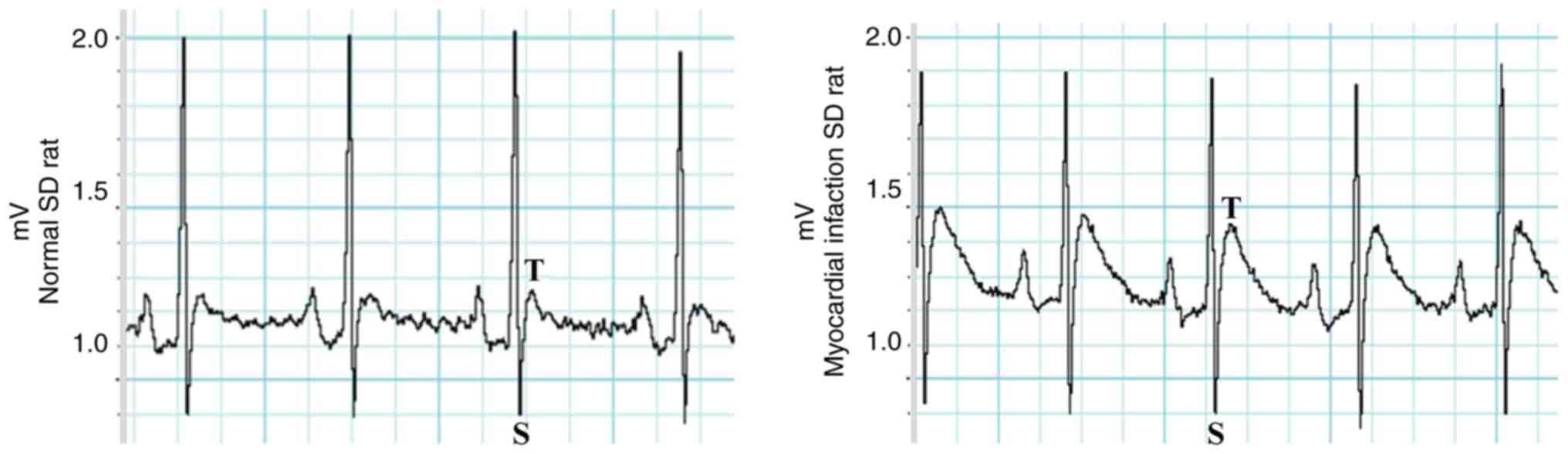
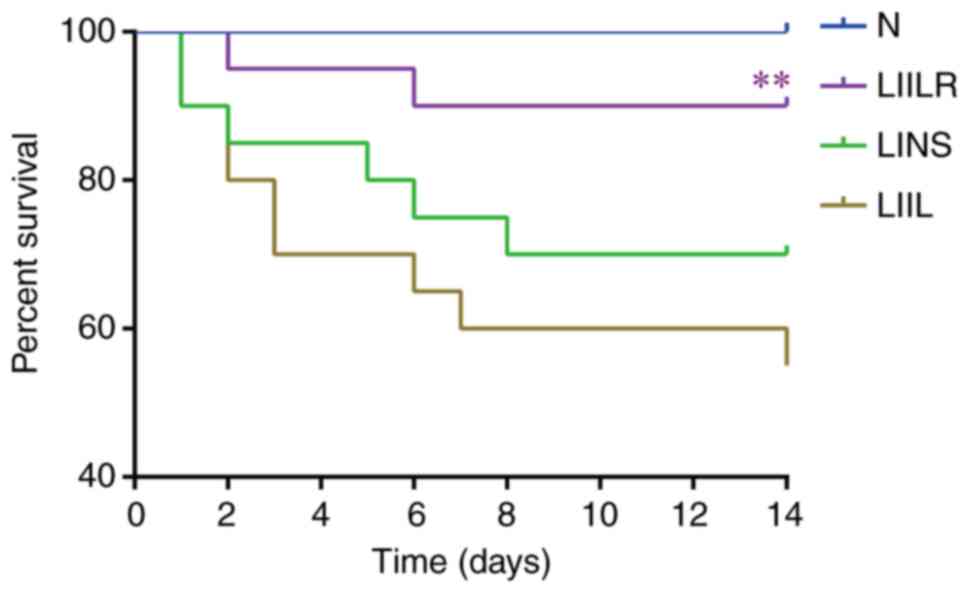
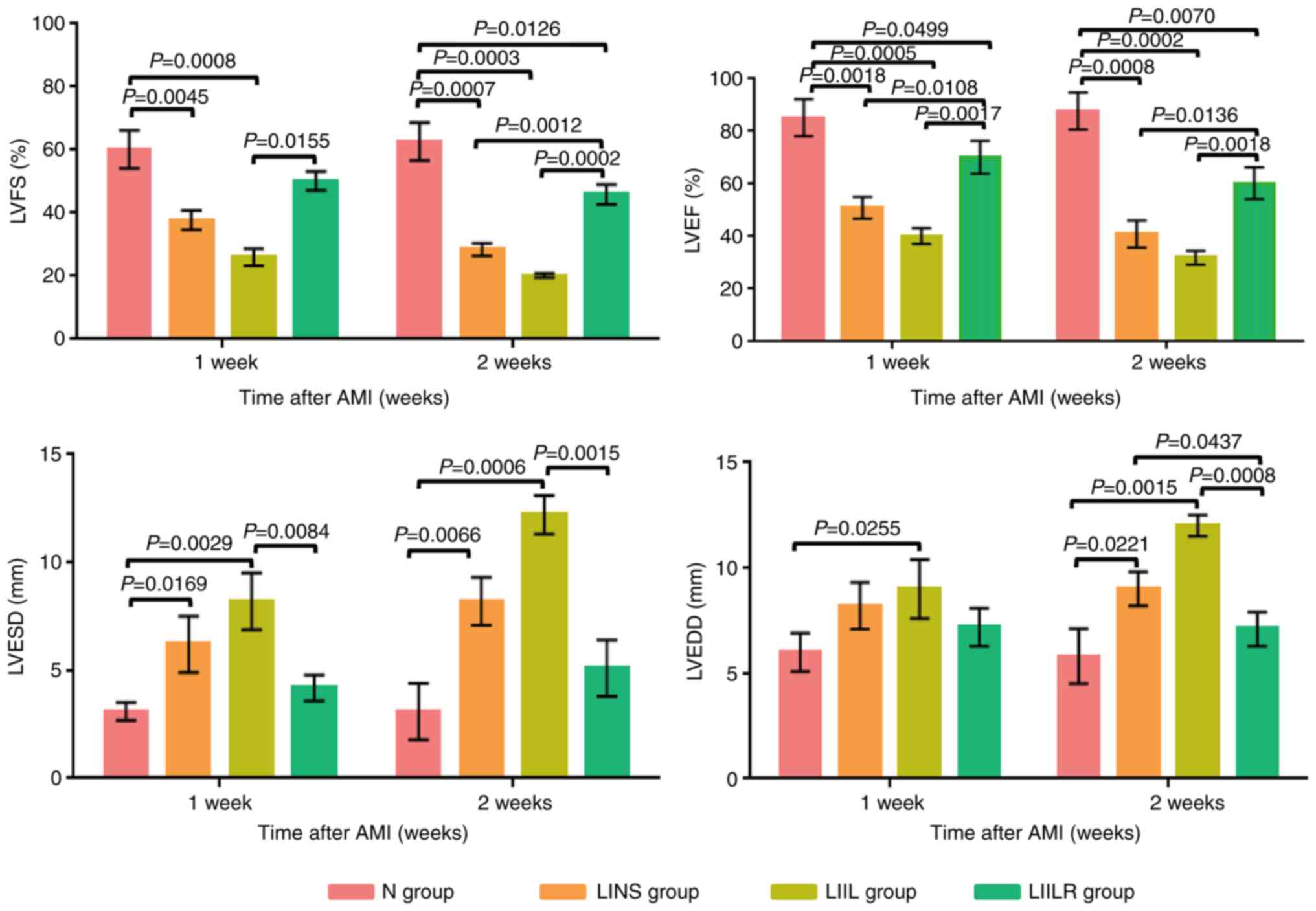
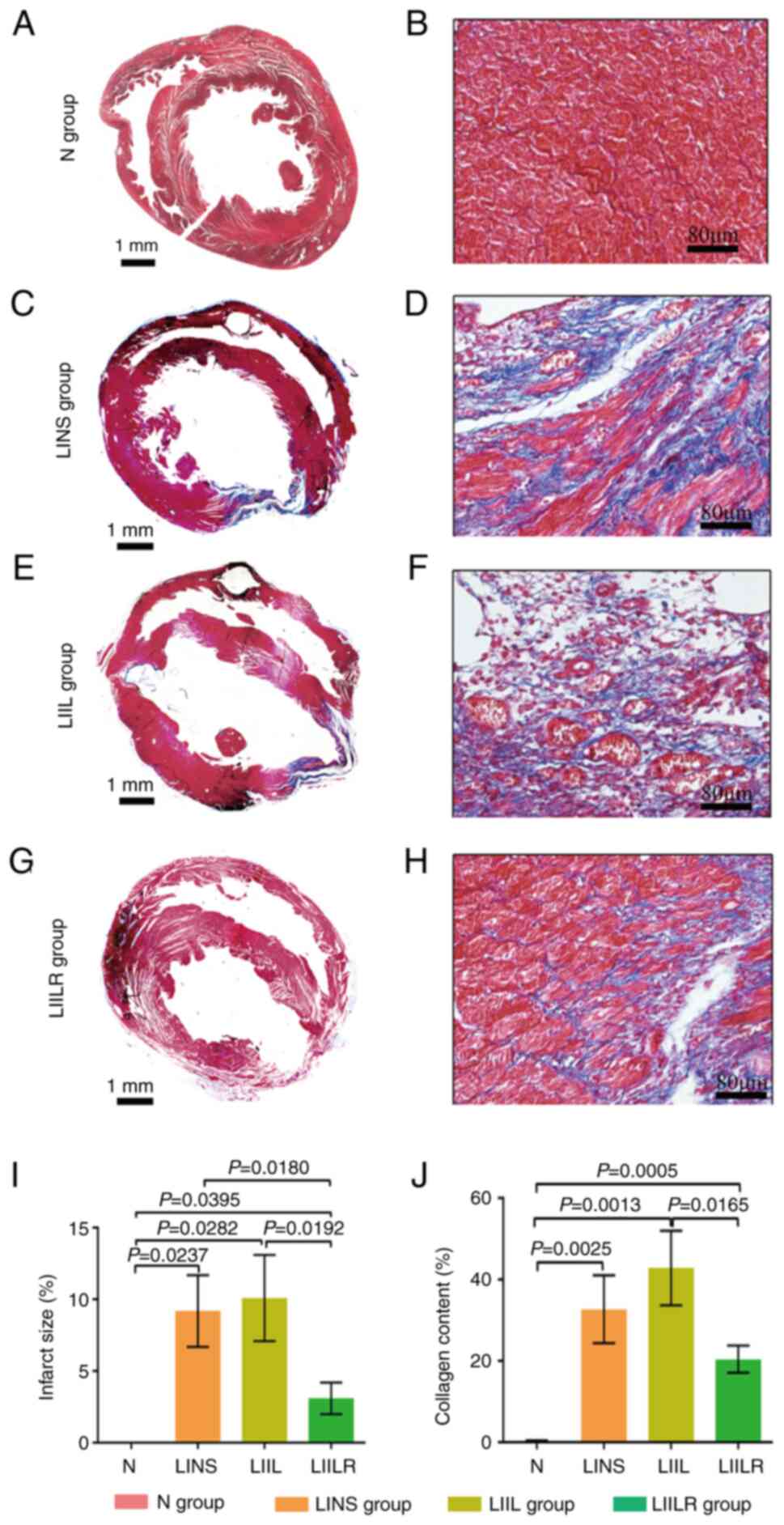
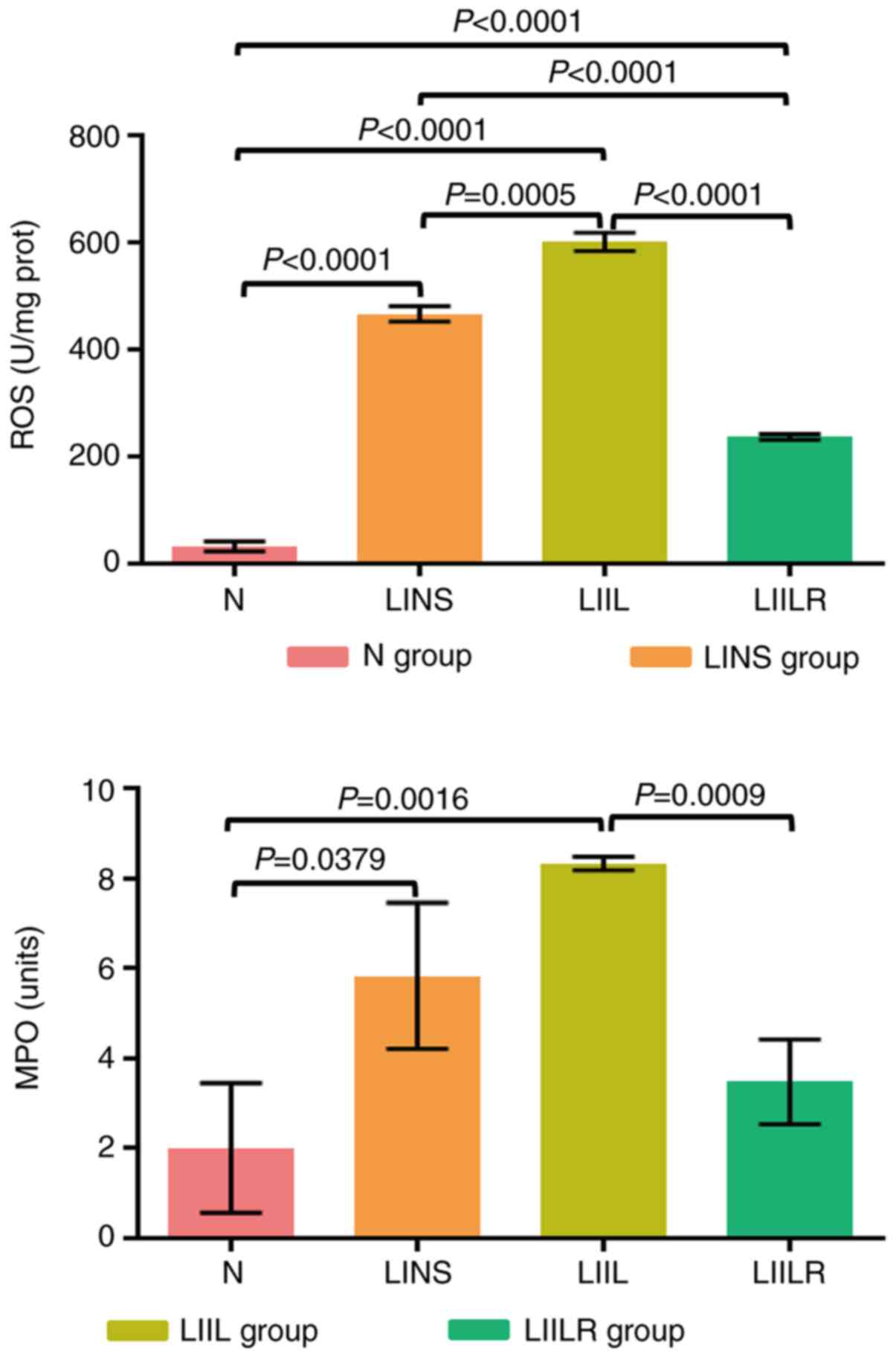
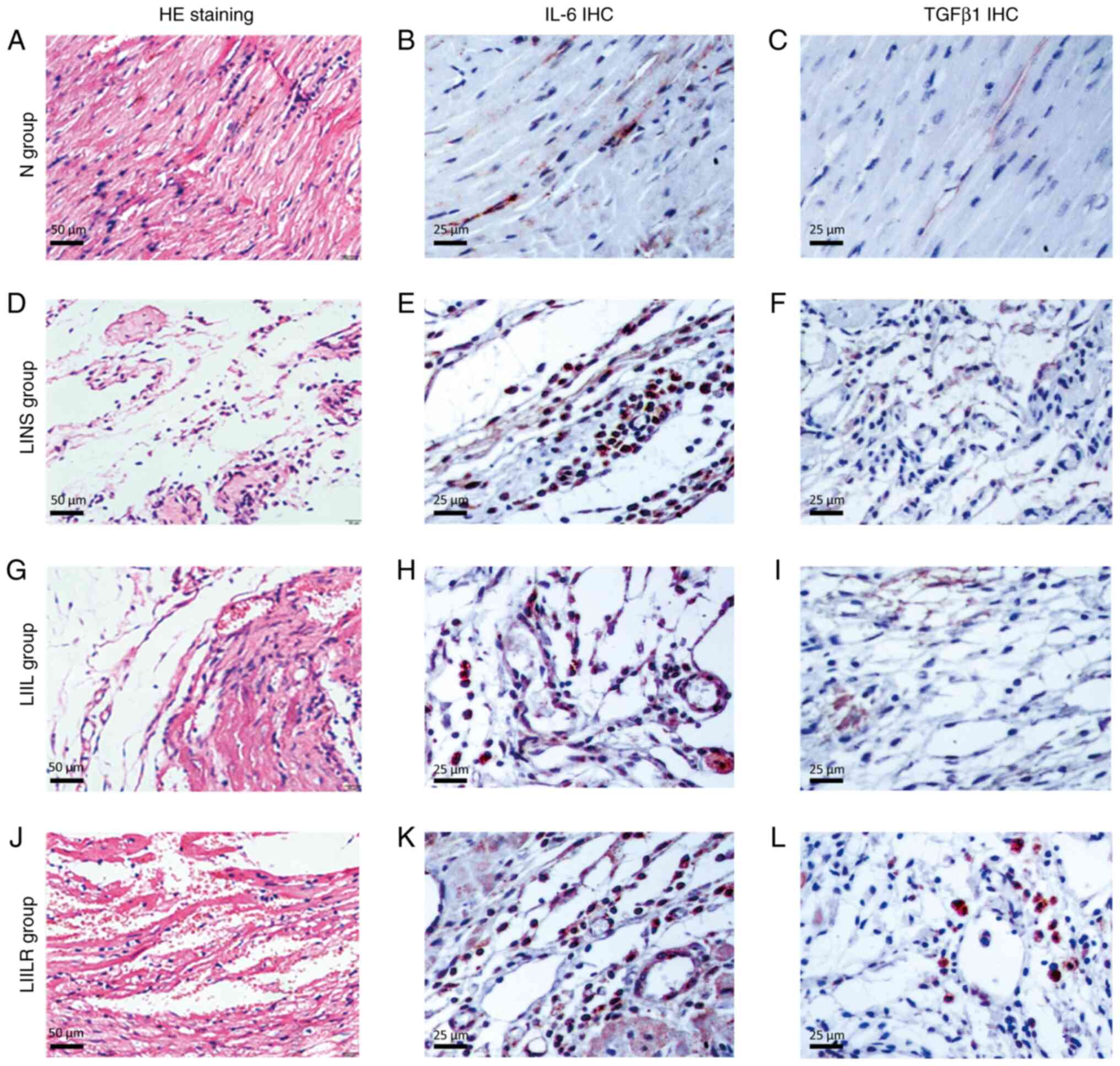
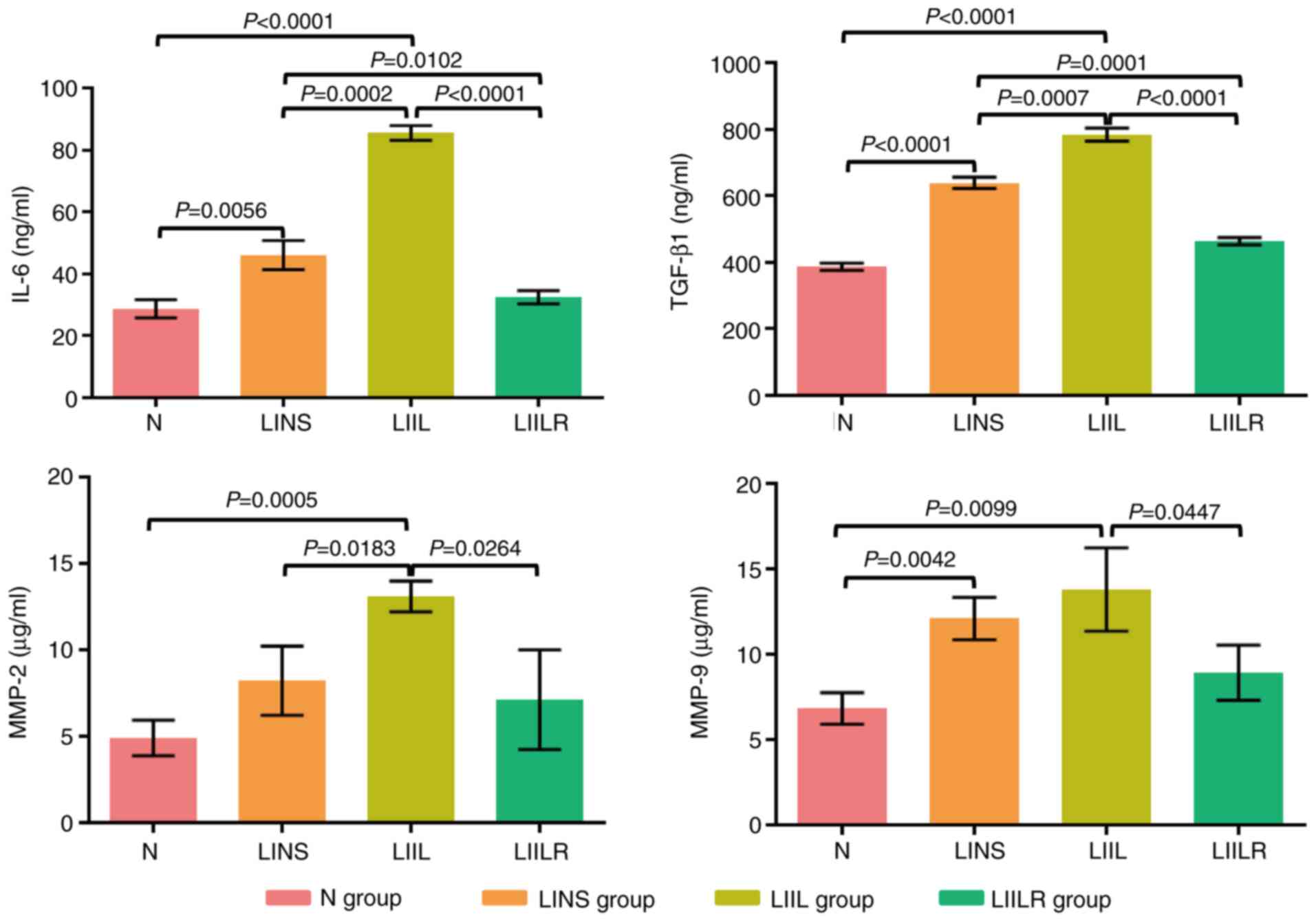
|
1
|
Iuchi A, Harada H and Tanaka T: IL-6
blockade for myocardial infarction. Int J Cardiol. 271:19–20.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ritschel VN, Seljeflot I, Arnesen H,
Halvorsen S, Weiss T, Eritsland J and Andersen GØ: IL-6 signalling
in patients with acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction. Results
