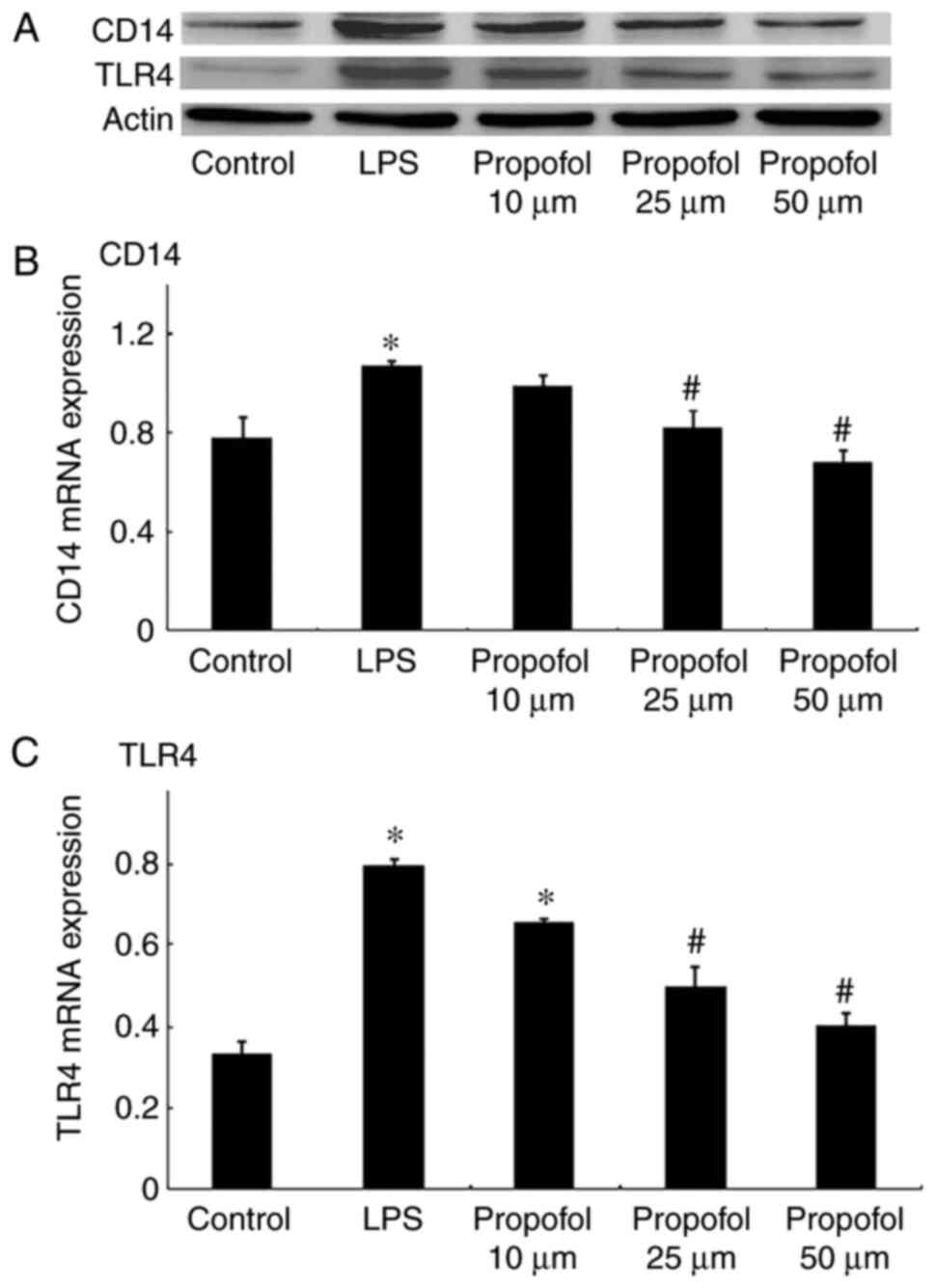
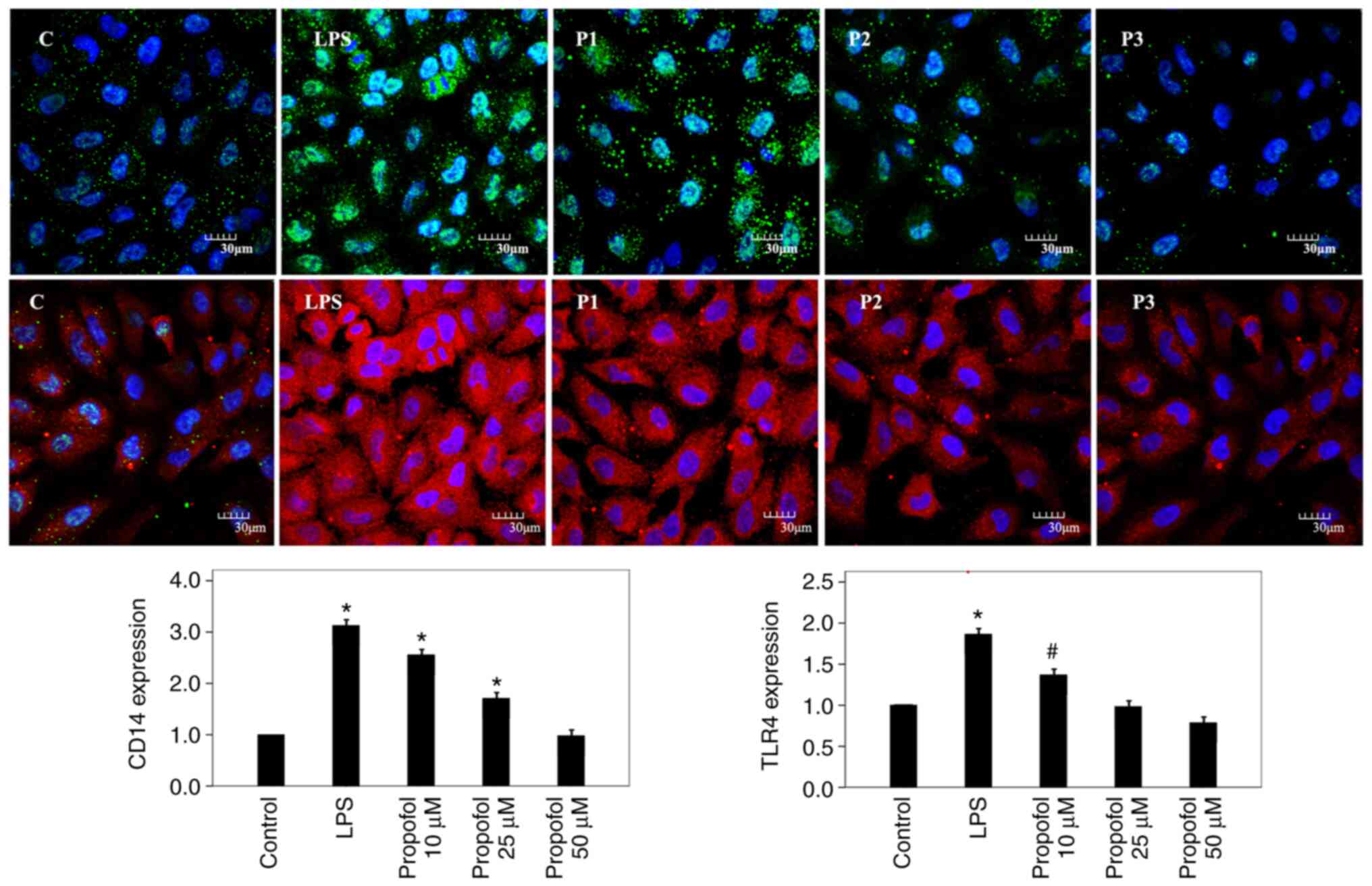
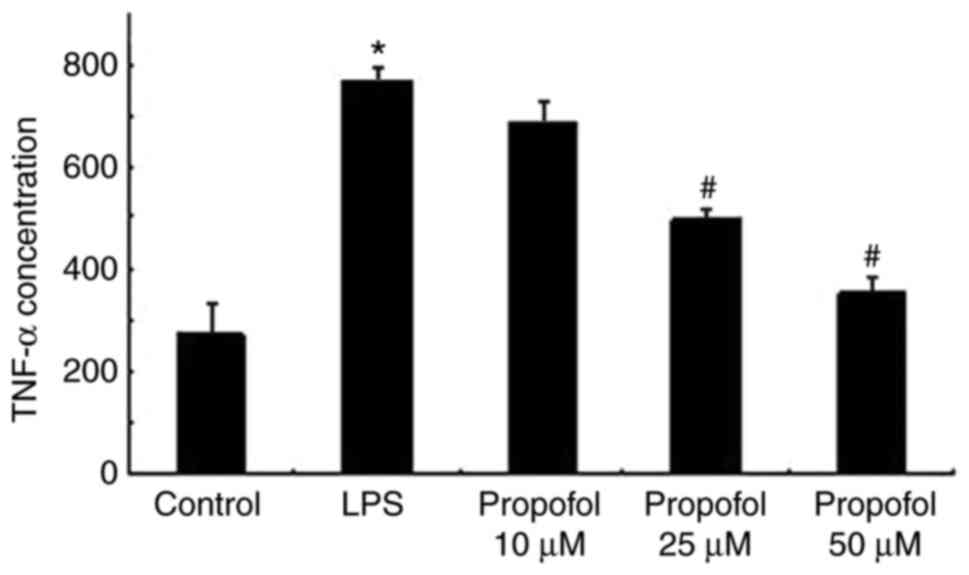
|
1
|
Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han
Y, Qiu Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Wei Y, et al: Epidemiological and clinical
characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in
Wuhan, China: A descriptive study. Lancet. 395:507–513.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Dorward DA, Russell CD, Um IH, Elshani M,
Armstrong SD, Penrice-Randal R, Millar T, Lerpiniere CEB,
Tagliavini G, Hartley CS, et al: Tissue-specific immunopathology in
fatal COVID-19. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 203:192–201.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Pairo-Castineira E, Clohisey S, Klaric L,
Bretherick AD, Rawlik K, Pasko D, Walker S, Parkinson N, Fourman
MH, Russell CD, et al: Genetic mechanisms of critical illness in
