|
1
|
Acter T, Uddin N, Das J, Akhter A,
Choudhury TR and Kim S: Evolution of severe acute respiratory
syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) as coronavirus disease 2019
(COVID-19) pandemic: A global health emergency. Sci Total Environ.
730(138996)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wang C, Horby PW, Hayden FG and Gao GF: A
novel coronavirus outbreak of global health concern. Lancet.
395:470–473. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Yang J, Zheng Y, Gou X, Pu K, Chen Z, Guo
Q, Ji R, Wang H, Wang Y and Zhou Y: Prevalence of comorbidities and
its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis. 94:91–95.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Burki T: COVID-19 in Latin America. Lancet
Infect Dis. 20:547–548. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Shereen MA, Khan S, Kazmi A, Bashir N and
Siddique R: COVID-19 infection: Origin, transmission, and
characteristics of human coronaviruses. J Adv Res. 24:91–98.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhang X, Chen X, Chen L, Deng C, Zou X,
Liu W, Yu H, Chen B and Sun X: The evidence of SARS-CoV-2 infection
on ocular surface. Ocul Surf. 18:360–362. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
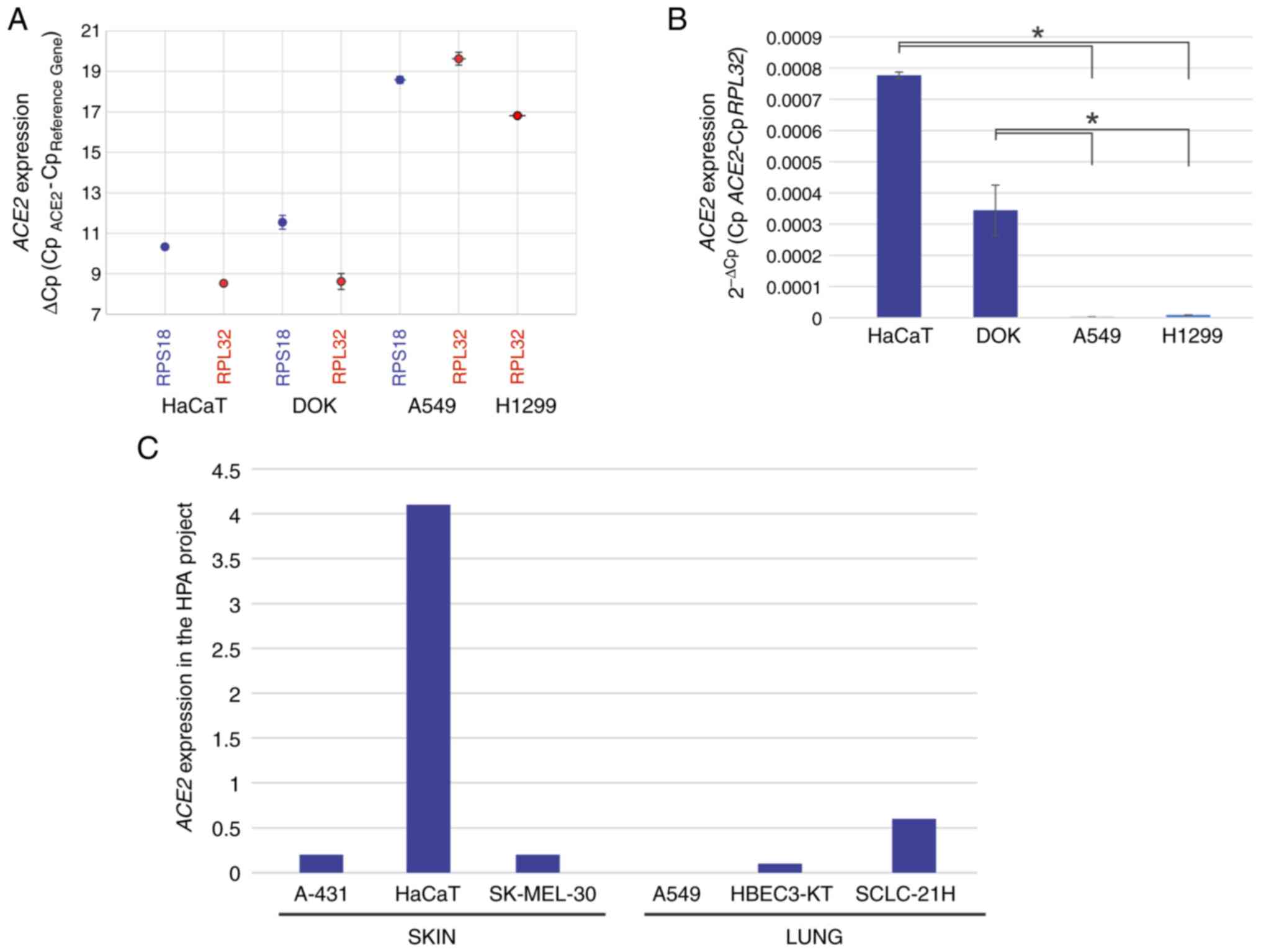
|
|
7
|
Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He
JX, Liu L, Shan H, Lei CL, Hui DS, et al: Clinical characteristics
of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 382:1708–1720.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Letko M, Marzi A and Munster V: Functional
assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and
other lineage B betacoronaviruses. Nat Microbiol. 5:562–569.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Song W, Gui M, Wang X and Xiang Y: Cryo-EM
structure of the SARS coronavirus spike glycoprotein in complex
with its host cell receptor ACE2. PLoS Pathog.
14(e1007236)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li F, Li W, Farzan M and Harrison SC:
Structure of SARS coronavirus spike receptor-binding domain
complexed with receptor. Science. 309:1864–1868. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Anguiano L, Riera M, Pascual J and Soler
MJ: Circulating ACE2 in cardiovascular and kidney diseases. Curr
Med Chem. 24:3231–3241. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Pacheco JM, Henry TM, O'Donnell VK,
Gregory JB and Mason PW: Role of nonstructural proteins 3A and 3B
