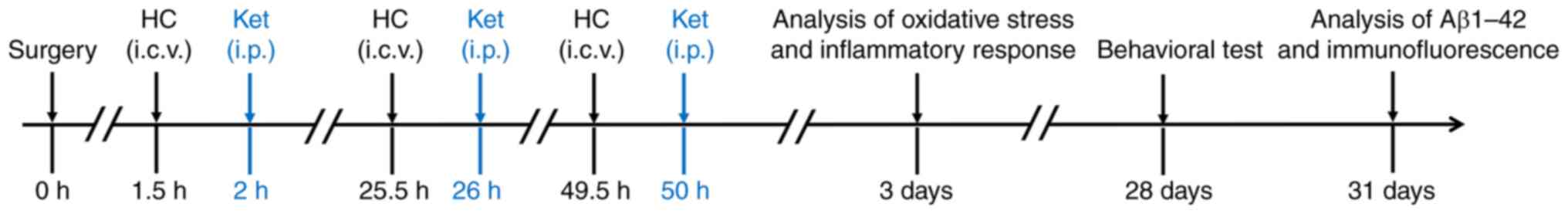
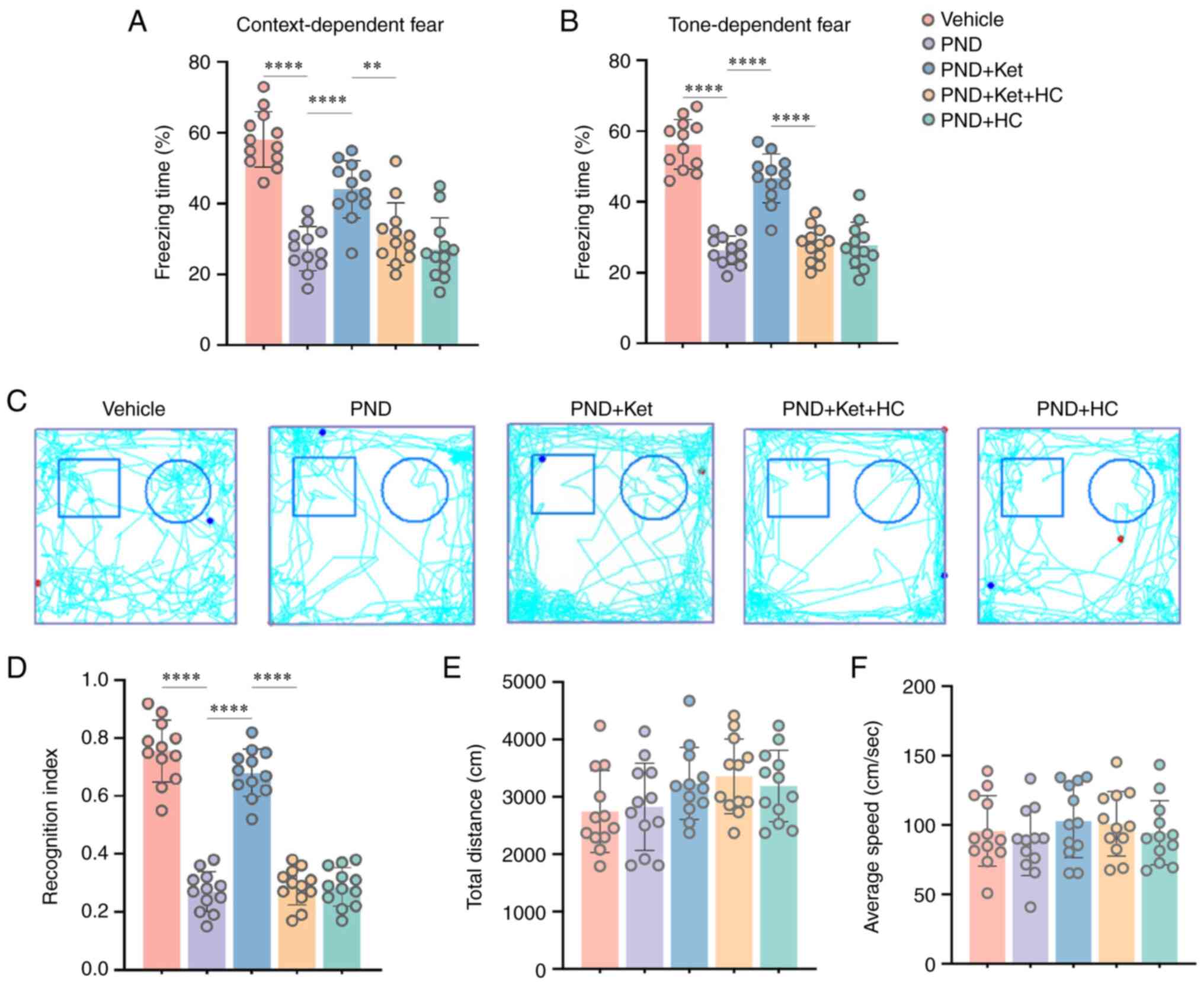