COVID-19. Nature. 591:92–98. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Baedorf Kassis E, Schaefer MS, Maley JH,
Hoenig B, Loo Y, Hayes MM, Moskowitz A and Talmor D: Transpulmonary
pressure measurements and lung mechanics in patients with early
ARDS and SARS-CoV-2. J Crit Care. 63:106–112. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Smith S, Skerrett SJ, Chi EY, Jonas M,
Mohler K and Wilson CB: The locus of tumor necrosis factor-alpha
action in lung inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 19:881–891.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Knox KW, Vesk M and Work E: Relation
between excreted lipopolysaccharide complexes and surface
structures of a lysine-limited culture of Escherichia coli. J
Bacteriol. 92:1206–1217. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Nova Z, Skovierova H and Calkovska A:
Alveolar-capillary membrane-related pulmonary cells as a target in
endotoxin-induced acute lung injury. Int J Mol Sci.
20(831)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chacko B, Peter JV, Tharyan P, John G and
Jeyaseelan L: Pressure-controlled versus volume-controlled
ventilation for acute respiratory failure due to acute lung injury
(ALI) or acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Cochrane
Database Syst Rev. 1(CD008807)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhu T, Zhang W, Feng SJ and Yu HP: Emodin
suppresses LPS-induced inflammation in RAW264.7 cells through a
PPARγ-dependent pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 34:16–24.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Sivanantham A, Pattarayan D, Bethunaickan
R, Kar A, Mahapatra SK, Thimmulappa RK, Palanichamy R and
Rajasekaran S: Tannic acid protects against experimental acute lung
injury through downregulation of TLR4 and MAPK. J Cell Physiol.