in host range and pathogenicity of foot-and-mouth disease virus. J
Virol. 77:13017–13027. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Lu W, Zheng BJ, Xu K, Schwarz W, Du L,
Wong CK, Chen J, Duan S, Deubel V and Sun B: Severe acute
respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus 3a protein forms an ion
channel and modulates virus release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:12540–12545. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chan CM, Tsoi H, Chan WM, Zhai S, Wong CO,
Yao X, Chan WY, Tsui SK and Chan HY: The ion channel activity of
the SARS-coronavirus 3a protein is linked to its pro-apoptotic
function. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 41:2232–2239. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wang X, Zhang Z and Wu SC: Health benefits
of Silybum marianum: Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and
applications. J Agric Food Chem. 68:11644–11664. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Saller R, Meier R and Brignoli R: The use
of silymarin in the treatment of liver diseases. Drugs.
61:2035–2063. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bosisio E, Benelli C and Pirola O: Effect
of the flavanolignans of Silybum marianum L. on lipid peroxidation
in rat liver microsomes and freshly isolated hepatocytes. Pharmacol
Res. 25:147–154. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Carini R, Comoglio A, Albano E and Poli G:
Lipid peroxidation and irreversible damage in the rat hepatocyte
model. Protection by the silybin-phospholipid complex IdB 1016.
Biochem Pharmacol. 43:2111–2115. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mira L, Silva M and Manso CF: Scavenging
of reactive oxygen species by silibinin dihemisuccinate. Biochem
Pharmacol. 48:753–759. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Lani R, Hassandarvish P, Chiam CW,
Moghaddam E, Chu JJ, Rausalu K, Merits A, Higgs S, Vanlandingham D,
Abu Bakar S and Zandi K: Antiviral activity of silymarin against
chikungunya virus. Sci Rep. 5(11421)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhao F, Shi D, Li T, Li L and Zhao M:
Silymarin attenuates paraquat-induced lung injury via Nrf2-mediated
pathway in vivo and in vitro. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
42:988–998. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Anderson ME and Meister A: Dynamic state
of glutathione in blood plasma. J Biol Chem. 255:9530–9533.
