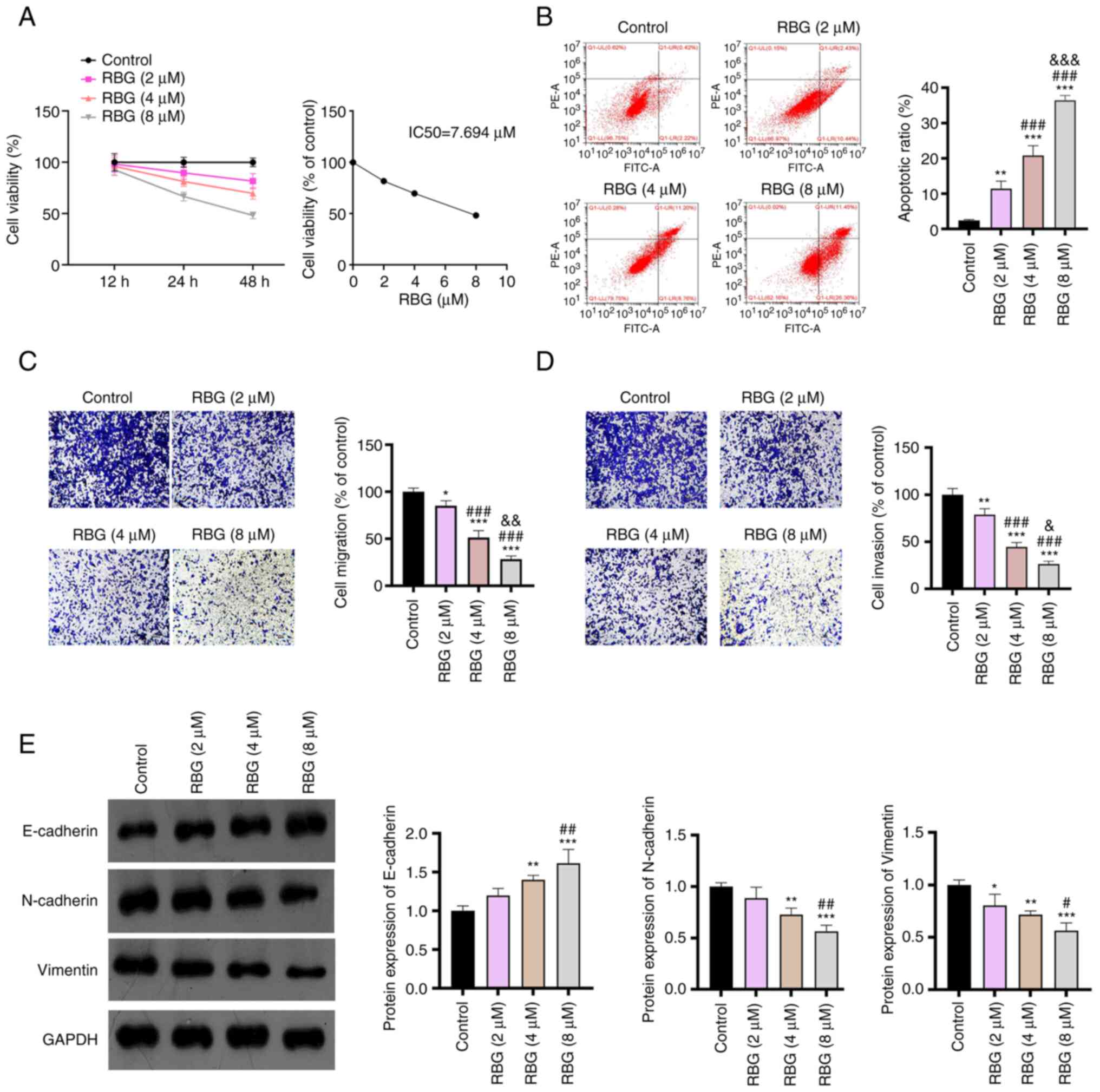
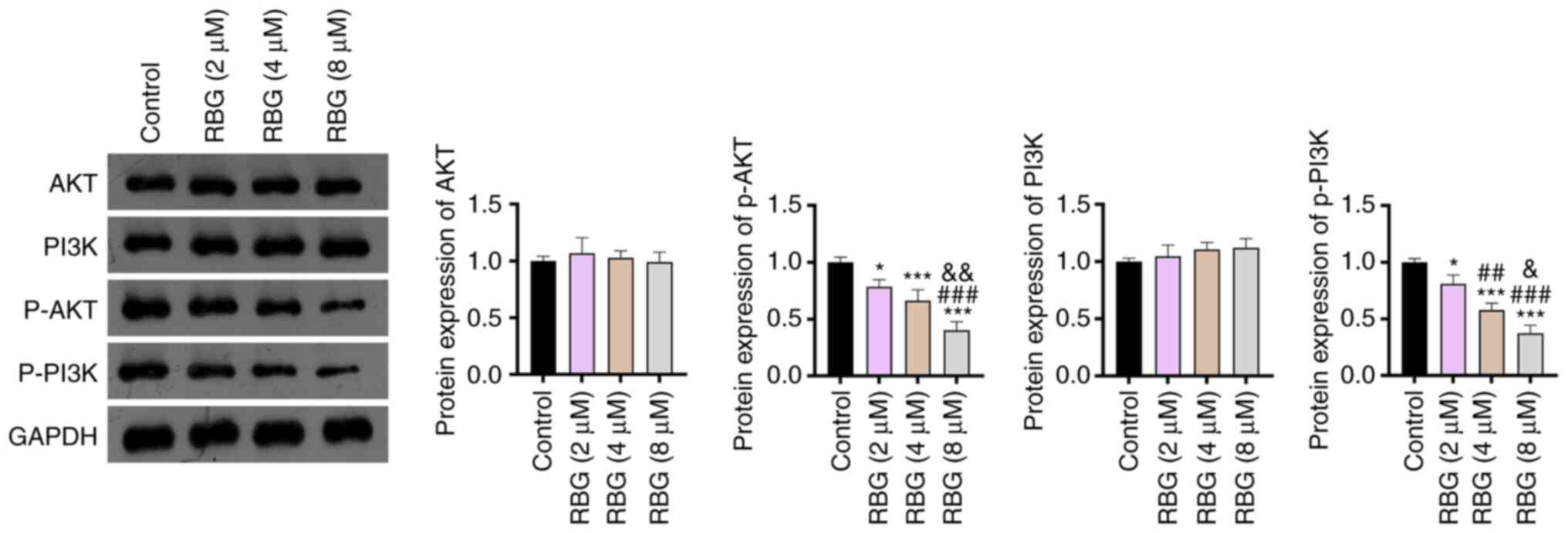
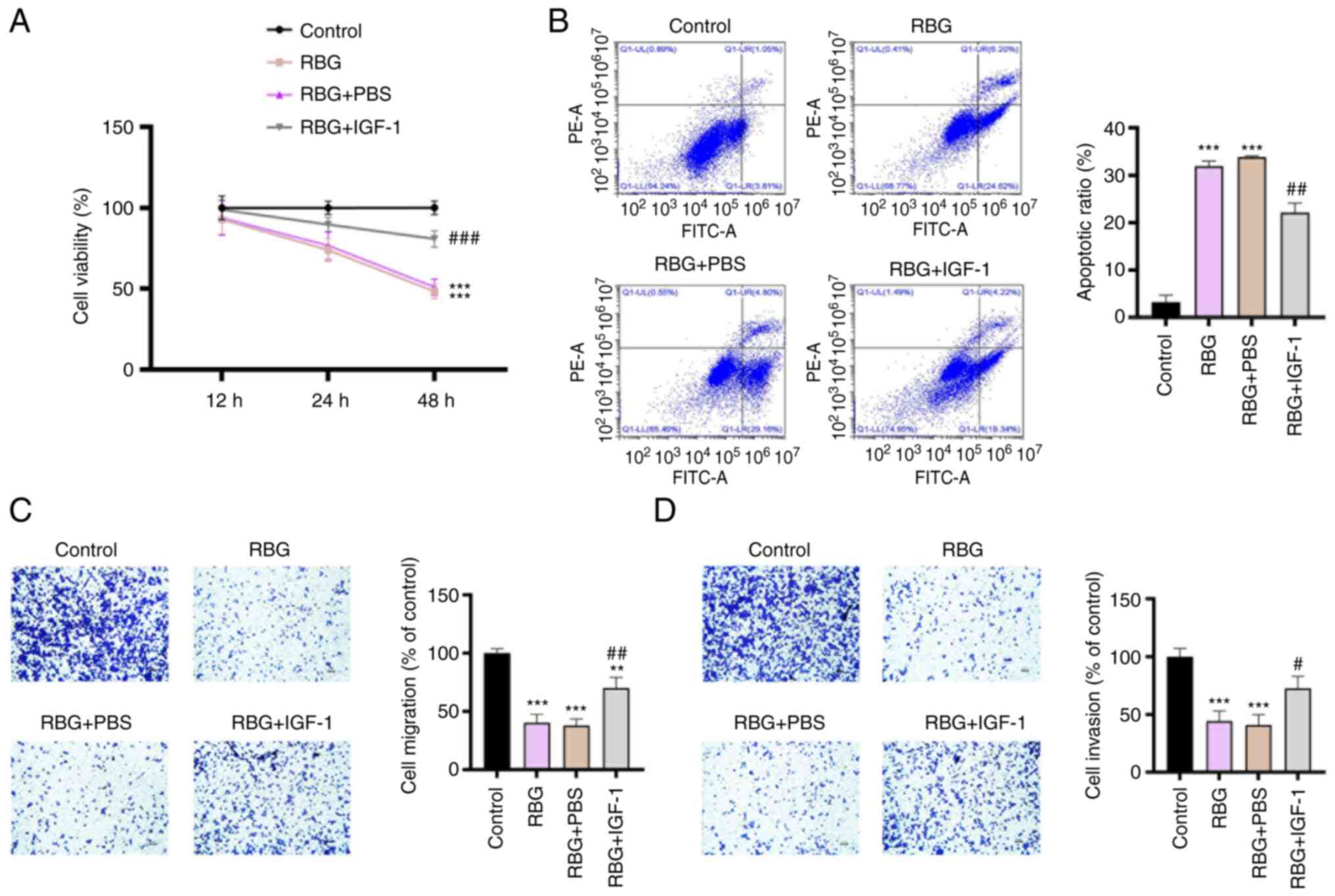
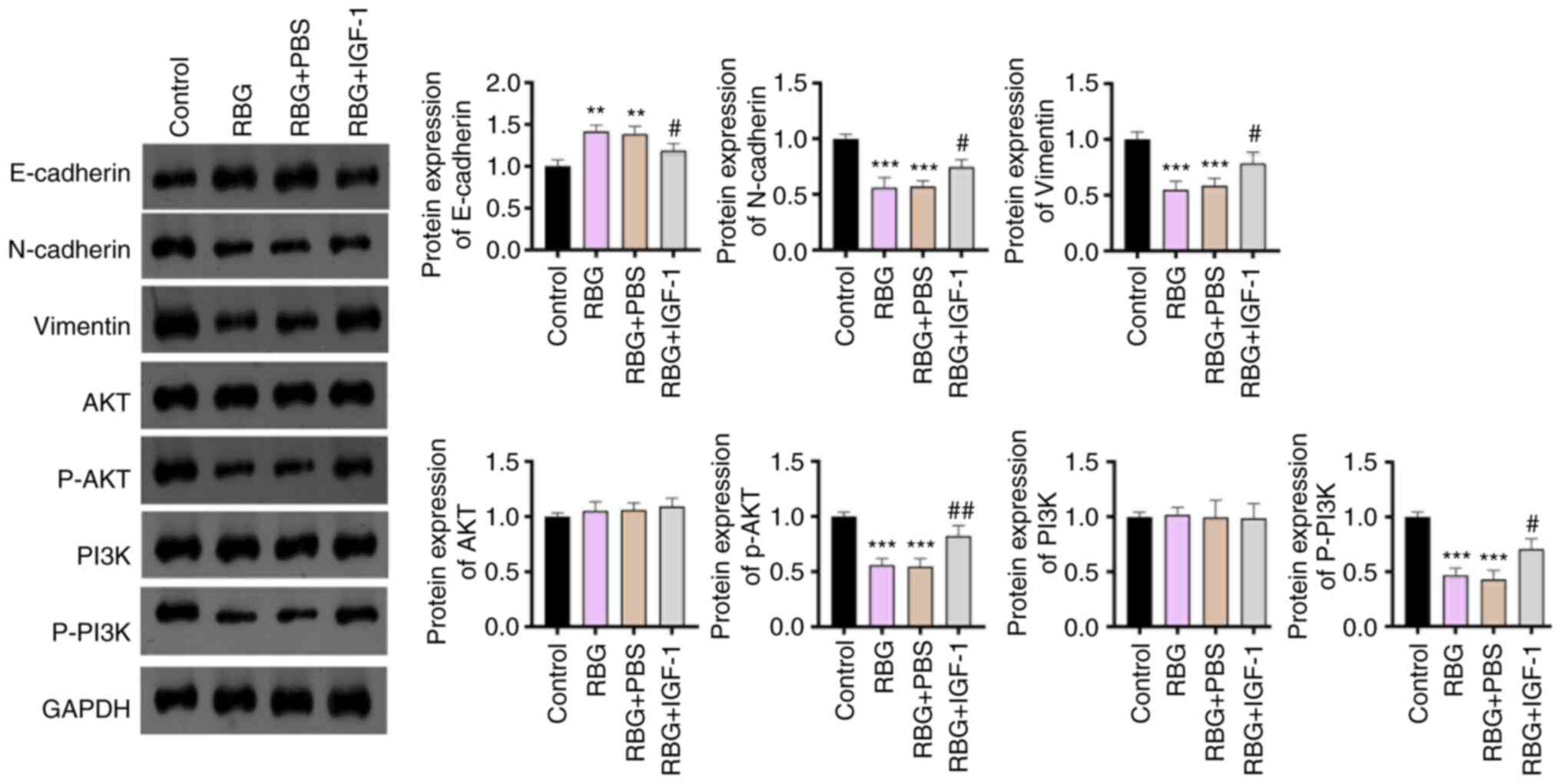
|
1
|
Rollig C, Knop S and Bornhauser M:
Multiple myeloma. Lancet. 385:2197–2208. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rashid N, Su Y, Gustavus Aranda J, Wu YL
and Han AK: Patterns and predictors of first-line therapy use among
newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients ineligible for stem cell
transplant in an integrated healthcare system. Internet J Hematol.
