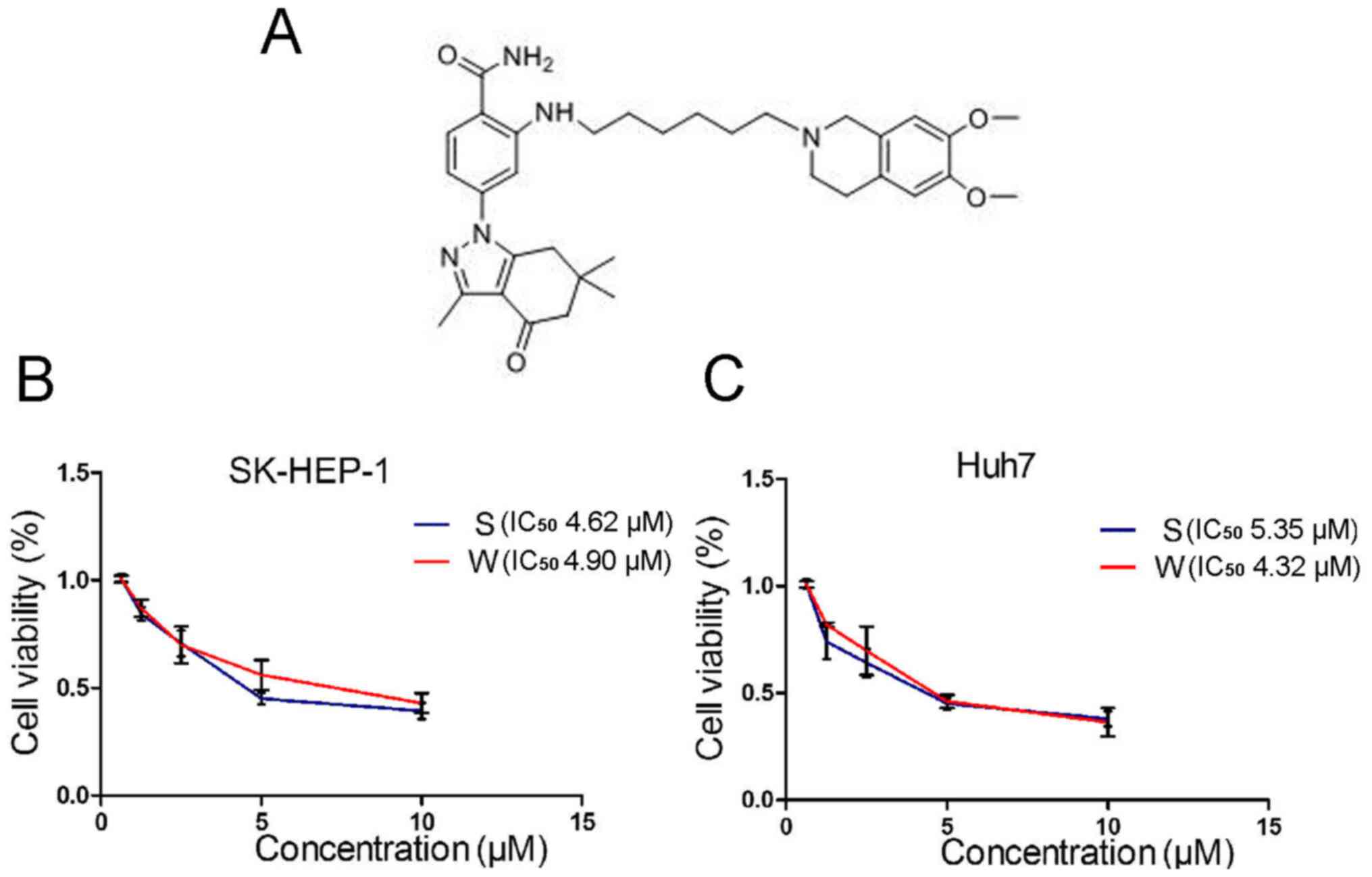
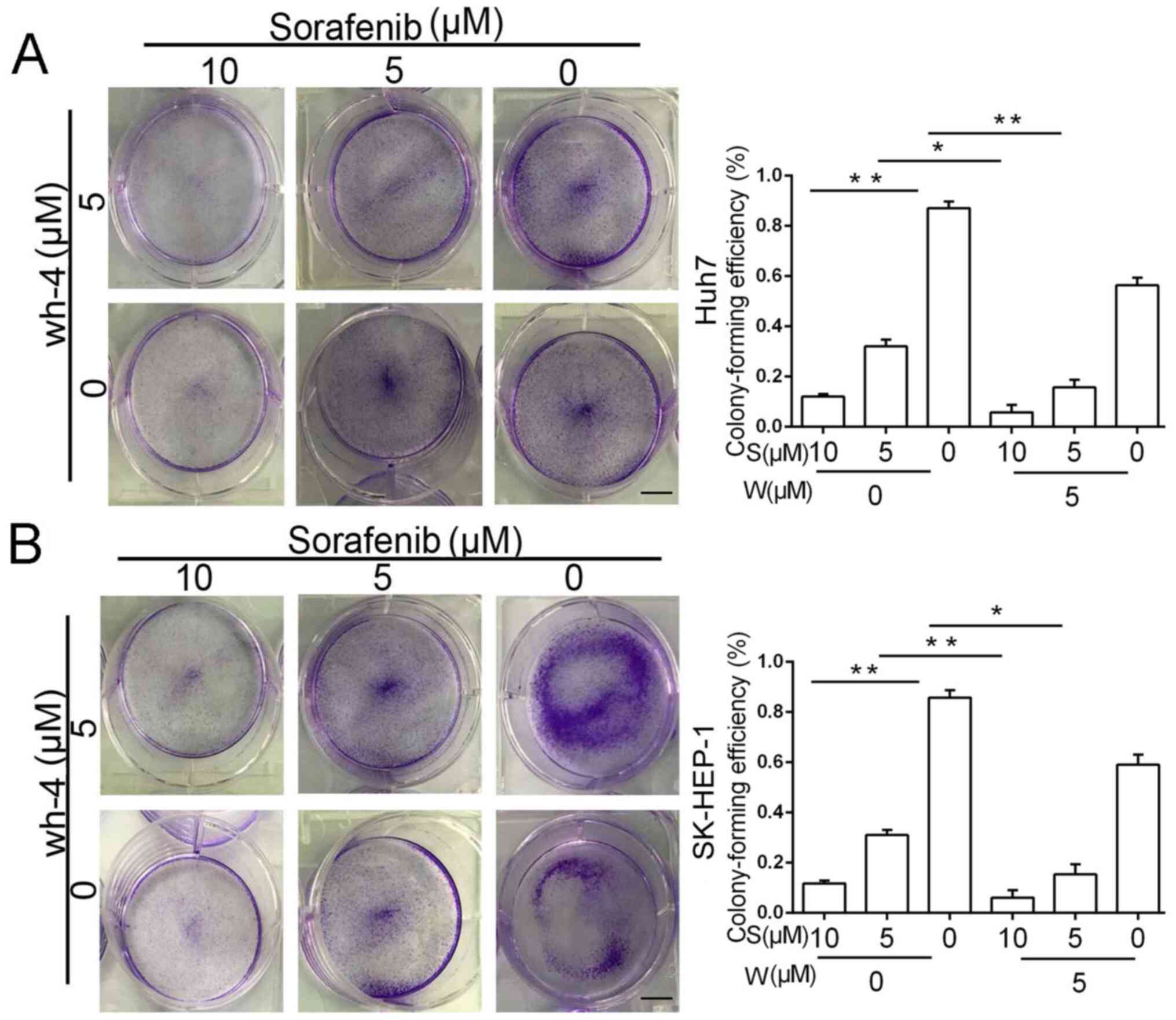
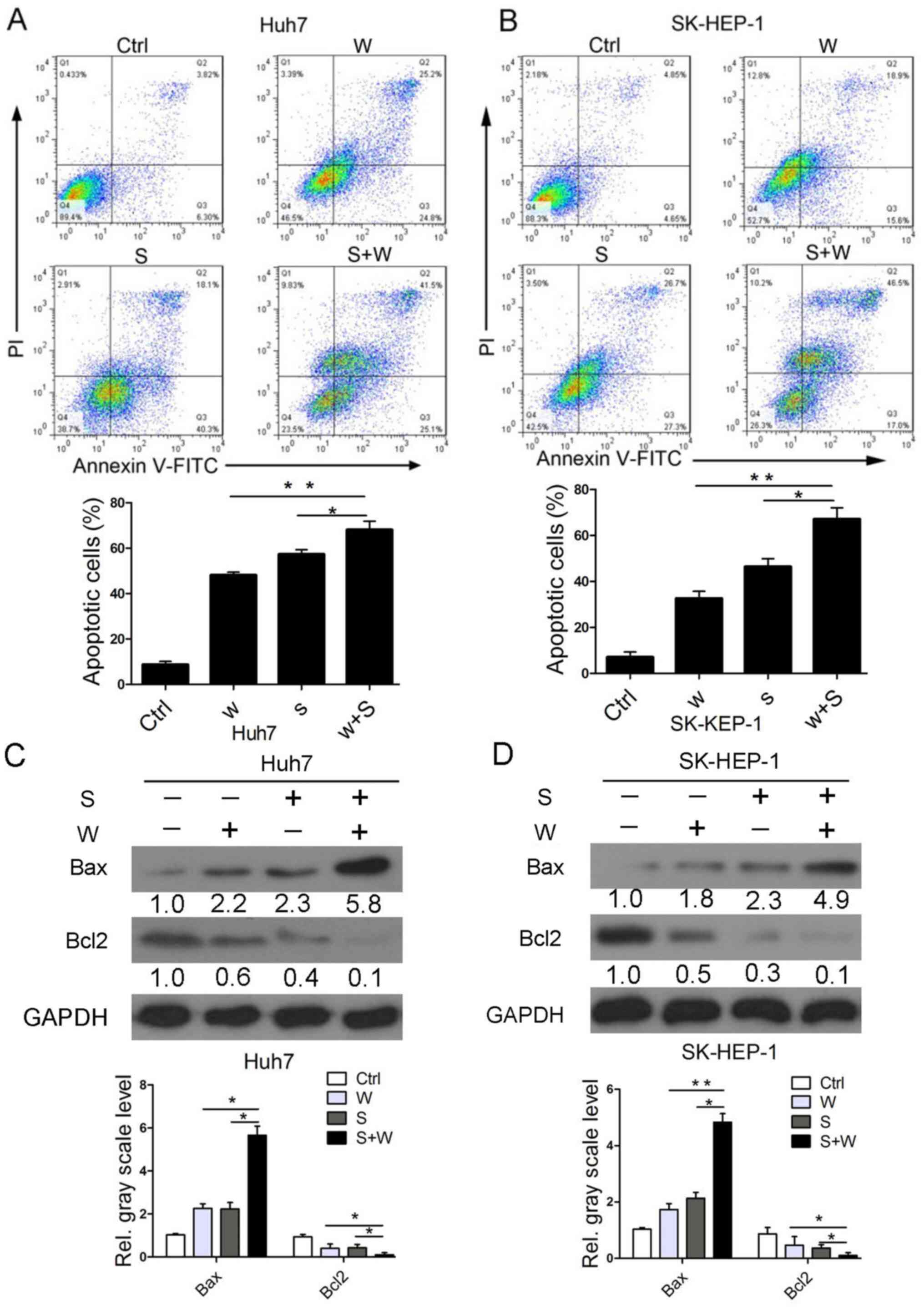
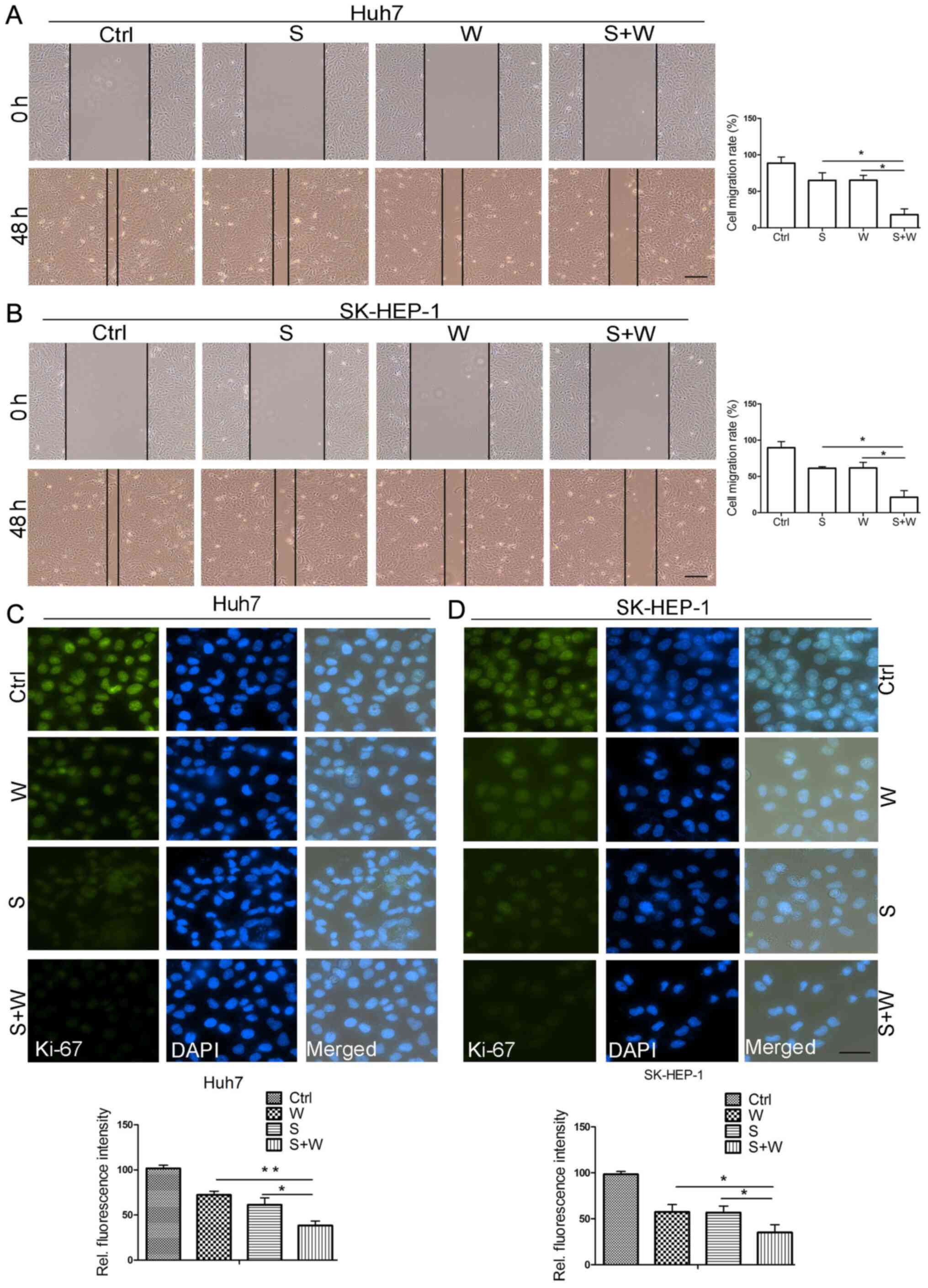
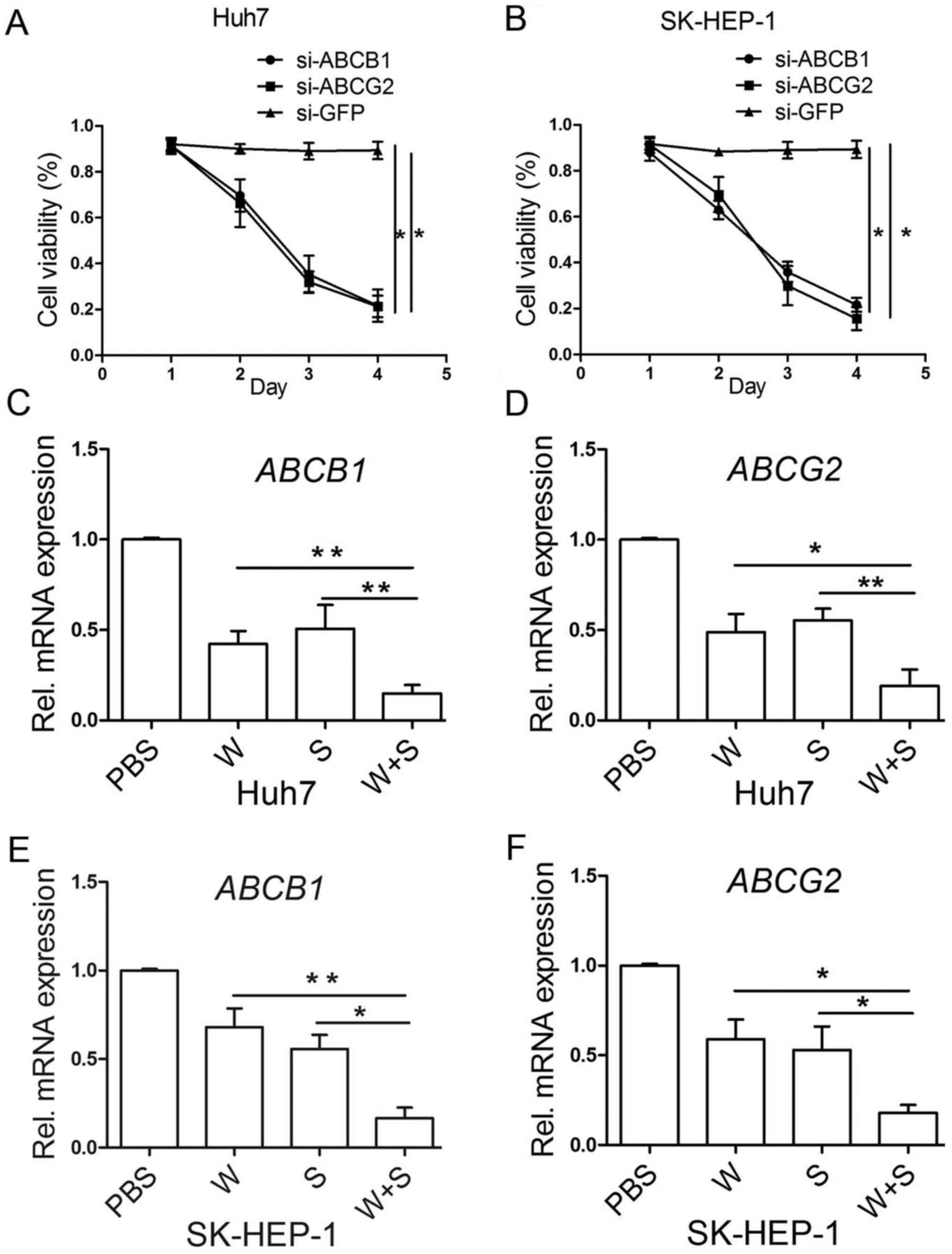
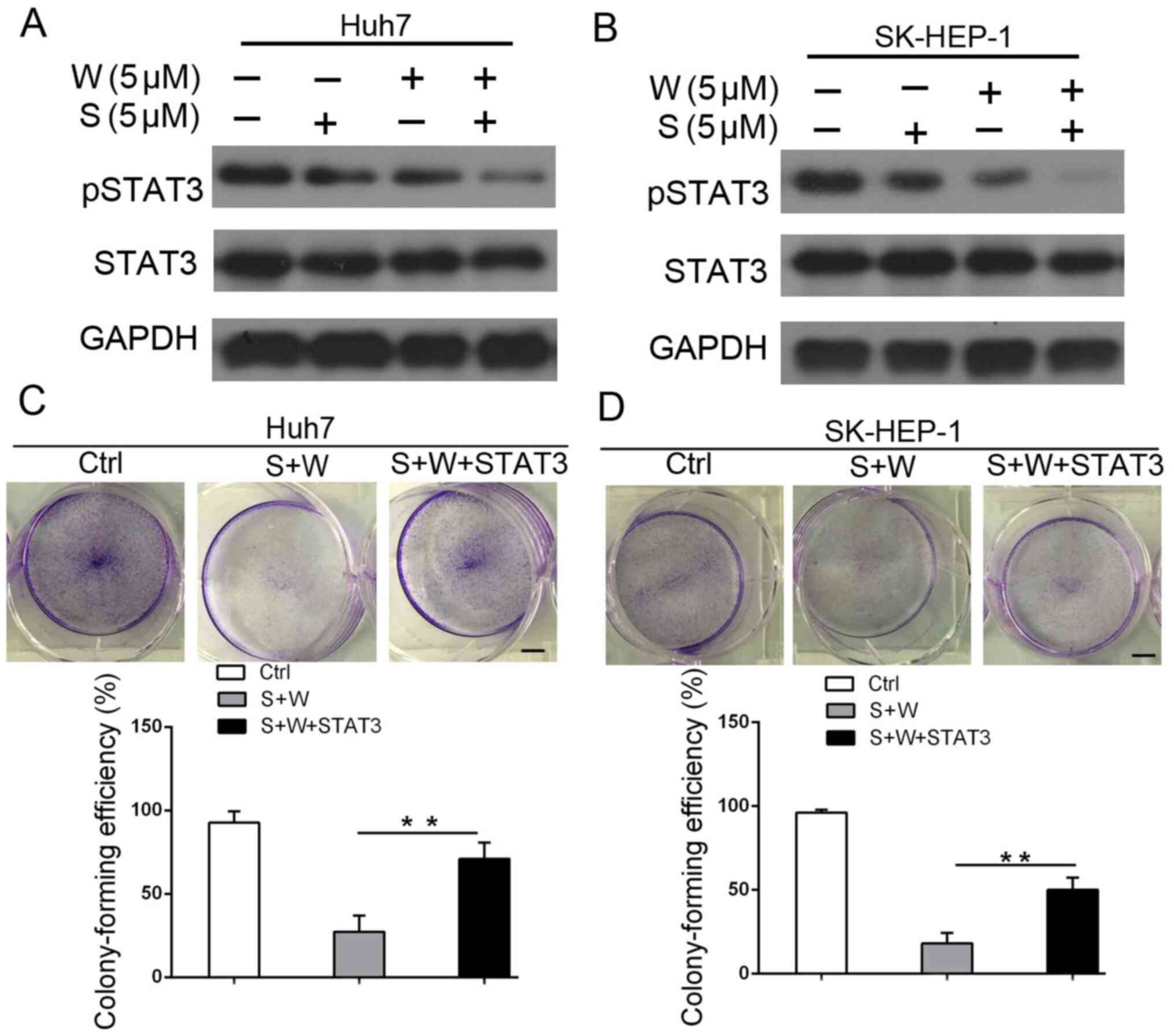
|
1
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Villanueva A, Minguez B, Forner A, Reig M
and Llovet JM: Hepatocellular carcinoma: Novel molecular approaches
for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Annu Rev Med. 61:317–328.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Vitale A, Volk ML, Pastorelli D, Lonardi
S, Farinati F, Burra P, Angeli P and Cillo U: Use of sorafenib in
patients with hepatocellular carcinoma before liver
transplantation: A cost-benefit analysis while awaiting data on
sorafenib safety. Hepatology. 51:165–173. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Reyes R, Wani NA, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST and
Motiwala T: Sorafenib and 2-Deoxyglucose synergistically inhibit
proliferation of both Sorafenib-Sensitive and -Resistant HCC cells
by inhibiting ATP production. Gene Expr. 17:129–140.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Shen YC, Hsu C and Cheng AL: Molecular
