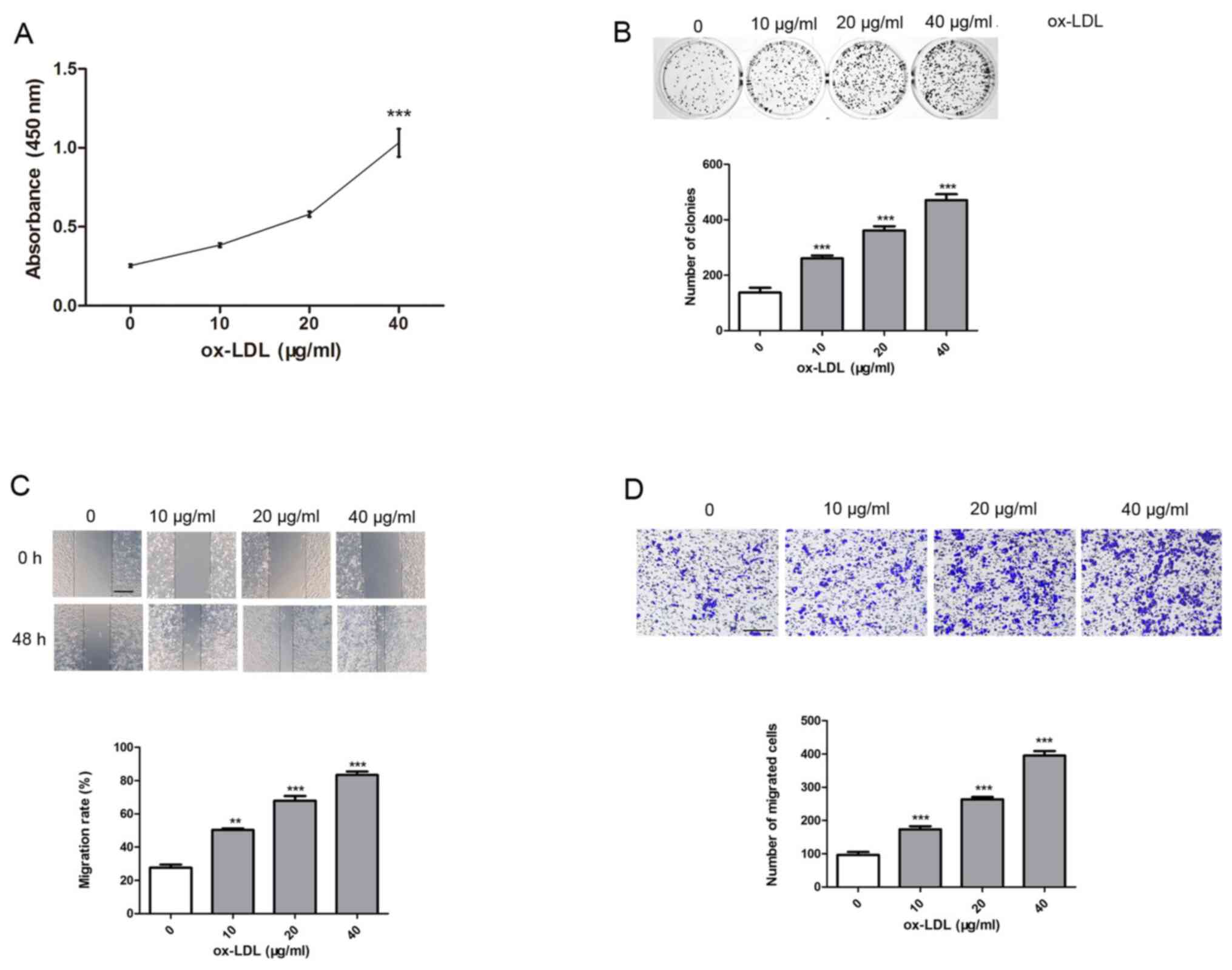
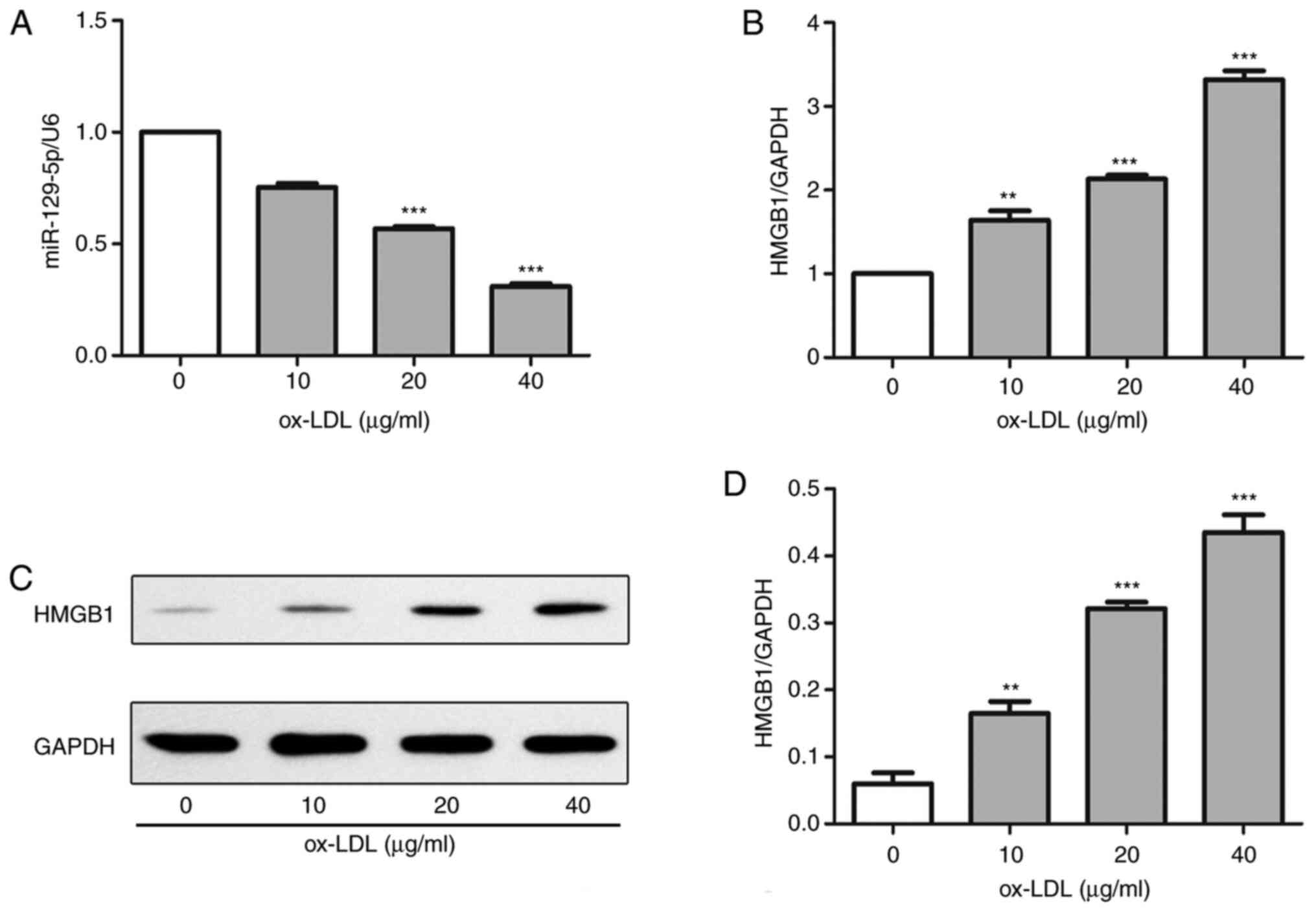
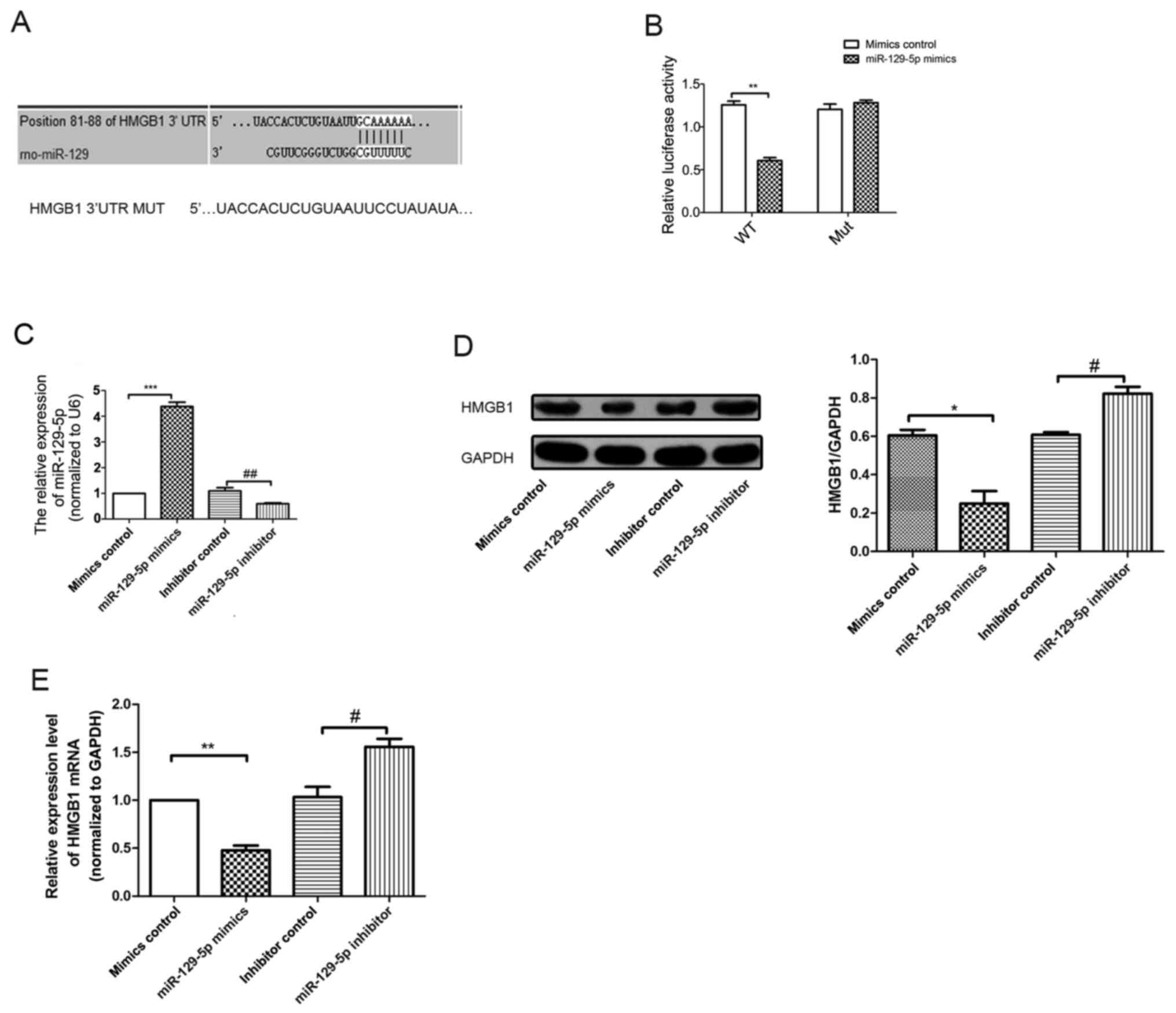
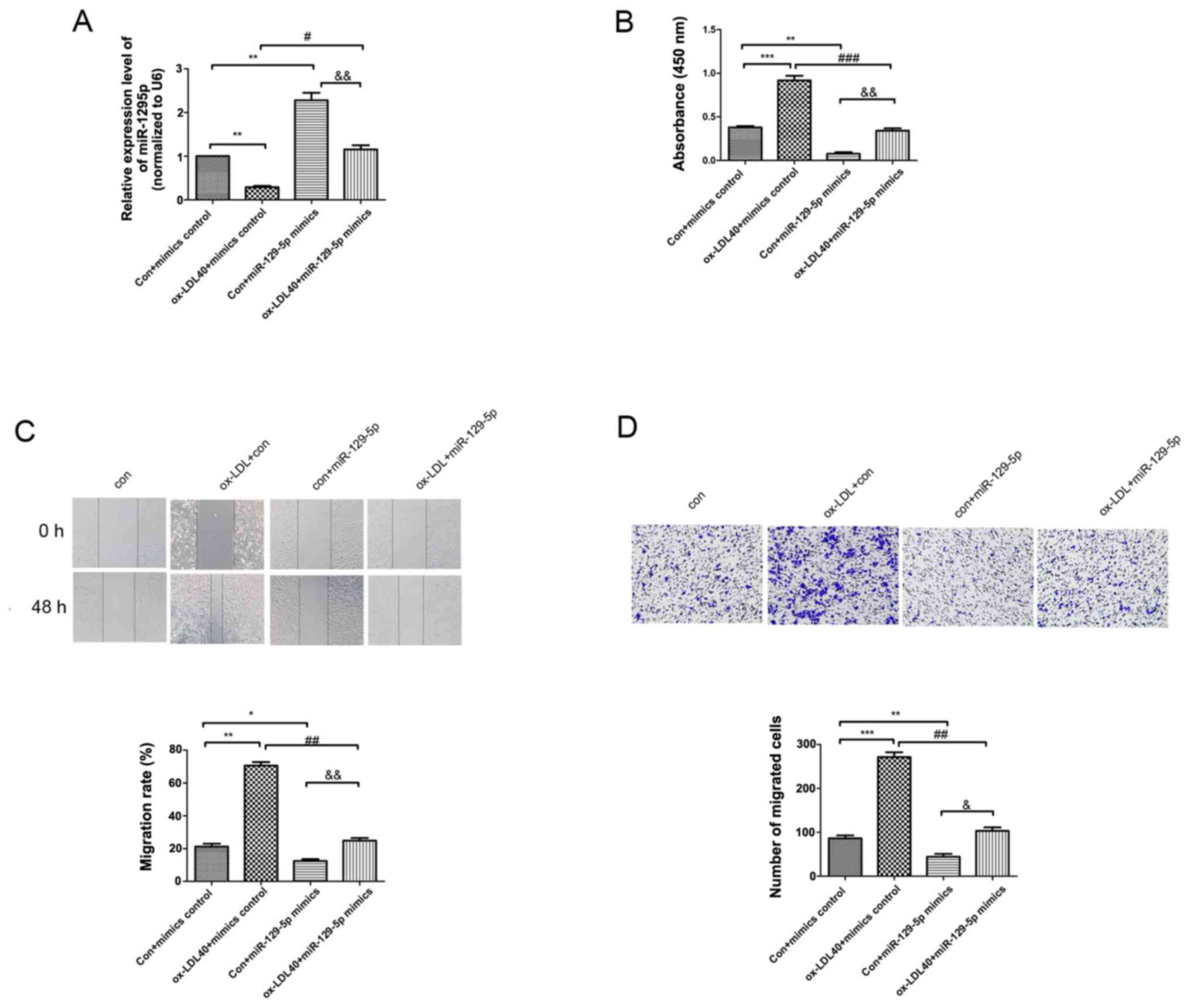
|
1
|
Jackson J, Patterson AJ, MacDonald-Wicks L
and McEvoy M: The role of inorganic nitrate and nitrite in CVD.
Nutr Res Rev. 30:247–264. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Veerbeek JH, Brouwers L, Koster MP, Koenen
SV, van Vliet EO, Nikkels PG, Franx A and van Rijn BB: Spiral
artery remodeling and maternal cardiovascular risk: The spiral
artery remodeling (SPAR) study. J Hypertens. 34:1570–1577.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sivasinprasasn S, Wikan N, Tocharus J,
