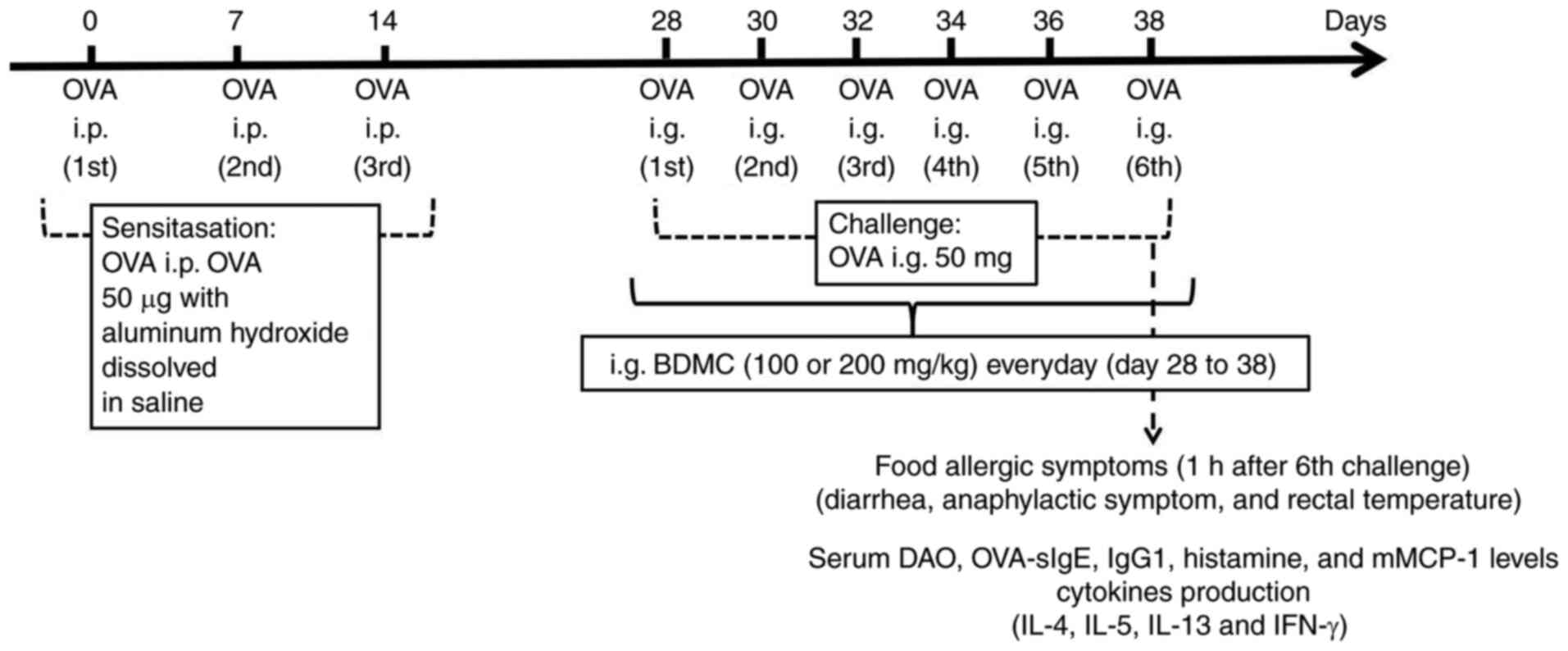
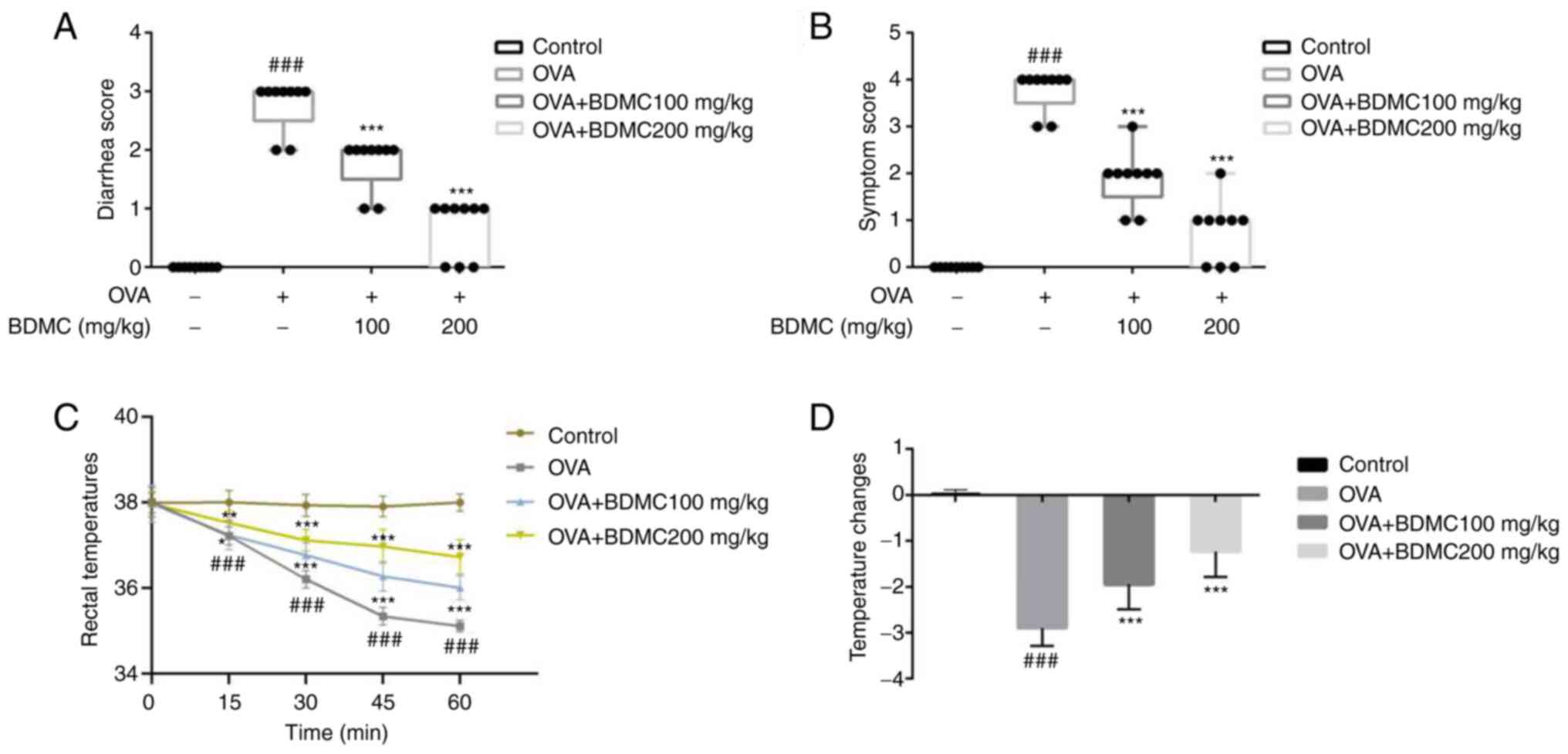
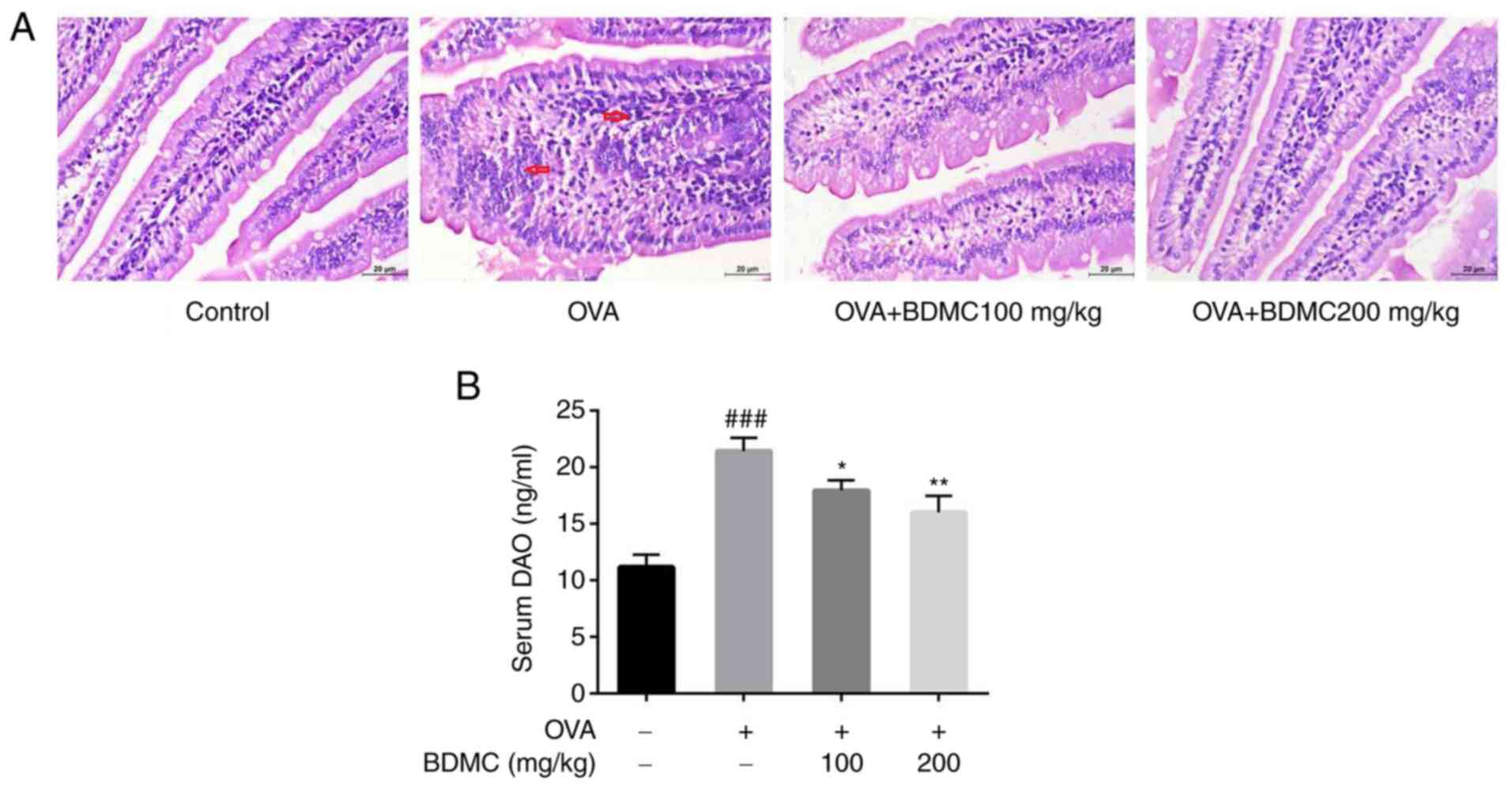
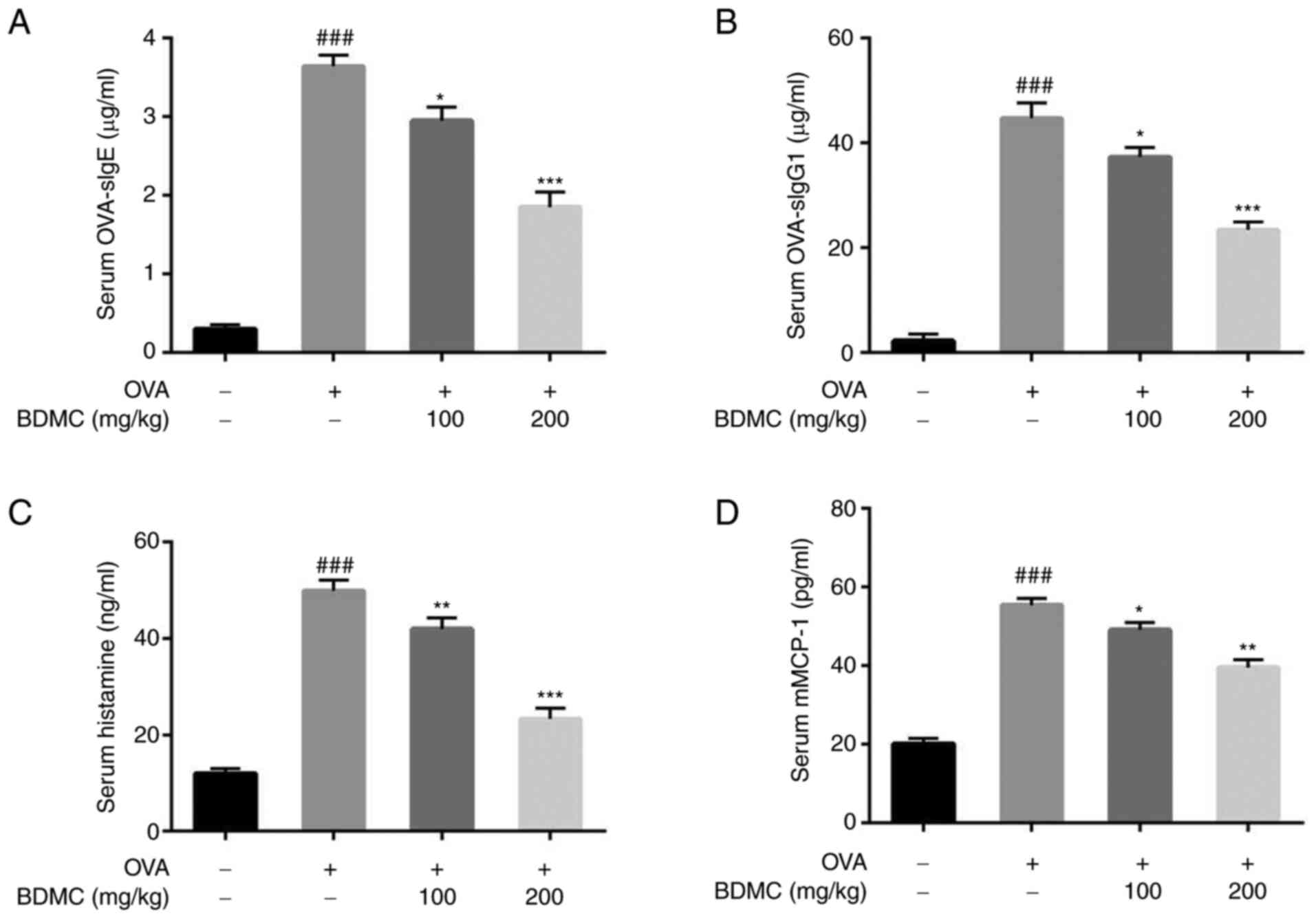
|
1
|
Prescott S and Allen KJ: Food allergy:
Riding the second wave of the allergy epidemic. Pediatr Allergy
Immunol. 22:155–160. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Johnston LK, Chien KB and Bryce PJ: The
immunology of food allergy. J Immunol. 192:2529–2534.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Sicherer SH: Epidemiology of food allergy.
J Allergy Clin Immunol. 127:594–602. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Sicherer SH and Sampson HA: Food allergy:
Recent advances in pathophysiology and treatment. Annu Rev Med.
60:261–277. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Venter C and Arshad SH: Epidemiology of
food allergy. Pediatr Clin North Am. 58:327–349. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Krogulska A, Polakowska E,
Wąsowska-Królikowska K, Małachowska B, Młynarski W and Borowiec M:
Decreased FOXP3 mRNA expression in children with atopic asthma and
IgE-mediated food allergy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 115:415–421.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kucuk ZY, Strait R, Khodoun MV, Mahler A,
Hogan S and Finkelman FD: Induction and suppression of allergic
diarrhea and systemic anaphylaxis in a murine model of food
allergy. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 129:1343–1348. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gendel SM: Bioinformatics and Food
Allergens. J AOAC Int. 87:1417–1422. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bernhisel-Broadbent J, Dintzis HM, Dintzis
RZ and Sampson HA: Allergenicity and antigenicity of chicken egg
ovomucoid (Gal d III) compared with ovalbumin (Gal d I) in children
with egg allergy and in mice. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 93:1047–1059.