10:1–8. 2014.
|
|
3
|
Rajkumar SV: Multiple myeloma: Every year
a new standard? Hematol Oncol. 37 (Suppl 1):S62–S65.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kazandjian D: Multiple myeloma
epidemiology and survival: A unique malignancy. Semin Oncol.
43:676–681. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kehrer M, Koob S, Strauss A, Wirtz DC and
Schmolders J: Multiple Myeloma-current status in diagnostic testing
and therapy. Z Orthop Unfall. 155:575–586. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In German).
|
|
6
|
Mimura N, Hideshima T and Anderson KC:
Novel therapeutic strategies for multiple myeloma. Exp Hematol.
43:732–741. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li FJ, Hu JH, Ren X, Zhou CM, Liu Q and
Zhang YQ: Toad venom: A comprehensive review of chemical
constituents, anticancer activities, and mechanisms. Arch Pharm
(Weinheim). 354(e2100060)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wei WL, An YL, Li ZW, Wang YY, Ji HJ, Hou
JJ, Wu WY and Guo DA: Simultaneous determination of resibufogenin
and its eight metabolites in rat plasma by LC-MS/MS for metabolic
profiles and pharmacokinetic study. Phytomedicine.
60(152971)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yang LX, Zhao HY, Yuan SF, Ya-Jun LI, Bian
BL and Wang HJ: Determination of Total Bufadienolides in
Cinobufotalin Injection Using Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry. Chin J
Exp Tradit Med Form. 6:87–89. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Han Q, Ma Y, Wang H, Dai Y, Chen C, Liu Y,
Jing L and Sun X: Resibufogenin suppresses colorectal cancer growth
and metastasis through RIP3-mediated necroptosis. J Transl Med.
16(201)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhou G, Zhu Z, Li L and Ding J:
Resibufogenin inhibits ovarian clear cell carcinoma (OCCC) growth
in vivo, and migration of OCCC cells in vitro, by down-regulating
the PI3K/AKT and actin cytoskeleton signaling pathways. Am J Transl
Res. 11:6290–6303. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Guo Y, Liang F, Zhao F and Zhao J:
Resibufogenin suppresses tumor growth and Warburg effect through
regulating miR-143-3p/HK2 axis in breast cancer. Mol Cell Biochem.
466:103–115. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Babaei G, Aziz SG and Jaghi NZZ: EMT,
cancer stem cells and autophagy; The three main axes of metastasis.
Biomed Pharmacother. 133(110909)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Peng Y, Li F, Zhang P, Wang X, Shen Y,
Feng Y, Jia Y, Zhang R, Hu J and He A: IGF-1 promotes multiple
myeloma progression through PI3K/Akt-mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Life Sci.