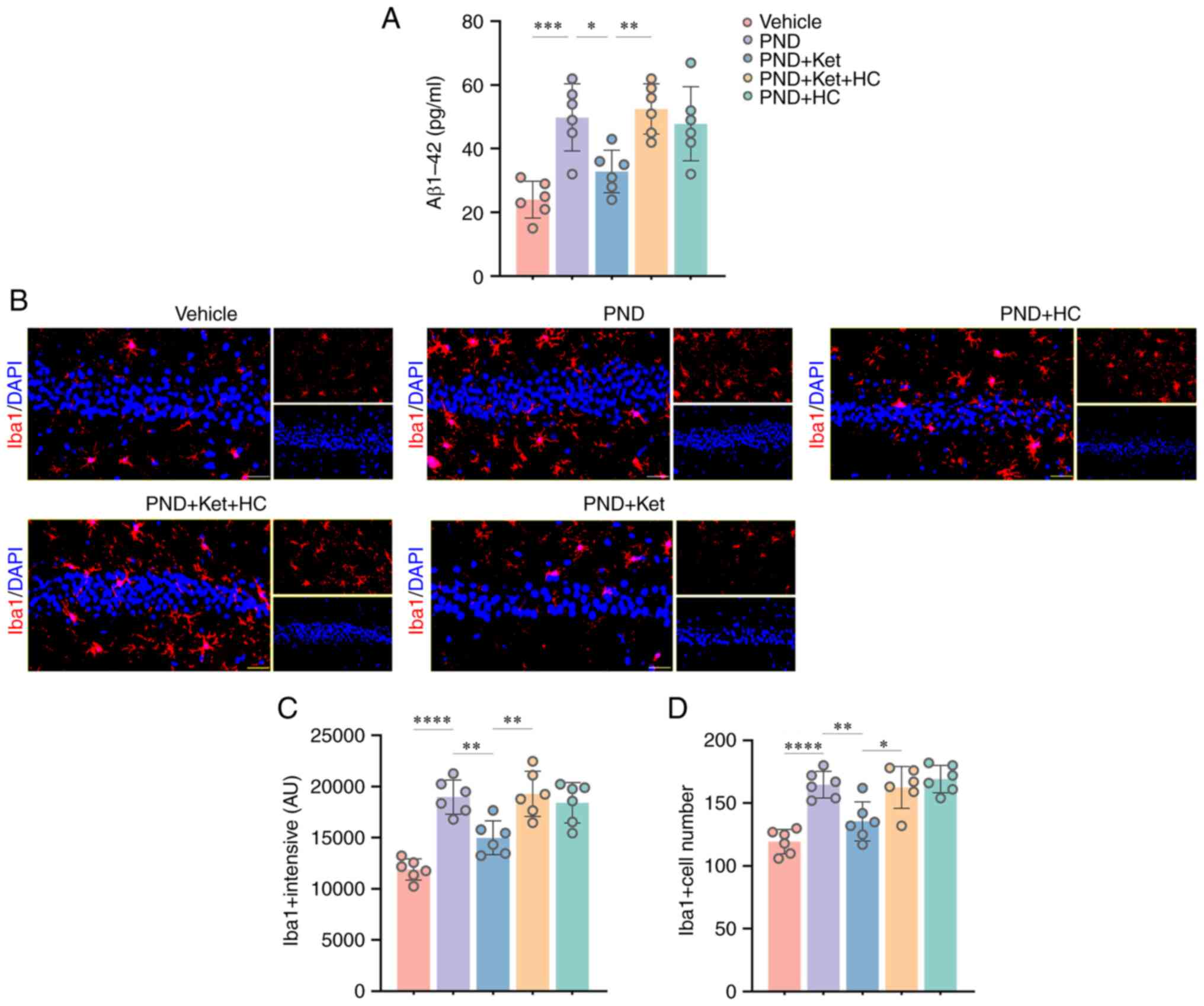
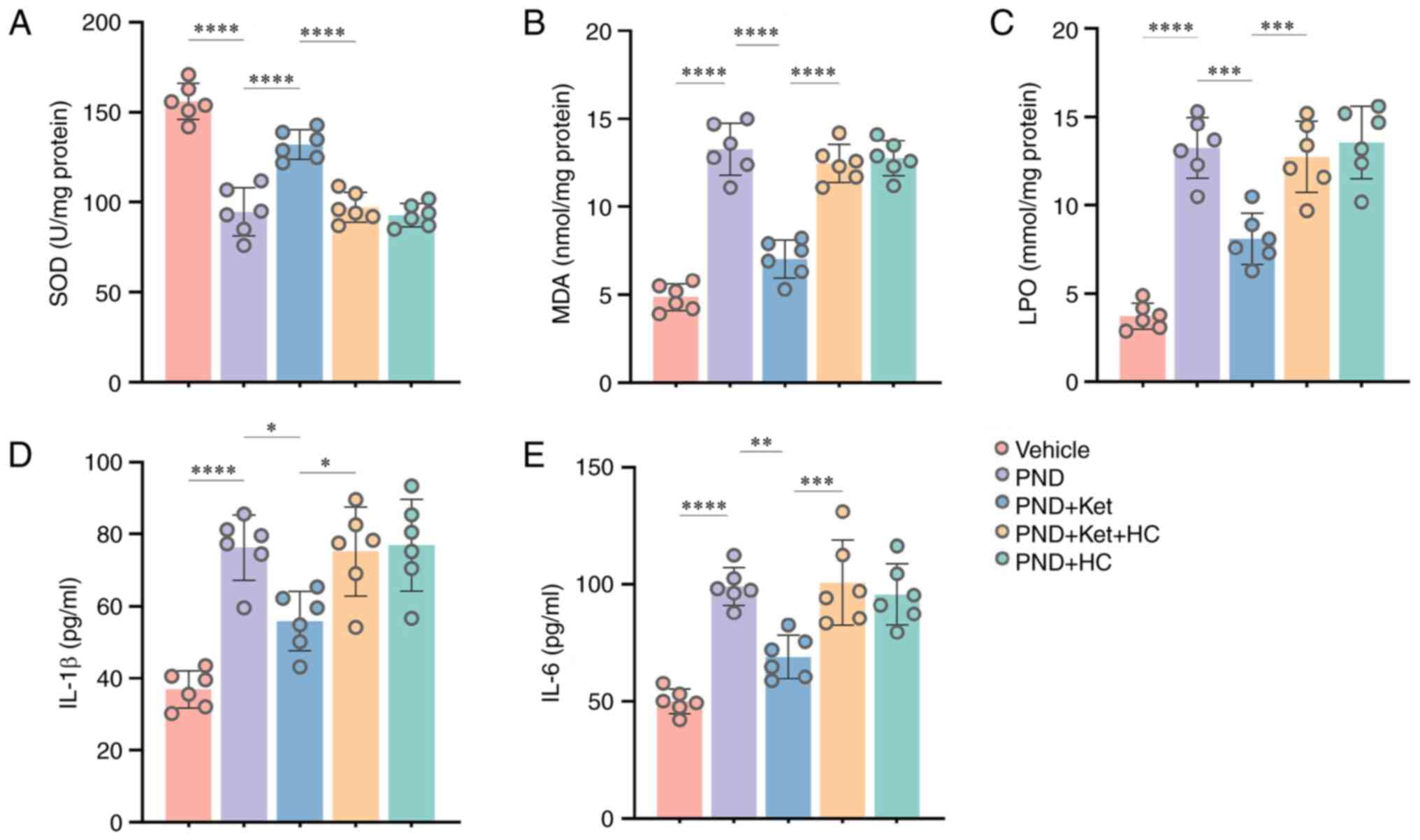
|
1
|
Evered LA and Silbert BS: Postoperative
cognitive dysfunction and noncardiac surgery. Anesth Analg.
