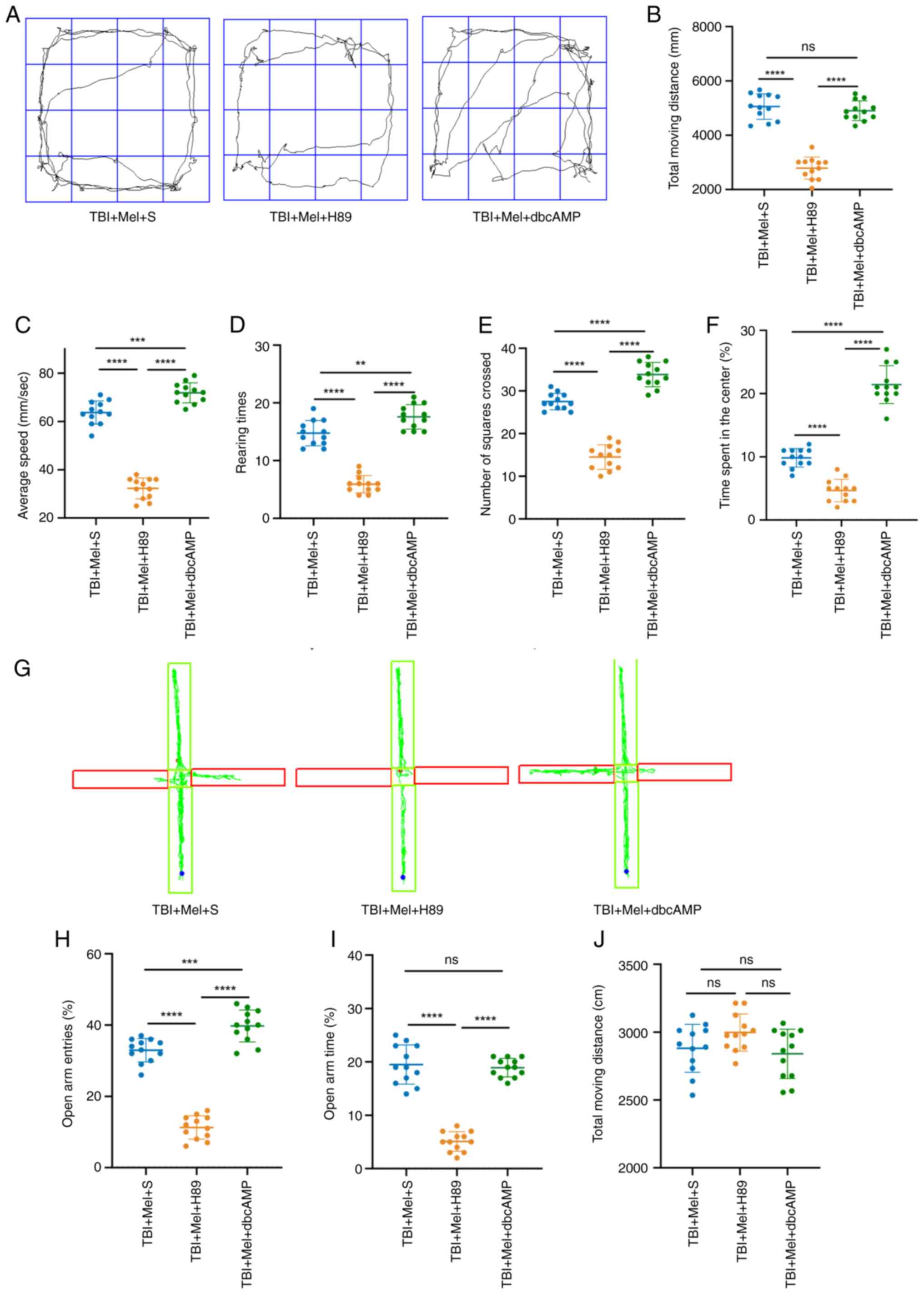
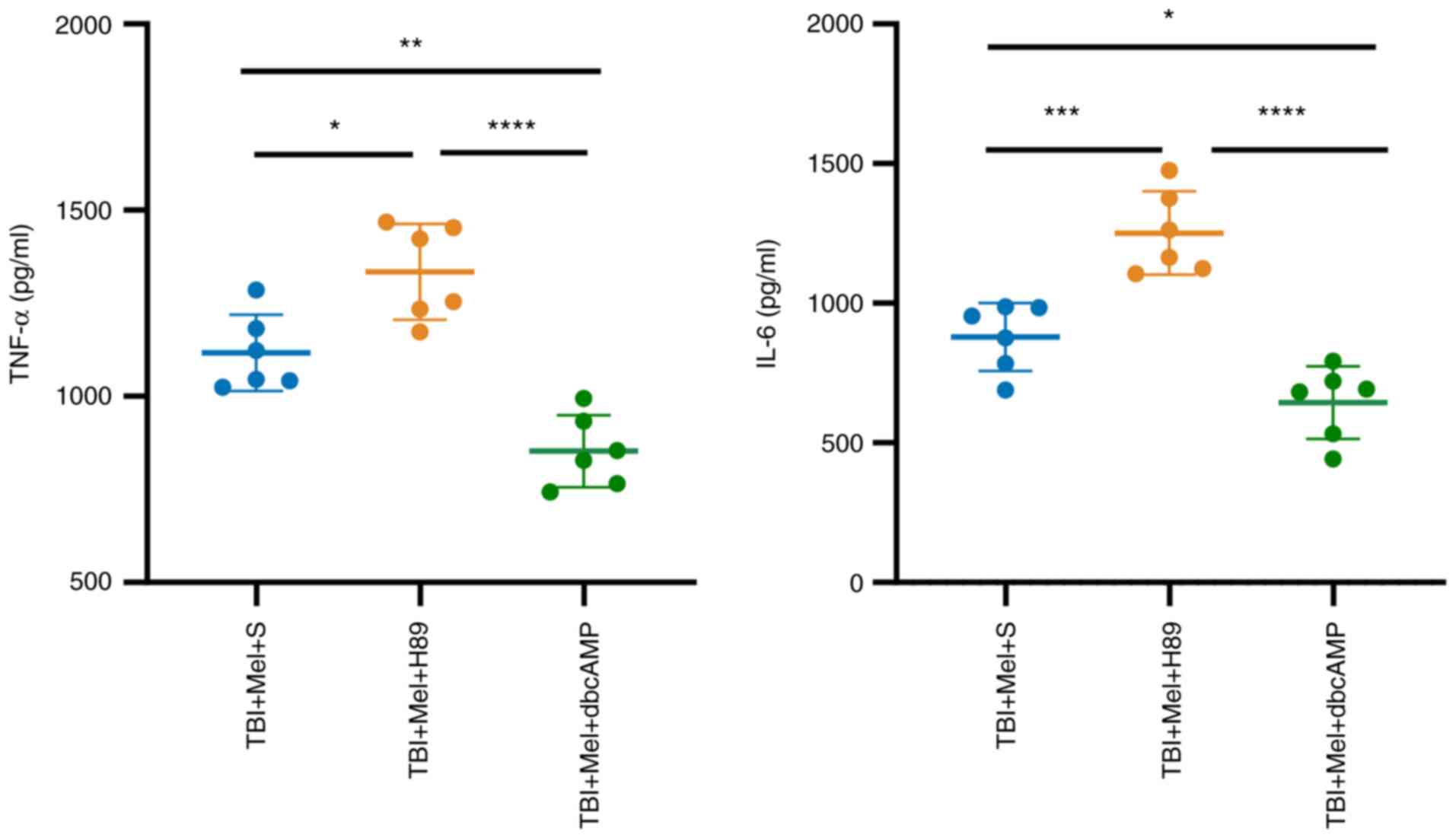
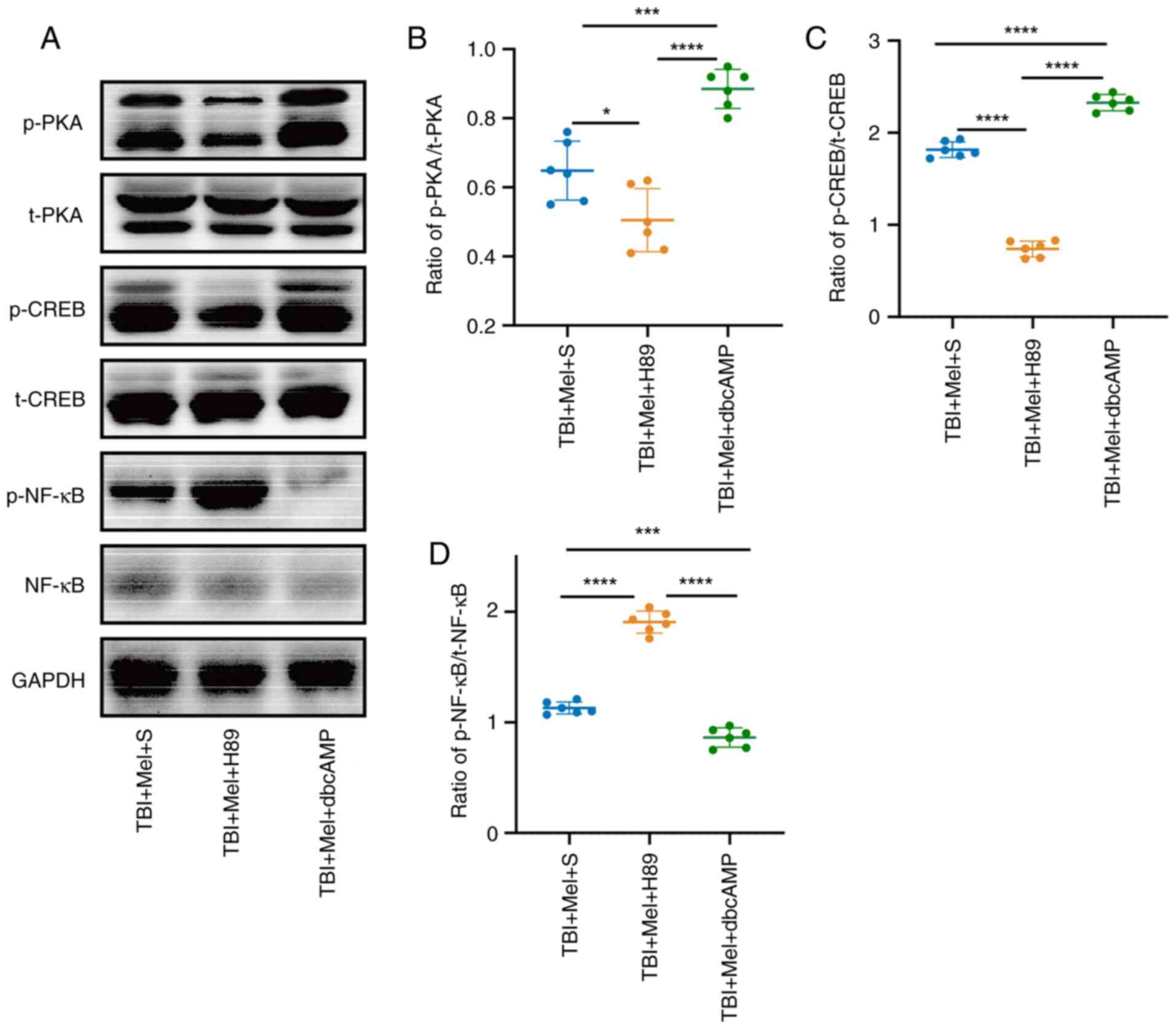
|
1
|
Studlack PE, Keledjian K, Farooq T,
Akintola T, Gerzanich V, Simard JM and Keller A: Blast-induced
brain injury in rats leads to transient vestibulomotor deficits and
persistent orofacial pain. Brain Inj. 32:1866–1878. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Capizzi A, Woo J and Verduzco-Gutierrez M:
Traumatic brain injury: An overview of epidemiology,
pathophysiology, and medical management. Med Clin North Am.
104:213–238. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Yatsiv I, Grigoriadis N, Simeonidou C,
Stahel PF, Schmidt OI, Alexandrovitch AG, Tsenter J and Shohami E:
Erythropoietin is neuroprotective, improves functional recovery,
and reduces neuronal apoptosis and inflammation in a rodent model
of experimental closed head injury. FASEB J. 19:1701–1703.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Adibhatla RM and Hatcher JF: Lipid
oxidation and peroxidation in CNS health and disease: From
molecular mechanisms to therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 12:125–169. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Adhikari A, Lerner TN, Finkelstein J, Pak
S, Jennings JH, Davidson TJ, Ferenczi E, Gunaydin LA, Mirzabekov
JJ, Ye L, et al: Basomedial amygdala mediates top-down control of
anxiety and fear. Nature. 527:179–185. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jayakar R, Tone EB, Crosson B, Turner JA,
Anderson PL, Phan KL and Klumpp H: Amygdala volume and social
anxiety symptom severity: Does segmentation technique matter?
Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging. 295(111006)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ji J, Kline AE, Amoscato A, Samhan-Arias
AK, Sparvero LJ, Tyurin VA, Tyurina YY, Fink B, Manole MD, Puccio
AM, et al: Lipidomics identifies cardiolipin oxidation as a
mitochondrial target for redox therapy of brain injury. Nat
Neurosci. 15:1407–1413. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hill RL, Singh IN, Wang JA, Kulbe JR and
Hall ED: Protective effects of phenelzine administration on
synaptic and non-synaptic cortical mitochondrial function and lipid
peroxidation-mediated oxidative damage following TBI in young adult
male rats. Exp Neurol. 2020(113322)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Chiu CC, Liao YE, Yang LY and Wang JY,
Tweedie D, Karnati HK, Greig NH and Wang JY: Neuroinflammation in
animal models of traumatic brain injury. J Neurosci Methods.
272:38–49. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Maas AI, Roozenbeek B and Manley GT:
Clinical trials in traumatic brain injury: Past experience and
current developments. Neurotherapeutics. 7:115–126. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Koh PO: Melatonin regulates the
calcium-buffering proteins, parvalbumin and hippocalcin, in
ischemic brain injury. J Pineal Res. 53:358–365. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ding K, Wang H, Xu J, Li T, Zhang L, Ding
Y, Zhu L, He J and Zhou M: Melatonin stimulates antioxidant enzymes
and reduces oxidative stress in experimental traumatic brain
injury: The Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway as a potential mechanism.
Free Radic Biol Med. 73:1–11. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang Z, Ma C, Meng CJ, Zhu GQ, Sun XB, Huo
L, Zhang J, Liu HX, He WC, Shen XM, et al: Melatonin activates the
Nrf2-ARE pathway when it protects against early brain injury in a
subarachnoid hemorrhage model. J Pineal Res. 53:129–137.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Osier N, McGreevy E, Pham L, Puccio A, Ren
D, Conley YP, Alexander S and Dixon CE: Melatonin as a therapy for
traumatic brain injury: A review of published evidence. Int J Mol
Sci. 19(1539)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Rehman SU, Ikram M, Ullah N, Alam SI, Park
HY, Badshah H, Choe K and Kim MO: Neurological Enhancement effects
of melatonin against brain injury-induced oxidative stress,
neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration via AMPK/CREB signaling.
Cells. 8(760)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Cheung RT, Tipoe GL, Tam S, Ma ES, Zou LY
and Chan PS: Preclinical evaluation of pharmacokinetics and safety
of melatonin in propylene glycol for intravenous administration. J
Pineal Res. 41:337–343. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kaur C, Sivakumar V, Robinson R, Foulds
WS, Luu CD and Ling EA: Neuroprotective effect of melatonin against
hypoxia-induced retinal ganglion cell death in neonatal rats. J
Pineal Res. 54:190–206. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zyuz'kov GN, Miroshnichenko LA, Polyakova
TY, Stavrova LA, Simanina EV, Agafonov VI and Zhdanov VV:
Participation of cAMP/PKA-Mediated signaling pathways in functional
activity of regeneration-competent cells in the nervous tissue
under conditions of ethanol-induced neurodegeneration. Bull Exp
Biol Med. 167:723–727. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gao X, Zhang X, Cui L, Chen R, Zhang C,
Xue J, Zhang L, He W, Li J, Wei S, et al: Ginsenoside Rb1 promotes
motor functional recovery and axonal regeneration in post-stroke
mice through cAMP/PKA/CREB signaling pathway. Brain Res Bull.
