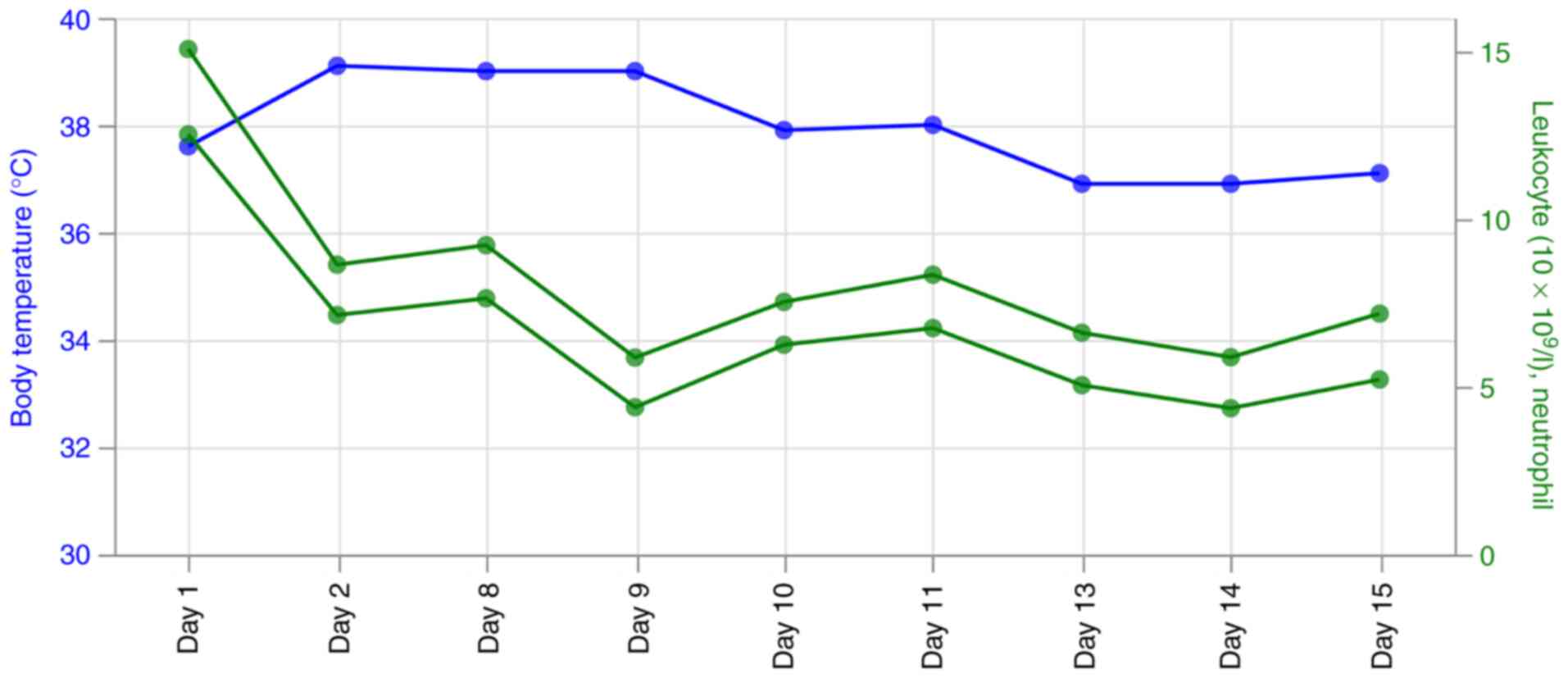
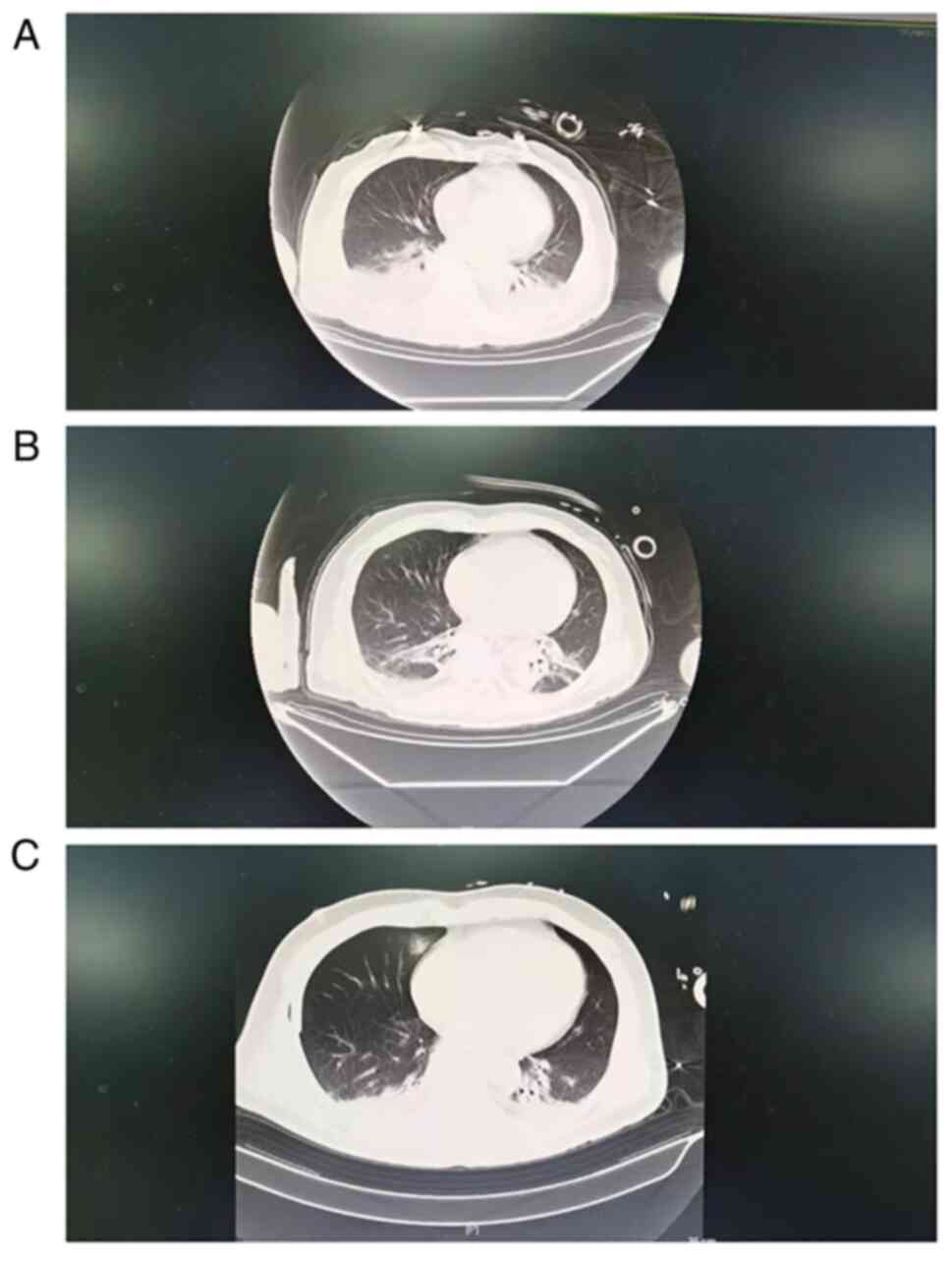
|
1
|
Baru A, Azazh A and Beza L: Injury
severity levels and associated factors among road traffic collision
victims referred to emergency departments of selected public
hospitals in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: The study based on the Haddon
matrix. BMC Emerg Med. 19(2)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Gopalakrishnan S: A public health
perspective of road traffic accidents. J Family Med Prim Care.
1:144–150. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wutzler S, Bläsius FM, Störmann P,
Lustenberger T, Frink M, Maegele M, Weuster M, Bayer J, Caspers M,
Seekamp A, et al: Pneumonia in severely injured patients with
thoracic trauma: Results of a retrospective observational
multi-centre study. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med.
27(31)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Markowitz S and Fanselow M: Exposure
Therapy for Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder: Factors of Limited
Success and Possible Alternative Treatment. Brain sci.
10(167)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Chhabra HS, Sharawat R and Vishwakarma G:
In-hospital mortality in people with complete acute traumatic
spinal cord injury at a tertiary care center in India-a
retrospective analysis. Spinal Cord. 60:210–215. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Rendeki S and Molnár TF: Pulmonary
contusion. J Thorac Dis. 11 (Suppl 2):S141–S151. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Bakowitz M, Bruns B and McCunn M: Acute
lung injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome in the
injured patient. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med.