127:496–505. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Evered L, Silbert B, Knopman DS, Scott DA,
DeKosky ST, Rasmussen LS, Oh ES, Crosby G, Berger M, Eckenhoff RG,
et al: Recommendations for the nomenclature of cognitive change
associated with anaesthesia and surgery-2018. Br J Anaesth.
121:1005–1012. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Urits I, Orhurhu V, Jones M, Hoyt D, Seats
A and Viswanath O: Current perspectives on postoperative cognitive
dysfunction in the ageing population. Turk J Anaesthesiol Reanim.
47:439–447. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Rundshagen I: Postoperative cognitive
dysfunction. Dtsch Arztebl Int. 111:119–125. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Haas DA and Harper DG: Ketamine: A review
of its pharmacologic properties and use in ambulatory anesthesia.
Anesth Prog. 39:61–68. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jonkman K, van de Donk T and Dahan A:
Ketamine for cancer pain: What is the evidence? Curr Opin Support
Palliat Care. 11:88–92. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Corriger A and Pickering G: Ketamine and
depression: A narrative review. Drug Des Devel Ther. 13:3051–3067.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ibrahim TH, Abdelrahman HS, Alharbi MA,
Zabani IA, Ismail MF and Kary H: Effect of ketamine on pro- and
anti-inflammatory cytokine response in paediatric cardiac surgery:
A prospective randomised controlled study. Indian J Anaesth.
61:549–555. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hudetz JA, Iqbal Z, Gandhi SD, Patterson
KM, Byrne AJ, Hudetz AG, Pagel PS and Warltier DC: Ketamine
attenuates post-operative cognitive dysfunction after cardiac
surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 53:864–872. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang Z, Zhou L, An D, Xu W, Wu C, Sha S,
Li Y, Zhu Y, Chen A, Du Y, et al: TRPV4-induced inflammatory
response is involved in neuronal death in pilocarpine model of
temporal lobe epilepsy in mice. Cell Death Dis.
10(386)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Woolums BM, McCray BA, Sung H, Tabuchi M,
Sullivan JM, Ruppell KT, Yang Y, Mamah C, Aisenberg WH,
Saavedra-Rivera PC, et al: TRPV4 disrupts mitochondrial transport
and causes axonal degeneration via a CaMKII-dependent elevation of
intracellular Ca(2). Nat Commun. 11(2679)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Vriens J, Watanabe H, Janssens A,
Droogmans G, Voets T and Nilius B: Cell swelling, heat, and
chemical agonists use distinct pathways for the activation of the
cation channel TRPV4. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:396–401.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Asao Y, Tobori S, Kakae M, Nagayasu K,
Shibasaki K, Shirakawa H and Kaneko S: Transient receptor potential
vanilloid 4 agonist GSK1016790A improves neurological outcomes
after intracerebral hemorrhage in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
529:590–595. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shibasaki K, Sugio S, Takao K, Yamanaka A,
Miyakawa T, Tominaga M and Ishizaki Y: TRPV4 activation at the
physiological temperature is a critical determinant of neuronal
excitability and behavior. Pflugers Arch. 467:2495–2507.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yang C, Si M and Zhou J: Silencing TRPV4
partially reverses the neurotoxic effects caused by excess
ketamine. J Toxicol Sci. 46:69–81. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang Z, Liu T, Yin C, Li Y, Gao F, Yu L
and Wang Q: Electroacupuncture pretreatment ameliorates anesthesia
and surgery-induced cognitive dysfunction via activation of an
α7-nAChR signal in aged rats. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat.