154:51–60. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ye J, Yin Y, Liu H, Fang L, Tao X, Wei L,
Zuo Y, Yin Y, Ke D and Wang JZ: Tau inhibits PKA by nuclear
proteasome-dependent PKAR2α elevation with suppressed CREB/GluA1
phosphorylation. Aging Cell. 19(e13055)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ma CL, Li L, Yang GM, Zhang ZB, Zhao YN,
Zeng XF, Zhang DX, Yu Y, Shi ZJ, Yan QW, et al: Neuroprotective
effect of gastrodin in methamphetamine-induced apoptosis through
regulating cAMP/PKA/CREB pathway in cortical neuron. Hum Exp
Toxicol. 39:1118–1129. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yang L, Shi LJ, Yu J and Zhang YQ:
Activation of protein kinase A in the amygdala modulates
anxiety-like behaviors in social defeat exposed mice. Mol Brain.
9(3)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sung JY, Bae JH, Lee JH, Kim YN and Kim
DK: The melatonin signaling pathway in a long-term memory in vitro
study. Molecules. 23(737)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Li C, Chen T, Zhou H, Feng Y, Hoi MPM, Ma
D, Zhao C, Zheng Y and Lee SMY: BHDPC is a novel neuroprotectant
that provides anti-neuroinflammatory and neuroprotective effects by
inactivating NF-κB and activating PKA/CREB. Front Pharmacol.
25(614)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ding K, Xu J, Wang H, Zhang L, Wu Y and Li
T: Melatonin protects the brain from apoptosis by enhancement of
autophagy after traumatic brain injury in mice. Neurochem Int.
91:46–54. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Song J, Cheon SY, Lee WT, Park KA and Lee
JE: PKA Inhibitor H89
(N-[2-p-bromocinnamylamino-ethyl]-5-isoquinolinesulfonamide)
attenuates synaptic dysfunction and neuronal cell death following
ischemic injury. Neural Plast. 2015(374520)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Salehi F, Hosseini-Zare MS, Aghajani H,
Seyedi SY, Hosseini-Zare MS and Sharifzadeh M: Effect of
bucladesine, pentoxifylline, and H-89 as cyclic adenosine
monophosphate analog, phosphodiesterase, and protein kinase A
inhibitor on acute pain. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 31:411–419.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Shishido H, Ueno M, Sato K, Matsumura M,
Toyota Y, Kirino Y, Tamiya T, Kawai N and Kishimoto Y: Traumatic
brain injury by weight-drop method causes transient amyloid-β
deposition and acute cognitive deficits in mice. Behav Neurol.
2019(3248519)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Oh HM, Lee JS, Kim SW, Oh YT, Kim WY, Lee
SB, Cho YR, Jeon YJ, Cho JH and Son CG: Uwhangchungsimwon, A
standardized herbal drug, exerts an anti-depressive effect in a
social isolation stress-induced mouse model. Front Pharmacol.
10(1674)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kondo A, Shahpasand K, Mannix R, Qiu J,
Moncaster J, Chen CH, Yao Y, Lin YM, Driver JA, Sun Y, et al:
Antibody against early driver of neurodegeneration cis P-tau blocks
brain injury and tauopathy. Nature. 523:431–436. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Tajiri N, Acosta SA, Shahaduzzaman M,
Ishikawa H, Shinozuka K, Pabon M, Hernandez-Ontiveros D, Kim DW,
Metcalf C, Staples M, et al: Intravenous transplants of human
adipose-derived stem cell protect the brain from traumatic brain
injury-induced neurodegeneration and motor and cognitive
impairments: Cell graft biodistribution and soluble factors in
young and aged rats. J Neurosci. 34:313–326. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yu S, Kaneko Y, Bae E, Stahl E, Wang Y,
van Loveren H, Sanberg PR and Borlongan CV: Severity of controlled
cortical impact traumatic brain injury in rats and mice dictates
degree of behavioral deficits. Brain Res. 1287:157–163.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chen H, Sun X, Yang X, Hou Y, Yu X, Wang
Y, Wu J, Liu D, Wang H, Yu J and Yi W: Dexmedetomidine reduces
ventilator-induced lung injury (VILI) by inhibiting Toll-like
receptor 4 (TLR4)/nuclear factor (NF)-κB signaling pathway. Bosn J
Basic Med Sci. 18:162–169. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Popovitz J, Mysore SP and Adwanikar H:
Long-term effects of traumatic brain injury on anxiety-like
behaviors in mice: Behavioral and neural correlates. Front Behav
Neurosci. 13(6)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Chitturi J, Li Y, Santhakumar V and
Kannurpatti SS: Early behavioral and metabolomic change after mild
to moderate traumatic brain injury in the developing brain.