targeted therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: Current
status and future perspectives. J Gastroenterol. 45:794–807.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Palmer DH: Sorafenib in advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 359:2498–2499.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Johnson P and Billingham L: Sorafenib for
liver cancer: The horizon broadens. Lancet Oncol. 10:4–5.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tejeda-Maldonado J, Garcia-Juarez I,
Aguirre-Valadez J, González-Aguirre A, Vilatobá-Chapa M,
Armengol-Alonso A, Escobar-Penagos F, Torre A, Sánchez-Ávila JF and
Carrillo-Pérez DL: Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular
carcinoma: An update. World J Hepatol. 7:362–376. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard
P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A,
et al: Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J
Med. 359:378–390. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Villanueva A and Llovet JM: Second-line
therapies in hepatocellular carcinoma: Emergence of resistance to
sorafenib. Clin Cancer Res. 18:1824–1826. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Xin HW, Ambe CM, Hari DM, Wiegand GW,
Miller TC, Chen JQ, Anderson AJ, Ray S, Mullinax JE, Koizumi T, et
al: Label-retaining liver cancer cells are relatively resistant to
sorafenib. Gut. 62:1777–1786. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tai WT, Cheng AL, Shiau CW, Liu CY, Ko CH,
Lin MW, Chen PJ and Chen KF: Dovitinib induces apoptosis and
overcomes sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma through
SHP-1-mediated inhibition of STAT3. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:452–463.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Marin JJ, Monte MJ, Blazquez AG, Macias
RI, Serrano MA and Briz O: The role of reduced intracellular
concentrations of active drugs in the lack of response to
anticancer chemotherapy. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 35:1–10.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Marin JJG, Macias RIR, Monte MJ, Romero
MR, Asensio M, Sanchez-Martin A, Cives-Losada C, Temprano AG,
Espinosa-Escudero R, Reviejo M, et al: Molecular bases of drug
resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers.
12(1663)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wang XQ, Ongkeko WM, Chen L, Yang ZF, Lu
P, Chen KK, Lopez JP, Poon RT and Fan ST: Octamer 4 (Oct4) mediates
chemotherapeutic drug resistance in liver cancer cells through a
potential Oct4-AKT-ATP-binding cassette G2 pathway. Hepatology.
52:528–539. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gao B, Yang FM, Yu ZT, Li R, Xie F, Chen
J, Luo HJ and Zhang JC: Relationship between the expression of MDR1
in hepatocellular cancer and its biological behaviors. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 8:6995–7001. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Nies AT, Konig J, Pfannschmidt M, Klar E,
Hofmann WJ and Keppler D: Expression of the multidrug resistance
proteins MRP2 and MRP3 in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Cancer. 94:492–499. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang S, Du Z, Luo J, Wang X, Li H, Liu Y,
Zhang Y, Ma J, Xiao W, Wang Y and Zhong X: Inhibition of heat shock
protein 90 suppresses squamous carcinogenic progression in a mouse
model of esophageal cancer. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 141:1405–1416.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu Y, Wang X, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Zheng K,
Yan H, Zhang L, Chen W, Wang X, Liu Q, et al: Combination of
SNX-2112 with 5-FU exhibits antagonistic effect in esophageal
cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 46:299–307. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wang X, Wang S, Liu Y, Ding W, Zheng K,
Xiang Y, Liu K, Wang D, Zeng Y, Xia M, et al: The Hsp90 inhibitor
SNX-2112 induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells:
The role of ER stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 446:160–166.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Liu KS, Liu H, Qi JH, Liu QY, Liu Z, Xia
M, Xing GW, Wang SX and Wang YF: SNX-2112, an Hsp90 inhibitor,
induces apoptosis and autophagy via degradation of Hsp90 client
proteins in human melanoma A-375 cells. Cancer Lett. 318:180–188.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu KS, Ding WC, Wang SX, Liu Z, Xing GW,
Wang Y and Wang YF: The heat shock protein 90 inhibitor SNX-2112
inhibits B16 melanoma cell growth in vitro and in
vivo. Oncol Rep. 27:1904–1910. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bachleitner-Hofmann T, Sun MY, Chen CT,
Liska D, Zeng Z, Viale A, Olshen AB, Mittlboeck M, Christensen JG,
Rosen N, et al: Antitumor activity of SNX-2112, a synthetic heat
shock protein-90 inhibitor, in MET-amplified tumor cells with or
without resistance to selective MET Inhibition. Clin Cancer Res.
17:122–133. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Borkovich KA, Farrelly FW, Finkelstein DB,
Taulien J and Lindquist S: hsp82 is an essential protein that is
required in higher concentrations for growth of cells at higher
temperatures. Mol Cell Biol. 9:3919–3930. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Trepel J, Mollapour M, Giaccone G and
Neckers L: Targeting the dynamic HSP90 complex in cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 10:537–549. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Cheng W, Ainiwaer A, Xiao L, Cao Q, Wu G,
Yang Y, Mao R and Bao Y: Role of the novel HSP90 inhibitor AUY922
in hepatocellular carcinoma: Potential for therapy. Mol Med Rep.