1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sies H and Graf P: Hepatic thiol and
glutathione efflux under the influence of vasopressin,
phenylephrine and adrenaline. Biochem J. 226:545–549.
1985.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kozak EM and Tate SS:
Glutathione-degrading enzymes of microvillus membranes. J Biol
Chem. 257:6322–6327. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kloek J, Van Ark I, De Clerck F, Bloksma
N, Nijkamp FP and Folkerts G: Modulation of airway
hyperresponsiveness by thiols in a murine in vivo model of allergic
asthma. Inflamm Res. 52:126–131. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lee YC, Lee KS, Park SJ, Park HS, Lim JS,
Park KH, Im MJ, Choi IW, Lee HK and Kim UH: Blockade of airway
hyperresponsiveness and inflammation in a murine model of asthma by
a prodrug of cysteine, L-2-oxothiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid. FASEB
J. 18:1917–1919. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hodge S, Matthews G, Mukaro V, Ahern J,
Shivam A, Hodge G, Holmes M, Jersmann H and Reynolds PN: Cigarette
smoke-induced changes to alveolar macrophage phenotype and function
are improved by treatment with procysteine. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 44:673–681. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Sido B, Braunstein J, Breitkreutz R,
Herfarth C and Meuer SC: Thiol-mediated redox regulation of
intestinal lamina propria T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 192:907–912.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Hadzic T, Li L, Cheng N, Walsh SA, Spitz
DR and Knudson CM: The role of low molecular weight thiols in T
lymphocyte proliferation and IL-2 secretion. J Immunol.
175:7965–7972. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Oliver JM, Albertini DF and Berlin RD:
Effects of glutathione-oxidizing agents on microtubule assembly and
microtubule-dependent surface properties of human neutrophils. J
Cell Biol. 71:921–932. 1976.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kuppner MC, Scharner A, Milani V, Von
Hesler C, Tschop KE, Heinz O and Issels RD: Ifosfamide impairs the
allostimulatory capacity of human dendritic cells by intracellular
glutathione depletion. Blood. 102:3668–3674. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Peterson JD, Herzenberg LA, Vasquez K and
Waltenbaugh C: Glutathione levels in antigen-presenting cells
modulate Th1 versus Th2 response patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
95:3071–3076. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Short S, Merkel BJ, Caffrey R and McCoy
KL: Defective antigen processing correlates with a low level of
intracellular glutathione. Eur J Immunol. 26:3015–3020.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Murata Y, Ohteki T, Koyasu S and Hamuro J:
IFN-gamma and pro-inflammatory cytokine production by
antigen-presenting cells is dictated by intracellular thiol redox
status regulated by oxygen tension. Eur J Immunol. 32:2866–2873.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Furuya A, Uozaki M, Yamasaki H, Arakawa T,
Arita M and Koyama AH: Antiviral effects of ascorbic and
dehydroascorbic acids in vitro. Int J Mol Med. 22:541–545.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
White LA, Freeman CY, Forrester BD and
Chappell WA: In vitro effect of ascorbic acid on infectivity of
herpesviruses and paramyxoviruses. J Clin Microbiol. 24:527–531.
1986.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Alkhatib A: Antiviral functional foods and
exercise lifestyle prevention of coronavirus. Nutrients.
12(2633)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang J, Saad R, Taylor EW and Rayman MP:
Selenium and selenoproteins in viral infection with potential
relevance to COVID-19. Redox Biol. 37(101715)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hiffler L and Rakotoambinina B: Selenium
and RNA virus interactions: Potential implications for SARS-CoV-2
infection (COVID-19). Front Nutr. 7(164)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Boukamp P, Petrussevska RT, Breitkreutz D,
Hornung J, Markham A and Fusenig NE: Normal keratinization in a
spontaneously immortalized aneuploid human keratinocyte cell line.
