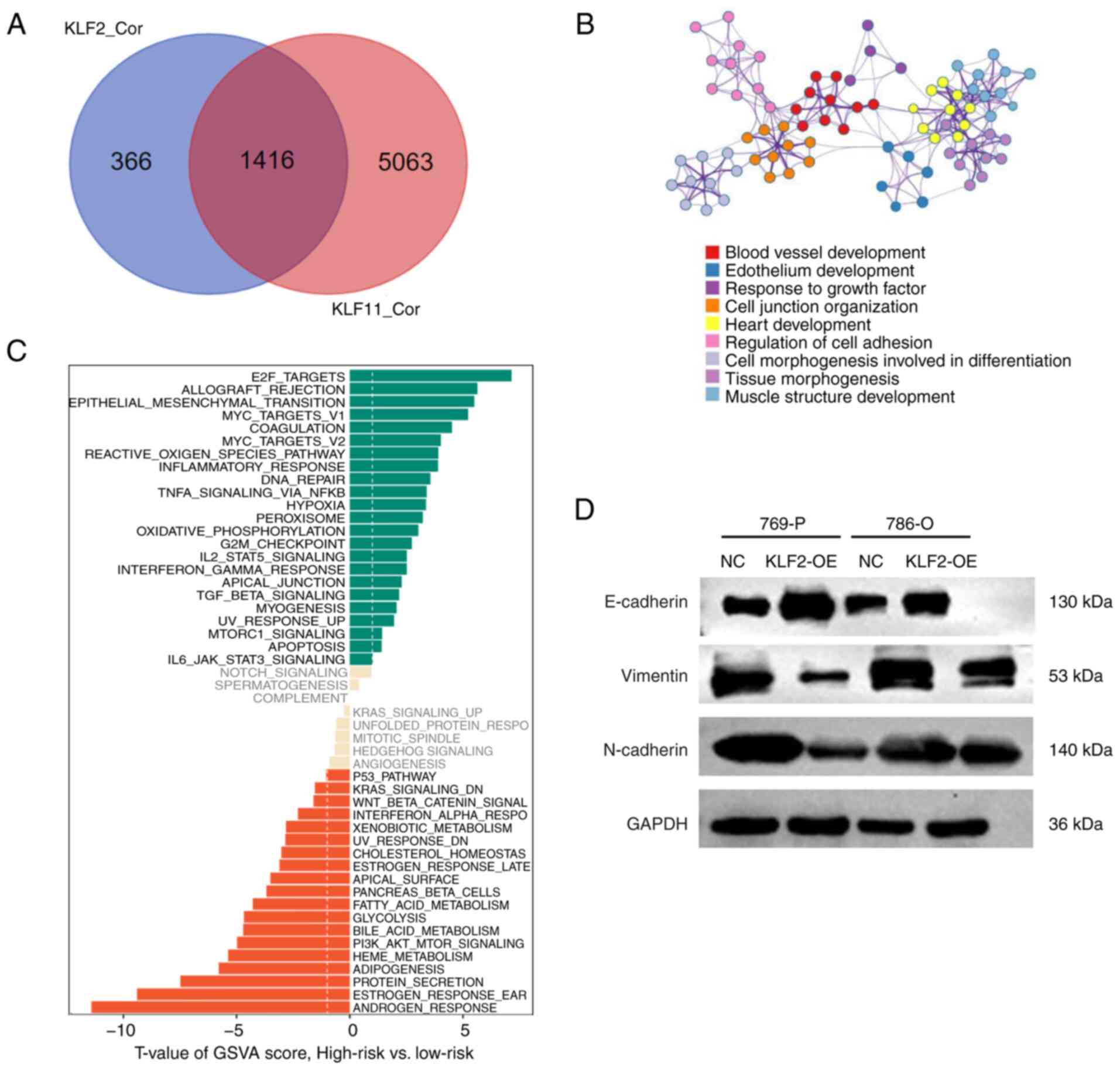
|
1
|
Cohen HT and McGovern FJ: Renal-cell
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 353:2477–2490. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mehdi A and Riazalhosseini Y: Epigenome
aberrations: Emerging driving factors of the clear cell renal cell
carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 18(1774)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Linehan WM and Ricketts CJ: The cancer
genome atlas of renal cell carcinoma: Findings and clinical
implications. Nat Rev Urol. 16:539–552. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lucarelli G, Loizzo D, Franzin R,
Battaglia S, Ferro M, Cantiello F, Castellano G, Bettocchi C,
Ditonno P and Batting M: Metabolomic insights into
pathophysiological mechanisms and biomarker discovery in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 19:397–407.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Allen A, Gau D, Francoeur P, Sturm J, Wand
Y, Martin R, Maranchie J, Duensing A, Kaczorowski A, Duensing S, et
al: Actin-binding protein profilin1 promotes aggressiveness of
clear-cell renal cell carcinoma cells. J Bio Chem. 295:15636–15649.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang Q, Zhang H, Chen Q, Wan Z, Gao X and
Qian W: Identification of METTL14 in kidney renal clear cell
carcinoma using bioinformatics analysis. Dis Markers.
