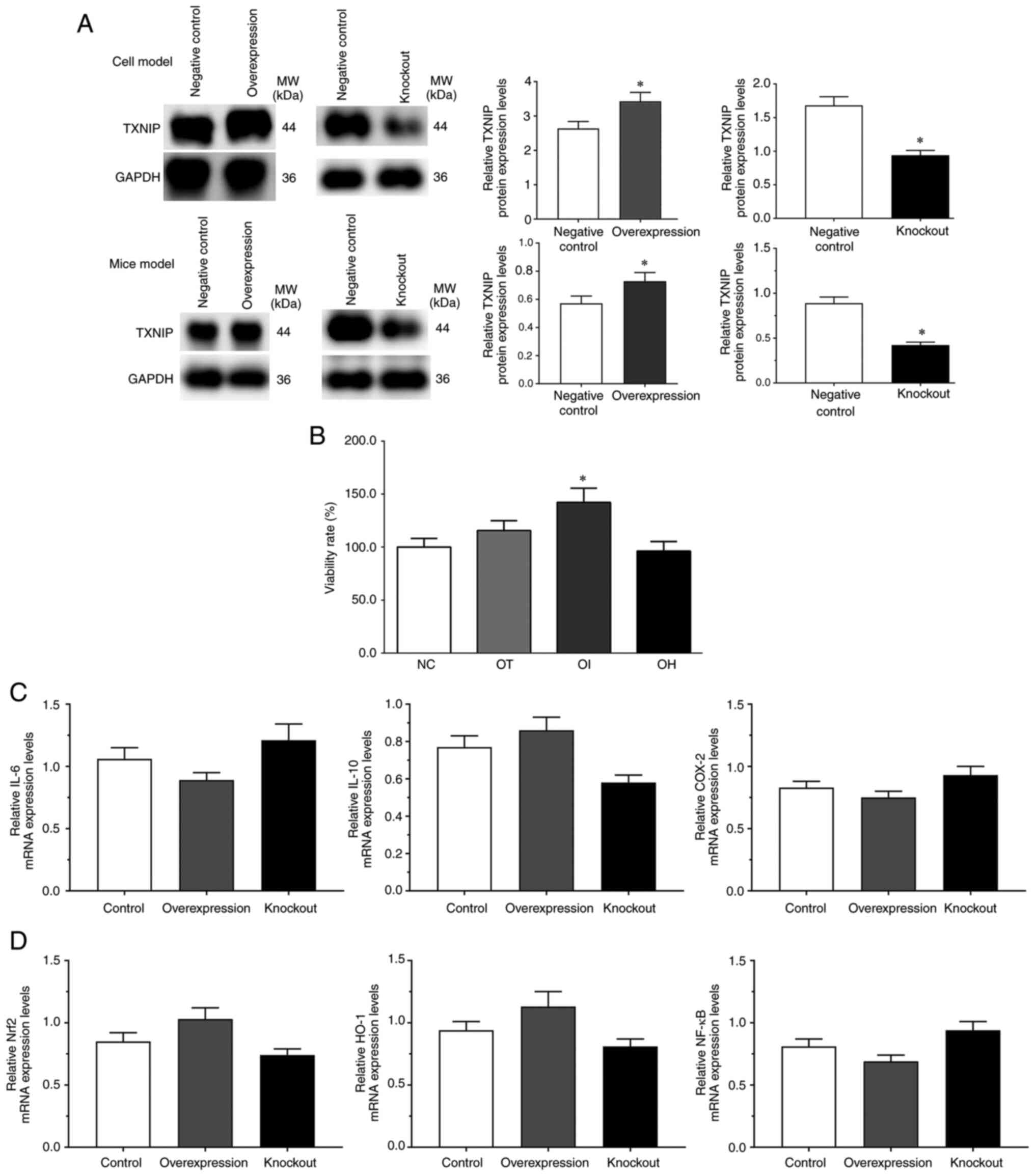
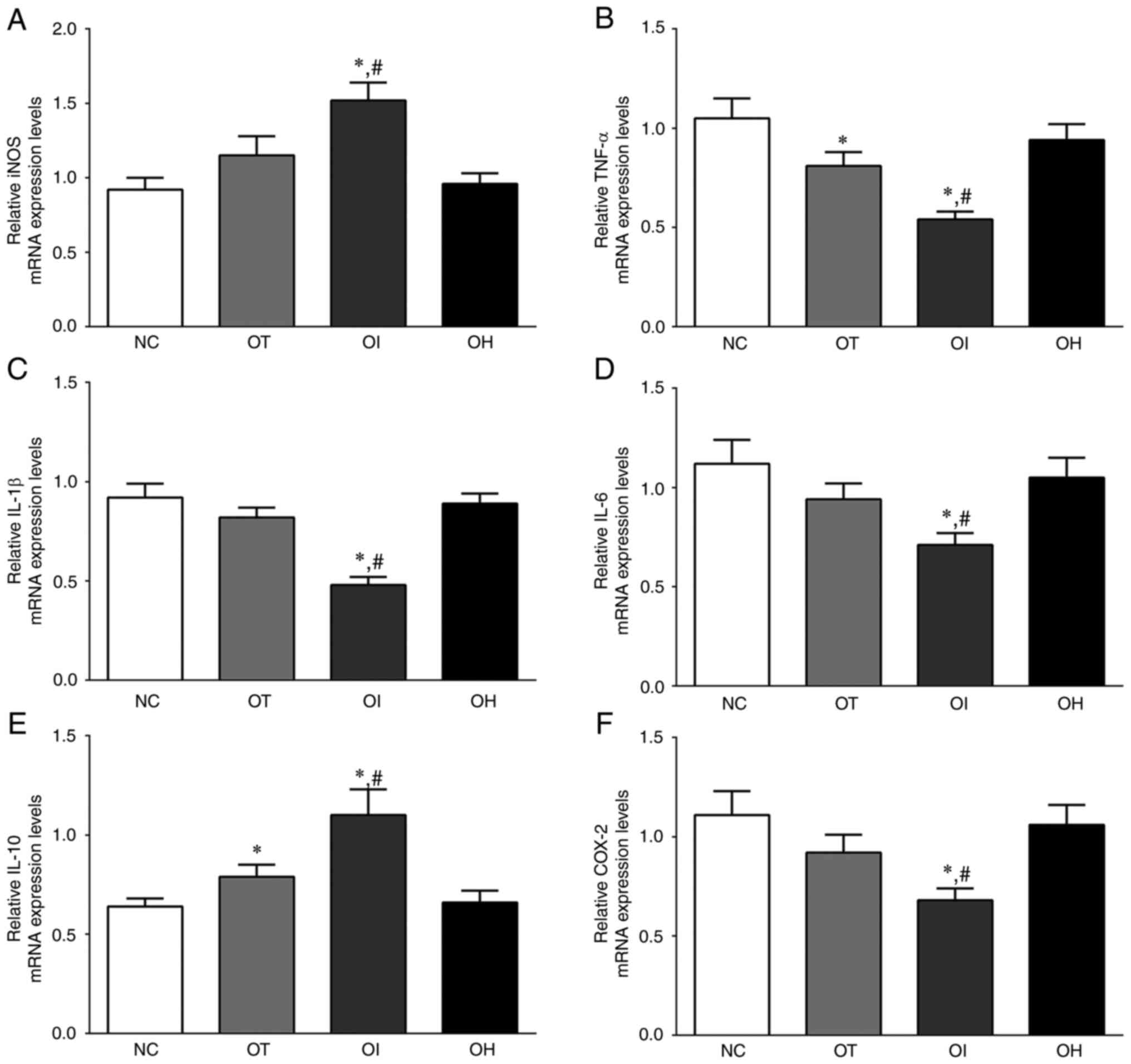
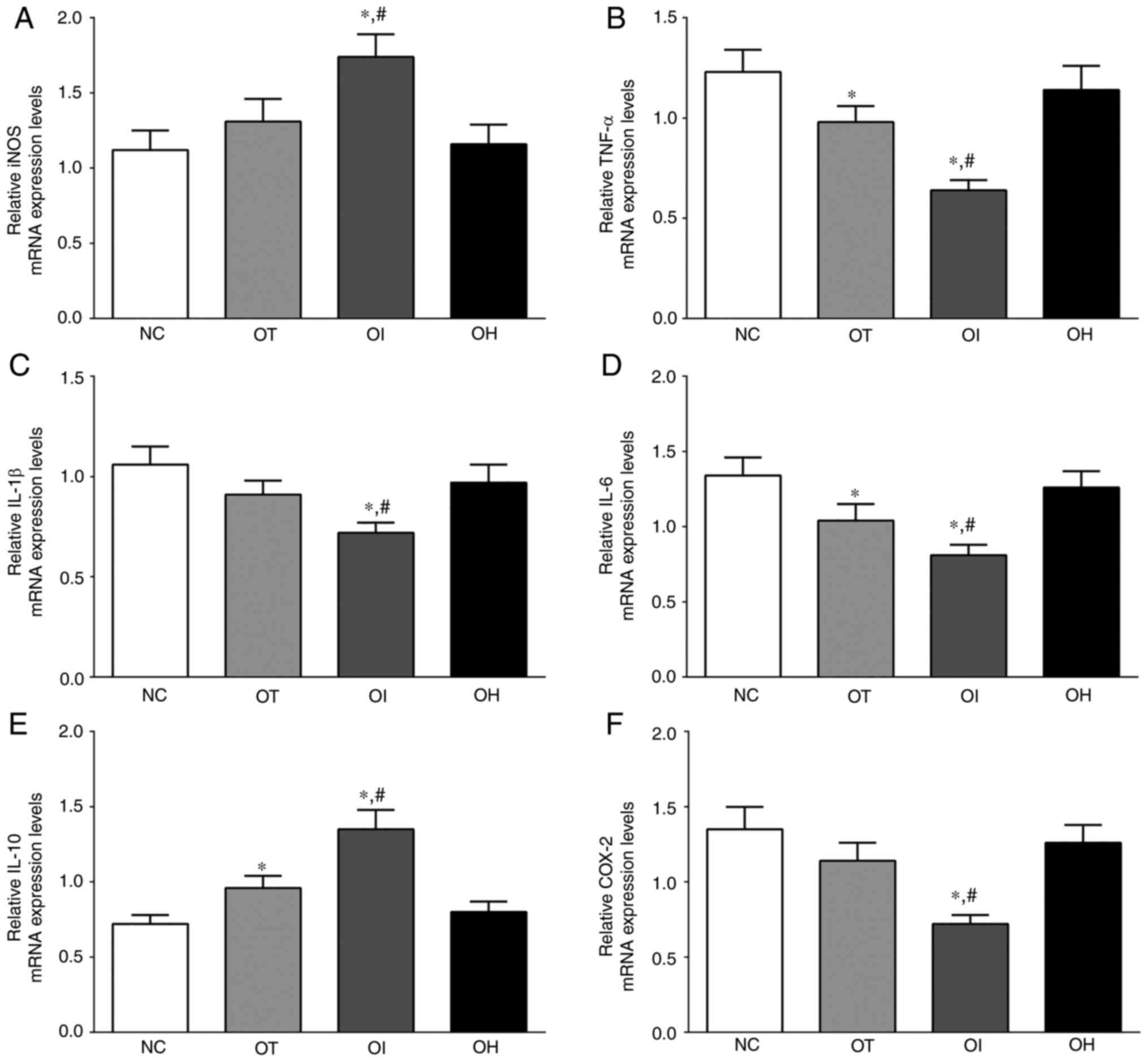
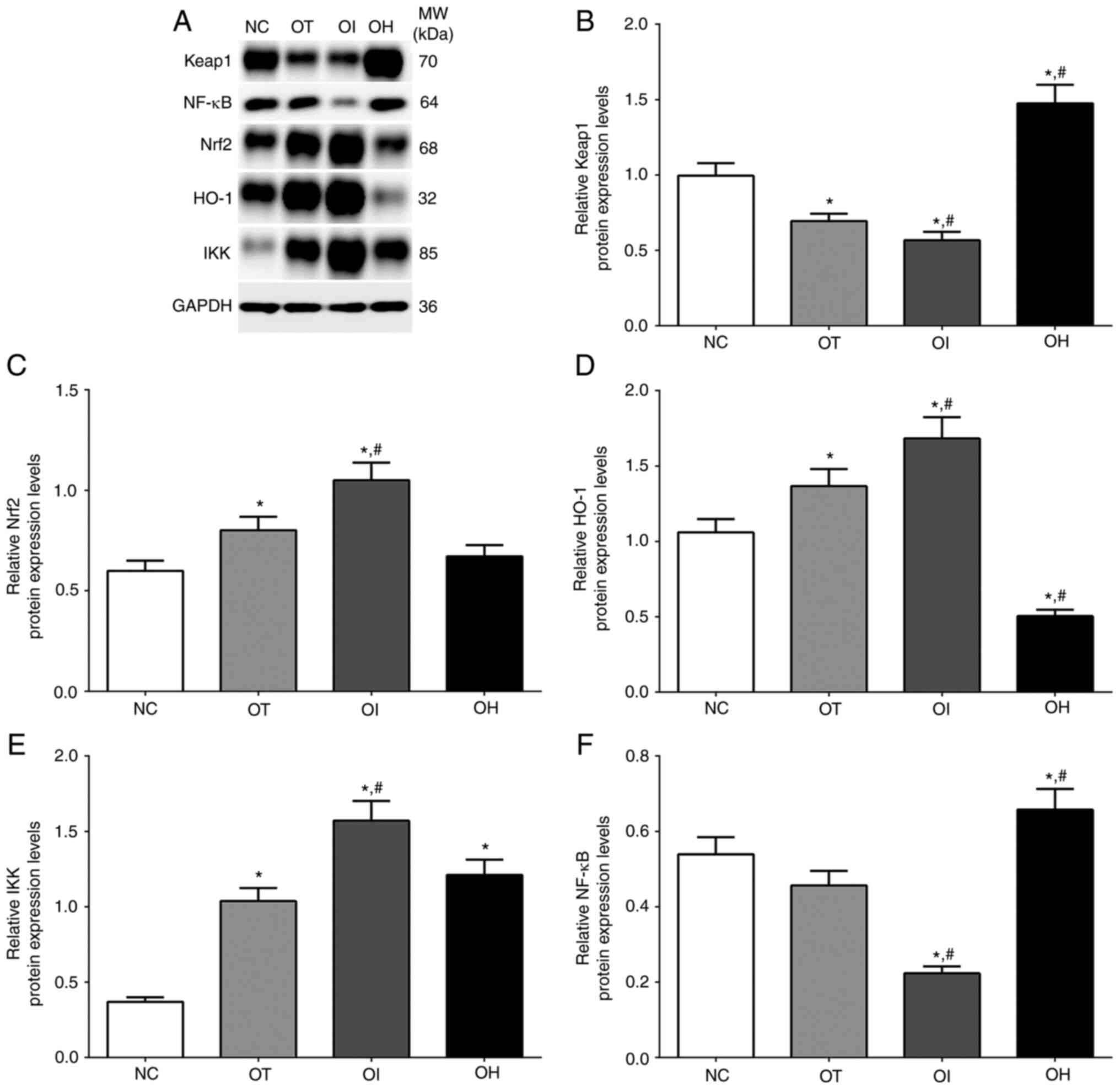
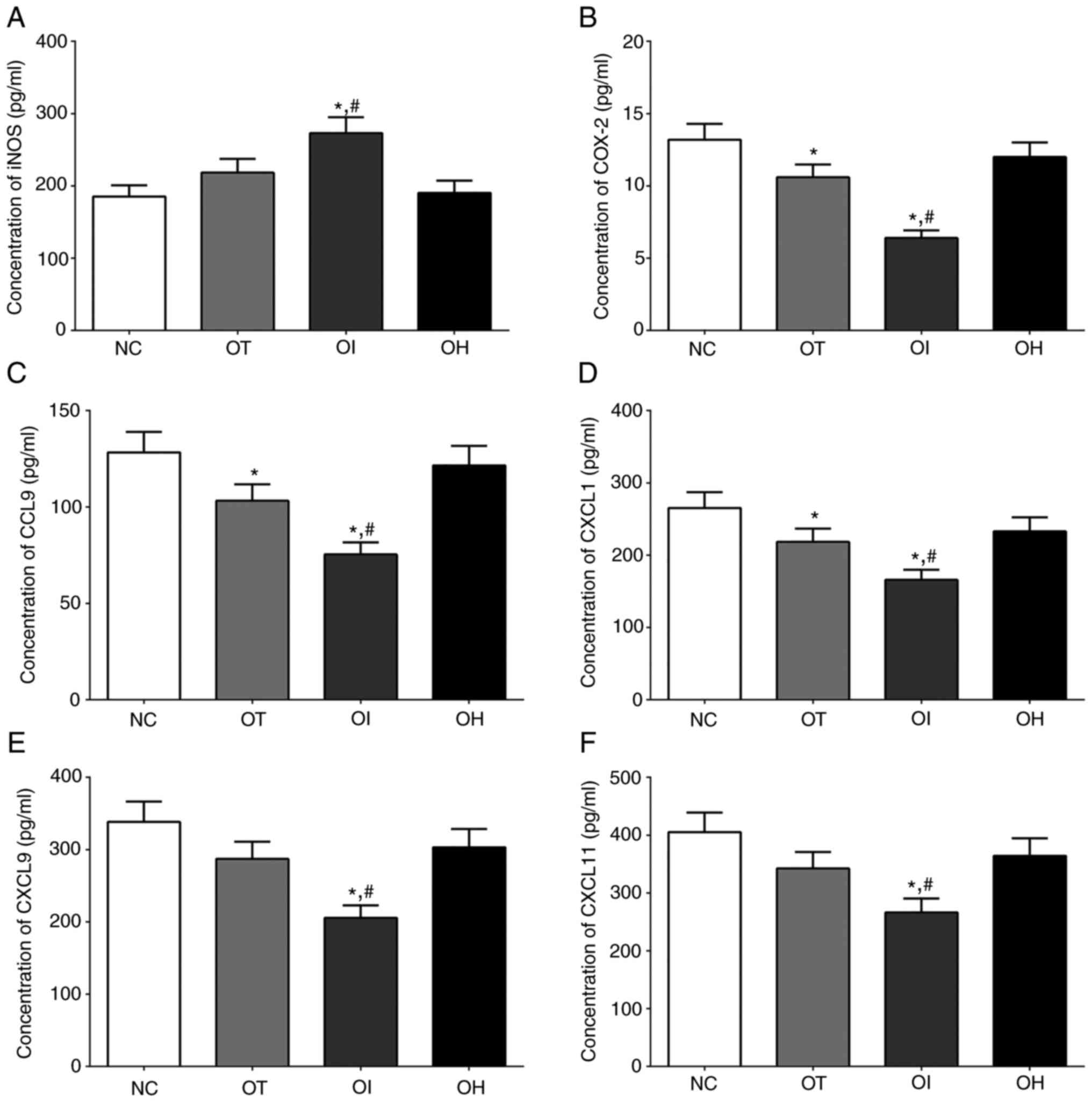
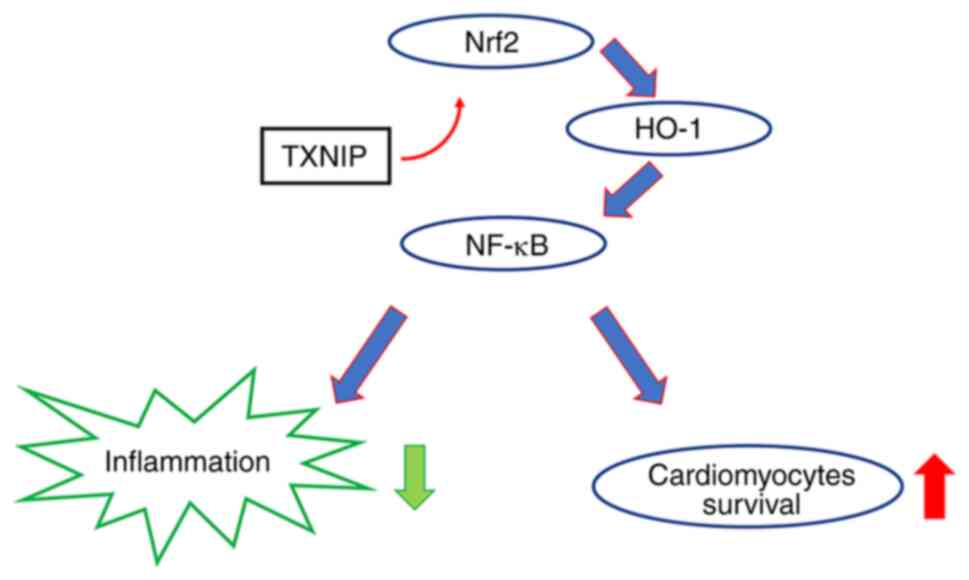
|
1
|