J Cell Biol. 106:761–771. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Chang SE, Foster S, Betts D and Marnock
WE: DOK, a cell line established from human dysplastic oral mucosa,
shows a partially transformed non-malignant phenotype. Int J
Cancer. 52:896–902. 1992.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Pfaffl MW: A new mathematical model for
relative quantification in real-time RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res.
29(e45)2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Gordon DE, Jang GM, Bouhaddou M, Xu J,
Obernier K, White KM, O'Meara MJ, Rezelj VV, Guo JZ, Swaney DL, et
al: A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug
repurposing. Nature. 583:459–468. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Katsura H, Sontake V, Tata A, Kobayashi Y,
Edwards CE, Heaton BE, Konkimalla A, Asakura T, Mikami Y, Fritch
EJ, et al: Human lung stem cell-based alveolospheres provide
insights into SARS-CoV-2-mediated interferon responses and
pneumocyte dysfunction. Cell Stem Cell. 27:890–904.e8.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Xu H, Zhong L, Deng J, Peng J, Dan H, Zeng
X, Li T and Chen Q: High expression of ACE2 receptor of 2019-nCoV
on the epithelial cells of oral mucosa. Int J Oral Sci.
12(8)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
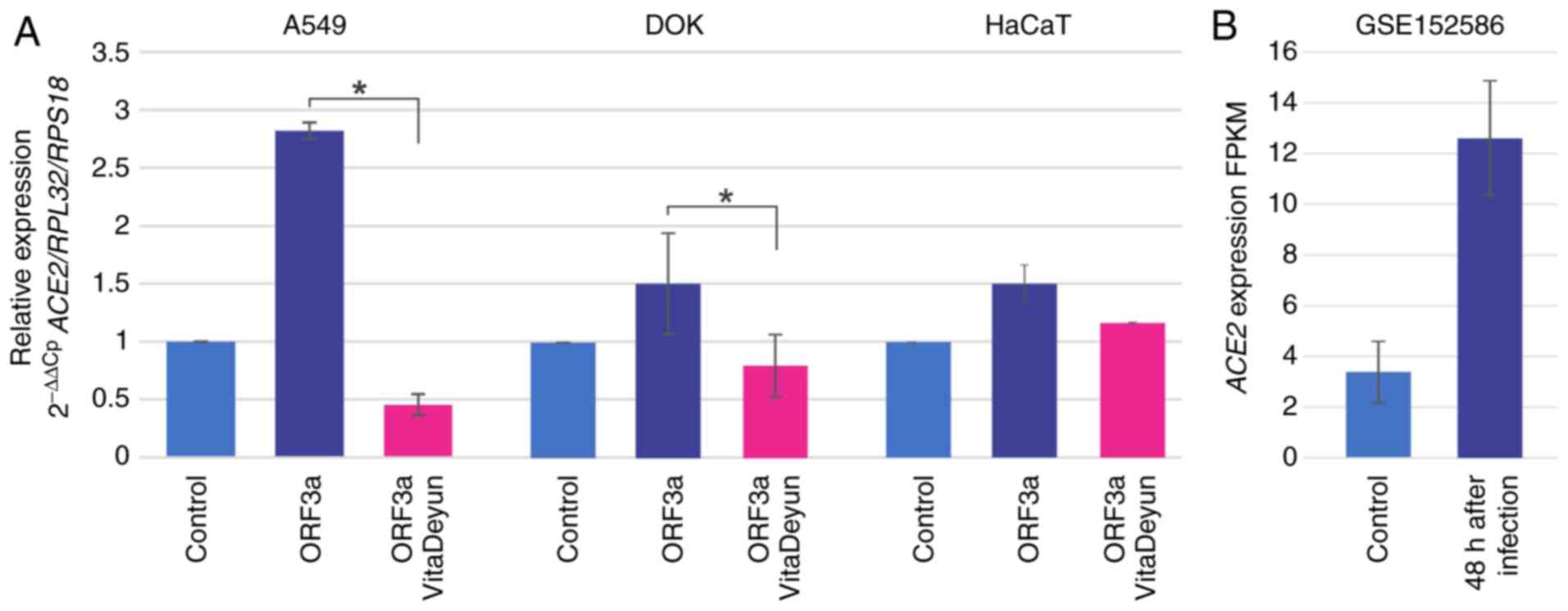
Ren Y, Shu T, Wu D, Mu J, Wang C, Huang M,
Han Y, Zhang XY, Zhou W, Qiu Y and Zhou X: The ORF3a protein of
SARS-CoV-2 induces apoptosis in cells. Cell Mol Immunol.