Immunol. 4:8–13. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gabriel AS, Martinsson A, Wretlind B and
Ahnve S: IL-6 levels in acute and post myocardial infarction: Their
relation to CRP levels, infarction size, left ventricular systolic
function, and heart failure. Eur J Intern Med. 15:523–528.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Azevedo PS, Polegato BF, Minicucci MF,
Paiva SA and Zornoff LA: Cardiac Remodeling: Concepts, clinical
impact, pathophysiological mechanisms and pharmacologic treatment.
Arq Bras Cardiol. 106:62–69. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Möttönen MJ, Ukkola O, Lumme J, Kesäniemi
YA, Huikuri HV and Perkiömäki JS: Cardiac remodeling from middle
age to senescence. Front Physiol. 8(341)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ellis SG, Tendera M, de Belder MA, van
Boven AJ, Widimsky P, Janssens L, Andersen HR, Betriu A, Savonitto
S, Adamus J, et al: Facilitated PCI in patients with ST-Elevation
myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 358:2205–2217. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ohtsuka T, Hamada M, Inoue K, Ohshima K,
Suzuki J, Matsunaka T, Ogimoto A, Hara Y, Shigematsu Y and Higaki
J: Relation of circulating interleukin-6 to left ventricular
remodeling in patients with reperfused anterior myocardial