1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Van Asperen P, Kemp AS and Mellis CM: Skin
test reactivity and clinical allergen sensitivity in infancy. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 73:381–386. 1984.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sampson HA: Food allergy. Part 1:
Immunopathogenesis and clinical disorders. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
103 (5 Pt 1):717–728. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yu W, Freeland DMH and Nadeau KC: Food
allergy: Immune mechanisms, diagnosis and immunotherapy. Nat Rev
Immunol. 16:751–765. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kumar S, Verma AK, Das M and Dwivedi PD:
Molecular mechanisms of IgE mediated food allergy. Int
Immunopharmacol. 13:432–439. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Duan W and Wong WS: Targeting
mitogen-activated protein kinases for asthma. Curr Drug Targets.
7:691–698. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li L, Zhang XH, Liu GR, Liu C and Dong YM:
Isoquercitrin suppresses the expression of histamine and
pro-inflammatory cytokines by inhibiting the activation of MAP
Kinases and NF-κB in human KU812 cells. Chin J Nat Med. 14:407–412.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhou Y, Yang Q, Xu H, Zhang J, Deng H, Gao
H, Yang J, Zhao D and Liu F: MiRNA-221-3p Enhances the secretion of
interleukin-4 in mast cells through the phosphatase and tensin
Homolog/p38/Nuclear Factor-kappaB pathway. PLoS One.
11(e0148821)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Shin HS, See HJ, Jung SY, Choi DW, Kwon
DA, Bae MJ, Sung KS and Shon DH: Turmeric (Curcuma longa)
attenuates food allergy symptoms by regulating type 1/2 helper T
cells (Th1/Th2) balance in a mouse model of food allergy. J
Ethnopharmacol. 175:21–29. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kinney SR, Carlson L, Ser-Dolansky J,
Thompson C, Shah S, Gambrah A, Xing W, Schneider SS and Mathias CB:
Curcumin ingestion inhibits mastocytosis and suppresses intestinal
anaphylaxis in a murine model of food allergy. PLoS One.
10(e0132467)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang N, Li H, Jia J and He M:
Anti-inflammatory effect of curcumin on mast cell-mediated allergic
responses in ovalbumin-induced allergic rhinitis mouse. Cell
Immunol. 298:88–95. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Gordon ON, Luis PB, Ashley RE, Osheroff N
and Schneider C: Oxidative transformation of demethoxy-and
bisdemethoxycurcumin: Products, mechanism of formation, and
poisoning of human topoisomerase IIα. Chem Res Toxicol. 28:989–996.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Ramezani M, Hatamipour M and Sahebkar A:
Promising Anti-tumor properties of Bisdemethoxycurcumin: A
naturally occurring curcumin analogue. J Cell Physiol. 233:880–887.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Xu JH, Yang HP, Zhou XD, Wang HJ, Gong L
and Tang CL: Role of Wnt inhibitory factor-1 in inhibition of
bisdemethoxycurcumin mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
in highly metastatic lung cancer 95D cells. Chin Med J (Engl).
128:1376–1383. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li YB, Gao JL, Zhong ZF, Hoi PM, Lee SM
and Wang YT: Bisdemethoxycurcumin suppresses MCF-7 cells
proliferation by inducing ROS accumulation and modulating
senescence-related pathways. Pharmacol Rep. 65:700–709.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Haukvik T, Bruzell E, Kristensen S and
Tønnesen HH: A screening of curcumin derivatives for antibacterial
phototoxic effects Studies on curcumin and curcuminoids. XLIII.
Pharmazie. 66:69–74. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fu M, Fu S, Ni S, Wang D and Hong T:
Inhibitory effects of bisdemethoxycurcumin on mast cell-mediated
allergic diseases. Int Immunopharmacol. 65:182–189. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lee D, Kim HS, Shin E, Do SG, Lee CK, Kim
YM, Lee MB, Min KY, Koo J, Kim SJ, et al: Polysaccharide isolated
from Aloe vera gel suppresses ovalbumin-induced food allergy
through inhibition of Th2 immunity in mice. Biomed Pharmacother.
101:201–210. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sicherer SH and Sampson HA: Food allergy:
Epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. J Allergy
Clin Immunol. 133:291–307. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Berin MC: Pathogenesis of IgE-mediated
food allergy. Clin Exp Allergy. 45:1483–1496. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Sicherer SH and Sampson HA: Food allergy.