Virani SS, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ,
Bittencourt MS, Callaway CW, Carson AP, Chamberlain AM, Chang AR,
Cheng S, Delling FN, et al: Heart disease and stroke
statistics-2020 Update: A report from the American Heart
association. Circulation. 141:e139–e596. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hofmann U and Frantz S: How can we cure a
heart ‘in flame’? A translational view on inflammation in heart
failure. Basic Res Cardiol. 108(356)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ammirati E, Cannistraci CV, Cristell NA,
Vecchio V, Palini AG, Tornvall P, Paganoni AM, Miendlarzewska EA,
Sangalli LM, Monello A, et al: Identification and predictive value
of interleukin-61 interleukin-101 and interleukin-62
interleukin-101 cytokine patterns in ST-elevation acute myocardial
infarction. Circ Res. 111:1336–1348. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bozkurt B, Torre-Amione G, Warren MS,
Whitmore J, Soran OZ, Feldman AM and Mann DL: Results of targeted
anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy with etanercept (ENBREL) in
patients with advanced heart failure. Circulation. 103:1044–1047.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Taniguchi M, Kataoka T, Suzuki H, Uramoto
M, Ando M, Arao K, Magae J, Nishimura T, Otake N and Nagai K:
Costunolide and dehydrocostus lactone as inhibitors of killing
function of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem.