infarction: Relation of circulating interleukin-6 to left
ventricular remodeling in patients with reperfused anterior
myocardial infarction. Clin Cardiol. 27:417–420. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
González A, Ravassa S, López B, Moreno MU,
Beaumont J, San José G, Querejeta R, Bayés-Genís A and Díez J:
Myocardial remodeling in hypertension. Hypertension. 72:549–558.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Williams A, Kamper SJ, Wiggers JH, O'Brien
KM, Lee H, Wolfenden L, Yoong SL, Robson E, McAuley JH, Hartvigsen
J and Williams CM: Musculoskeletal conditions may increase the risk
of chronic disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort
studies. BMC Med. 16(167)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
French BA and Kramer CM: Mechanisms of
postinfarct left ventricular remodeling. Drug Discov Today Dis
Mech. 4:185–196. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Segura AM, Frazier OH and Buja LM:
Fibrosis and heart failure. Heart Fail Rev. 19:173–185.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lan HY: Diverse roles of TGF-β/Smads in
renal fibrosis and inflammation. Int J Biol Sci. 7:1056–1067.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Nakao A, Imamura T, Souchelnytskyi S,
Kawabata M, Ishisaki A, Oeda E, Tamaki K, Hanai J, Heldin CH,
Miyazono K and ten Dijke P: TGF-beta receptor-mediated signalling
through Smad2, Smad3 and Smad4. EMBO J. 16:5353–5362.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Arrigo M, Jessup M, Mullens W, Reza N,
Shah AM, Sliwa K and Mebazaa A: Acute heart failure. Nat Rev Dis
Primers. 6(16)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Mebazaa A, Pitsis AA, Rudiger A, Toller W,
Longrois D, Ricksten SE, Bobek I, De Hert S, Wieselthaler G,
Schirmer U, et al: Clinical review: Practical recommendations on
the management of perioperative heart failure in cardiac surgery.