J Allergy Clin Immunol. 125 (Suppl 2):S116–S125. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kweon MN, Yamamoto M, Kajiki M, Takahashi
I and Kiyono H: Systemically derived large intestinal CD4(+) Th2
cells play a central role in STAT6-mediated allergic diarrhea. J
Clin Invest. 106:199–206. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Yamaki K and Yoshino S: Remission of food
allergy by the Janus kinase inhibitor ruxolitinib in mice. Int
Immunopharmacol. 18:217–224. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Bischoff S and Crowe SE: Gastrointestinal
food allergy: New insights into pathophysiology and clinical
perspectives. Gastroenterology. 128:1089–1113. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wollin A, Wang X and Tso P: Nutrients
regulate diamine oxidase release from intestinal mucosa. Am J
Physiol. 275:R969–R975. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Jiang S, Han S, Chen J, Li X and Che H:
Inhibition effect of blunting Notch signaling on food allergy
through improving TH1/TH2 balance in mice.
Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 118:94–102. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Galli SJ, Tsai M and Piliponsky AM: The
development of allergic inflammation. Nature. 454:445–454.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ciprandi G, Marseglia GL, Castagnoli R,
Valsecchi C, Tagliacarne C, Caimmi S and Licari A: From IgE to
clinical trials of allergic rhinitis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol.
11:1321–1333. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wang M, Takeda K, Shiraishi Y, Okamoto M,
Dakhama A, Joetham A and Gelfand EW: Peanut-induced intestinal
allergy is mediated through a mast cell-IgE-FcepsilonRI-IL-13
pathway. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 126:306–316, 316.e1-12.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Hua X and He SH: Roles of histamine and
its receptors in allergic and inflammatory bowel diseases. World J
Gastroenterol. 11:2851–2857. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Maintz L and Novak N: Histamine and
histamine intolerance. Am J Clin Nutr. 85:1185–1196.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Yamamoto T, Fujiwara K, Yoshida M,
Kageyama-Yahara N, Kuramoto H, Shibahara N and Kadowaki M:
Therapeutic effect of kakkonto in a mouse model of food allergy
with gastrointestinal symptoms. Int Arch Allergy Immunol.
148:175–185. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Brandt EB, Strait RT, Hershko D, Wang Q,
Muntel EE, Scribner TA, Zimmermann N, Finkelman FD and Rothenberg
ME: Mast cells are required for experimental oral allergen-induced
diarrhea. J Clin Invest. 112:1666–1677. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Matsui T, Yamashita H, Mori M, Tanaka H
and Inagaki N: Eppikajutsuto protects against food allergy induced
by ovalbumin in a murine model. Int Arch Allergy Immunol.
173:71–83. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Wang C, Collins M and Kuchroo VK: Effector
T cell differentiation: Are master regulators of effector T cells
still the masters? Curr Opin Immunol. 37:6–10. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Cook PC, Jones LH, Jenkins SJ, Wynn TA,
Allen JE and MacDonald AS: Alternatively activated dendritic cells
regulate CD4+ T-cell polarization in vitro and in vivo.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:9977–9982. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yamane H and Paul WE: Cytokines of the
γ(c) family control CD4+ T cell differentiation and
function. Nat Immunol. 13:1037–1044. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Manise M, Holtappels G, Van Crombruggen K,
Schleich F, Bachert C and Louis R: Sputum IgE and cytokines in
asthma: Relationship with sputum cellular profile. PLoS One.
8(e58388)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Gilfillan AM and Tkaczyk C: Integrated
signalling pathways for mast-cell activation. Nat Rev Immunol.
6:218–230. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Qi M and Elion EA: MAP kinase pathways. J
Cell Sci. 118(Pt 16):3569–3572. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Azzolina A, Bongiovanni A and Lampiasi N:
Substance P. induces TNF alpha and IL-6 production through NF kappa
B in peritoneal mast cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1643:75–83.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Schuliga M: NF-kappaB signaling in chronic
inflammatory airway disease. Biomolecules. 5:1266–1283.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Kong R, Kang OH, Seo YS, Zhou T, Kim SA,
Shin DW and Kwon DY: MAPKs and NF-κB pathway inhibitory effect of
bisdemethoxycurcumin on phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate and
A23187-induced inflammation in human mast cells. Mol Med Rep.
17:630–635. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|