20(54)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Matthay MA, Zemans RL, Zimmerman GA, Arabi
YM, Beitler JR, Mercat A, Herridge M, Randolph AG and Calfee CS:
Acute respiratory distress syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
5(18)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wu C, Chen X, Cai Y, Xia J, Zhou X, Xu S,
Huang H, Zhang L, Zhou X, Du C, et al: Risk factors associated with
acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with
coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern
Med. 180:934–943. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
de Prost N, Pham T, Carteaux G, Mekontso
Dessap A, Brun-Buisson C, Fan E, Bellani G, Laffey J, Mercat A,
Brochard L, et al: Etiologies, diagnostic work-up and outcomes of
acute respiratory distress syndrome with no common risk factor: A
prospective multicenter study. Ann Intensive Care.
7(69)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Fernando SM, Ferreyro BL, Urner M, Munshi
L and Fan E: Diagnosis and management of acute respiratory distress
syndrome. CMAJ. 193:E761–E768. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Beitler JR, Schoenfeld DA and Thompson BT:
Preventing ARDS: Progress, promise, and pitfalls. Chest.
146:1102–1113. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wu D, Wu C, Zhang S and Zhong Y: Risk
factors of ventilator-associated pneumonia in critically III
patients. Front Pharmacol. 10(482)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Luo J, Yu H, Hu YH, Liu D, Wang YW, Wang
MY, Liang BM and Liang ZA: Early identification of patients at risk
for acute respiratory distress syndrome among severe pneumonia: A
retrospective cohort study. J Thorac Dis. 9:3979–3995.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Gadsby NJ, Russell CD, McHugh MP, Mark H,
Conway Morris A, Laurenson IF, Hill AT and Templeton KE:
Comprehensive molecular testing for respiratory pathogens in
community-acquired pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 62:817–823.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Teng XQ, Gong WC, Qi TT, Li GH, Qu Q, Lu Q
and Qu J: Clinical analysis of metagenomic next-generation
sequencing confirmed chlamydia psittaci pneumonia: A case series
and literature review. Infect Drug Resist. 14:1481–1492.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen X, Ding S, Lei C, Qin J, Guo T, Yang
D, Yang M, Qing J, He W, Song M, et al: Blood and bronchoalveolar
lavage fluid metagenomic next-generation sequencing in pneumonia.
Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2020(6839103)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ho CC, Wu AK, Tse CW, Yuen KY, Lau SK and
Woo PC: Automated pangenomic analysis in target selection for PCR
detection and identification of bacteria by use of ssGeneFinder
Webserver and its application to Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi.
J Clin Microbiol. 50:1905–1911. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wang CX, Huang Z, Fang X, Li W, Yang B and
Zhang W: Comparison of broad-range polymerase chain reaction and
metagenomic next-generation sequencing for the diagnosis of
prosthetic joint infection. Int J Infect Dis. 95:8–12.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Huang J, Jiang E, Yang D, Wei J, Zhao M,
Feng J and Cao J: Metagenomic next-generation sequencing versus
traditional pathogen detection in the diagnosis of peripheral
pulmonary infectious lesions. Infect Drug Resist. 13:567–576.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zheng Y, Qiu X, Wang T and Zhang J: The
diagnostic value of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in lower
respiratory tract infection. Front Cell Infect Microbiol.
11(694756)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Wu HH, Feng LF and Fang SY: Application of
metagenomic next-generation sequencing in the diagnosis of severe
pneumonia caused by Chlamydia psittaci. BMC Pulm Med.
21(300)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Li H, Gao H, Meng H, Wang Q, Li S, Chen H,
Li Y and Wang H: Detection of pulmonary infectious pathogens from
lung biopsy tissues by metagenomic next-generation sequencing.
Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 8(205)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Shi CL, Han P, Tang PJ, Chen MM, Ye ZJ, Wu
MY, Shen J, Wu HY, Tan ZQ, Yu X, et al: Clinical metagenomic
sequencing for diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis. J Infect.
81:567–574. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Wu Z, Zhang R, Liu D and Liu X, Zhang J,
Zhang Z, Chen S, He W, Li Y, Xu Y and Liu X: Acute respiratory
distress syndrome caused by human adenovirus in adults: A
prospective observational study in Guangdong, China. Front Med
(Lausanne). 8(791163)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Langmead B and Salzberg SL: Fast
gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods. 9:357–359.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Beshay M, Mertzlufft F, Kottkamp HW,
Reymond M, Schmid RA, Branscheid D and Vordemvenne T: Analysis of
risk factors in thoracic trauma patients with a comparison of a
modern trauma centre: A mono-centre study. World J Emerg Surg.