59:2064–2067. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yuuya S, Hagiwara H, Suzuki T, Ando M,
Yamada A, Suda K, Kataoka T and Nagai K: Guaianolides as
immunomodulators. Synthesis and biological activities of
dehydrocostus lactone, mokko lactone, eremanthin, and their
derivatives. J Nat Prod. 62:22–30. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jeong GS, Pae HO, Jeong SO, Kim YC, Kwon
TO, Lee HS, Kim NS, Park SD and Chung HT: The
alpha-methylenegamma-butyrolactone moiety in dehydrocostus lactone
is responsible for cytoprotective heme oxygenase-1 expression
through activation of the nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 in
HepG2 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 565:37–44. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang HW, Liu YM, Fang X, Gu L, Luo C,
Chen L and Wang Q: Vitamin D3 protects mice from
Diquat-induced oxidative stress through the NF-κB/Nrf2/HO-1
signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2021(6776956)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wu YX, Jiang FJ, Liu G, Wang YY, Gao ZQ,
Jin SH, Nie YJ, Chen D, Chen JL and Pang QF: Dehydrocostus lactone
attenuates methicillin-resistant staphylococcus Aureus-induced
inflammation and acute lung injury via modulating macrophage
polarization. Int J Mol Sci. 22(9754)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kim HR, Kim JM, Kim MS, Hwang JK, Park YJ,
Yang SH, Kim HJ, Ryu DG, Lee DS, Oh H, et al: Saussurea
lappa extract suppresses TPA-induced cell invasion via
inhibition of NF-κB-dependent MMP-9 expression in MCF-7 breast
cancer cells. BMC Complement Altern Med. 14(170)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Kim EJ, Lim SS, Park SY, Shin HK, Kim JS
and Park JH: Apoptosis of DU145 human prostate cancer cells induced
by dehydrocostus lactone isolated from the root of Saussurea
lappa. Food Chem Toxicol. 46:3651–3658. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nie Y, Wang Z, Chai G, Xiong Y, Li B,
Zhang H, Xin R, Qian X, Tang Z, Wu J and Zhao P: Dehydrocostus
lactone suppresses LPS-induced acute lung injury and macrophage
activation through NF-κB signaling pathway mediated by p38 MAPK and
Akt. Molecules. 24(1510)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Masutani H, Yoshihara E, Masaki S, Chen Z
and Yodoi J: Thioredoxin binding protein (TBP)-2/Txnip and
alpha-arrestin proteins in cancer and diabetes mellitus. J Clin
Biochem Nutr. 50:23–34. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Dai X, Liao R, Liu C, Liu S, Huang H, Liu
J, Jin T, Guo H, Zheng Z, Xia M, et al: Epigenetic regulation of
TXNIP-mediated oxidative stress and NLRP3 inflammasome activation
contributes to SAHH inhibition-aggravated diabetic nephropathy.
Redox Biol. 45(102033)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Neville ES, Ophir S and Zhang F: Improved
vectors and genome-wide libraries for CRISPR screening. Nat
Methods. 11:783–784. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wen JX, Zhang L, Liu H, Wang J, Li J, Yang
Y, Wang Y, Cai H, Li R and Zhao Y: Salsolinol attenuates
doxorubicin-induced chronic heart failure in rats and improves
mitochondrial function in H9c2 cardiomyocytes. Front Pharmacol.
10(1135)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang K, Zhou A, Ruan M, Jin Z, Lu J, Wang
Q and Lu C: Dehydrocostus lactone suppresses ox-LDL-induced
attachment of monocytes to endothelial cells. Am J Transl Res.
11:6159–6169. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
National Research Council (US) Institute
for Laboratory Animal Research. Guide for the Care and Use of
Laboratory Animals. Washington (DC), National Academies Press (US),
1996.
|
|
19
|
Wang X, Gao Y, Tian Y, Liu X, Zhang G and
Wang Q, Xie W, Liu K, Qian Q and Wang Q: Integrative serum
metabolomics and network analysis on mechanisms exploration of
Ling-Gui-Zhu-Gan Decoction on doxorubicin-induced heart failure
mice. J Ethnopharmacol. 250(112397)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25: 402-408.
|
|
21
|
Freddy AS and David G: Cardiac
contractility modulation: A novel approach for the treatment of
heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 21:645–660. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Benjamin EJ, Blaha MJ, Chiuve SE, Cushman
M, Das SR, Deo R, de Ferranti SD, Floyd J, Fornage M, Gillespie C,
et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2017 update: A report
from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 135:e146–e603.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Peng Z, Wang Y, Fan J, Lin X, Liu C, Xu Y,
Ji W, Yan C and Su C: Costunolide and dehydrocostuslactone
combination treatment inhibit breast cancer by inducing cell cycle
arrest and apoptosis through c-Myc/p53 and AKT/14-3-3 pathway. Sci
Rep. 7(41254)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sun X, Kang H, Yao Y, Chen H, Sun L, An W,
Jiang E, Wang S and Hu X: Dehydrocostus lactone suppressed the
proliferation, migration, and invasion of colorectal carcinoma
through the downregulation of eIF4E expression. Anticancer Drugs.