249(117503)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Jafari M, Ghadami E, Dadkhah T and
Akhavan-Niaki H: PI3k/AKT signaling pathway: Erythropoiesis and
beyond. J Cell Physiol. 234:2373–2385. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Alzahrani AS: PI3K/Akt/mTOR inhibitors in
cancer: At the bench and bedside. Semin Cancer Biol. 59:125–132.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Keane NA, Glavey SV, Krawczyk J and
O'Dwyer M: AKT as a therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. Expert
Opin Ther Targets. 18:897–915. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Younes H, Leleu X, Hatjiharissi E, Moreau
AS, Hideshima T, Richardson P, Anderson KC and Ghobrial IM:
Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in multiple
myeloma. Clin Cancer Res. 13:3771–3775. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Mimura N, Hideshima T, Shimomura T, Suzuki
R, Ohguchi H, Rizq O, Kikuchi S, Yoshida Y, Cottini F, Jakubikova
J, et al: Selective and potent Akt inhibition triggers anti-myeloma
activities and enhances fatal endoplasmic reticulum stress induced
by proteasome inhibition. Cancer Res. 74:4458–4469. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Spencer A, Yoon SS, Harrison SJ, Morris
SR, Smith DA, Brigandi RA, Gauvin J, Kumar R, Opalinska JB and Chen
C: The novel AKT inhibitor afuresertib shows favorable safety,
pharmacokinetics, and clinical activity in multiple myeloma. Blood.
124:2190–2195. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Safaroghli-Azar A, Bashash D, Kazemi A,
Pourbagheri-Sigaroodi A and Momeny M: Anticancer effect of pan-PI3K
inhibitor on multiple myeloma cells: Shedding new light on the
mechanisms involved in BKM120 resistance. Eur J Pharmacol.
842:89–98. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Feng N, Luo J and Guo X: Silybin
suppresses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis of multiple
myeloma cells via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep.
13:3243–3248. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wu H, Dai X and Wang E: Plumbagin inhibits
cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells
through inhibition of the PI3K/Akt-mTOR pathway. Oncol Lett.
12:3614–3618. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yang M, Huang J, Pan HZ and Jin J:
Triptolide overcomes dexamethasone resistance and enhanced
PS-341-induced apoptosis via PI3k/Akt/NF-kappaB pathways in human
multiple myeloma cells. Int J Mol Med. 22:489–496. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yang XJ, Xi YM and Li ZJ: Icaritin: A
novel natural candidate for hematological malignancies therapy.
Biomed Res Int. 2019(4860268)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Lu Z, Xu A, Yuan X, Chen K, Wang L and Guo
T: Anticancer effect of resibufogenin on gastric carcinoma cells
through the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B/glycogen
synthase kinase 3β signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 16:3297–3302.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yang T, Jiang YX, Wu Y, Lu D, Huang R,
Wang LL, Wang SQ, Guan YY, Zhang H and Luan X: Resibufogenin
suppresses triple-negative breast cancer angiogenesis by blocking
VEGFR2-mediated signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol.
12(682735)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Ma J, Sawai H, Matsuo Y, Ochi N, Yasuda A,
Takahashi H, Wakasugi T, Funahashi H, Sato M and Takeyama H: IGF-1
mediates PTEN suppression and enhances cell invasion and
proliferation via activation of the IGF-1/PI3K/Akt signaling
pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. J Surg Res. 160:90–101.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Minnie SA and Hill GR: Immunotherapy of
multiple myeloma. J Clin Invest. 130:1565–1575. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu Y, Yang S, Wang K, Lu J, Bao X, Wang
R, Qiu Y, Wang T and Yu H: Cellular senescence and cancer: Focusing
on traditional Chinese medicine and natural products. Cell Prolif.
53(e12894)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Huang H, Cao Y, Wei W, Liu W, Lu SY, Chen
YB, Wang Y, Yan H and Wu YL: Targeting poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
partially contributes to bufalin-induced cell death in multiple
myeloma cells. PLoS One. 8(e66130)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Baek SH, Kim C, Lee JH, Nam D, Lee J, Lee
SG, Chung WS, Jang HJ, Kim SH and Ahn KS: Cinobufagin exerts
anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects through the modulation
ROS-mediated MAPKs signaling pathway. Immunopharmacol
Immunotoxicol. 37:265–273. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Dongre A and Weinberg RA: New insights
into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and
implications for cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 20:69–84.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Harvey RD and Lonial S: PI3 kinase/AKT
pathway as a therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. Future Oncol.
3:639–647. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhu J, Wang M, Cao B, Hou T and Mao X:
Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/AKT pathway for the
treatment of multiple myeloma. Curr Med Chem. 21:3173–3187.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Han K, Xu X, Chen G, Zeng Y, Zhu J, Du X,
Zhang Z, Cao B, Liu Z and Mao X: Identification of a promising PI3K
inhibitor for the treatment of multiple myeloma through the
structural optimization. J Hematol Oncol. 7(9)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhu J, Wang M, Yu Y, Qi H, Han K, Tang J,
Zhang Z, Zeng Y, Cao B, Qiao C, et al: A novel PI3K inhibitor
PIK-C98 displays potent preclinical activity against multiple
myeloma. Oncotarget. 6:185–195. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|