17:2599–2611. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Stephenson W: Deficiencies in the national
institute of health's guidelines for the care and protection of
laboratory animals. J Med Philos. 18:375–388. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kilkenny C, Browne W, Cuthill IC, Emerson
M and Altman DG: NC3Rs Reporting Guidelines Working Group: NC3Rs
reporting guidelines working group. Animal research: Reporting in
vivo experiments: The ARRIVE guidelines. J Gene Med. 12:561–563.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Netto MB, de Oliveira Junior AN, Goldim M,
Mathias K, Fileti ME, da Rosa N, Laurentino AO, de Farias BX, Costa
AB, Rezin GT, et al: Oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction
contributes to postoperative cognitive dysfunction in elderly rats.
Brain Behav Immun. 73:661–669. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Feng X, Valdearcos M, Uchida Y, Lutrin D,
Maze M and Koliwad SK: Microglia mediate postoperative hippocampal
inflammation and cognitive decline in mice. JCI Insight.
2(e91229)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Amiri S, Haj-Mirzaian A, Amini-khoei H,
Momeny M, Shirzadian A, Rahimi-Balaei M, Zarrinrad G,
Ghazi-Khansari M, Azizi R, Dehpour AR and Mehr SE: NMDA receptor
antagonists attenuate the proconvulsant effect of juvenile social
isolation in male mice. Brain Res Bull. 121:158–168.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Berrino L, Oliva P, Massimo F, Aurilio C,
Maione S, Grella A and Rossi F: Antinociceptive effect in mice of
intraperitoneal N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists in the
formalin test. Eur J Pain. 7:131–137. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jiang XL, Gu XY, Zhou XX, Chen XM, Zhang
X, Yang YT, Qin Y, Shen L, Yu WF and Su DS: Intestinal
dysbacteriosis mediates the reference memory deficit induced by
anaesthesia/surgery in aged mice. Brain Behav Immun. 80:605–615.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Meng B, Li X, Lu B, Liu R, Yuan H, Zhai X,
Qin J, Chen Z, Zheng J and Chen J: The investigation of
hippocampus-dependent cognitive decline induced by
anesthesia/surgery in mice through integrated behavioral Z-scoring.
Front Behav Neurosci. 13(282)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Faria RS, Gutierres LF, Sobrinho FC, do
Vale Miranda I, Reis JD, Dias EV, Sartori CR and Moreira DAR:
Effects of the swimming exercise on the consolidation and
persistence of auditory and contextual fear memory. Neurosci Lett.
628:147–152. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sun L, Zhou R, Yang G and Shi Y: Analysis
of 138 pathogenic mutations in presenilin-1 on the in vitro
production of Aβ42 and Aβ40 peptides by γ-secretase. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 114:E476–E485. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tamano H and Takeda A: Is interaction of
amyloid β-peptides with metals involved in cognitive activity?
Metallomics. 7:1205–1212. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Socodato R, Portugal CC, Canedo T,
Rodrigues A, Almeida TO, Henriques JF, Vaz SH, Magalhães J, Silva
CM, Baptista FI, et al: Microglia dysfunction caused by the loss of
rhoa disrupts neuronal physiology and leads to neurodegeneration.