Chaichompoo W, Suksamrarn A and Tocharus C: Pelargonic acid
vanillylamide and rosuvastatin protect against oxidized low-density
lipoprotein-induced endothelial dysfunction by inhibiting the
NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway and improving cell-cell junctions. Chem Biol
Interact. 345(109572)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Groenen AG, Halmos B, Tall AR and
Westerterp M: Cholesterol efflux pathways, inflammation, and
atherosclerosis. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 56:426–439.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Valanti EK, Dalakoura-Karagkouni K, Siasos
G, Kardassis D, Eliopoulos AG and Sanoudou D: Advances in
biological therapies for dyslipidemias and atherosclerosis.
Metabolism. 116(154461)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Zhou Z, Subramanian P, Sevilmis G, Globke
B, Soehnlein O, Karshovska E, Megens R, Heyll K, Chun J,
Saulnier-Blache JS, et al: Lipoprotein-derived lysophosphatidic
acid promotes atherosclerosis by releasing CXCL1 from the
endothelium. Cell Metab. 13:592–600. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pirillo A, Norata GD and Catapano AL:
LOX-1, OxLDL, and atherosclerosis. Mediators Inflamm.
2013(152786)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yu Q, Chen S, Tang H, Zhang X, Tao R, Yan
Z, Shi J, Guo W and Zhang S: Veratric acid alleviates liver
ischemia/reperfusion injury by activating the Nrf2 signaling
pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 101(108294)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Gu Y, Xiao ZH, Wu J, Guo M, Lv P and Dou
N: Anti-atherosclerotic effect of afrocyclamin A against vascular
smooth muscle cells is mediated via p38 MAPK signaling pathway.