12:2451–2456. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sarto C, Binz PA and Mocarelli P: Heat
shock proteins in human cancer. Electrophoresis. 21:1218–1226.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
McConnell JR and McAlpine SR: Heat shock
proteins 27, 40, and 70 as combinational and dual therapeutic
cancer targets. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 23:1923–1928. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Kamal A, Thao L, Sensintaffar J, Zhang L,
Boehm MF, Fritz LC and Burrows FJ: A high-affinity conformation of
Hsp90 confers tumour selectivity on Hsp90 inhibitors. Nature.
425:407–410. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Solit DB, Zheng FF, Drobnjak M, Münster
PN, Higgins B, Verbel D, Heller G, Tong W, Cordon-Cardo C, Agus DB,
et al: 17-Allylamino-17-demethoxygeldanamycin induces the
degradation of androgen receptor and HER-2/neu and inhibits the
growth of prostate cancer xenografts. Clin Cancer Res. 8:986–993.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Newman B, Liu Y, Lee HF, Sun D and Wang Y:
HSP90 inhibitor 17-AAG selectively eradicates lymphoma stem cells.
Cancer Res. 72:4551–4561. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Okawa Y, Hideshima T, Steed P, Vallet S,
Hall S, Huang K, Rice J, Barabasz A, Foley B, Ikeda H, et al:
SNX-2112, a selective Hsp90 inhibitor, potently inhibits tumor cell
growth, angiogenesis, and osteoclastogenesis in multiple myeloma
and other hematologic tumors by abrogating signaling via Akt and
ERK. Blood. 113:846–855. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Eilard MS, Andersson M, Naredi P,
Geronymakis C, Lindnér P, Cahlin C, Bennet W and Rizell M: A
prospective clinical trial on sorafenib treatment of hepatocellular
carcinoma before liver transplantation. BMC Cancer.
19(568)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Kim JB, Lee M, Park SY, Lee S, Kim HR, Lee
HS, Yoon JH and Kim YJ: Sorafenib inhibits cancer side population
cells by targeting cJun Nterminal kinase signaling. Mol Med Rep.
12:8247–8252. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Ha TY, Hwang S, Hong HN, Choi YI, Yoon SY,
Won YJ, Song GW, Kim N, Tak E and Ryoo BY: Synergistic effect of
sorafenib and vitamin K on suppression of hepatocellular carcinoma
cell migration and metastasis. Anticancer Res. 35:1985–1995.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yi P, Higa A, Taouji S, Bexiga MG, Marza
E, Arma D, Castain C, Le Bail B, Simpson JC, Rosenbaum J, et al:
Sorafenib-mediated targeting of the AAA+ ATPase p97/VCP
leads to disruption of the secretory pathway, endoplasmic reticulum
stress, and hepatocellular cancer cell death. Mol Cancer Ther.
11:2610–2620. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sauzay C, Louandre C, Bodeau S, Anglade F,
Godin C, Saidak Z, Fontaine JX, Usureau C, Martin N, Molinie R, et
al: Protein biosynthesis, a target of sorafenib, interferes with
the unfolded protein response (UPR) and ferroptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncotarget. 9:8400–8414.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Vaishampayan UN, Burger AM, Sausville EA,
Heilbrun LK, Li J, Horiba MN, Egorin MJ, Ivy P, Pacey S and Lorusso
PM: Safety, efficacy, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of the
combination of sorafenib and tanespimycin. Clin Cancer.
16:3795–3804. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Booth L, Shuch B, Albers T, Roberts JL,
Tavallai M, Proniuk S, Zukiwski A, Wang D, Chen CS, Bottaro D, et
al: Multi-kinase inhibitors can associate with heat shock proteins
through their NH2-termini by which they suppress chaperone
function. Oncotarget. 7:12975–12996. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Barta TE, Veal JM, Rice JW, Partridge JM,
Fadden RP, Ma W, Jenks M, Geng L, Hanson GJ, Huang KH, et al:
Discovery of benzamide tetrahydro-4H-carbazol-4-ones as novel small
molecule inhibitors of Hsp90. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 18:3517–3521.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Xu WW, Li B, Guan XY, Chung SK, Wang Y,
Yip YL, Law SY, Chan KT, Lee NP, Chan KW, et al: Cancer
cell-secreted IGF2 instigates fibroblasts and bone marrow-derived
vascular progenitor cells to promote cancer progression. Nat
Commun. 8(14399)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wang J, Lian Y, Gu Y, Wang H, Gu L and
Huang Y, Zhou L and Huang Y: Synergistic effect of farnesyl
transferase inhibitor lonafarnib combined with chemotherapeutic
agents against the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
Oncotarget. 8:105047–105060. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Nishanth RP, Ramakrishna BS, Jyotsna RG,
Roy KR, Reddy GV, Reddy PK and Reddanna P: C-Phycocyanin inhibits
MDR1 through reactive oxygen species and cyclooxygenase-2 mediated
pathways in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Eur J
Pharmacol. 649:74–83. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Kuzuya T, Ishigami M, Ito T, Ishizu Y,
Honda T, Ishikawa T, Hirooka Y and Fujishiro M: Clinical
characteristics and outcomes of candidates for second-line therapy,
including regorafenib and ramucirumab, for advanced hepatocellular
carcinoma after sorafenib treatment. Hepatol Res. 49:1054–1065.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yurdacan B, Egeli U, Guney Eskiler G,
