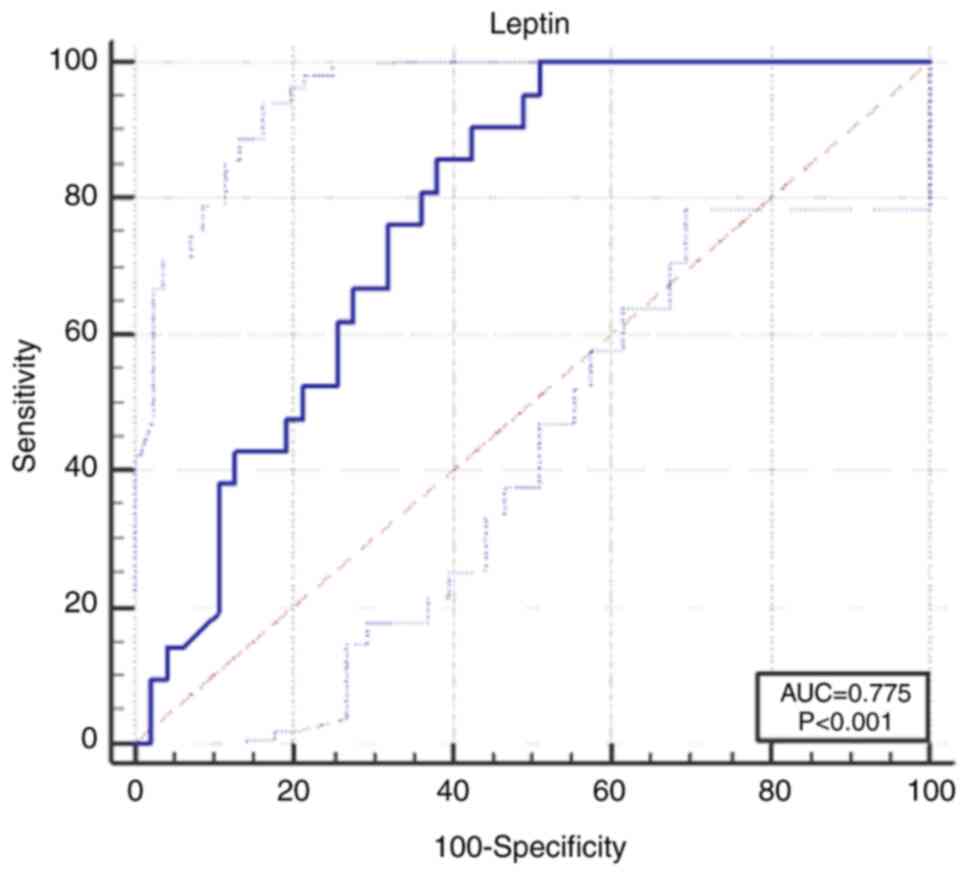
|
1
|
Soheilykhah S, Mojibian M, Rahimi-Saghand
S, Rashidi M and Hadinedoushan H: Maternal serum leptin
concentration in gestational diabetes. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol.
50:149–153. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Moini J: Chapter 6: The Health Impact of
Diabetes. In: Epidemiology of Diabetes. Elsevier, pp115-145,
2019.
|
|
3
|
Sacks DA, Hadden DR, Maresh M,
Deerochanawong C, Dyer AR, Metzger BE, Lowe LP, Coustan DR, Hod M,
Oats JJ, et al: Frequency of gestational diabetes mellitus at
collaborating centers based on IADPSG consensus panel-recommended
criteria: The hyperglycemia and adverse pregnancy outcome (HAPO)
study. Diabetes Care. 35:526–528. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Ornoy A, Reece EA, Pavlinkova G, Kappen C
and Miller RK: Effect of maternal diabetes on the embryo, fetus,
and children: Congenital anomalies, genetic and epigenetic changes
and developmental outcomes. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today.
105:53–72. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Standards of Medical Care in
Diabetes-2016: Summary of revisions. Diabetes Care. 39 (Suppl
1):S4–S5. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Skvarca A, Tomazic M, Blagus R, Krhin B
and Janez A: Adiponectin/leptin ratio and insulin resistance in
pregnancy. J Int Med Res. 41:123–128. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li H, Dong A and Lv X: Advanced glycation
end products and adipocytokines and oxidative stress in placental
tissues of pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Exp
Ther Med. 18:685–691. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Prentice KJ, Luu L, Allister EM, Liu Y,
Jun LS, Sloop KW, Hardy AB, Wei L, Jia W, Fantus IG, et al: The
furan fatty acid metabolite CMPF is elevated in diabetes and
induces β cell dysfunction. Cell Metab. 19:653–666. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Diaz SO, Pinto J, Graça G, Duarte IF,
Barros AS, Galhano E, Pita C, Almeida Mdo C, Goodfellow BJ,
Carreira IM and Gil AM: Metabolic biomarkers of prenatal disorders:
An exploratory NMR metabonomics study of second trimester maternal
urine and blood plasma. J Proteome Res. 10:3732–3742.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Nolan CJ: Lipotoxicity, β cell
dysfunction, and gestational diabetes. Cell Metab. 19:553–554.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
von Elm E, Altman DG, Egger M, Pocock SJ,
Gøtzsche PC and Vandenbroucke JP: STROBE Initiative. The
strengthening the reporting of observational studies in
epidemiology (STROBE) Statement: Guidelines for reporting
observational studies. PLoS Med. 16(e296)2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
International Association of Diabetes and
Pregnancy Study Groups Consensus Panel. Metzger BE, Gabbe SG,
Persson B, Buchanan TA, Catalano PA, Damm P, Dyer AR, Leiva Ad, Hod
M, et al: International Association of Diabetes and Pregnancy Study
Groups recommendations on the diagnosis and classification of
hyperglycemia in pregnancy. Diabetes Care. 33:676–682.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Thagaard IN, Krebs L, Holm JC, Lange T,
Larsen T and Christiansen M: Adiponectin and leptin as first
trimester markers for gestational diabetes mellitus: A cohort
study. Clin Chem Lab Med. 55:1805–1812. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Savvidou M, Nelson SM, Makgoba M, Messow
CM, Sattar N and Nicolaides K: First-trimester prediction of
gestational diabetes mellitus: Examining the potential of combining
maternal characteristics and laboratory measures. Diabetes.