Cell J. 23:191–198. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yang Y, Yang L, Liang X and Zhu G:
MicroRNA-155 promotes atherosclerosis inflammation via targeting
SOCS1. Cell Physiol Biochem. 36:1371–1381. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Toba H, Cortez D, Lindsey ML and Chilton
RJ: Applications of miRNA technology for atherosclerosis. Curr
Atheroscler Rep. 16(386)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zhang Z, Pan X, Yang S, Ma A, Wang K, Wang
Y, Li T and Liu S: miR-155 promotes ox-LDL-induced autophagy in
human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mediators Inflamm.
2017(9174801)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Arai K, Jin G, Navaratna D and Lo EH:
Brain angiogenesis in developmental and pathological processes:
Neurovascular injury and angiogenic recovery after stroke. FEBS J.
276:4644–4652. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Geng Z, Xu F and Zhang Y:
MiR-129-5p-mediated Beclin-1 suppression inhibits endothelial cell
autophagy in atherosclerosis. Am J Transl Res. 8:1886–1894.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun X, Icli B, Wara AK, Belkin N, He S,
Kobzik L, Hunninghake GM and Vera MP: MICU Registry. Blackwell TS,
et al: MicroRNA-181b regulates NF-κB-mediated vascular
inflammation. J Clin Invest. 122:1973–1990. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Liu X, Cheng Y, Yang J, Xu L and Zhang C:
Cell-specific effects of miR-221/222 in vessels: Molecular
mechanism and therapeutic application. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
52:245–255. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Xin M, Small EM, Sutherland LB, Qi X,
McAnally J, Plato CF, Richardson JA, Bassel-Duby R and Olson EN:
MicroRNAs miR-143 and miR-145 modulate cytoskeletal dynamics and
responsiveness of smooth muscle cells to injury. Genes Dev.
23:2166–2178. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu YR, Chen JJ and Dai M: Paeonol
protects rat vascular endothelial cells from ox-LDL-induced injury
via downregulating microRNA-21 expression and TNF-α release. Acta
Pharmacol Sin. 35:483–488. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xu C, Shao Y, Xia T, Yang Y, Dai J, Luo L,
Zhang X, Sun W, Song H, Xiao B and Guo J: lncRNA-AC130710 targeting
by miR-129-5p is upregulated in gastric cancer and associates with
poor prognosis. Tumor Biol. 35:9701–9706. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Long XH, Zhou YF, Peng AF, Zhang ZH, Chen
XY, Chen WZ, Liu JM, Huang SH and Liu ZL: Demethylation-mediated
miR-129-5p up-regulation inhibits malignant phenotype of osteogenic
osteosarcoma by targeting Homo sapiens valosin-containing protein
(VCP). Tumor Biol. 36:3799–3806. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Feng J, Guo J, Wang JP and Chai BF:
MiR-129-5p inhibits proliferation of gastric cancer cells through
targeted inhibition on HMGB1 expression. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
24:3665–3673. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Pang X, Zhang Y and Zhang S: High-mobility
group box 1 is overexpressed in cervical carcinoma and promotes
cell invasion and migration. Oncol Rep. 37:831–840. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wu CY, Zhou ZF, Wang B, Ke ZP, Ge ZC and
Zhang XJ: MicroRNA-328 ameliorates oxidized low-density
lipoprotein-induced endothelial cells injury through targeting
HMGB1 in atherosclerosis. J Cell Biochem, Oct 15, 2018 (Epub ahead
of print). doi: 10.1002/jcb.27469.
|
|
24
|
Moreno JA, Sastre C, Madrigal-Matute J,
Muñoz-García B, Ortega L, Burkly LC, Egido J, Martín-Ventura JL and
Blanco-Colio LM: HMGB1 expression and secretion are increased via
TWEAK-Fn14 interaction in atherosclerotic plaques and cultured
monocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 33:612–620.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Chen Y, Jiang J, Miao H, Chen X, Sun X and
Li Y: Hydrogen-rich saline attenuates vascular smooth muscle cell
proliferation and neointimal hyperplasia by inhibiting reactive
oxygen species production and inactivating the Ras-ERK1/2-MEK1/2
and Akt pathways. Int J Mol Med. 31:597–606. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Xiao S, Zhang D, Liu Z, Jin W, Huang G,
Wei Z, Wang D and Deng C: Diabetes-induced glucolipotoxicity
impairs wound healing ability of adipose-derived stem cells-through
the miR-1248/CITED2/HIF-1α pathway. Aging (Albany NY).
