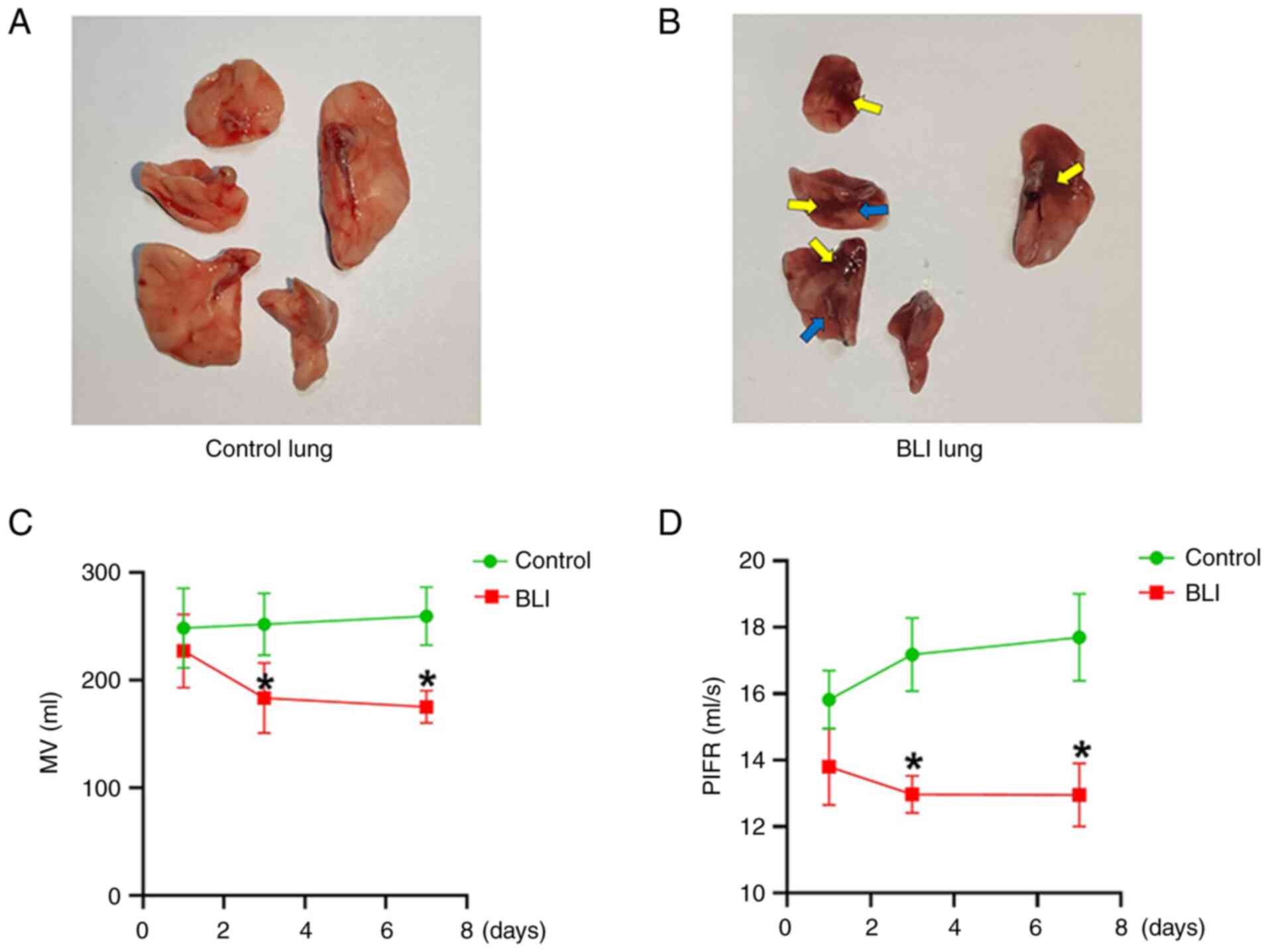
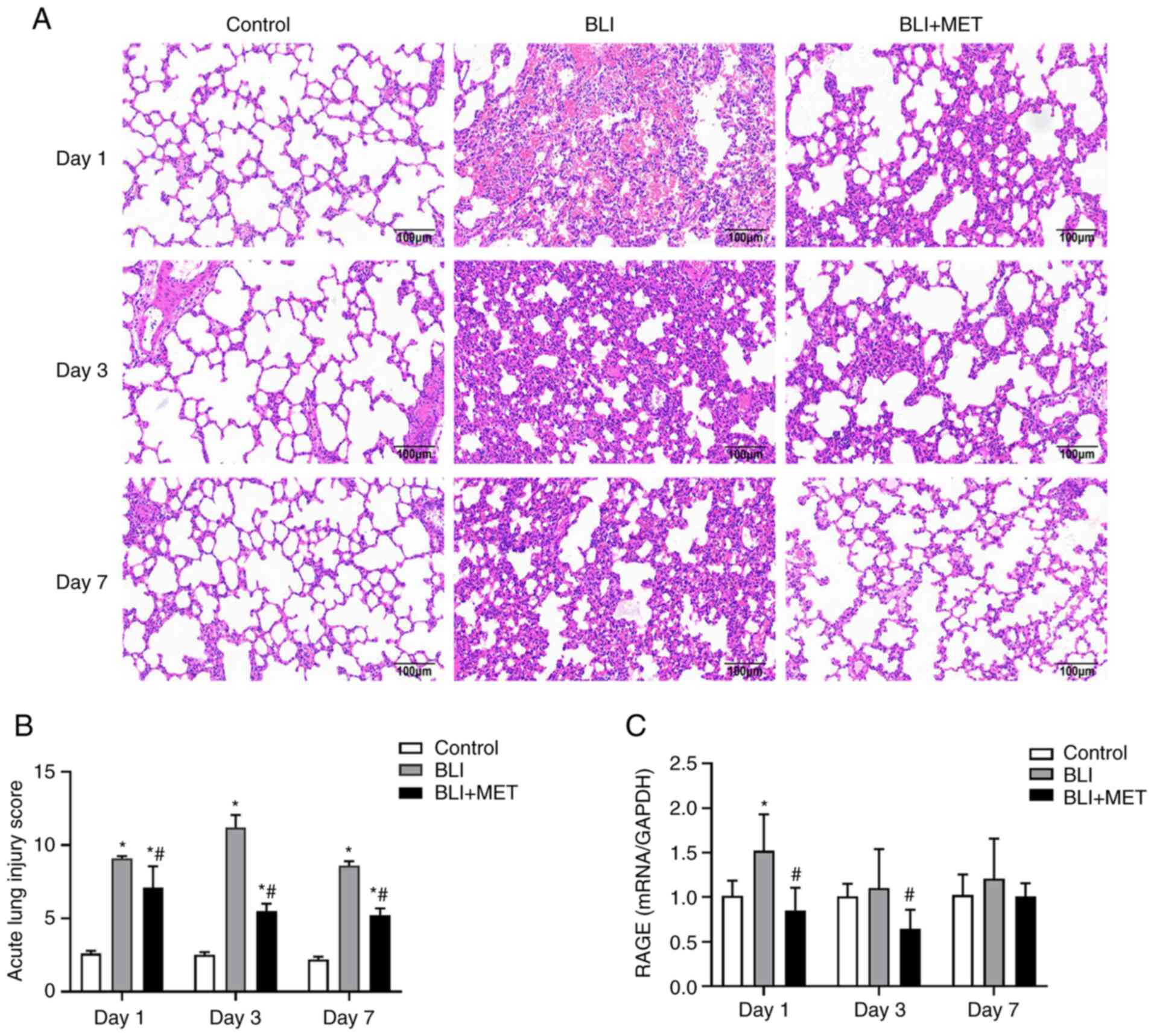
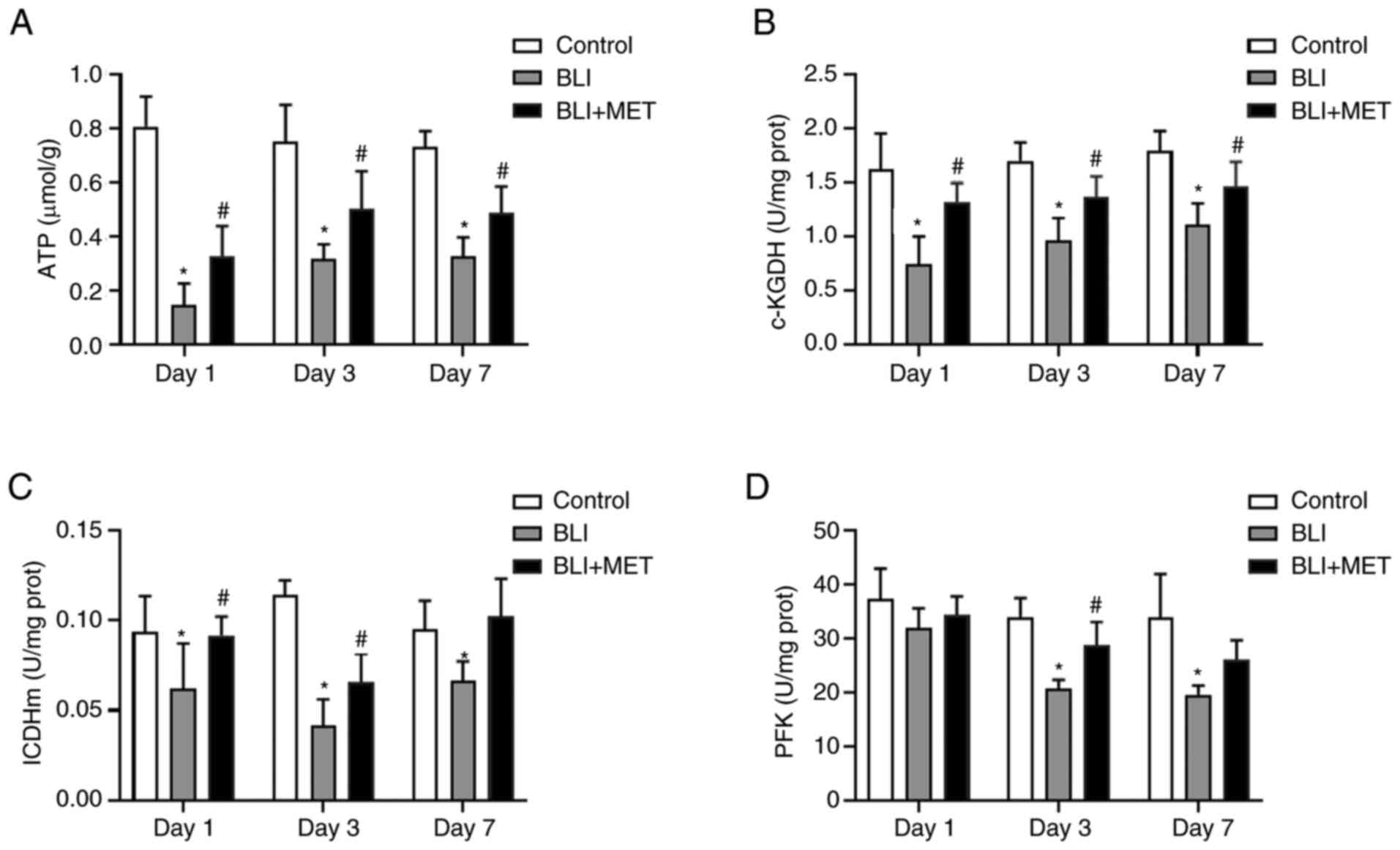
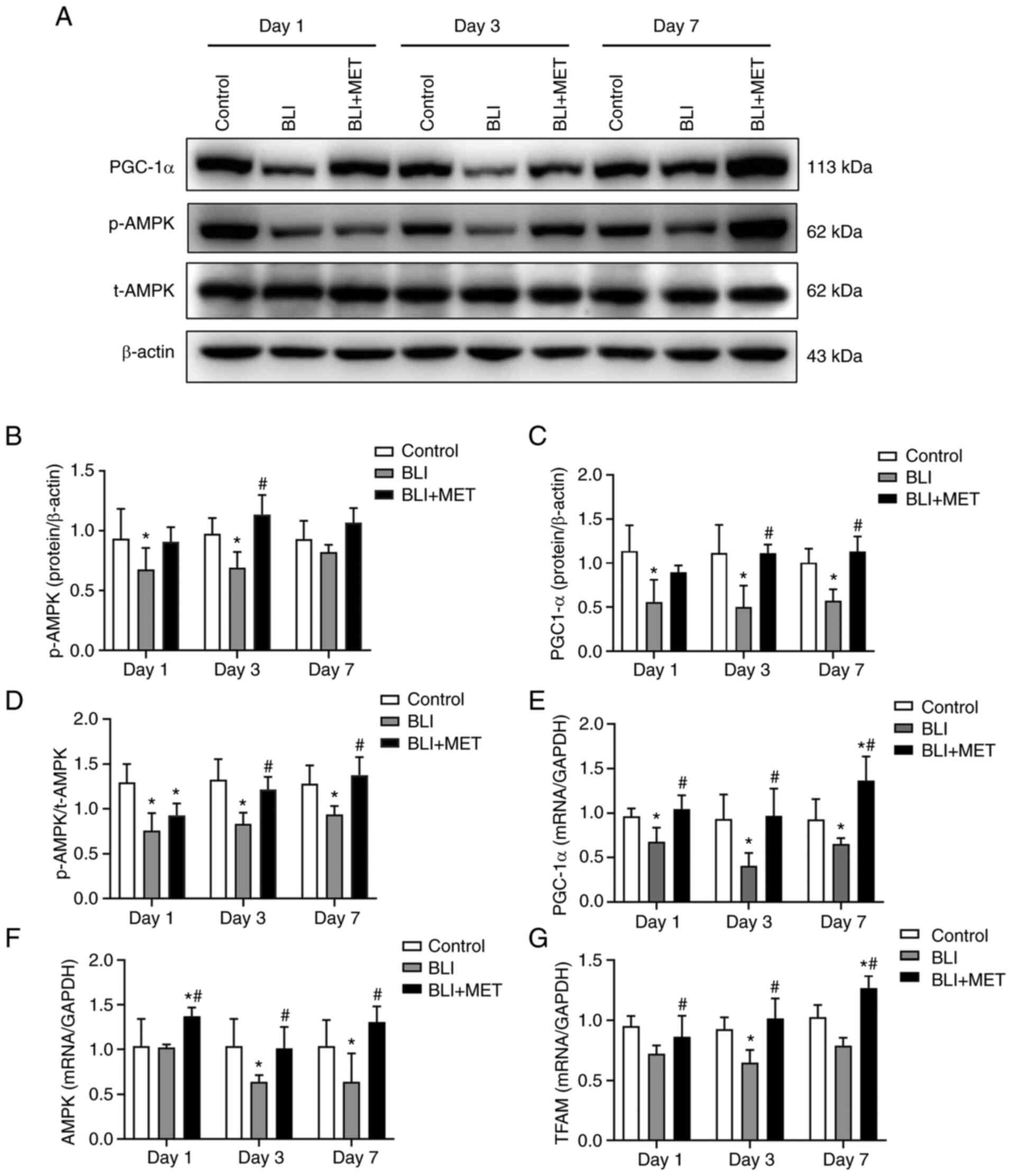
|
1
|
Li J, Qin Y, Wang Z and Xin Y: How to
analyse the injury based on 24Model: A case study of coal mine gas
explosion injury. Inj Prev. 27:542–553. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Li N, Geng C, Hou S, Fan H and Gong Y:
Damage-associated molecular patterns and their signaling pathways
in primary blast lung injury: New research progress and future
directions. Int J Mol Sci. 21(6303)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wolf SJ, Bebarta VS, Bonnett CJ, Pons PT
and Cantrill SV: Blast injuries. Lancet. 374:405–415.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Smith JE and Garner J: Pathophysiology of
primary blast injury. J R Army Med Corps. 165:57–62.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang Z, Li H, Liang Z, Li C, Yang Z, Li
Y, Cao L, She Y, Wang W, Liu C and Chen L: Vaporized
perfluorocarbon inhalation attenuates primary blast lung injury in
canines by inhibiting mitogen-activated protein kinase/nuclear
factor-κB activation and inducing nuclear factor, erythroid 2 like
2 pathway. Toxicol Lett. 319:49–57. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Dong X, Wu W, Yao S, Cao J, He L, Ren H
and Ren W: Evaluation of gas explosion injury based on analysis of
rat serum profile by ultra-performance liquid chromatography/mass
spectrometry-based metabonomics techniques. Biomed Res Int.