59:3017–3022. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hedderson MM, Xu F, Darbinian JA,
Quesenberry CP, Sridhar S, Kim C, Gunderson EP and Ferrara A:
Prepregnancy SHBG concentrations and risk for subsequently
developing gestational diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care.
37:1296–1303. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Bao W, Baecker A, Song Y, Kiely M, Liu S
and Zhang C: Adipokine levels during the first or early second
trimester of pregnancy and subsequent risk of gestational diabetes
mellitus: A systematic review. Metabolism. 64:756–764.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Qiu C, Williams MA, Vadachkoria S,
Frederick IO and Luthy DA: Increased maternal plasma leptin in
early pregnancy and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus. Obstet
Gynecol. 103:519–525. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Maple-Brown L, Ye C, Hanley AJ, Connelly
PW, Sermer M, Zinman B and Retnakaran R: Maternal pregravid weight
is the primary determinant of serum leptin and its metabolic
associations in pregnancy, irrespective of gestational glucose
tolerance status. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 97:4148–4155.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Eriksson B, Löf M, Olausson H and Forsum
E: Body fat, insulin resistance, energy expenditure and serum
concentrations of leptin, adiponectin and resistin before, during
and after pregnancy in healthy Swedish women. Br J Nutr. 103:50–57.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Misra VK and Trudeau S: The influence of
overweight and obesity on longitudinal trends in maternal serum
leptin levels during pregnancy. Obesity (Silver Spring).
19:416–421. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Cruciat G, Nemeti G, Goidescu I, Anitan S
and Florian A: Hypertriglyceridemia triggered acute pancreatitis in
pregnancy-diagnostic approach, management and follow-up care.
Lipids Health Dis. 19(2)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Park S, Kim MY, Baik SH, Woo JT, Kwon YJ,
Daily JW, Park YM, Yang JH and Kim SH: Gestational diabetes is
associated with high energy and saturated fat intakes and with low
plasma visfatin and adiponectin levels independent of prepregnancy
BMI. Eur J Clin Nutr. 67:196–201. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Froy O, Sherman H, Bhargava G, Chapnik N,
Cohen R, Gutman R, Kronfeld-Schor N and Miskin R: Spontaneous
caloric restriction associated with increased leptin levels in
obesity-resistant αmUPA mice. Int J Obes. 35:226–235.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Nanda S, Akolekar R, Sarquis R, Mosconi AP
and Nicolaides KH: Maternal serum adiponectin at 11 to 13 weeks of
gestationin the prediction of macrosomia. Prenat Diagn. 31:479–483.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Saucedo R, Zarate A, Basurto L, Hernandez
M, Puello E, Galvan R and Campos S: Relationship between
circulating adipokines and insulin resistance during pregnancy and
postpartum in women with gestational diabetes. Arch Med Res.
42:318–323. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yamamoto Y, Hirose H, Saito I, Tomita M,
Taniyama M, Matsubara K, Okazaki Y, Ishii T, Nishikai K and Saruta
T: Correlation of the adipocyte-derived protein adiponectin with
insulin resistance index and serum high-density
lipoprotein-cholesterol, independent of body mass index, in the
Japanese population. Clin Sci. 103:137–142. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Mohammadi T and Paknahad Z: Adiponectin
concentration in gestational diabetic Women: A case-control study.
Clin Nutr Res. 6:267–276. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Vernini JM, Moreli JB, Antônio RA, Costa
RA, Negrato CA, Rudge MV and Calderon IM: Maternal adipokines and
insulin as biomarkers of pregnancies complicated by overweight and
obesity. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 8(68)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Paradisi G, Ianniello F, Tomei C,
Bracaglia M, Carducci B, Gualano MR, La Torre G, Banci M and Caruso
A: Longitudinal changes of adiponectin, carbohydrate and lipid
metabolism in pregnant women at high risk for gestational diabetes.
Gynecol Endocrinol. 26:539–545. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lain KY, Daftary AR, Ness RB and Roberts
JM: First trimester adipocytokine concentrations and risk of
developing gestational diabetes later in pregnancy. Clin Endocrinol
(Oxf). 69:407–411. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lacroix M, Battista MC, Doyon M, Ménard J,
Ardilouze JL, Perron P and Hivert MF: Lower adiponectin levels at
first trimester of pregnancy are associated with increased insulin
resistance and higher risk of developing gestational diabetes
mellitus. Diabetes Care. 36:1577–1583. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Lankinen MA, Hanhineva K, Kolehmainen M,
Lehtonen M, Auriola S, Mykkänen H, Poutanen K, Schwab U and
Uusitupa M: CMPF does not associate with impaired glucose
metabolism in individuals with features of metabolic syndrome. PLoS
One. 10(e0124379)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|