17:881–883. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wan Y, Shang J, Graham R, Baric RS and Li
F: Receptor recognition by the novel coronavirus from Wuhan: An
analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS
Coronavirus. J Virol. 94:e00127–20. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Wagoner J, Negash A, Kane OJ, Martinez LE,
Nahmias Y, Bourne N, Owen DM, Grove J, Brimacombe C, McKeating JA,
et al: Multiple effects of silymarin on the hepatitis C virus
lifecycle. Hepatology. 51:1912–1921. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Patel CN, Kumar SP, Pandya HA and Rawal
RM: Identification of potential inhibitors of coronavirus
hemagglutinin-esterase using molecular docking, molecular dynamics
simulation and binding free energy calculation. Mol Divers.
25:421–433. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Kumar S, Kashyap P, Chowdhury S, Kumar S,
Panwar A and Kumar A: Identification of phytochemicals as potential
therapeutic agents that binds to Nsp15 protein target of
coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) that are capable of inhibiting virus
replication. Phytomedicine. (153317)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
51
|
Gorla US, Rao GK, Kulandaivelu US, Alavala
RR and Panda SP: Lead finding from selected flavonoids with
antiviral (SARS-CoV-2) potentials against COVID-19: An in-silico
evaluation. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen: Aug 18, 2020 (Epub
ahead of print).
|
|
52
|
Kim J, Zhang J, Cha Y, Kolitz S, Funt J,
Escalante Chong R, Barrett S, Kusko R, Zeskind B and Kaufman H:
Advanced bioinformatics rapidly identifies existing therapeutics
for patients with coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19). J Transl
Med. 18(257)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
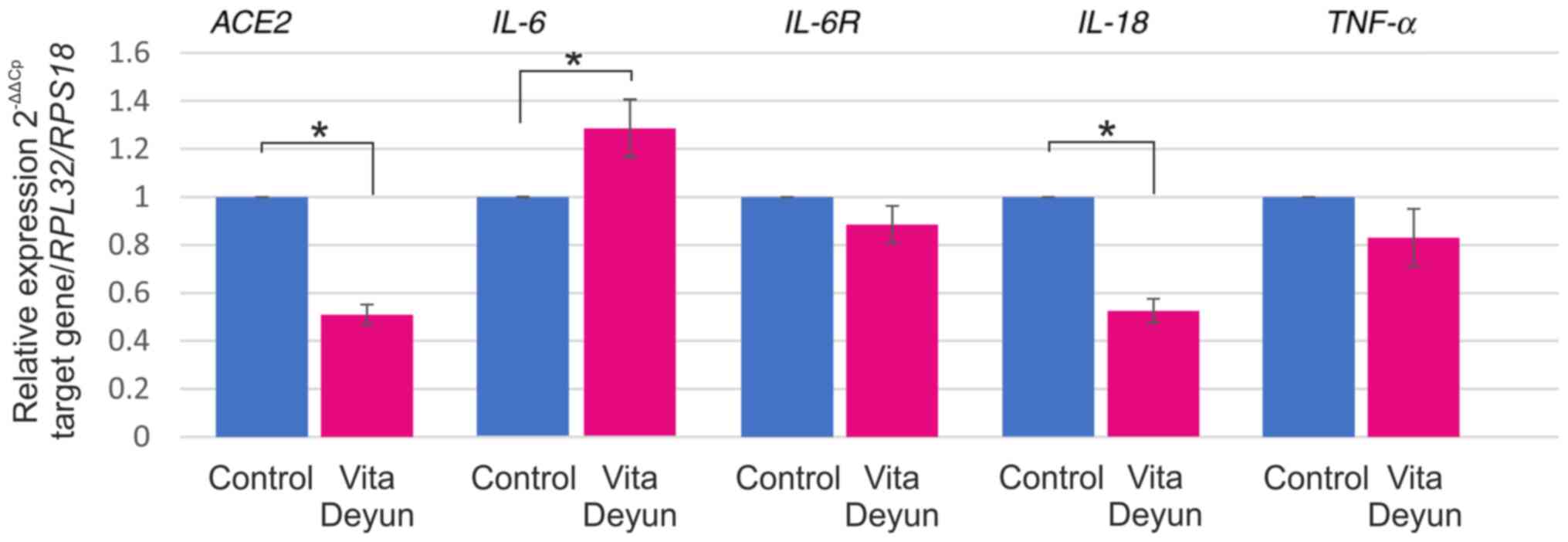
Silvagno F, Vernone A and Pescarmona GP:
The role of glutathione in protecting against the severe
inflammatory response triggered by COVID-19. Antioxidants (Basel).
9(624)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Guloyan V, Oganesian B, Baghdasaryan N,
Yeh C, Singh M, Guilford F, Ting YS and Venketaraman V: Glutathione
supplementation as an adjunctive therapy in COVID-19. Antioxidants