234:6463–6476. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li HF, Wu YL, Tseng TL, Chao SW, Lin H and
Chen HH: Inhibition of miR-155 potentially protects against
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury through the
IRF2BP2-NFAT1 pathway. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 319:C1070–C1081.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Wang H, Wang T, Yuan Z, Cao Y, Zhou Y, He
J, Shen Y, Zeng N, Dai L, Wen F and Chen L: Role of receptor for
advanced glycation end products in regulating lung fluid balance in
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and infection-related
acute respiratory distress syndrome. Shock. 50:472–482.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Meyer K, Patra T, Vijayamahantesh
and Ray R: SARS-CoV-2 spike protein induces paracrine senescence
and leukocyte adhesionin endothelial cells. J Virol.
95(E0079421)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Schiller HB, van Breugel M and Nawijn MC:
SARS-CoV-2-specific hotspots in virus-host interaction networks.
Nat Immunol. 22:806–808. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Nakamura M, Takeuchi T, Shirakawa K and
Furusako S: Anti-human CD14 monoclonal antibody improves survival
following sepsis induced by endotoxin, but not following
polymicrobial infection. Eur J Pharmacol. 806:18–24.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lappin MJ, Brown V, Zaric SS, Lundy FT,
Coulter WA and Irwin CR: Interferon-γ stimulates CD14, TLR2 and
TLR4 mRNA expression in gingival fibroblasts increasing
responsiveness to bacterial challenge. Arch Oral Biol. 61:36–43.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Huynh DTN, Baek N, Sim S, Myung CS and Heo
KS: Minor ginsenoside Rg2 and Rh1 attenuates LPS-induced acute
liver and kidney damages via downregulating activation of
TLR4-STAT1 and inflammatory cytokine production in macrophages. Int
J Mol Sci. 21(6656)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Iannucci A, Caneparo V, Raviola S,
Debernardi I, Colangelo D, Miggiano R, Griffante G, Landolfo S,
Gariglio M and De Andrea M: Toll-like receptor 4-mediated
inflammation triggered by extracellular IFI16 is enhanced by
lipopolysaccharide binding. PLoS Pathog.
16(e1008811)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Plociennikowska A, Hromada-Judycka A,
Dembinska J, Roszczenko P, Ciesielska A and Kwiatkowska K:
Contribution of CD14 and TLR4 to changes of the PI(4,5)P2 level in
LPS-stimulated cells. J Leukoc Biol. 100:1363–1373. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Liu P, Cui L and Shen L: Knockdown of
TRIM52 alleviates LPS-induced inflammatory injury in human
periodontal ligament cells through the TLR4/NF-ĸB pathway. Biosci
Rep. 40(BSR20201223)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Aboudounya MM and Heads RJ: COVID-19 and
toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4): SARS-CoV-2 may bind and activate TLR4
to Increase ACE2 expression, facilitating entry and causing
hyperinflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2021(8874339)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bowman ER, Cameron CMA, Avery A, Gabriel
J, Kettelhut A, Hecker M, Sontich CU, Tamilselvan B, Nichols CN,
Richardson B, et al: Levels of soluble CD14 and tumor necrosis
factor receptors 1 and 2 may be predictive of death in severe
coronavirus disease 2019. J Infect Dis. 223:805–810.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Singhal S, Kumar P, Singh S, Saha S and
Dey AB: Clinical features and outcomes of COVID-19 in older adults:
A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Geriatr.
21(321)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Fernandez-Botran R, Furmanek S,
Ambadapoodi RS, Exposito Gonzalez E, Cahill M, Carrico R, Akca O
and Ramirez JA: University of Louisville COVID-19 Study Group.
Association and predictive value of biomarkers with severe outcomes
in hospitalized patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cytokine.
149(155755)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Tufan A, Avanoglu Guler A and
Matucci-Cerinic M: COVID-19, immune system response,
hyperinflammation and repurposing antirheumatic drugs. Turk J Med
Sci. 50:620–632. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zheng X, Huang H, Liu J, Li M, Liu M and
Luo T: Propofol attenuates inflammatory response in LPS-activated
microglia by regulating the miR-155/SOCS1 pathway. Inflammation.