26:641–648. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Han X, Wu YC, Meng M, Sun QS, Gao SM and
Sun H: Linarin prevents LPS-induced acute lung injury by
suppressing oxidative stress and inflammation via inhibition of
TXNIP/NLRP3 and NF-κB pathways. Int J Mol Med. 42:1460–1472.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Iannucci J, Renehan W and Grammas P:
Thrombin, a mediator of coagulation, inflammation, and
neurotoxicity at the neurovascular interface: Implications for
Alzheimer's disease. Front Neurosci. 14(762)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pawlinski R, Pedersen B, Kehrle B, Aird
WC, Frank RD, Guha M and Mackman N: Regulation of tissue factor and
inflammatory mediators by Egr-1 in a mouse endotoxemia model.
Blood. 10:3940–3947. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Scotton CJ, Krupiczojc MA, Königshoff M,
Mercer PF, Lee YC, Kaminski N, Morser J, Post JM, Maher TM,
Nicholson AG, et al: Increased local expression of coagulation
factor X contributes to the fibrotic response in human and murine
lung injury. J Clin Invest. 1199:2550–2563. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Motley ED, Eguchi K, Patterson MM, Palmer
PD, Suzuki H and Eguchi S: Mechanism of endothelial nitric oxide
synthase phosphorylation and activation by thrombin. Hypertension.
49:577–583. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Stasch JP and Hobbs AJ: NO-independent,
haem-dependent soluble guanylate cyclase stimlators. Handb Exp
Pharmacol: 277-308, 2009 doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-68964-5_13.
|
|
31
|
Yang Y and Loscalzo J: Regulation of
tissue factor expression in human microvascular endothelial cells
by nitric oxide. Circulation. 101:2144–2148. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Tschudi MR and Luscher TF: Nitric oxide:
The endogenous nitrate in the cardiovascular system. Herz.
21:50–60. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rakoff-Nahoum S and Medzhitov R: Toll-like
receptors and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 9:57–63. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Piras V and Selvarajoo K: Beyond MyD88 and
TRIF pathways in Toll-like receptor signaling. Front Immunol.
5(70)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Bauernfeind FG, Horvath G, Stutz A,
Alnemri ES, MacDonald K, Speert D, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Wu J, Monks
BG, Fitzgerald KA, et al: Cutting edge: NF-kappaB activating
pattern recognition and cytokine receptors license NLRP3
inflammasome activation by regulating NLRP3 expression. J Immunol.
183:787–791. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Franchi L, Muñoz-Planillo R and Núñez G:
Sensing and reacting to microbes through the inflammasomes. Nat
Immunol. 13:325–332. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mariathasan S, Weiss DS, Newton K, McBride
J, O'Rourke K, Roose-Girma M, Lee WP, Weinrauch Y, Monack DM and
Dixit VM: Cryopyrin activates the inflammasome in response to
toxins and ATP. Nature. 440:228–232. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Franchi L, Eigenbrod T and Núñez G:
Cutting edge: TNF-alpha mediates sensitization to ATP and silica
via the NLRP3 inflammasome in the absence of microbial stimulation.
J Immunol. 183:792–796. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kapitulnik J: Bilirubin: An endogenous
product of heme degradation with both cytotoxic and cytoprotective
properties. Mol Pharmacol. 66:773–779. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Srisook K, Kim C and Cha YN: Molecular
mechanisms involved in enhancing HO-1 expression: De-repression by
heme and activation by Nrf2, the ‘one-two’ punch. Antioxid Redox
Signa. l7:1674–1687. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Farombi EO and Surh YJ: Heme oxygenase-1
as a potential therapeutic target for hepatoprotection. J Biochem
Mol Biol. 39:479–491. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Owuor ED and Kong AN: Antioxidants and
oxidants regulated signal transduction pathways. Biochem Pharmacol.
64:765–770. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|