Crit Care. 14(201)2010.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hanif K, Bid HK and Konwar R: Reinventing
the ACE inhibitors: Some old and new implications of ACE
inhibition. Hypertens Res. 33:11–21. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Rich MW, Chyun DA, Skolnick AH, Alexander
KP, Forman DE, Kitzman DW, Maurer MS, McClurken JB, Resnick BM,
Shen WK, et al: Knowledge Gaps in cardiovascular care of the older
adult population: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart
Association, American College of Cardiology, and American
Geriatrics Society. J Am Coll Cardiol. 67:2419–2140.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Moffat K and Mercer SW: Challenges of
managing people with multimorbidity in today's healthcare systems.
BMC Fam Pract. 16(129)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Granger CB, Goldberg RJ, Dabbous O, Pieper
KS, Eagle KA, Cannon CP, Van De Werf F, Avezum A, Goodman SG,
Flather MD, et al: Predictors of hospital mortality in the global
registry of acute coronary events. Arch Intern Med. 163:2345–2353.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Siddiqi S and Sussman MA: Cardiac hegemony
of senescence. Curr Transl Geriatr Exp Gerontol Rep 2:
10.1007/s13670-013-0064-3, 2013.
|
|
21
|
Sussman MA and Anversa P: Myocardial aging
and senescence: Where have the stem cells gone? Annu Rev Physiol.
66:29–48. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Torella D, Rota M, Nurzynska D, Musso E,
Monsen A, Shiraishi I, Zias E, Walsh K, Rosenzweig A, Sussman MA,
et al: Cardiac stem cell and myocyte aging, heart failure, and
insulin-like growth factor-1 overexpression. Circ Res. 94:514–524.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
van Merode T, van de Ven K and van den
Akker M: Patients with multimorbidity and their treatment burden in
different daily life domains: A qualitative study in primary care
in the Netherlands and Belgium. J Comorb. 8:9–15. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Faustino-Rocha AI, Ginja M, Ferreira R and
Oliveira PA: Studying humane endpoints in a rat model of mammary
carcinogenesis. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 22:643–649. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mohamed AS, Hosney M, Bassiony H,
Hassanein SS, Soliman AM, Fahmy SR and Gaafar K: Sodium
pentobarbital dosages for exsanguination affect biochemical,
molecular and histological measurements in rats. Sci Rep.
10(378)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wu Y, Wan Q, Shi L, Ou J, Li Y, He F, Wang
H and Gao J: Siwu granules and erythropoietin synergistically
ameliorated anemia in adenine-induced chronic renal failure rats.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019(5832105)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kobara M, Noda K, Kitamura M, Okamoto A,
Shiraishi T, Toba H, Matsubara H and Nakata T: Antibody against
interleukin-6 receptor attenuates left ventricular remodelling
after myocardial infarction in mice. Cardiovasc Res. 87:424–430.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mochizuki D, Adams A, Warner KA, Zhang Z,
Pearson AT, Misawa K, McLean SA, Wolf GT and Nör JE: Anti-tumor
effect of inhibition of IL-6 signaling in mucoepidermoid carcinoma.
Oncotarget. 6:22822–22835. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Arora G, Morss AM, Piazza G, Ryan JW,
Dinwoodey DL, Rofsky NM, Manning WJ and Chuang ML: Differences in
left ventricular ejection fraction using teichholz formula and
volumetric methods by cmr: Implications for patient stratification
and selection of therapy. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson.
12(P202)2010.
|
|
30
|
Wandt B, Bojö L, Tolagen K and Wranne B:
Echocardiographic assessment of ejection fraction in left
ventricular hypertrophy. Heart. 82:192–198. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Konstam MA, Kramer DG, Patel AR, Maron MS
and Udelson JE: Left ventricular remodeling in heart failure
current concepts in clinical significance and assessment. JACC
Cardiovasc Imaging. 4:98–108. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Eltzschig HK and Collard CD: Vascular
ischaemia and reperfusion injury. Br Med Bull. 70:71–86.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wu N, Zhang X, Du S, Chen D and Che R:
Upregulation of miR-335 ameliorates myocardial ischemia reperfusion
injury via targeting hypoxia inducible factor 1-alpha subunit
inhibitor. Am J Transl Res. 10:4082–4094. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Turer AT and Hill JA: Pathogenesis of
myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury and rationale for therapy.