2019(5648783)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Boustany J, Abdessater M, Hachem CE,
Khoury ZE, Khoury WE and Khoury RE: Recurrent metastatic clear cell
renal carcinoma with sarcomatoid dedifferentiation treated with
surgery and Cabozantinib. Oncotarget. 11:1922–1928. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Cakici MC, Kır G, Akalın MK and Yıldırım
A: Clear cell renal cell carcinoma with osseous metaplasia: Two
extremely rare cases and review of the literature. Arch Esp Uro.
73:651–654. 2020.PubMed/NCBI(In English, Spanish).
|
|
9
|
Zhao J and Eyzaguirre E: Clear cell
papillary renal cell carcinoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 143:1154–1158.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Aeppli S, Eboulet EI, Eisen T, Escudier B,
Fischer S, Larkin J, Gruenwald V, McDermott D, Oldenburg J, Omlin
A, et al: Impact of COVID-19 pandemic on treatment patterns in
metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma. ESMO Open. 5 (Suppl
3)(e000852)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bersanelli M, Brunelli M, Gnetti L,
Maestroni U and Buti S: Pazopanib as a possible option for the
treatment of metastatic non-clear cell renal carcinoma patients: A
systematic review. Ther Adv Med Oncol.
12(1758835920915303)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Rajandram R, Perumal K and Yap NY:
Prognostic biomarkers in renal cell carcinoma: Is there a
relationship with obesity? Transl Androl Urol. 8 (Suppl
2):S138–S146. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Oates AC, Pratt SJ, Vail B, Yan YI, Ho RK,
Johnson SL, Postlethwait JH and Zon LI: The zebrafish klf gene
family. Blood. 98:1792–1801. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Moore DL, Blackmore MG, Hu Y, Kaestner KH,
Bixby JL, Lemmon VP and Goldberg JL: KLF family members regulate
intrinsic axon regeneration ability. Science. 326:298–301.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Chen Z, Lei T, Chen X, Zhang J, Yu A, Long
Q, Long H, Jin D, Gan L and Yang Z: Porcine KLF gene family:
Structure, mapping, and phylogenetic analysis. Genomics.
95:111–119. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Miller IJ and Bieker JJ: A novel,
erythroid cell-specific murine transcription factor that binds to
the CACCC element and is related to the Krüppel family of nuclear
proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 13:2776–2786. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ali A, Zhang P, Liangfang Y, Wenshe S,
Wang H, Lin X, Dai Y, Feng XH, Moses R, Wang D, et al: KLF17
empowers TGF-β/Smad signaling by targeting Smad3-dependent pathway
to suppress tumor growth and metastasis during cancer progression.
Cell Death Dis. 6(e1681)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Reidling JC and Said HM: Regulation of the
human biotin transporter hSMVT promoter by KLF-4 and AP-2:
Confirmation of promoter activity in vivo. Am J Physiol Cell
physiol. 292:C1305–C1312. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Saifudeen Z, Dipp S, Fan H and El-Dahr SS:
Combinatorial control of the bradykinin B2 receptor promoter by
p53, CREB, KLF-4, and CBP: Implications for terminal nephron
differentiation. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 288:F899–F909.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Seiler K, Soroush Noghabi M, Karjalainen
K, Hummel M, Melchers F and Tsuneto M: Induced pluripotent stem
cells expressing elevated levels of sox-2, oct-4, and klf-4 are
severely reduced in their differentiation from mesodermal to
hematopoietic progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev. 20:1131–1142.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Shao M, Ge GZ, Liu WJ, Xiao J, Xia HJ, Fan
Y, Zhao F, He BL and Chen C: Characterization and phylogenetic
analysis of Krüppel-like transcription factor (KLF) gene family in
tree shrews (Tupaia belangeri chinensis). Oncotarget.