41:11–19. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yang N, Liang Y, Yang P and Ji F: Propofol
suppresses LPS-induced nuclear accumulation of HIF-1α and tumor
aggressiveness in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep.
37:2611–2619. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yeh CH, Cho W, So EC, Chu CC, Lin MC, Wang
JJ and Hsing CH: Propofol inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced lung
epithelial cell injury by reducing hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha
expression. Br J Anaesth. 106:590–599. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Huang T, Zhang Y, Wang C and Gao J:
Propofol reduces acute lung injury by up-regulating
gamma-aminobutyric acid type a receptors. Exp Mol Pathol.
110(104295)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Witenko CJ, Littlefield AJ, Abedian S, An
A, Barie PS and Berger K: The safety of continuous infusion
propofol in mechanically ventilated adults with coronavirus disease
2019. Ann Pharmacother. 56:5–15. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Gerard L, Lecocq M, Bouzin C, Hoton D,
Schmit G, Pereira JP, Montiel V, Plante-Bordeneuve T, Laterre PF
and Pilette C: Increased angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 and loss
of alveolar type II Cells in COVID-19 Related ARDS. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 204:1024–1034. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Bridges JP, Vladar EK, Huang H and Mason
RJ: Respiratory epithelial cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 in
COVID-19. Thorax. 77:203–209. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Sasaki M, Kishimoto M, Itakura Y, Tabata
K, Intaruck K, Uemura K, Toba S, Sanaki T, Sato A, Hall WW, et al:
Air-liquid interphase culture confers SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility to
A549 alveolar epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
577:146–151. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang Y, Fan Y, Huang Y, Du T, Liu Z, Huang
D, Wang Y, Wang N and Zhang P: TRIM28 regulates SARS-CoV-2 cell
entry by targeting ACE2. Cell Signal. 85(110064)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Choudhury A and Mukherjee S: In silico
studies on the comparative characterization of the interactions of
SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein with ACE-2 receptor homologs and
human TLRs. J Med Virol. 92:2105–2113. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Leifer CA and Medvedev AE: Molecular
mechanisms of regulation of Toll-like receptor signaling. J Leukoc
Biol. 100:927–941. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Kim S, Kim SY, Pribis JP, Lotze M, Mollen
KP, Shapiro R, Loughran P, Scott MJ and Billiar TR: Signaling of
high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) through toll-like receptor 4 in
macrophages requires CD14. Mol Med. 19:88–98. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Sancho Ferrando E, Hanslin K, Hultström M,
Larsson A, Frithiof R and Lipcsey M: Uppsala Intensive Care
COVID-19 Research Group. Soluble TNF receptors predict acute kidney
injury and mortality in critically ill COVID-19 patients: A
prospective observational study. Cytokine.
149(155727)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yu X and Li C: Protective effects of
propofol on experimental neonatal acute lung injury. Mol Med Rep.
19:4507–4513. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhao H, Gu Y and Chen H: Propofol
ameliorates endotoxin induced myocardial cell injury by inhibiting
inflammation and apoptosis via the PPARγ/HMGB1/NLRP3 axis. Mol Med
Rep. 23(176)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ma L, Yang Y, Sun X, Jiang M, Ma Y, Yang X
and Guo Z: Propofol regulates the expression of TLR4 through miR-21
in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep.
16:9074–9080. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wang Y, Lin C, Wang J, Zhou M, Fang T,
Miao L and Wei Y: Propofol rescues LPS-induced toxicity in
HRT-8/SVneo cells via miR-216a-5p/TLR4 axis. Arch Gynecol Obstet:
Jan 4, 2022 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
44
|
Shafer A, Doze VA, Shafer SL and White PF:
Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of propofol infusions during
general anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 69:348–356. 1988.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Gepts E, Camu F, Cockshott ID and Douglas
EJ: Disposition of propofol administered as constant rate
intravenous infusions in humans. Anesth Analg. 66:1256–1263.
1987.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Schüttler J and Ihmsen H: Population
pharmacokinetics of propofol: A multicenter study. Anesthesiology.
92:727–738. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|