12:6947–6965. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Soares AC and Fonseca DA: Cardiovascular
diseases: A therapeutic perspective around the clock. Drug Discov
Today. 25:1086–1098. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Benjamin EJ, Virani SS, Callaway CW,
Chamberlain AM, Chang AR, Cheng S, Chiuve SE, Cushman M, Delling
FN, Deo R, et al: Heart disease and stroke statistics-2018 update:
A report from the american heart association. Circulation.
137:e67–e492. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Pastore I, Bolla AM, Montefusco L, Lunati
ME, Rossi A, Assi E, Zuccotti GV and Fiorina P: The impact of
diabetes mellitus on cardiovascular risk onset in children and
adolescents. Int J Mol Sci. 21(4928)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ezzatvar Y, Izquierdo M, Núñez J,
Calatayud J, Ramírez-Vélez R and García-Hermoso A:
Cardiorespiratory fitness measured with cardiopulmonary exercise
testing and mortality in patients with cardiovascular disease: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. J Sport Health Sci.
10:609–619. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mehta D and Malik AB: Signaling mechanisms
regulating endothelial permeability. Physiol Rev. 86:279–367.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Koshman YE, Patel N, Chu M, Iyengar R, Kim
T, Ersahin C, Lewis W, Heroux A and Samarel AM: Regulation of
connective tissue growth factor gene expression and fibrosis in
human heart failure. J Card Fail. 19:283–294. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Soltani A, Argani H, Rahimipour H,
Soleimani F, Rahimi F and Kazerouni F: Oxidized LDL: As a risk
factor for cardiovascular disease in renal transplantation. J Bras
Nefrol. 38:147–152. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In English,
Portuguese).
|
|
35
|
Maiolino G, Rossitto G, Caielli P, Bisogni
V, Rossi GP and Calò LA: The role of oxidized low-density
lipoproteins in atherosclerosis: The myths and the facts. Mediators
Inflamm. 2013(714653)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Chang TY, Tsai WC, Huang TS, Su SH, Chang
CY, Ma HY, Wu CH, Yang CY, Lin CH, Huang PH, et al: Dysregulation
of endothelial colony-forming cell function by a negative feedback
loop of circulating miR-146a and -146b in cardiovascular disease
patients. PLoS One. 12(e0181562)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Li W, Zhi W, Liu F, He Z, Wang X and Niu
X: Atractylenolide I restores HO-1 expression and inhibits
Ox-LDL-induced VSMCs proliferation, migration and inflammatory
responses. Exp Cell Res. 353:26–34. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang L, Cheng H, Yue Y, Li S, Zhang D and
He R: H19 knockdown suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis
by regulating miR-148b/WNT/β-catenin in ox-LDL-stimulated vascular
smooth muscle cells. J Biomed Sci. 25(11)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Madrigal-Matute J, Rotllan N, Aranda JF
and Fernández-Hernando C: MicroRNAs and atherosclerosis. Curr
Atheroscler Rep. 15(322)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Florijn BW, Bijkerk R, van der Veer EP and
van Zonneveld AJ: Gender and cardiovascular disease: Are sex-biased
microRNA networks a driving force behind heart failure with
preserved ejection fraction in women? Cardiovasc Res. 114:210–225.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Ruan Z, Chu T, Wu L, Zhang M, Zheng M,
Zhang Q, Zhou M and Zhu G: miR-155 inhibits oxidized low-density
lipoprotein-induced apoptosis in different cell models by targeting
the p85α/AKT pathway. J Physiol Biochem. 76:329–343.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Luo J, Chen J and He L: mir-129-5p
attenuates irradiation-induced autophagy and decreases
radioresistance of breast cancer cells by targeting HMGB1. Med Sci
Monit. 21:4122–4129. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Han JS, Kim K and Lee M: A high mobility
group B-1 box A peptide combined with an artery wall binding
peptide targets delivery of nucleic acids to smooth muscle cells. J
Cell Biochem. 107:163–170. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lamb FS, Choi H, Miller MR and Stark RJ:
TNFα and reactive oxygen signaling in vascular smooth muscle cells
in hypertension and atherosclerosis. Am J Hypertens. 33:902–913.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zhu XS, Zhou HY, Yang F, Zhang HS and Ma
KZ: miR-381-3p inhibits high glucose-induced vascular smooth muscle
cell proliferation and migration by targeting HMGB1. J Gene Med.
23(e3274)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Chen Z, Pan X, Sheng Z, Yan G, Chen L and
Ma G: Baicalin suppresses the proliferation and migration of
Ox-LDL-VSMCs in atherosclerosis through upregulating miR-126-5p.
Biol Pharm Bull. 42:1517–1523. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|