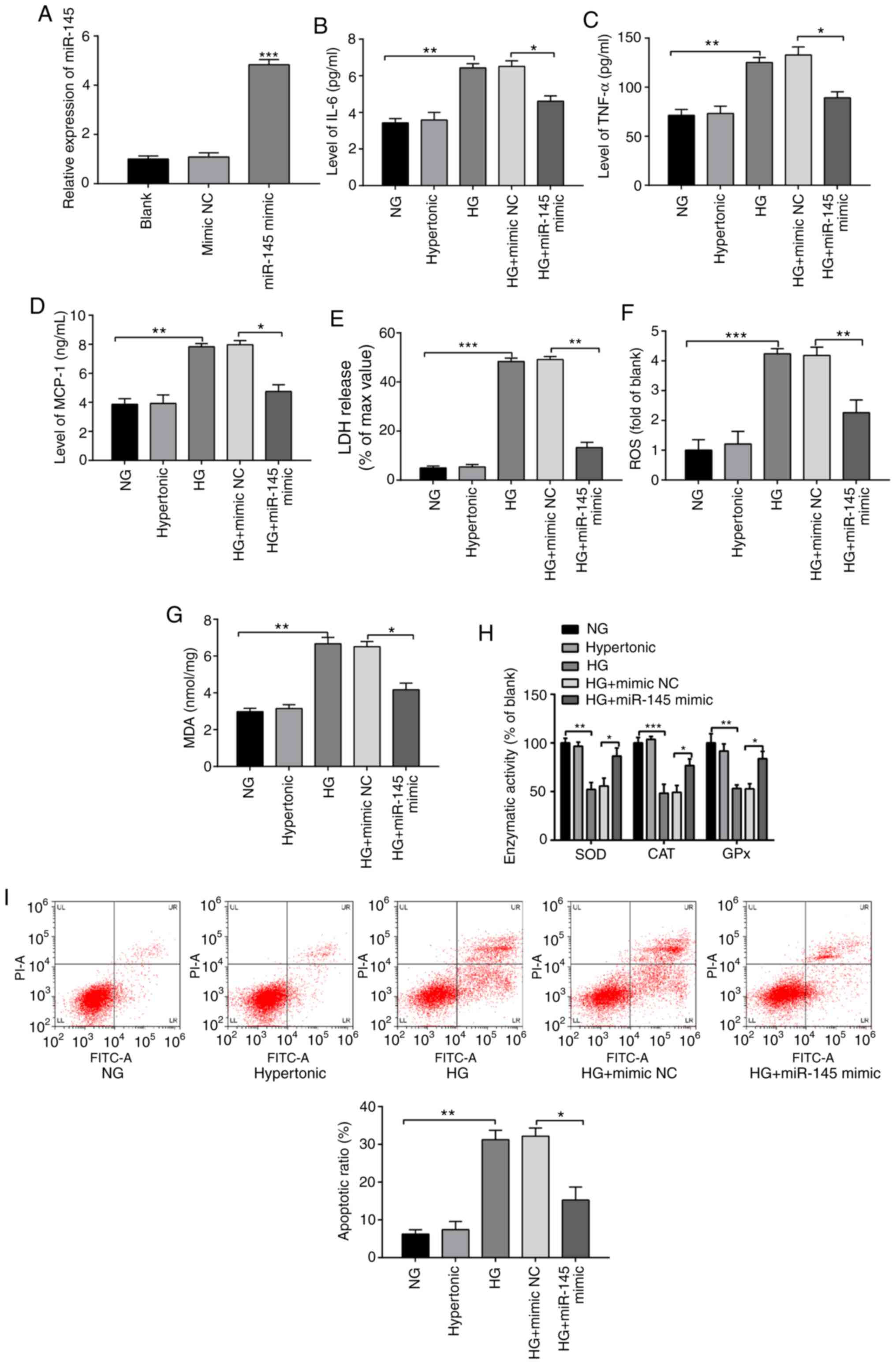
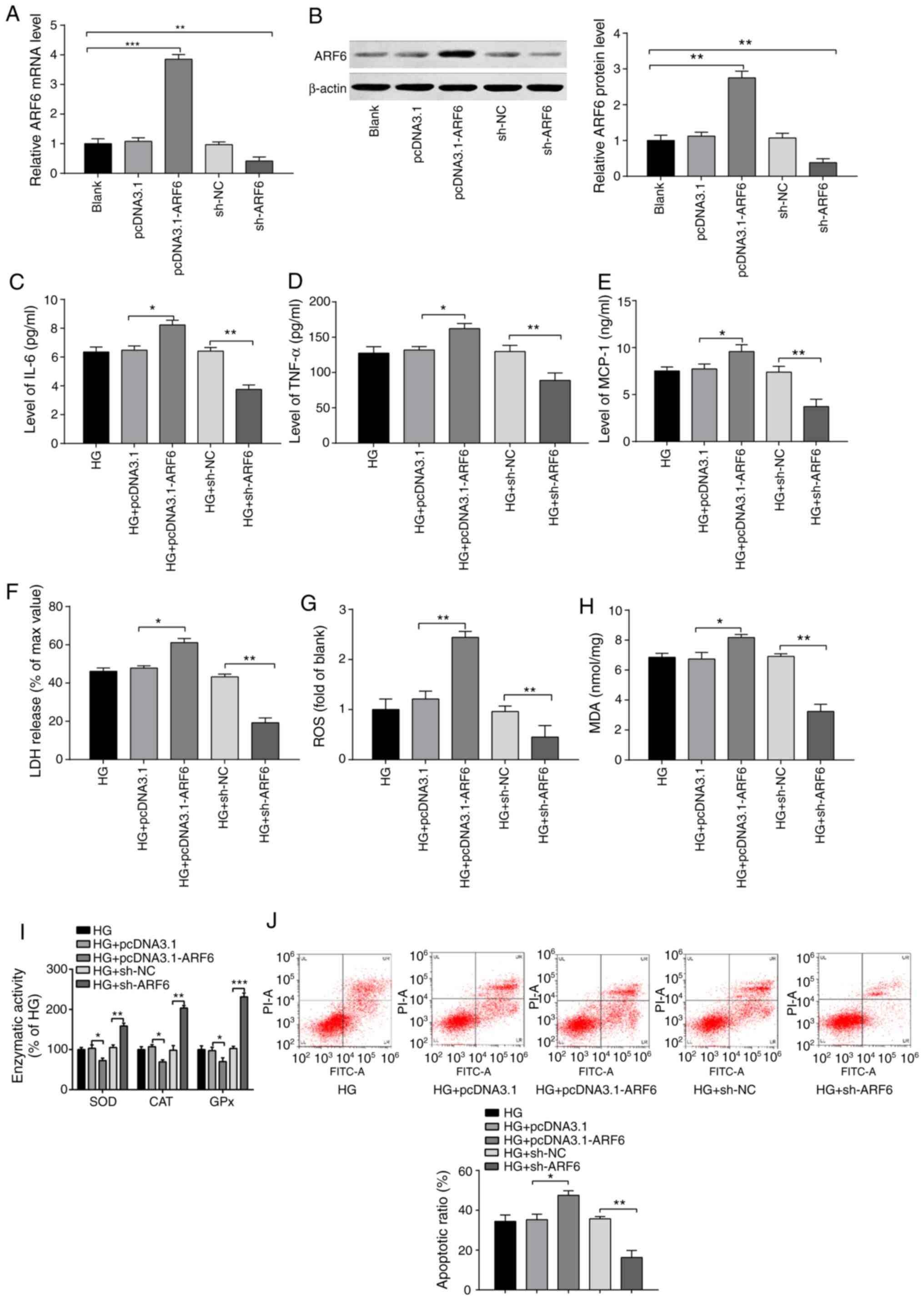
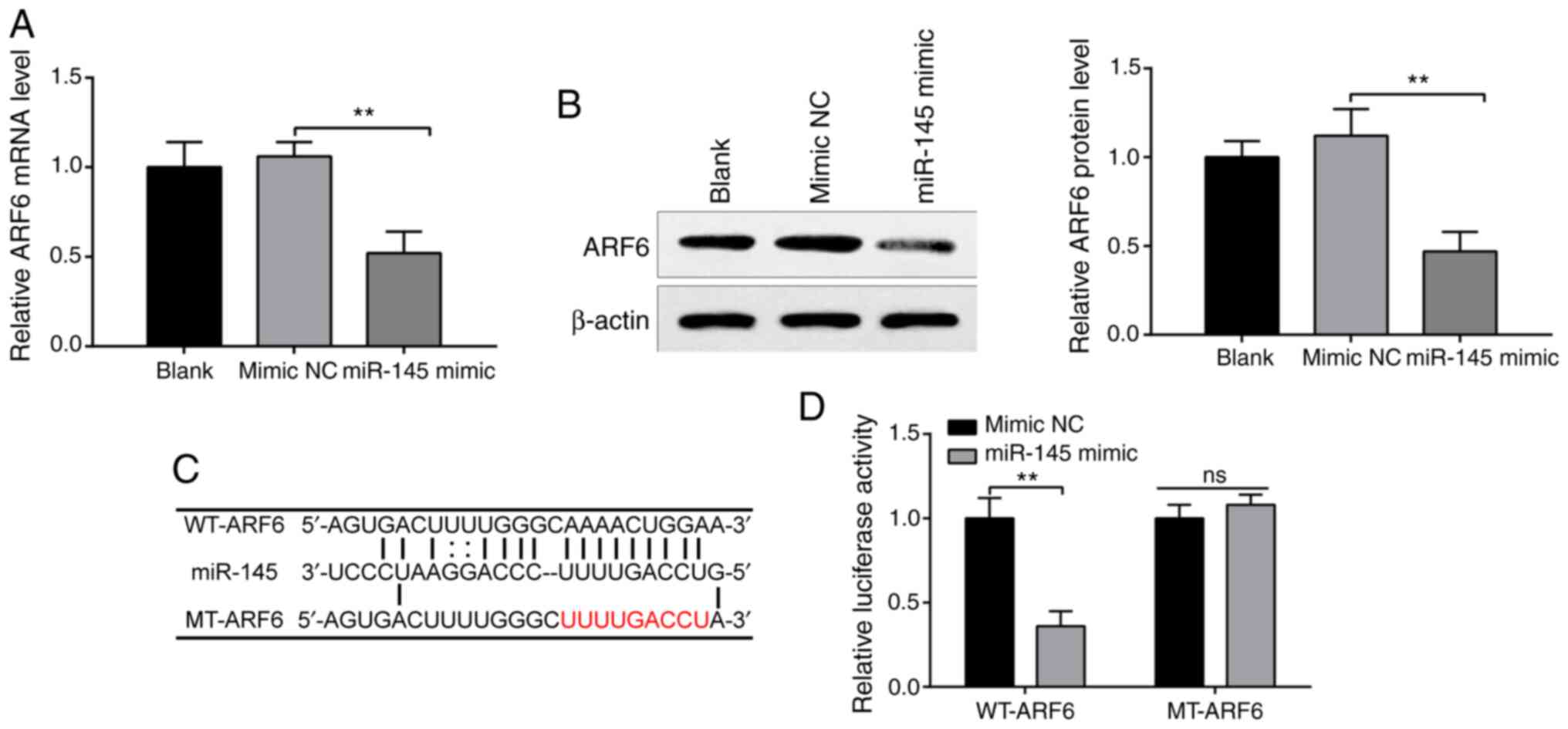
|
1
|
Newman JD, Vani AK, Aleman JO, Weintraub
HS, Berger JS and Schwartzbard AZ: The changing landscape of
diabetes therapy for cardiovascular risk reduction: JACC
state-of-the-art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 72:1856–1869.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jia G, Whaley-Connell A and Sowers JR:
Diabetic cardiomyopathy: A hyperglycaemia- and
insulin-resistance-induced heart disease. Diabetologia. 61:21–28.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bugger H and Abel ED: Molecular mechanisms
of diabetic cardiomyopathy. Diabetologia. 57:660–671.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Karam BS, Chavez-Moreno A, Koh W, Akar JG
and Akar FG: Oxidative stress and inflammation as central mediators
of atrial fibrillation in obesity and diabetes. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 16(120)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Newsholme P, Cruzat VF, Keane KN, Carlessi
R and de Bittencourt PI Jr: Molecular mechanisms of ROS production
and oxidative stress in diabetes. Biochem J. 473:4527–4550.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Qadir MMF, Klein D, Alvarez-Cubela S,
Dominguez-Bendala J and Pastori RL: The role of MicroRNAs in
diabetes-related oxidative stress. Int J Mol Sci.