Cell Rep. 31(107796)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Koskenkorva-Frank TS, Weiss G, Koppenol WH
and Burckhardt S: The complex interplay of iron metabolism,
reactive oxygen species, and reactive nitrogen species: Insights
into the potential of various iron therapies to induce oxidative
and nitrosative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 65:1174–1194.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
El Tabaa MM, Sokkar SS, Ramadan ES, Abd El
Salam IZ and Zaid A: Neuroprotective role of Ginkgo biloba against
cognitive deficits associated with bisphenol a exposure: An animal
model study. Neurochem Int. 108:199–212. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zhang J, Yu C, Zhang X, Chen H, Dong J, Lu
W, Song Z and Zhou W: Porphyromonas gingivalis lipopolysaccharide
induces cognitive dysfunction, mediated by neuronal inflammation
via activation of the TLR4 signaling pathway in C57BL/6 mice. J
Neuroinflammation. 15(37)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu Y, Zhang Y, Zheng X, Fang T, Yang X,
Luo X, Guo A, Newell KA, Huang XF and Yu Y: Galantamine improves
cognition, hippocampal inflammation, and synaptic plasticity
impairments induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice. J
Neuroinflammation. 15(112)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Tian Y, Qi M, Wang Z, Wu C, Sun Z, Li Y,
Sha S, Du Y and Chen L and Chen L: Activation of transient receptor
potential vanilloid 4 impairs the dendritic arborization of newborn
neurons in the hippocampal dentate gyrus through the AMPK and Akt
signaling pathways. Front Mol Neurosci. 10(190)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hattori K, Takahashi N, Terabe K, Ohashi
Y, Kishimoto K, Yokota Y, Suzuki M, Kojima T and Imagama S:
Activation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 4 protects
articular cartilage against inflammatory responses via
CaMKK/AMPK/NF-κB signaling pathway. Sci Rep.
11(15508)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Feng J, Xu Y, Lin P, Peng X, Wang Y and
Zhang Z: Identification of IκBα in Japanese eel Anguilla japonica
that impairs the IKKα-dependent activation of NF-κB, AP1, and type
I IFN signaling pathways. Dev Comp Immunol.
122(104044)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zhang B, Wang PP, Hu KL, Li LN, Yu X, Lu Y
and Chang HS: Antidepressant-like effect and mechanism of action of
honokiol on the mouse lipopolysaccharide (LPS) depression model.
Molecules. 24(2035)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Harris WH and Sledge CB: Total hip and
total knee replacement (1). N Engl J Med. 323:725–731.
1990.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ancelin ML, de Roquefeuil G, Scali J,
Bonnel F, Adam JF, Cheminal JC, Cristol JP, Dupuy AM, Carrière I
and Ritchie K: Long-term post-operative cognitive decline in the
elderly: the effects of anesthesia type, apolipoprotein E genotype,
and clinical antecedents. J Alzheimers Dis. 22 (Suppl 3):S105–S113.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Evered L, Scott DA, Silbert B and Maruff
P: Postoperative cognitive dysfunction is independent of type of
surgery and anesthetic. Anesth Analg. 112:1179–1185.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Williams-Russo P, Sharrock NE, Mattis S,
Liguori GA, Mancuso C, Peterson MG, Hollenberg J, Ranawat C,
Salvati E and Sculco T: Randomized trial of hypotensive epidural
anesthesia in older adults. Anesthesiology. 91:926–935.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Li PJ, Guo YQ, Ding PY, Liu RB, Deng F,
Feng XX and Yan WJ: Neuroprotective effects of a Smoothened
receptor agonist against postoperative cognitive dysfunction by
promoting autophagy in the dentate gyrus of aged rats. Neurol Res.
41:867–874. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhang X, Jiang X, Huang L, Tian W, Chen X,
Gu X, Yu W, Tian J and Su D: Central cholinergic system mediates
working memory deficit induced by anesthesia/surgery in adult mice.
Brain Behav. 8(e00957)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Cibelli M, Fidalgo AR, Terrando N, Ma D,
Monaco C, Feldmann M, Takata M, Lever IJ, Nanchahal J, Fanselow MS
and Maze M: Role of interleukin-1beta in postoperative cognitive
dysfunction. Ann Neurol. 68:360–368. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wang P, Velagapudi R, Kong C, Rodriguiz
RM, Wetsel WC, Yang T, Berger M, Gelbard HA, Colton CA and Terrando
N: Neurovascular and immune mechanisms that regulate postoperative
delirium superimposed on dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 16:734–749.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Subramaniyan S and Terrando N:
Neuroinflammation and perioperative neurocognitive disorders.
Anesth Analg. 128:781–788. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Liu Q, Sun YM, Huang H, Chen C, Wan J, Ma
LH, Sun YY, Miao HH and Wu YQ: Sirtuin 3 protects against
anesthesia/surgery-induced cognitive decline in aged mice by
suppressing hippocampal neuroinflammation. J Neuroinflammation.