Eryilmaz IE, Cecener G and Tunca B: Investigation of new treatment
option for hepatocellular carcinoma: A combination of sorafenib
with usnic acid. J Pharmacy Pharmacol. 71:1119–1132.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Cheng AL, Guan Z, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S,
Kim JS, Yang TS, Tak WY, Pan H, Yu S, et al: Efficacy and safety of
sorafenib in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
according to baseline status: Subset analyses of the phase III
Sorafenib Asia-Pacific trial. Eur J Cancer. 48:1452–1465.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, Tsao CJ, Qin S,
Kim JS, Luo R, Feng J, Ye S, Yang TS, et al: Efficacy and safety of
sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma: A phase III randomised, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:25–34. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Morisaki T, Umebayashi M, Kiyota A, Koya
N, Tanaka H, Onishi H and Katano M: Combining celecoxib with
sorafenib synergistically inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma cells
in vitro. Anticancer Res. 33:1387–1395. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ceballos MP, Rigalli JP, Cere LI, Semeniuk
M, Catania VA and Ruiz ML: ABC Transporters: Regulation and
association with multidrug resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma
and colorectal carcinoma. Curr Med Chemistry. 26:1224–1250.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Wilhelm S, Carter C, Lynch M, Lowinger T,
Dumas J, Smith RA, Schwartz B, Simantov R and Kelley S: Discovery
and development of sorafenib: A multikinase inhibitor for treating
cancer. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:835–844. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Meyer A, Cygan P, Tolzien K, Galvez AG,
Bitran JD, Lestingi TM and Nabhan C: Role of sorafenib in
overcoming resistance of chemotherapy-failure castration-resistant
prostate cancer. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 12:100–105.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Decker T, Overkamp F, Rösel S, Nusch A,
Göhler T, Indorf M, Sahlmann J and Trarbach T: A randomized phase
II study of paclitaxel alone versus paclitaxel plus sorafenib in
second- and third-line treatment of patients with HER2-negative
metastatic breast cancer (PASO). BMC Cancer. 17(499)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Gongora C: Sorafenib inhibits ABCG2 and
overcomes irinotecan resistance-response. Mol Cancer Ther.
13(764)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Sun Y, Zhang J, Zhou J, Huang Z, Hu H,
Qiao M, Zhao X and Chen D: Synergistic effect of cucurbitacin B in
combination with curcumin via enhancing apoptosis induction and
reversing multidrug resistance in human hepatoma cells. Eur J
Pharmacol. 768:28–40. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Kim JE, Kim SG, Goo JS, Park DJ, Lee YJ,
Hwang IS, Lee HR, Choi SI, Lee YJ, Oh CH, et al: The
α-iso-cubebenol compound isolated from Schisandra chinensis induces
p53-independent pathway-mediated apoptosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 28:1103–1109. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Subramaniam A, Shanmugam MK, Perumal E, Li
F, Nachiyappan A, Dai X, Swamy SN, Ahn KS, Kumar AP, Tan BK, et al:
Potential role of signal transducer and activator of transcription
(STAT)3 signaling pathway in inflammation, survival, proliferation
and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1835:46–60. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Schindler C and Darnell JE Jr:
Transcriptional responses to polypeptide ligands: The JAK-STAT
pathway. Ann Rev Biochem. 64:621–651. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Zeidler MP, Bach EA and Perrimon N: The
roles of the drosophila JAK/STAT pathway. Oncogene. 19:2598–2606.
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Hirano T, Ishihara K and Hibi M: Roles of
STAT3 in mediating the cell growth, differentiation and survival
signals relayed through the IL-6 family of cytokine receptors.
Oncogene. 19:2548–2556. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Yoshikawa H, Matsubara K, Qian GS, Jackson
P, Groopman JD, Manning JE, Harris CC and Herman JG: SOCS-1, a
negative regulator of the JAK/STAT pathway, is silenced by
methylation in human hepatocellular carcinoma and shows
growth-suppression activity. Nat Genet. 28:29–35. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Niwa Y, Kanda H, Shikauchi Y, Saiura A,
Matsubara K, Kitagawa T, Yamamoto J, Kubo T and Yoshikawa H:
Methylation silencing of SOCS-3 promotes cell growth and migration
by enhancing JAK/STAT and FAK signalings in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncogene. 24:6406–6417. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Feng DY, Zheng H, Tan Y and Cheng RX:
Effect of phosphorylation of MAPK and Stat3 and expression of c-fos
and c-jun proteins on hepatocarcinogenesis and their clinical
significance. World J Gastroenterol. 7:33–36. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Lee C and Cheung ST: STAT3: An emerging
therapeutic target for hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel).
11(1646)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|