20(5423)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kyrychenko S, Kyrychenko V, Badr MA, Ikeda
Y, Sadoshima J and Shirokova N: Pivotal role of miR-448 in the
development of ROS-induced cardiomyopathy. Cardiovasc Res.
108:324–334. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tang Q, Li MY, Su YF, Fu J, Zou ZY, Wang Y
and Li SN: Absence of miR-223-3p ameliorates hypoxia-induced injury
through repressing cardiomyocyte apoptosis and oxidative stress by
targeting KLF15. Eur J Pharmacol. 841:67–74. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Su Q, Yao J and Sheng C: Geniposide
attenuates LPS-induced injury via up-regulation of miR-145 in H9c2
cells. Inflammation. 41:1229–1237. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li L, Liu M, He L, Wang S and Cui S:
Baicalin relieves TNF-α-evoked injury in human aortic endothelial
cells by up-regulation of miR-145. Phytother Res. 34:836–845.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
He M, Wu N, Leong MC, Zhang W, Ye Z, Li R,
Huang J, Zhang Z, Li L, Yao X, et al: miR-145 improves metabolic
inflammatory disease through multiple pathways. J Mol Cell Biol.
12:152–162. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yuan M, Zhang L, You F, Zhou J, Ma Y, Yang
F and Tao L: MiR-145-5p regulates hypoxia-induced inflammatory
response and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by targeting CD40. Mol
Cell Biochem. 431:123–131. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hui Y and Yin Y: MicroRNA-145 attenuates
high glucose-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in retinal
endothelial cells through regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling. Life
Sci. 207:212–218. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Padival AK, Hawkins KS and Huang C: High
glucose-induced membrane translocation of PKC betaI is associated
with Arf6 in glomerular mesangial cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
258:129–135. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Fang Z, Miao Y, Ding X, Deng H, Liu S,
Wang F, Zhou R, Watson C, Fu C, Hu Q, et al: Proteomic
identification and functional characterization of a novel ARF6
GTPase-activating protein, ACAP4. Mol Cell Proteomics. 5:1437–1449.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Karnik R, Ludlow MJ, Abuarab N, Smith AJ,
Hardy ME, Elliott DJ and Sivaprasadarao A: Endocytosis of HERG is
clathrin-independent and involves arf6. PLoS One.
8(e85630)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Li R, Shen Q, Wu N, He M, Liu N, Huang J,
Lu B, Yao Q, Yang Y and Hu R: MiR-145 improves macrophage-mediated
inflammation through targeting Arf6. Endocrine. 60:73–82.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gilca GE, Stefanescu G, Badulescu O,
Tanase DM, Bararu I and Ciocoiu M: Diabetic cardiomyopathy: Current
approach and potential diagnostic and therapeutic targets. J
Diabetes Res. 2017(1310265)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Li H, Fan J, Zhao Y, Zhang X, Dai B, Zhan
J, Yin Z, Nie X, Fu XD, Chen C and Wang DW: Nuclear miR-320
mediates diabetes-induced cardiac dysfunction by activating
transcription of fatty acid metabolic genes to cause lipotoxicity
in the heart. Circ Res. 125:1106–1120. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang Y, Zhao RZ, Chen PK, Xu GX, Liu ZJ,
Long XP, Qiu ZM and Shi B: Impact and related mechanism on the
improvement of hyperglycemia-induced pyroptosis in H9c2 cells by
mircoRNA-214. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 47:820–828.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Yang X, Li X, Lin Q and Xu Q:
Up-regulation of microRNA-203 inhibits myocardial fibrosis and
oxidative stress in mice with diabetic cardiomyopathy through the
inhibition of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway via PIK3CA. Gene.