2020(8645869)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Quijano C, Trujillo M, Castro L and
Trostchansky A: Interplay between oxidant species and energy
metabolism. Redox Biol. 8:28–42. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kellner M, Noonepalle S, Lu Q, Srivastava
A, Zemskov E and Black SM: ROS signaling in the pathogenesis of
acute lung injury (ALI) and acute respiratory distress syndrome
(ARDS). Adv Exp Med Biol. 967:105–137. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Liu X and Chen Z: The pathophysiological
role of mitochondrial oxidative stress in lung diseases. J Transl
Med. 15(207)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Fathi H, Ebrahimzadeh MA, Ziar A and
Mohammadi H: Oxidative damage induced by retching; antiemetic and
neuroprotective role of Sambucus ebulus L. Cell Biol Toxicol.
31:231–239. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hardie DG: AMP-activated protein kinase:
Maintaining energy homeostasis at the cellular and whole-body
levels. Annu Rev Nutr. 34:31–55. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Magnani ND, Marchini T, Vanasco V, Tasat
DR, Alvarez S and Evelson P: Reactive oxygen species produced by
NADPH oxidase and mitochondrial dysfunction in lung after an acute
exposure to residual oil fly ashes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
270:31–38. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Aviello G and Knaus UG: NADPH oxidases and
ROS signaling in the gastrointestinal tract. Mucosal Immunol.
11:1011–1023. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Nadeem A, Al-Harbi NO, Ahmad SF, Ibrahim
KE, Siddiqui N and Al-Harbi MM: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
inhibition attenuates acute lung injury through reduction in NADPH
oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species. Clin Exp Immunol.
191:279–287. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Rodríguez C, Contreras C, Sáenz-Medina J,
Muñoz M, Corbacho C, Carballido J, García-Sacristán A, Hernandez M,
López M, Rivera L and Prieto D: Activation of the AMP-related
kinase (AMPK) induces renal vasodilatation and downregulates
Nox-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation. Redox Biol.
34(101575)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Nunnari J and Suomalainen A: Mitochondria:
In sickness and in health. Cell. 148:1145–1159. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chang M, Xu G, Xiong C, Yang X, Yan S, Tao
Y, Li H, Li Y, Yao S and Zhao Y: Alpha-lipoic acid attenuates
silica-induced pulmonary fibrosis by improving mitochondrial
function via AMPK/PGC1α pathway activation in C57BL/6J mice.
Toxicol Lett. 350:121–132. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang Y, An H, Liu T, Qin C, Sesaki H, Guo
S, Radovick S, Hussain M, Maheshwari A, Wondisford FE, et al:
Metformin improves mitochondrial respiratory activity through
activation of AMPK. Cell Rep. 29:1511–1523.e5. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang G, Song Y, Feng W, Liu L, Zhu Y, Xie
X, Pan Y, Ke R, Li S, Li F, et al: Activation of AMPK attenuates
LPS-induced acute lung injury by upregulation of PGC1α and SOD1.
Exp Ther Med. 12:1551–1555. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
National Research Council (US) Institute
for Laboratory Animal Research. Guide for the care and use of
laboratory animals, 8th edition. National Academies
Press,Washington, DC, 2011.
|
|
21
|
Mikawa K, Nishina K, Takao Y and Obara H:
ONO-1714, a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, attenuates
endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in rabbits. Anesth Analg.
97:1751–1755. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Creagh-Brown BC, Quinlan GJ, Evans TW and
Burke-Gaffney A: The RAGE axis in systemic inflammation, acute lung
injury and myocardial dysfunction: An important therapeutic target?
Intensive Care Med. 36:1644–1656. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Tretter L and Adam-Vizi V:
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase: A target and generator of
oxidative stress. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci.
