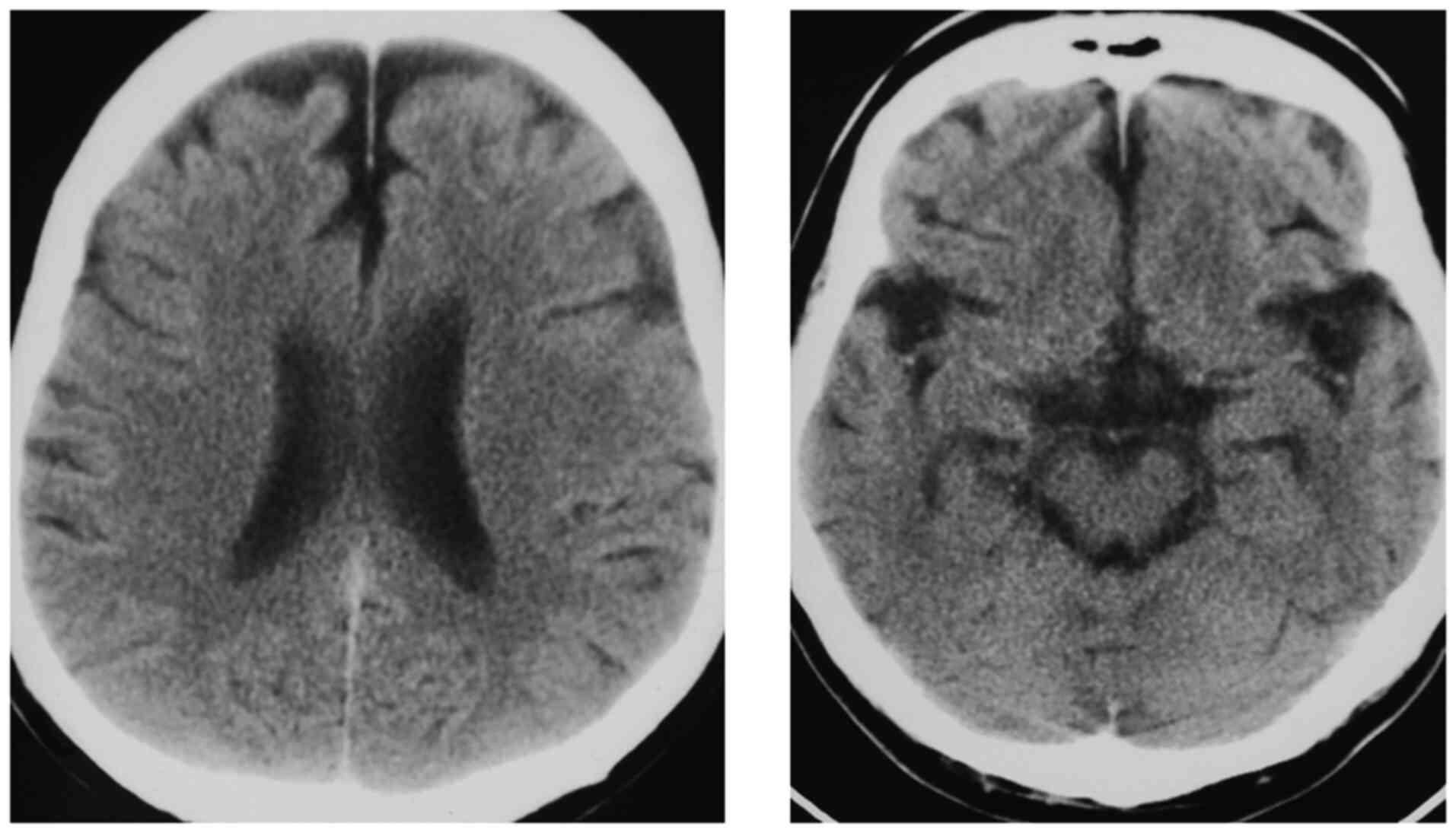
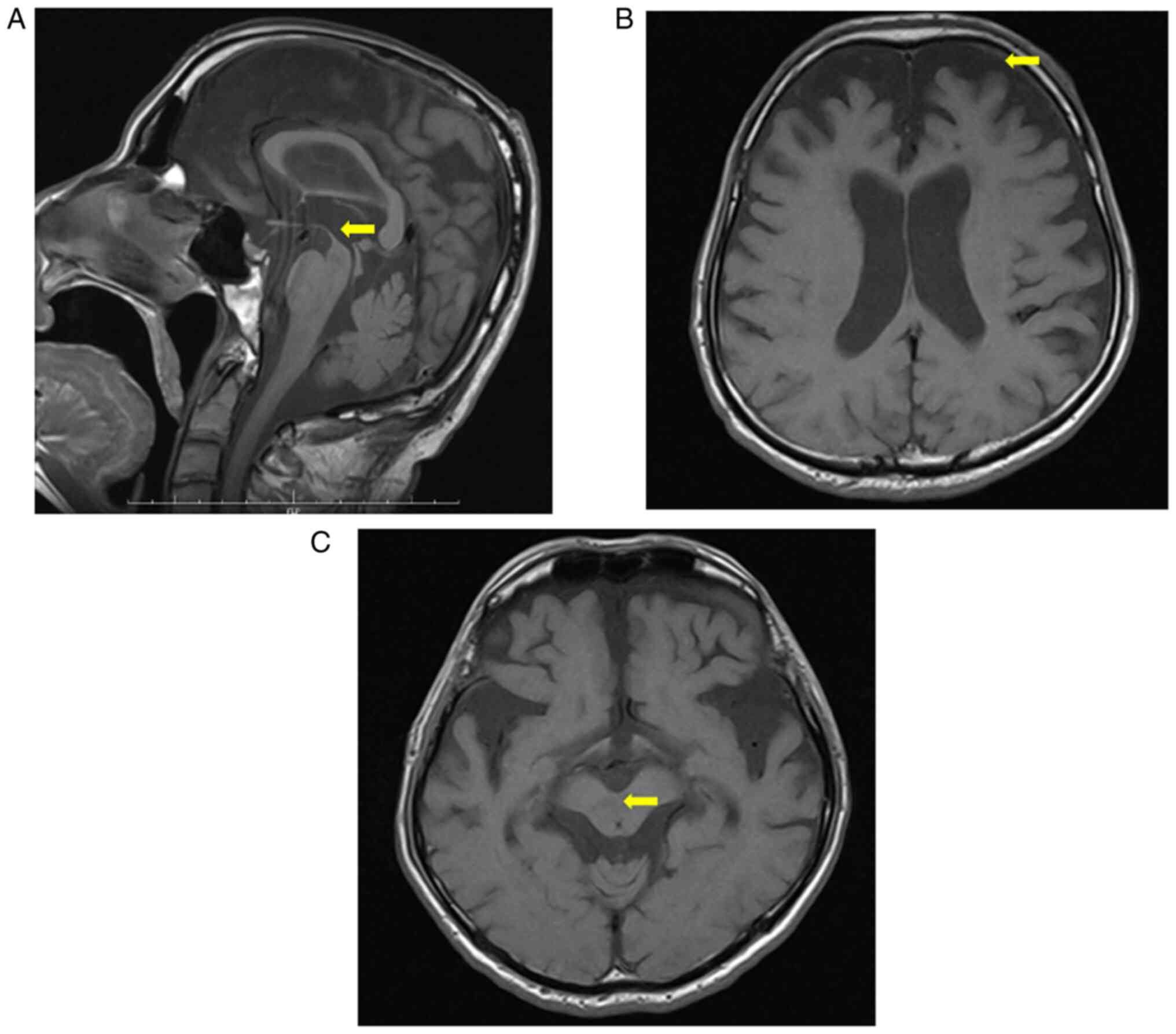
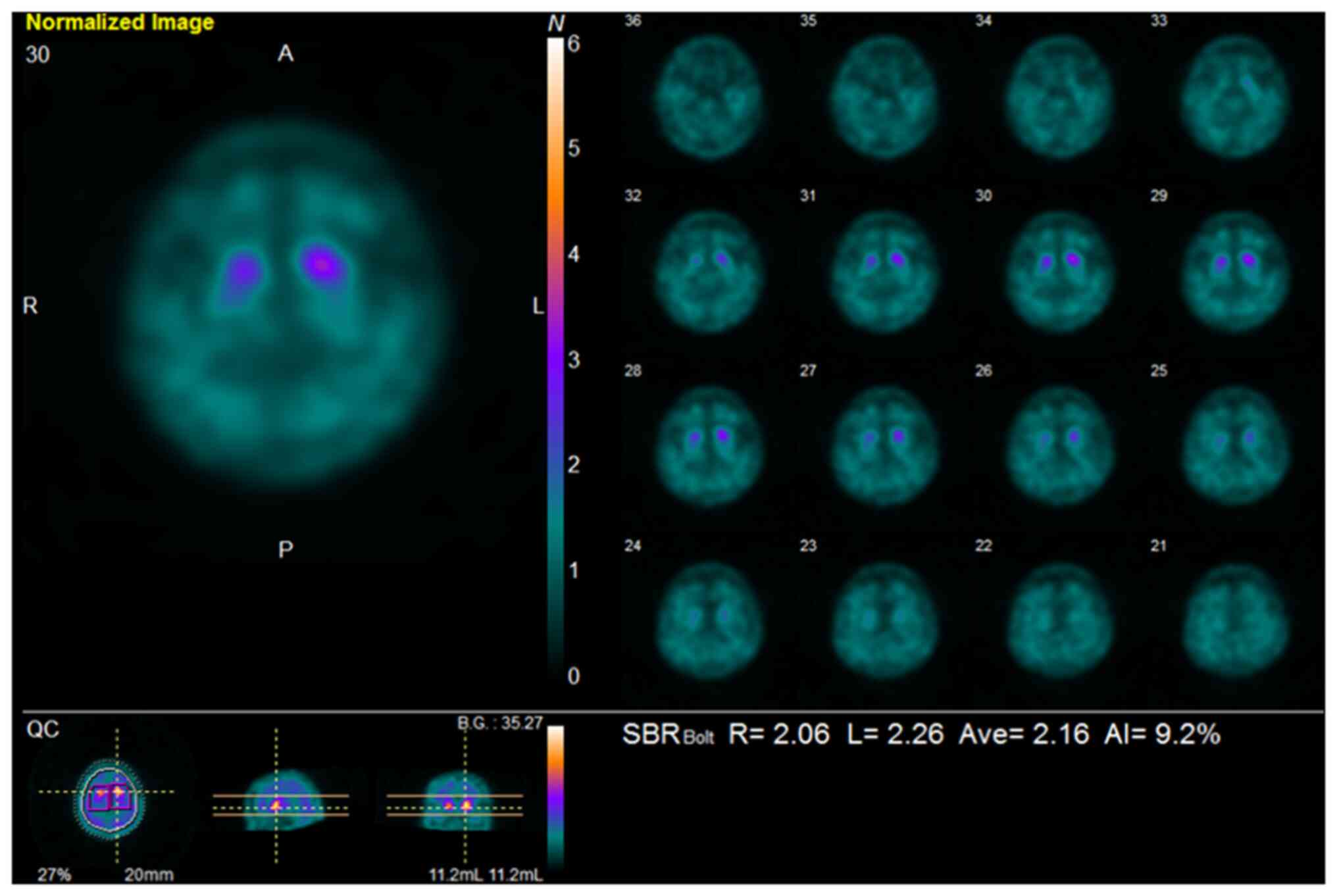
|
1
|
Savica R, Grossardt BR, Bower JH, Ahlskog
JE, Mielke MM and Rocca WA: Incidence and time trends of
drug-induced parkinsonism: A 30-year population-based study. Mov
Disord. 32:227–234. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Komatsu H, Kato M, Kinpara T, Ono T and
Kakuto Y: Possible multiple system atrophy with predominant
parkinsonism in a patient with chronic schizophrenia: A case
report. BMC Psychiatry. 18(141)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Steele JC, Richardson JC and Olszewski J:
Progressive supranuclear palsy. A heterogeneous degeneration
involving the brain stem, basal ganglia and cerebellum with
vertical gaze and pseudobulbar palsy, nuchal dystonia and dementia.
