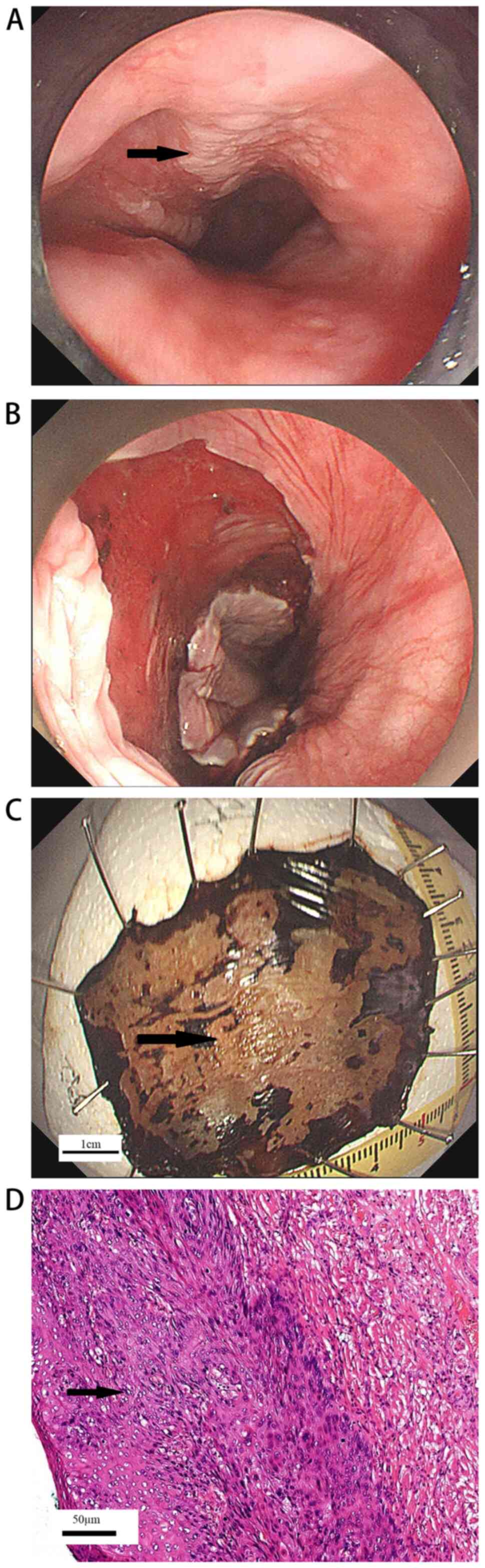
|
1
|
Zhang L, Zhou Y, Cheng C, Cui HY, Cheng L,
Kong PZ, Wang JQ, Li Y, Chen WL, Song B, et al: Genomic analyses
reveal mutational signatures and frequently altered genes in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Hum Genet. 96:597–611.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Njei B, McCarty TR and Birk JW: Trends in
esophageal cancer survival in United States adults from 1973 to
2009: A SEER database analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
31:1141–1146. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Naveed M and Kubiliun N: Endoscopic
treatment of early-stage esophageal cancer. Curr Oncol Rep.
20(71)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wani S, Early D, Edmundowicz S and Sharma
P: Management of high-grade dysplasia and intramucosal
adenocarcinoma in Barrett's esophagus. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
10:704–711. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Neuhaus H: Endoscopic submucosal
dissection in the upper gastrointestinal tract: Present and future
view of Europe. Dig Endosc. 21 (Suppl 1):S4–S6. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chennat J, Konda VJ, Ross AS, de Tejada
AH, Noffsinger A, Hart J, Lin S, Ferguson MK, Posner MC and Waxman
I: Complete Barrett's eradication endoscopic mucosal resection: an
effective treatment modality for high-grade dysplasia and
intramucosal carcinoma-an American single-center experience. Am J
Gastroenterol. 104:2684–2692. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Oyama T, Tomori A, Hotta K, Morita S,
Kominato K, Tanaka M and Miyata Y: Endoscopic submucosal dissection
of early esophageal cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 3 (Suppl
1):S67–S70. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Mariette C, Fabre S, Balon JM, Finzi L and
Triboulet JP: Factors predictive of complete resection of operable
esophageal cancer: review of 746 patients. Gastroenterol Clin Biol.