8:16325–16339. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Shimeld SM: C2H2 zinc finger genes of the
Gli, Zic, KLF, SP, Wilms' tumour, Huckebein, Snail, Ovo, Spalt,
Odd, Blimp-1, Fez and related gene families from Branchiostoma
floridae. Dev Genes Evol. 218:639–649. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sun Y, Li Y, Wang M, Yue M, Bai L, Bian J,
Hao W, Sun J, Zhang S and Liu H: Increased AT2R
expression is induced by AT1R autoantibody via two axes,
Klf-5/IRF-1 and circErbB4/miR-29a-5p, to promote VSMC migration.
Cell Death Dis. 11(432)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sunadome K, Yamamoto T, Ebisuya M, Kondoh
K, Sehara-Fujisawa A and Nishida E: ERK5 regulates muscle cell
fusion through Klf transcription factors. Dev Cell. 20:192–205.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Suske G, Bruford E and Philipsen S:
Mammalian SP/KLF transcription factors: Bring in the family.
Genomics. 85:551–556. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Fisch S, Gray S, Heymans S, Halder SM,
Wang B, Pfister O, Cui L, Kumar A, Lin Z, Sen-Banerjee S, et al:
Kruppel-like factor 15 is a regulator of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy.
Pro Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:7074–7079. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Matsumoto N, Kubo A, Liu H, Akita K, Laub
F, Ramirez F, Keller G and Friedman SL: Developmental regulation of
yolk sac hematopoiesis by Kruppel-like factor 6. Blood.
107:1357–1365. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Nuez B, Michalovich D, Bygrave A,
Ploemacher R and Grosveld F: Defective haematopoiesis in fetal
liver resulting from inactivation of the EKLF gene. Nature.
375:316–318. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wani MA, Means RT and Lingrel JB: Loss of
LKLF function results in embryonic lethality in mice. Transgenic
Res. 7:229–238. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Shindo T, Manabe I, Fukushima Y, Tobe K,
Aizawa K, Miyamoto S, Kawai-Kowase K, Moriyama N, Imai Y, Kawakami
H, et al: Krüppel-like zinc-finger transcription factor KLF5/BTEB2
is a target for angiotensin II signaling and an essential regulator
of cardiovascular remodeling. Nat Med. 8:856–863. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Han M, Wang Y, Guo G, Li L, Dou D, Ge X,
Lv P, Wang F and Gu Y: microRNA-30d mediated breast cancer
invasion, migration, and EMT by targeting KLF11 and activating
STAT3 pathway. J Cell Biochem. 119:8138–8145. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Wang X, Li X, Huang C, Li L, Qu H, Yu X,
Ni H and Cui Q: Kruppel-like factor 4 (KLF-4) inhibits the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and proliferation of human
endometrial carcinoma cells. Gynecol Endocrinol. 32:772–776.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Meng J, Lu X, Zhou Y, Zhang M, Gao L, Gao
S, Yan F and Liang C: Characterization of the prognostic values and
response to immunotherapy/chemotherapy of Krüppel-like factors in
prostate cancer. J Cell Mol Med. 24:5797–5810. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wen Y, Lu X, Ren J, Privratsky JR, Yang B,
Rudemiller NP, Zhang J, Griffiths R, Jain MK, Nedospasov SA, et al:
KLF4 in macrophages attenuates TNFα-mediated kidney injury and
fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 30:1925–1938. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Liang K, Liu T, Chu N, Kang J, Zhang R, Yu
Y and Li D and Li D: KLF8 is required for bladder cancer cell
proliferation and migration. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. 62:628–633.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Maclean A, Bunni E, Makrydima S,
Withington A, Kamal AM, Valentijn AJ and Hapangama DK: Fallopian
tube epithelial cells express androgen receptor and have a distinct
hormonal responsiveness when compared with endometrial epithelium.
Hum Reprod. 35:2097–2106. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Dogan S, Vasudevaraja V, Xu B, Serrano J,
Ptashkin RN, Jung HJ, Chiang S, Jungbluth AA, Cohen MA, Ganly I, et
al: DNA methylation-based classification of sinonasal
undifferentiated carcinoma. Mod Pathol. 32:1447–1459.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yu J, Mao W, Sun S, Hu Q, Wang C, Xu Z,
Liu R, Chen S, Xu B and Chen M: Identification of an m6A-related
lncRNA signature for predicting the prognosis in patients with
kidney renal clear cell carcinoma. Front Oncol.