Am J Cardiol. 106:360–368. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Jones NR, Hobbs FR and Taylor CJ:
Prognosis following a diagnosis of heart failure and the role of
primary care: A review of the literature. BJGP Open.
1(bjgpopen17X101013)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Price JF: Congestive heart failure in
children. Pediatr Rev. 40:60–70. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Klaeboe LG and Edvardsen T:
Echocardiographic assessment of left ventricular systolic function.
J Echocardiogr. 17:10–16. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Malik J, Zaidi SMJ, Rana AS, Haider A and
Tahir S: Post-cardiac injury syndrome: An evidence-based approach
to diagnosis and treatment. Am Heart J Plus Cardiol Res Practice.
12(100068)2021.
|
|
39
|
Cahill TJ and Kharbanda RK: Heart failure
after myocardial infarction in the era of primary percutaneous
coronary intervention: Mechanisms, incidence and identification of
patients at risk. World J Cardiol. 9:407–415. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Cao Y, Chen L, Zhang W, Liu Y,
Papaconstantinou HT, Bush CR, Townsend CM Jr, Thompson EA and Ko
TC: Identification of apoptotic genes mediating TGF-β/Smad3-induced
cell death in intestinal epithelial cells using a genomic approach.
Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 292:G28–G38.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Walia B, Wang L, Merlin D and Sitaraman
SV: TGF-beta down-regulates IL-6 signaling in intestinal epithelial
cells: Critical role of SMAD-2. FASEB J. 17:2130–2132.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Ge Q, Moir LM, Black JL, Oliver BG and
Burgess JK: TGFβ1 induces IL-6 and inhibits IL-8 release in human
bronchial epithelial cells: The role of Smad2/3. J Cell Physiol.
225:846–854. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ramesh S, Wildey GM and Howe PH:
Transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta)-induced apoptosis: The
rise & fall of Bim. Cell Cycle. 8:11–17. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Su JH, Luo MY, Liang N, Gong SX, Chen W,
Huang WQ, Tian Y and Wang AP: Interleukin-6: A Novel Target for
Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases. Front Pharmacol.
12(745061)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Shinde AV and Frangogiannis NG:
Fibroblasts in myocardial infarction: A role in inflammation and
repair. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 70:74–82. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Venugopal H, Hanna A, Humeres C and
Frangogiannis NG: Properties and functions of fibroblasts and
myofibroblasts in myocardial infarction. Cells.
11(1386)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wang JH, Zhao L, Pan X, Chen NN, Chen J,
Gong QL, Su F, Yan J, Zhang Y and Zhang SH: Hypoxia-stimulated
cardiac fibroblast production of IL-6 promotes myocardial fibrosis
via the TGF-β1 signaling pathway. Lab Invest. 96:839–852.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Yang L, Roh YS, Song J, Zhang B, Liu C,
Loomba R and Seki E: Transforming growth factor beta signaling in
hepatocytes participates in steatohepatitis through regulation of
cell death and lipid metabolism in mice. Hepatology. 59:483–495.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Okina Y, Sato-Matsubara M, Matsubara T,
Daikoku A, Longato L, Rombouts K, Thanh Thuy LT, Ichikawa H,
Minamiyama Y, Kadota M, et al: TGF-β1-driven reduction of
cytoglobin leads to oxidative DNA damage in stellate cells during
non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J Hepatol. 73:882–895.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Xu F, Liu C, Zhou D and Zhang L:
TGF-β/SMAD pathway and its regulation in hepatic fibrosis. J
Histochem Cytochem. 64:157–167. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Tarantino G, Conca P, Riccio A, Tarantino
M, Di Minno MN, Chianese D, Pasanisi F, Contaldo F, Scopacasa F and
Capone D: Enhanced serum concentrations of transforming growth
factor-beta1 in simple fatty liver: Is it really benign? J Transl
Med. 6(72)2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Machado MV and Cortez-Pinto H:
Non-invasive diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. A
critical appraisal. J Hepatol. 58:1007–1019. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Veldhoen M, Hocking RJ, Atkins CJ,
Locksley RM and Stockinger B: TGFbeta in the context of an
inflammatory cytokine milieu supports de novo differentiation of
IL-17-producing T cells. Immunity. 24:179–189. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Brun P, Giron MC, Qesari M, Porzionato A,
Caputi V, Zoppellaro C, Banzato S, Grillo AR, Spagnol L, De Caro R,
et al: Toll-like receptor 2 regulates intestinal inflammation by
controlling integrity of the enteric nervous system.
Gastroenterology. 145:1323–1333. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|