18(41)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Guéniot L, Lepere V, De Medeiros GF,
Danckaert A, Flamant P, Dudal ML, Langeron O, Goossens PL, Chrétien
F and Jouvion G: Muscle injury induces postoperative cognitive
dysfunction. Sci Rep. 10(2768)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Xu J, Dong H, Qian Q, Zhang X, Wang Y, Jin
W and Qian Y: Astrocyte-derived CCL2 participates in
surgery-induced cognitive dysfunction and neuroinflammation via
evoking microglia activation. Behav Brain Res. 332:145–153.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Lai IK, Valdearcos M, Morioka K, Saxena S,
Feng X, Li R, Uchida Y, Lijun A, Li W, Pan J, et al: Blocking Kv1.3
potassium channels prevents postoperative neuroinflammation and
cognitive decline without impairing wound healing in mice. Br J
Anaesth. 125:298–307. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Lambertsen KL, Finsen B and Clausen BH:
Post-stroke inflammation-target or tool for therapy? Acta
Neuropathol. 137:693–714. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Diaz-Cañestro C, Reiner MF, Bonetti NR,
Liberale L, Merlini M, Wüst P, Amstalden H, Briand-Schumacher S,
Semerano A and Giacalone G: AP-1 (Activated Protein-1)
transcription factor JunD regulates ischemia/reperfusion brain
damage via IL-1β (Interleukin-1β). Stroke. 50:469–477.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Patterson SL: Immune dysregulation and
cognitive vulnerability in the aging brain: Interactions of
microglia, IL-1β, BDNF and synaptic plasticity. Neuropharmacology.
96:11–18. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Wang X and Michaelis EK: Selective
neuronal vulnerability to oxidative stress in the brain. Front
Aging Neurosci. 2(12)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Skvarc DR, Berk M, Byrne LK, Dean OM, Dodd
S, Lewis M, Marriott A, Moore EM, Morris G, Page RS and Gray L:
Post-operative cognitive dysfunction: An exploration of the
inflammatory hypothesis and novel therapies. Neurosci Biobehav Rev.
84:116–133. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zhang X, Dong H, Li N, Zhang S, Sun J,
Zhang S and Qian Y: Activated brain mast cells contribute to
postoperative cognitive dysfunction by evoking microglia activation
and neuronal apoptosis. J Neuroinflammation. 13(127)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Yuan N, Wang X, Zhang Y, Kong L, Yuan L
and Ge Y: Intervention of NF-Κb signaling pathway and preventing
post-operative cognitive dysfunction as well as neuronal apoptosis.
Iran J Public Health. 51:124–132. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Konsman JP, Parnet P and Dantzer R:
Cytokine-induced sickness behaviour: Mechanisms and implications.
Trends Neurosci. 25:154–159. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Peng S, Li P, Liu P, Yan H, Wang J, Lu W,
Liu C and Zhou Y: Cistanches alleviates sevoflurane-induced
cognitive dysfunction by regulating PPAR-γ-dependent antioxidant
and anti-inflammatory in rats. J Cell Mol Med. 24:1345–1359.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Liu PR, Cao F, Zhang Y and Peng S:
Electroacupuncture reduces astrocyte number and oxidative stress in
aged rats with surgery-induced cognitive dysfunction. J Int Med
Res. 47:3860–3873. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Nelissen S, Lemmens E, Geurts N, Kramer P,
Maurer M, Hendriks J and Hendrix S: The role of mast cells in
neuroinflammation. Acta Neuropathol. 125:637–650. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Li N, Zhang X, Dong H, Hu Y and Qian Y:
Bidirectional relationship of mast cells-neurovascular unit
communication in neuroinflammation and its involvement in POCD.
Behav Brain Res. 322:60–69. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Zhang S, Dong H, Zhang X, Li N, Sun J and
Qian Y: Cerebral mast cells contribute to postoperative cognitive
dysfunction by promoting blood brain barrier disruption. Behav
Brain Res. 298:158–166. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Liang J, Wu S, Xie W and He H: Ketamine
ameliorates oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in experimental
traumatic brain injury via the Nrf2 pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther.