715(143995)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Zhong F, Xu J, Yang X, Zhang Q, Gao Z,
Deng Y, Zhang L and Yu C: miR-145 eliminates
lipopolysaccharides-induced inflammatory injury in human
fibroblast-like synoviocyte MH7A cells. J Cell Biochem.
119:10059–10066. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Shi J, Jiang K and Li Z: MiR-145
ameliorates neuropathic pain via inhibiting inflammatory responses
and mTOR signaling pathway by targeting Akt3 in a rat model.
Neurosci Res. 134:10–17. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lin H, You B, Lin X, Wang X, Zhou D, Chen
Z, Chen Y and Wang R: Silencing of long non-coding RNA Sox2ot
inhibits oxidative stress and inflammation of vascular smooth
muscle cells in abdominal aortic aneurysm via microRNA-145-mediated
Egr1 inhibition. Aging (Albany NY). 12:12684–12702. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Abdul-Salam VB, Russomanno G, Chien-Nien
C, Mahomed AS, Yates LA, Wilkins MR, Zhao L, Gierula M, Dubois O,
Schaeper U, et al: CLIC4/Arf6 pathway. Circ Res. 124:52–65.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Onodera Y, Nam JM, Horikawa M, Shirato H
and Sabe H: Arf6-driven cell invasion is intrinsically linked to
TRAK1-mediated mitochondrial anterograde trafficking to avoid
oxidative catastrophe. Nat Commun. 9(2682)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Jayaram B and Kowluru A: Phagocytic NADPH
oxidase links ARNO-Arf6 signaling pathway in glucose-stimulated
insulin secretion from the pancreatic β-cell. Cell Physiol Biochem.
30:1351–1362. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Li C, Zhang J, Xue M, Li X, Han F, Liu X,
Xu L, Lu Y, Cheng Y, Li T, et al: SGLT2 inhibition with
empagliflozin attenuates myocardial oxidative stress and fibrosis
in diabetic mice heart. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 18(15)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ke Y, Wang C, Zhang J, Zhong X, Wang R,
Zeng X and Ba X: The role of PARPs in inflammation-and
metabolic-related diseases: Molecular mechanisms and beyond. Cells.
8(1047)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Fehr AR, Singh SA, Kerr CM, Mukai S,
Higashi H and Aikawa M: The impact of PARPs and ADP-ribosylation on
inflammation and host-pathogen interactions. Genes Dev. 34:341–359.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Dani N, Barbosa AJ, Del Rio A and Di
Girolamo M: ADP-ribosylated proteins as old and new drug targets
for anticancer therapy: The example of ARF6. Curr Pharm Des.
19:624–633. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ren C, Yuan Q, Jian X, Randazzo PA, Tang W
and Wu D: Small GTPase ARF6 is a coincidence-detection code for
RPH3A polarization in neutrophil polarization. J Immunol.
204:1012–1021. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Eades G, Wolfson B, Zhang Y, Li Q, Yao Y
and Zhou Q: lincRNA-RoR and miR-145 regulate invasion in
triple-negative breast cancer via targeting ARF6. Mol Cancer Res.
13:330–338. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hsu WC, Li WM, Lee YC, Huang AM, Chang LL,
Lin HH, Wu WJ, Li CC, Liang PI and Ke HL: MicroRNA-145 suppresses
cell migration and invasion in upper tract urothelial carcinoma by
targeting ARF6. FASEB J. 34:5975–5992. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|