26:454–462. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kakushima N,
Kodashima S, Muraki Y, Ono S, Yamamichi N, Tateishi A, Shimizu Y,
Oka M, et al: Endoscopic submucosal dissection of esophageal
squamous cell neoplasms. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 4:688–694.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Repici A, Hassan C, Carlino A, Pagano N,
Zullo A, Rando G, Strangio G, Romeo F, Nicita R, Rosati R and
Malesci A: Endoscopic submucosal dissection in patients with early
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Results from a prospective
Western series. Gastrointest Endosc. 71:715–721. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ono S, Fujishiro M, Niimi K, Goto O,
Kodashima S, Yamamichi N and Omata M: Long-term outcomes of
endoscopic submucosal dissection for superficial esophageal
squamous cell neoplasms. Gastrointest Endosc. 70:860–886.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hamilton SR and Aaltonen LA: World Health
Organization classification of tumours: Pathology and genetics of
tumours of the digestive system. IARC Press, Lyon, pp11-36,
2000.
|
|
13
|
Birkmeyer JD, Siewers AE, Finlayson EV,
Stukel TA, Lucas FL, Batista I, Welch HG and Wennberg DE: Hospital
volume and surgical mortality in the United States. N Engl J Med.
346:1128–1137. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ell C, May A, Pech O, Gossner L, Guenter
E, Behrens A, Nachbar L, Huijsmans J, Vieth M and Stolte M:
Curative endoscopic resection of early esophageal adenocarcinomas
(Barrett's cancer). Gastrointest Endosc. 65:3–10. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Pech O, Behrens A, May A, Nachbar L,
Gossner L, Rabenstein T, Manner H, Guenter E, Huijsmans J, Vieth M,
et al: Long-term results and risk factor analysis for recurrence
after curative endoscopic therapy in 349 patients with high-grade
intraepithelial neoplasia and mucosal adenocarcinoma in Barrett's
oesophagus. Gut. 57:1200–1206. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Pech O, Gossner L, May A, Vieth M, Stolte
M and Ell C: Endoscopic resection of superficial esophageal
squamous-cell carcinomas: Western experience. Am J Gastroenterol.
99:1226–1232. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Stahl M, Budach W, Meyer HJ and Cervantes
A: Esophageal cancer: Clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis,
treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol. 21 (Suppl 5):v46–v49.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Manner H, May A, Pech O, Gossner L,
Rabenstein T, Günter E, Vieth M, Stolte M and Ell C: Early
Barrett's carcinoma with ‘low-risk’ submucosal invasion: Long-term
results of endoscopic resection with a curative intent. Am J
Gastroenterol. 103:2589–2597. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hazama H, Tanaka M, Kakushima N, Yabuuchi
Y, Yoshida M, Kawata N, Takizawa K, Ito S, Imai K, Hotta K, et al:
Predictors of technical difficulty during endoscopic submucosal
dissection of superficial esophageal cancer. Surg Endosc.
33:2909–2915. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Plum PS, Hölscher AH, Pacheco Godoy K,
Schmidt H, Berlth F, Chon SH, Alakus H and Bollschweiler E:
Prognosis of patients with superficial T1 esophageal cancer who
underwent endoscopic resection before esophagectomy-A propensity
score-matched comparison. Surg Endosc. 32:3972–3980.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang HY, Zeng X, Bai SY, Pu K, Zheng Y, Ji
R, Guo QH, Guan QL, Wang YP and Zhou YN: The safety and efficacy of
endoscopic submucosal dissection for treating early oesophageal
carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 102:702–711.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sgourakis G, Gockel I and Lang H:
Endoscopic and surgical resection of T1a/T1b esophageal neoplasms:
A systematic review. World J Gastroenterol. 19:1424–1437.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Qi ZP, Chen T, Li B, Ren Z, Yao LQ, Shi Q,
Cai SL, Zhong YS and Zhou PH: Endoscopic submucosal dissection for
early esophageal cancer in elderly patients with relative
indications for endoscopic treatment. Endoscopy. 50:839–845.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wu Y, Zhang H, Zhou B, Han SY and Zhang
YR: Clinical efficacy of endoscopic submucosal dissection in the
treatment of early esophageal cancer and precancerous lesions. J
Cancer Res Ther. 14:52–56. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yip HC and Chiu PW: Endoscopic diagnosis
and management of early squamous cell carcinoma of esophagus. J
Thorac Dis. 9 (Suppl 8):S689–S696. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Isomoto H, Shikuwa S, Yamaguchi N, Fukuda
E, Ikeda K, Nishiyama H, Ohnita K, Mizuta Y, Shiozawa J and Kohno
S: Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer: A
large-scale feasibility study. Gut. 58:331–336. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chung IK, Lee JH, Lee SH, Kim SJ, Cho JY,
Cho WY, Hwangbo Y, Keum BR, Park JJ, Chun HJ, et al: Therapeutic
outcomes in 1000 cases of endoscopic submucosal dissection for
early gastric neoplasms: Korean ESD study group multicenter study.