11(663263)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Xi Z, Zhang R, Zhang F, Ma S and Feng T:
KLF11 expression predicts poor prognosis in glioma patients. Int J
Gen Med. 14:2923–2929. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Dai X, Ren T, Zhang Y and Nan N:
Methylation multiplicity and its clinical values in cancer. Expert
Rev Mol Med. 23(e2)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Luo Y and Chen C: The roles and regulation
of the KLF5 transcription factor in cancers. Cancer Sci.
112:2097–2117. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Marrero-Rodríguez D, la Cruz HA,
Taniguchi-Ponciano K, Gomez-Virgilio L, Huerta-Padilla V,
Ponce-Navarrete G, Andonegui-Elguera S, Jimenez-Vega F,
Romero-Morelos P, Rodriguez-Esquivel M, et al: Krüppel like factors
family expression in cervical cancer cells. Arch Med Res.
48:314–322. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Black AR, Black JD and Azizkhan-Clifford
J: Sp1 and krüppel-like factor family of transcription factors in
cell growth regulation and cancer. J Cell Physiol. 188:143–160.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Turpaev KT: Transcription factor KLF2 and
its role in the regulation of inflammatory processes. Biochemistry
(Mosc). 85:54–67. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Jha P and Das H: KLF2 in regulation of
NF-κB-mediated immune cell function and inflammation. Int J Mol
Sci. 18(2383)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Novodvorsky P and Chico TJ: The role of
the transcription factor KLF2 in vascular development and disease.
Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 124:155–188. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Rolph D and Das H: Transcriptional
regulation of osteoclastogenesis: The emerging role of KLF2. Front
Immunol. 11(937)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zhang D, Dai Y, Cai Y, Suo T and Liu H,
Wang Y, Cheng Z and Liu H: KLF2 is downregulated in pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma and inhibits the growth and migration of
cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 37:3425–3431. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Xue P, Yan M, Wang K, Gu J, Zhong B and Tu
C: Up-regulation of LINC00665 facilitates the malignant progression
of prostate cancer by epigenetically silencing KLF2 through EZH2
and LSD1. Front Oncol. 11(639060)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Xu TP, Liu XX, Xia R, Yin L, Kong R, Chen
WM, Huang MD and Shu YQ: SP1-induced upregulation of the long
noncoding RNA TINCR regulates cell proliferation and apoptosis by
affecting KLF2 mRNA stability in gastric cancer. Oncogene.
34:5648–5661. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Rane MJ, Zhao Y and Cai L: Krüppel-like
factors (KLFs) in renal physiology and disease. EBioMedicine.
40:743–750. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Holland WS, Tepper CG, Pietri JE, Chinn
DC, Gandara DR, Mack PC and Lara PN Jr: Evaluating rational
non-cross-resistant combination therapy in advanced clear cell
renal cell carcinoma: Combined mTOR and AKT inhibitor therapy.
Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 69:185–194. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Lu Y, Qin H, Jiang B, Lu W, Hao J, Cao W,
Du L, Chen W, Zhao X and Guo H: KLF2 inhibits cancer cell migration
and invasion by regulating ferroptosis through GPX4 in clear cell
renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 522:1–13. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Li M, Zhang M, Chen M, Xiao J, Mu X, Peng
J and Fan J: KLF2-induced circZKSCAN1 potentiates the tumorigenic
properties of clear cell renal cell carcinoma by targeting the
miR-1294/PIM1 axis. Cell Cycle. 1–15. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
56
|
Zou K, Lu X, Ye K, Wang C, You T and Chen
J: Krüppel-like factor 2 promotes cell proliferation in
hepatocellular carcinoma through up-regulation of c-myc. Cancer
Biol Ther. 17:20–26. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Jin L, He Y, Tang S and Huang S: LncRNA
GHET1 predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma and
promotes cell proliferation by silencing KLF2. J Cell Physiol.
233:4726–4734. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Jiang W, Xu X, Deng S, Luo J, Xu H, Wang
C, Sun T, Lei G, Zhang F, Yang C, et al: Methylation of
kruppel-like factor 2 (KLF2) associates with its expression and
non-small cell lung cancer progression. Am J Transl Res.
9:2024–2037. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhang Y and Weinberg RA:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer: Complexity and
opportunities. Front Med. 12:361–373. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|