15(45)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Haider T, Halat G, Heinz T, Hajdu S and
Negrin LL: Thoracic trauma and acute respiratory distress syndrome
in polytraumatized patients: A retrospective analysis. Minerva
Anestesiol. 83:1026–1033. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bauer TT, Ewig S, Rodloff AC and Müller
EE: Acute respiratory distress syndrome and pneumonia: A
comprehensive review of clinical data. Clin Infect Dis. 43:748–756.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Komori A, Iriyama H, Kainoh T, Aoki M,
Naito T and Abe T: The impact of infection complications after
trauma differs according to trauma severity. Sci Rep.
11(13803)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lazarus HM, Fox J, Lloyd JF, Evans RS,
Abouzelof R, Taylor C, Pombo DJ, Stevens MH, Mehta R and Burke JP:
A six-year descriptive study of hospital-associated infection in
trauma patients: Demographics, injury features, and infection
patterns. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 8:463–473. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yan W, Hu Z, Zhang Y, Wu X and Zhang H:
Case report: Metagenomic next-generation sequencing for diagnosis
of human encephalitis and endophthalmitis caused by pseudorabies
virus. Front Med (Lausanne). 8(753988)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu Y, Zhang J, Han B, Du L, Shi Z, Wang
C, Xu M and Luo Y: Case report: Diagnostic value of metagenomics
next generation sequencing in intracranial infection caused by
mucor. Front Med (Lausanne). 8(682758)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wang Q, Wang K, Zhang Y, Lu C, Yan Y,
Huang X, Zhou J, Chen L and Wang D: Neonatal Ureaplasma parvum
meningitis: A case report and literature review. Transl Pediatr.
9:174–179. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zhang XJ, Zheng JY, Li X, Liang YJ and
Zhang ZD: Usefulness of metagenomic next-generation sequencing in
adenovirus 7-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome: A case
report. World J Clin Cases. 9:6067–6072. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wang L, Shi Z, Chen W, Du X and Zhan L:
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in severe acute respiratory
distress syndrome caused by chlamydia psittaci: A case report and
review of the literature. Front Med (Lausanne).
8(731047)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wu S, Hu W, Xiao W, Li Y, Huang Y and
Zhang X: Metagenomic next-generation sequencing assists in the
diagnosis of gardnerella vaginalis in males with pleural effusion
and lung infection: A case report and literature review. Infect
Drug Resist. 14:5253–5259. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhang H, Zhan D, Chen D, Huang W, Yu M, Li
Q, Marcos PJ, Tattevin P, Wu D and Wang L: Next-generation
sequencing diagnosis of severe pneumonia from fulminant psittacosis
with multiple organ failure: A case report and literature review.
Ann Transl Med. 8(401)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Zhan L, Huang K, Xia W, Chen J, Wang L, Lu
J, Wang J, Lin J and Wu W: The diagnosis of severe fever with
thrombocytopenia syndrome using metagenomic next-generation
sequencing: Case report and literature review. Infect Drug Resist.
15:83–89. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Duan J, Zhang C, Wang J, Fu J, Song P,
Pang F, Zhao Q and You Z: Diagnosis of Ureaplasma parvum meningitis
by mNGS in an extremely low birth weight infant with multi-system
lesions. Indian J Med Microbiol: May 24, 2022 (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
41
|
Zhang M, Wang W, Li X, Zhang X and Yang D:
Fast and precise pathogen detection and identification of
overlapping infection in patients with CUTI based on metagenomic
next-generation sequencing: A case report. Medicine (Baltimore).
100(e27902)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kolenda C, Ranc AG, Boisset S, Caspar Y,
Carricajo A, Souche A, Dauwalder O, Verhoeven PO, Vandenesch F and
Laurent F: Assessment of respiratory bacterial coinfections among
severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2-positive patients
hospitalized in intensive care units using conventional culture and
BioFire, FilmArray pneumonia panel plus assay. Open Forum Infect
Dis. 7(ofaa484)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Giuliano C, Patel CR and Kale-Pradhan PB:
A guide to bacterial culture identification and results
interpretation. P T. 44:192–200. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Su SS, Chen XB, Zhou LP, Lin PC, Chen JJ,
Chen CS, Wu Q, Ye JR and Li YP: Diagnostic performance of the
metagenomic next-generation sequencing in lung biopsy tissues in
patients suspected of having a local pulmonary infection. BMC Pulm
Med. 22(112)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Peleg AY and Hooper DC: Hospital-acquired
infections due to gram-negative bacteria. N Engl J Med.
362:1804–1813. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Luyt CE, Hekimian G, Koulenti D and
Chastre J: Microbial cause of ICU-acquired pneumonia:
Hospital-acquired pneumonia versus ventilator-associated pneumonia.
Curr Opin Crit Care. 24:332–338. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|