Arch Neurol. 10:333–359. 1964.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Höglinger GU, Respondek G, Stamelou M,
Kurz C, Josephs KA, Lang AE, Mollenhauer B, Müller U, Nilsson C,
Whitwell JL, et al: Clinical diagnosis of progressive supranuclear
palsy: The movement disorder society criteria. Mov Disord.
32:853–864. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Coyle-Gilchrist IT, Dick KM, Patterson K,
Vázquez Rodríquez P, Wehmann E, Wilcox A, Lansdall CJ, Dawson KE,
Wiggins J, Mead S, et al: Prevalence, characteristics, and survival
of frontotemporal lobar degeneration syndromes. Neurology.
86:1736–1743. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Nath U, Ben-Shlomo Y, Thomson RG, Morris
HR, Wood NW, Lees AJ and Burn DJ: The prevalence of progressive
supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome) in the
UK. Brain. 124:1438–1449. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Respondek G, Kurz C, Arzberger T, Compta
Y, Englund E, Ferguson LW, Gelpi E, Giese A, Irwin DJ, Meissner WG,
et al: Which ante mortem clinical features predict progressive
supranuclear palsy pathology. Mov Disord. 32:995–1005.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Boxer AL, Yu JT, Golbe LI, Litvan I, Lang
AE and Höglinger GU: Advances in progressive supranuclear palsy:
New diagnostic criteria, biomarkers, and therapeutic approaches.
Lancet Neurol. 16:552–563. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Williams DR and Lees AJ: Progressive
supranuclear palsy: Clinicopathological concepts and diagnostic
challenges. Lancet Neurol. 8:270–279. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gerstenecker A, Duff K, Mast B and Litvan
I: ENGENE-PSP Study Group. Behavioral abnormalities in progressive
supranuclear palsy. Psychiatry Res. 210:1205–1210. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Massey LA, Micallef C, Paviour DC,
O'Sullivan SS, Ling H, Williams DR, Kallis C, Holton JL, Revesz T,
Burn DJ, et al: Conventional magnetic resonance imaging in confirmed
progressive supranuclear palsy and multiple system atrophy. Mov
Disord. 27:1754–1762. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Whitwell JL, Höglinger GU, Antonini A,
Bordelon Y, Boxer AL, Colosimo C, van Eimeren T, Golbe LI, Kassubek
J, Kurz C, et al: Radiological biomarkers for diagnosis in PSP:
Where are we and where do we need to be. Mov Disord. 32:955–971.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
DeMaagd G and Philip A: Parkinson's
disease and its management: Part 1: Disease entity, risk factors,
pathophysiology, clinical presentation, and diagnosis. P T.
40:504–532. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lee PE, Sykora K, Gill SS, Mamdani M,
Marras C, Anderson G, Shulman KI, Stukel T, Normand SL and Rochon
PA: Antipsychotic medications and drug-induced movement disorders
other than parkinsonism: A population-based cohort study in older
adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 53:1374–1379. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hayes MT: Parkinson's disease and
parkinsonism. Am J Med. 132:802–807. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tolosa E, Coelho M and Gallardo M: DAT
imaging in drug-induced and psychogenic parkinsonism. Mov Disord.
18 (Suppl 7):S28–S33. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Oh J, Shen G and Nan G: Comorbid
schizophrenia and Parkinson's disease: A case series and brief
review. Neurol Asia. 22:139–142. 2017.
|
|
18
|
Grover S, Sahoo S and Goyal MK:
Schizophrenia with comorbid idiopathic Parkinson's disease: A
difficult clinical management scenario. Indian J Psychol Med.
39:823–827. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Winter C, Juckel G, Plotkin M, Niehaus L
and Kupsch A: Paranoid schizophrenia and idiopathic Parkinson's
disease do coexist: A challenge for clinicians. Psychiatry Clin
Neurosci. 60(639)2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Waddington JL: Psychosis in Parkinson's
disease and parkinsonism in antipsychotic-naive schizophrenia
spectrum psychosis: Clinical, nosological and pathobiological
challenges. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 41:464–470. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|