Gastrointest Endosc. 69:1228–1235. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Thosani N, Singh H, Kapadia A, Ochi N, Lee
JH, Ajani J, Swisher SG, Hofstetter WL, Guha S and Bhutani MS:
Diagnostic accuracy of EUS in differentiating mucosal versus
submucosal invasion of superficial esophageal cancers: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Gastrointest Endosc. 75:242–253.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yang J, Luo GY, Liang RB, Zeng TS, Long H,
Fu LH, Xu GL, Yang MZ, Li S, Zhang LJ, et al: Efficacy of
endoscopic ultrasonography for determining clinical T category for
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Data from 1434 surgical cases.
Ann Surg Oncol. 25:2075–2082. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ishii N, Horiki N, Itoh T, Maruyama M,
Matsuda M, Setoyama T, Suzuki S, Uchida S, Uemura M, Iizuka Y, et
al: Endoscopic submucosal dissection and preoperative assessment
with endoscopic ultrasonogra-phy for the treatment of rectal
carcinoid tumors. Surg Endosc. 24:1413–1419. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Zhou FR, Huang LY and Wu CR: Endoscopic
mucosal resection for rectal carcinoids under micro-probe
ultrasound guidance. World J Gastroenterol. 19:2555–2559.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Lee TH, Cho JY, Chang YW, Kim JO, Lee JS,
Cho WY, Kim HG, Kim WJ, Park YS and Jin SY: Appropriate indications
for endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer
according to tumor size and histologic type. Gastrointest Endosc.
71:920–926. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Fujishiro M, Kodashima S, Goto O, Ono S,
Niimi K, Yamamichi N, Oka M, Ichinose M and Omata M: Endoscopic
submucosal dissection for esophageal squamous cell neoplasms. Dig
Endosc. 21:109–115. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yoshida T, Inoue H, Usui S, Satodate H,
Fukami N and Kudo SE: Narrow-band imaging system with magnifying
endoscopy for superficial esophageal lesions. Gastrointest Endosc.
59:288–295. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kakushima N, Ono H, Tanaka M, Takizawa K,
Yamaguchi Y and Matsubayashi H: Factors related to lateral margin
positivity for cancer in gastric specimens of endoscopic submucosal
dissection. Dig Endosc. 23:227–232. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wen J, Linghu EQ, Yang YS, Liu QS, Yang J
and Lu ZS: Associated risk factor analysis for positive resection
margins after endoscopic submucosal dissection in early-stage
gastric cancer. J BUON. 20:421–427. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hwang JJ, Park KJ, Park YS, Lee HS, Yoon
H, Shin CM, Kim N and Lee DH: A scoring system for patients with a
tumor-positive lateral resection margin after endoscopic resection
of early gastric cancer. Surg Endosc. 30:2751–2758. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Oyama T, Inoue H, Arima M, Momma K, Omori
T, Ishihara R, Hirasawa D, Takeuchi M, Tomori A and Goda K:
Prediction of the invasion depth of superficial squamous cell
carcinoma based on microvessel morphology: Magnifying endoscopic
classification of the Japan esophageal society. Esophagus.
14:105–112. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hatta W, Gotoda T, Oyama T, Kawata N,
Takahashi A, Yoshifuku Y, Hoteya S, Nakagawa M, Hirano M and Esaki
M: , et al: Is the eCura system useful for selecting
patients who require radical surgery after noncurative endoscopic
submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer? A comparative
study. Gastric Cancer. 21:481–489. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|