Neurochem Int. 120:75–86. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Šimić G, Tkalčić M, Vukić V, Mulc D,
Španić E, Šagud M, Olucha-Bordonau FE, Vukšić M and R Hof P:
Understanding emotions: Origins and roles of the amygdala.
Biomolecules. 11(823)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Herrington JD, Miller JS, Pandey J and
Schultz RT: Anxiety and social deficits have distinct relationships
with amygdala function in autism spectrum disorder. Soc Cogn Affect
Neurosci. 11:907–914. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sullivan PG, Sebastian AH and Hall ED:
Therapeutic window analysis of the neuroprotective effects of
cyclosporine A after traumatic brain injury. J Neurotrauma.
28:311–318. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Neal M and Richardson JR: Epigenetic
regulation of astrocyte function in neuroinflammation and
neurodegeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1864:432–443. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Chávez CE, Oyarzún JE, Avendaño BC,
Mellado LA, Inostroza CA, Alvear TF and Orellana JA: The opening of
connexin 43 hemichannels alters hippocampal astrocyte function and
neuronal survival in prenatally LPS-Exposed adult offspring. Front
Cell Neurosci. 13(460)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Fujita A, Yamaguchi H, Yamasaki R, Cui Y,
Matsuoka Y, Yamada KI and Kira JI: Connexin 30 deficiency
attenuates A2 astrocyte responses and induces severe
neurodegeneration in a 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine
hydrochloride Parkinson's disease animal model. J
Neuroinflammation. 15(227)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Witcher KG, Bray CE, Dziabis JE, McKim DB,
Benner BN, Rowe RK, Kokiko-Cochran ON, Popovich PG, Lifshitz J,
Eiferman DS and Godbout JP: Traumatic brain injury-induced neuronal
damage in the somatosensory cortex causes formation of rod-shaped
microglia that promote astrogliosis and persistent
neuroinflammation. Glia. 66:2719–2736. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Gao TL, Yuan XT, Yang D, Dai HL, Wang WJ,
Peng X, Shao HJ, Jin ZF and Fu ZJ: Expression of HMGB1 and RAGE in
rat and human brains after traumatic brain injury. J Trauma Acute
Care Surg. 72:643–649. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Hirsch EC, Breidert T, Rousselet E, Hunot
S, Hartmann A and Michel PP: The role of glial reaction and
inflammation in Parkinson's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 991:214–228.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ley EJ, Clond MA, Singer MB, Shouhed D and
Salim A: IL6 deficiency affects function after traumatic brain
injury. J Surg Res. 170:253–256. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Baratz R, Tweedie D, Wang JY, Rubovitch V,
Luo W, Hoffer BJ, Greig NH and Pick CG: Transiently lowering tumor
necrosis factor-alpha synthesis ameliorates neuronal cell loss and
cognitive impairments induced by minimal traumatic brain injury in
mice. J Neuroinflammation. 12(45)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Xing J, Han D, Xu D, Li X and Sun L: CREB
Protects against temporal lobe epilepsy associated with cognitive
impairment by controlling oxidative neuronal damage. Neurodegener
Dis. 19:225–237. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Yang Y, Ma S, Wei F, Liang G, Yang X,
Huang Y, Wang J and Zou Y: Pivotal role of cAMP-PKA-CREB signaling
pathway in manganese-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells. Environ
Toxicol. 34:1052–1062. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Ciani E, Guidi S, Della Valle G, Perini G,
Bartesaghi R and Contestabile A: Withdrawal: Nitric oxide protects
neuroblastoma cells from apoptosis induced by serum deprivation
through cAMP-response element-binding protein (CREB) activation. J
Biol Chem. 295(3391)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Purves GI, Kamishima T, Davies LM, Quayle
JM and Dart C: Exchange protein activated by cAMP (Epac) mediates
cAMP-dependent but protein kinase A-insensitive modulation of
vascular ATP-sensitive potassium channels. J Physiol.
587:3639–3650. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Aesoy R, Muwonge H, Asrud KS, Sabir M,
Witsoe SL, Bjornstad R, Kopperud RK, Hoivik EA, Doskeland SO and
Bakke M: Deletion of exchange proteins directly activated by cAMP
(Epac) causes defects in hippocampal signaling in female mice. PLoS
One. 13(e0200935)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|