12:845–853. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Zanos P, Moaddel R, Morris PJ, Riggs LM,
Highland JN, Georgiou P, Pereira EFR, Albuquerque EX, Thomas CJ,
Zarate CA Jr and Gould TD: Ketamine and ketamine metabolite
pharmacology: Insights into therapeutic mechanisms. Pharmacol Rev.
70:621–660. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Yang Y, Song Y, Zhang X, Zhao W, Ma T, Liu
Y, Ma P, Zhao Y and Zhang H: Ketamine relieves depression-like
behaviors induced by chronic postsurgical pain in rats through
anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant effects and regulating BDNF
expression. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 237:1657–1669.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Lu Y, Ding X, Wu X and Huang S: Ketamine
inhibits LPS-mediated BV2 microglial inflammation via NMDA receptor
blockage. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 34:229–237. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Li X, Wang J, Song X, Wu H, Guo P, Jin Z,
Wang C, Tang C, Wang Y and Zhang Z: Ketamine ameliorates
ischemia-reperfusion injury after liver autotransplantation by
suppressing activation of Kupffer cells in rats. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 96:886–892. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Wang C, Gao Y, Zhang Z, Chi Q, Liu Y, Yang
L and Xu K: Safflower yellow alleviates osteoarthritis and prevents
inflammation by inhibiting PGE2 release and regulating
NF-κB/SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathways. Phytomedicine.
78(153305)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Xu SX, Zhou ZQ, Li XM, Ji MH, Zhang GF and
Yang JJ: The activation of adenosine monophosphate-activated
protein kinase in rat hippocampus contributes to the rapid
antidepressant effect of ketamine. Behav Brain Res. 253:305–309.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Xiang HC, Lin LX, Hu XF, Zhu H, Li HP,
Zhang RY, Hu L, Liu WT, Zhao YL, Shu Y, et al: AMPK activation
attenuates inflammatory pain through inhibiting NF-κB activation
and IL-1β expression. J Neuroinflammation. 16(34)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Sakai T, Ichiyama T, Whitten CW, Giesecke
AH and Lipton JM: Ketamine suppresses endotoxin-induced NF-kappaB
expression. Can J Anaesth. 47:1019–1024. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Liedtke W and Kim C: Functionality of the
TRPV subfamily of TRP ion channels: Add mechano-TRP and osmo-TRP to
the lexicon! Cell Mol Life Sci. 62:2985–3001. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Suzuki T, Notomi T, Miyajima D, Mizoguchi
F, Hayata T, Nakamoto T, Hanyu R, Kamolratanakul P, Mizuno A,
Suzuki M, et al: Osteoblastic differentiation enhances expression
of TRPV4 that is required for calcium oscillation induced by
mechanical force. Bone. 54:172–178. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Liu L, Guo M, Lv X, Wang Z, Yang J, Li Y,
Yu F, Wen X, Feng L and Zhou T: Role of transient receptor
potential vanilloid 4 in vascular function. Front Mol Biosci.
8(677661)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Dutta B, Arya RK, Goswami R, Alharbi MO,
Sharma S and Rahaman SO: Role of macrophage TRPV4 in inflammation.
Lab Invest. 100:178–185. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
De Logu F, Trevisan G, Marone IM, Coppi E,
Dalenogare DP, Titiz M, Marini M, Landini L, de Araujo DSM, Puma
SL, et al: Oxidative stress mediates thalidomide-induced pain by
targeting peripheral TRPA1 and central TRPV4. BMC Biol.
18(197)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Liu X, Chhipa RR, Nakano I and Dasgupta B:
The AMPK inhibitor compound C is a potent AMPK-independent
antiglioma agent. Mol Cancer Ther. 13:596–605. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Ross FA, Hawley SA, Auciello FR, Gowans
GJ, Atrih A, Lamont DJ and Hardie DG: Mechanisms of paradoxical
activation of AMPK by the kinase inhibitors SU6656 and sorafenib.
Cell Chem Biol. 24:813–824. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|