360:2335–2345. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Legendre F, MacLean A, Appanna VP and
Appanna VD: Biochemical pathways to α-ketoglutarate, a
multi-faceted metabolite. World J Microbiol Biotechnol.
36(123)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang JN, Li HB, Dong XW, Wu WD, Ren WJ and
Yao SQ: Role of pyroptosis pathway related molecules in acute lung
injury induced by gas explosion in rats. Zhonghua Lao Dong Wei
Sheng Zhi Ye Bing Za Zhi. 40:97–102. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Svetlov SI, Larner SF, Kirk DR, Atkinson
J, Hayes RL and Wang KK: Biomarkers of blast-induced neurotrauma:
Profiling molecular and cellular mechanisms of blast brain injury.
J Neurotrauma. 26:913–921. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mathews ZR and Koyfman A: Blast injuries.
J Emerg Med. 49:573–587. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Dong X, Yao S, Wu W, Cao J, Sun L, Li H,
Ren H and Ren W: Gas explosion-induced acute blast lung injury
assessment and biomarker identification by a LC-MS-based serum
metabolomics analysis. Hum Exp Toxicol. 40:608–621. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Podhorecka M, Ibanez B and Dmoszyńska A:
Metformin-its potential anti-cancer and anti-aging effects. Postepy
Hig Med Dosw (Online). 71:170–175. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Luo F, Das A, Chen J, Wu P, Li X and Fang
Z: Metformin in patients with and without diabetes: A paradigm
shift in cardiovascular disease management. Cardiovasc Diabetol.
18(54)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ren H, Shao Y, Wu C, Ma X, Lv C and Wang
Q: Metformin alleviates oxidative stress and enhances autophagy in
diabetic kidney disease via AMPK/SIRT1-FoxO1 pathway. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 500(110628)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Håkansson HF, Smailagic A, Brunmark C,
Miller-Larsson A and Lal H: Altered lung function relates to
inflammation in an acute LPS mouse model. Pulm Pharmacol Ther.
25:399–406. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Papa S, Martino PL, Capitanio G, Gaballo
A, De Rasmo D, Signorile A and Petruzzella V: The oxidative
phosphorylation system in mammalian mitochondria. Adv Exp Med Biol.
942:3–37. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Jin X, Su H, Ding G, Sun Z and Li Z:
Exposure to ambient fine particles causes abnormal energy
metabolism and ATP decrease in lung tissues. Chemosphere.
224:29–38. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhao M, Wang Y, Li L, Liu S, Wang C, Yuan
Y, Yang G, Chen Y, Cheng J, Lu Y and Liu J: Mitochondrial ROS
promote mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation in ischemic
acute kidney injury by disrupting TFAM-mediated mtDNA maintenance.
Theranostics. 11:1845–1863. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Scarpulla RC: Transcriptional paradigms in
mammalian mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Physiol Rev.
88:611–638. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Schoors S, Bruning U, Missiaen R, Queiroz
KC, Borgers G, Elia I, Zecchin A, Cantelmo AR, Christen S, Goveia
J, et al: Fatty acid carbon is essential for dNTP synthesis in
endothelial cells. Nature. 520:192–197. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Brown RF, Cooper GJ and Maynard RL: The
ultrastructure of rat lung following acute primary blast injury.
Int J Exp Pathol. 74:151–162. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Joseph LC, Kokkinaki D, Valenti MC, Kim
GJ, Barca E, Tomar D, Hoffman NE, Subramanyam P, Colecraft HM,
Hirano M, et al: Inhibition of NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2) prevents
sepsis-induced cardiomyopathy by improving calcium handling and
mitochondrial function. JCI Insight. 2(e94248)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Moore T, Yanes RE, Calton MA, Vollrath D,
Enns GM and Cowan TM: AMP-independent activator of AMPK for
treatment of mitochondrial disorders. PLoS One.
15(e0240517)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Schuhmacher S, Foretz M, Knorr M, Jansen
T, Hortmann M, Wenzel P, Oelze M, Kleschyov AL, Daiber A, Keaney JF
Jr, et al: α1AMP-activated protein kinase preserves endothelial
function during chronic angiotensin II treatment by limiting Nox2
upregulation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:560–566.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|