(Basel). 9(914)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Taylor EW and Radding W: Understanding
selenium and glutathione as antiviral factors in COVID-19: Does the
Viral Mpro Protease target host selenoproteins and
glutathione synthesis? Front Nutr. 7(143)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Moghaddam A, Heller RA, Sun Q, Seelig J,
Cherkezov A, Seibert L, Hackler J, Seemann P, Diegmann J, Pilz M,
et al: Selenium deficiency is associated with mortality risk from
COVID-19. Nutrients. 12(2098)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Abobaker A, Alzwi A and Alraied AHA:
Overview of the possible role of vitamin C in management of
COVID-19. Pharmacol Rep. 72:1517–1528. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Mousavi S, Bereswill S and Heimesaat MM:
Immunomodulatory and antimicrobial effects of vitamin C. Eur J
Microbiol Immunol (Bp). 9:73–79. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Waqas Khan HM, Parikh N, Megala SM and
Predeteanu GS: Unusual early recovery of a critical COVID-19
patient after administration of intravenous vitamin C. Am J Case
Rep. 21(e925521)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Liu F, Zhu Y, Zhang J, Li Y and Peng Z:
Intravenous high-dose vitamin C for the treatment of severe
COVID-19: Study protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled
trial. BMJ Open. 10(e039519)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Feyaerts AF and Luyten W: Vitamin C as
prophylaxis and adjunctive medical treatment for COVID-19?
Nutrition. 79-80(110948)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Carr AC and Rowe S: The emerging role of
vitamin C in the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. Nutrients.
12(3286)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Abdel-Magied N and Elkady AA: Possible
curative role of curcumin and silymarin against nephrotoxicity
induced by gamma-rays in rats. Exp Mol Pathol.
111(104299)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Mrityunjaya M, Pavithra V, Neelam R,
Janhavi P, Halami PM and Ravindra PV: Immune-boosting, antioxidant
and anti-inflammatory food supplements targeting pathogenesis of
COVID-19. Front Immunol. 11(570122)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|