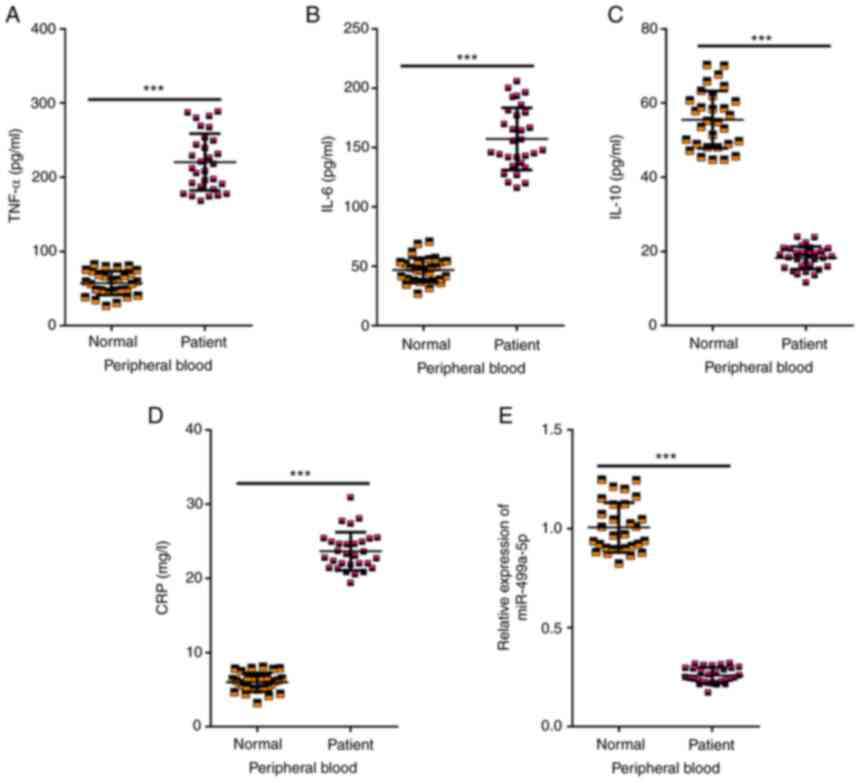
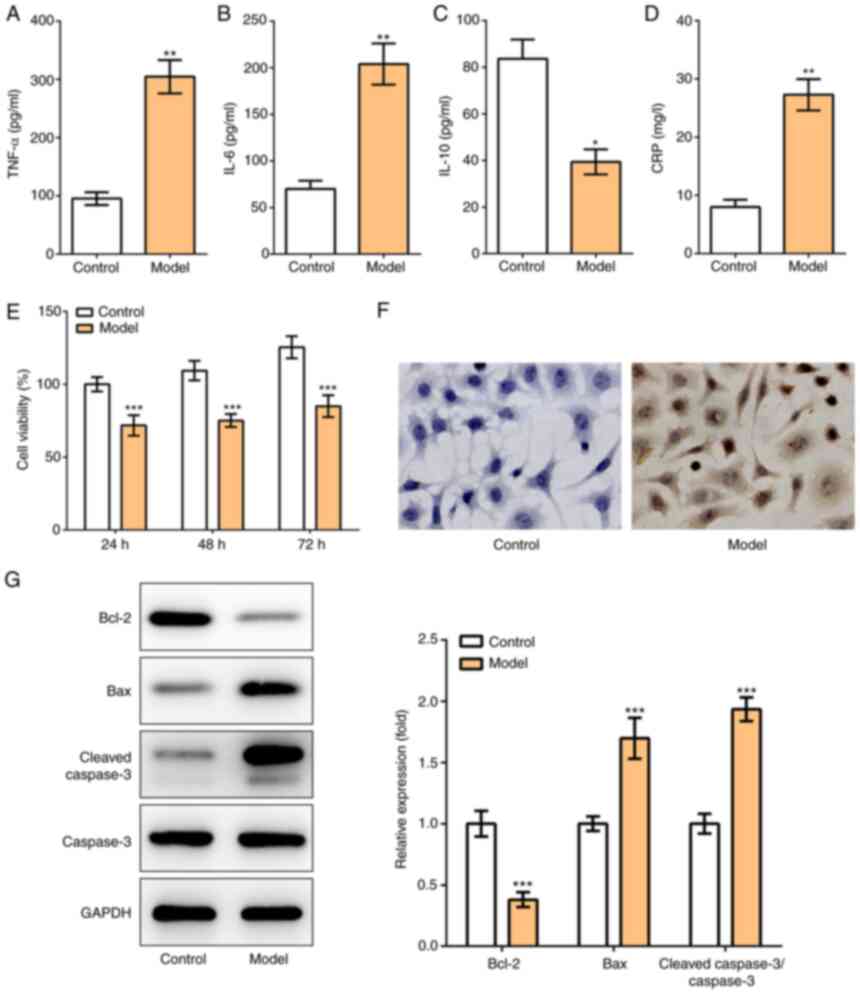
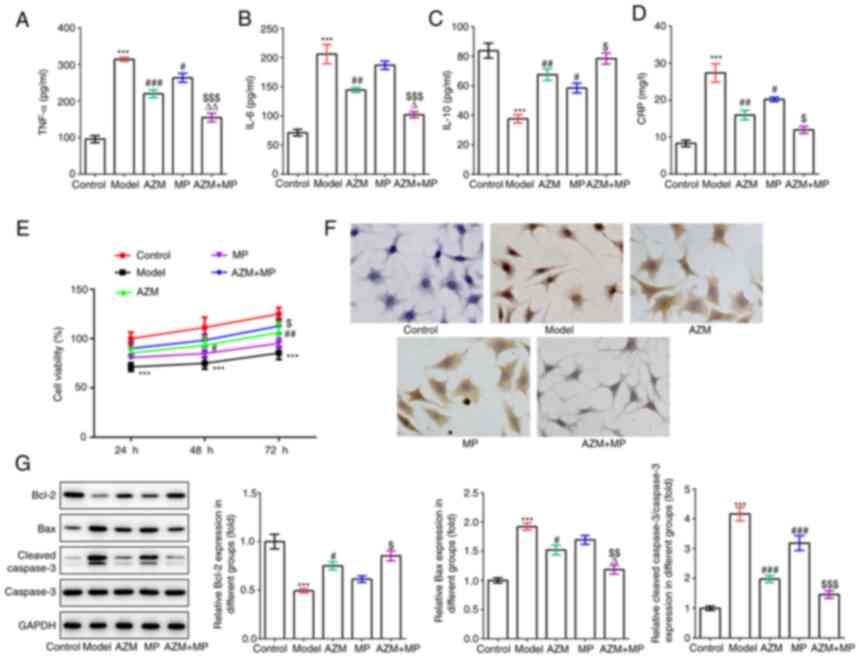
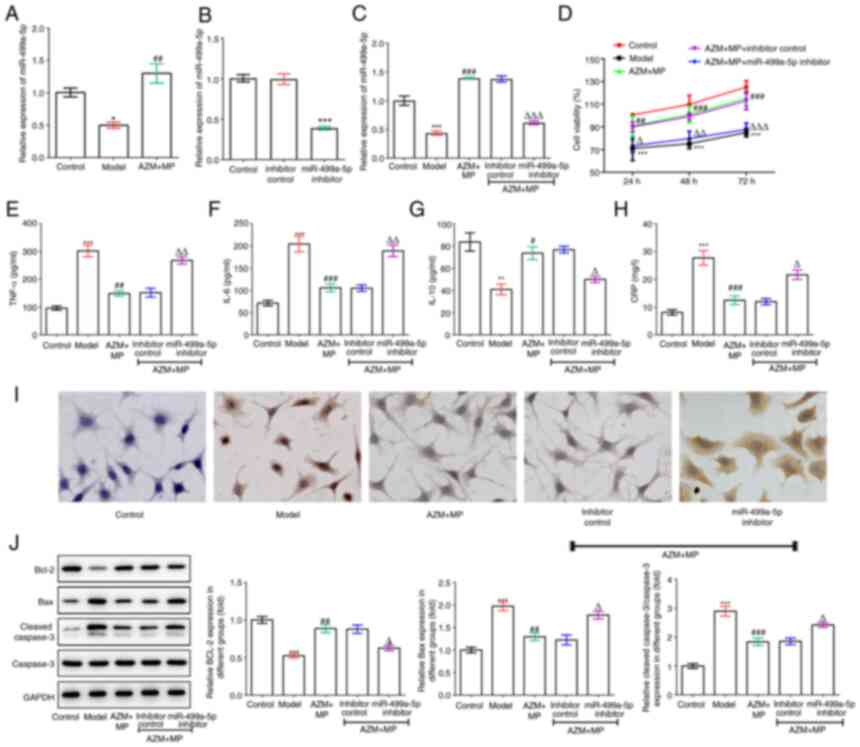
|
1
|
Wang X, Chen X, Tang H, Zhu J, Zhou S, Xu
Z, Liu F and Su C: Increased frequency of Th17 cells in children
with Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. J Clin Lab Anal.
30:1214–1219. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Atkinson TP and Waites KB: Mycoplasma
pneumoniae infections in childhood. Pediatr Infect Dis J.
33:92–94. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cartner SC, Lindsey JR, Gibbs-Erwin J,
Cassell GH and Simecka JW: Roles of innate and adaptive immunity in
respiratory mycoplasmosis. Infect Immun. 66:3485–3491.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Waites KB and Talkington DF: Mycoplasma
pneumoniae and its role as a human pathogen. Clin Microbiol
Rev. 17:697–728. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Ferwerda A, Moll HA and de Groot R:
Respiratory tract infections by Mycoplasma pneumoniae in
children: A review of diagnostic and therapeutic measures. Eur J
Pediatr. 160:483–491. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gao S, Wang L, Zhu W and Jiang J:
Mycoplasma pneumonia infection and asthma: A clinical study. Pak J
Med Sci. 31:548–551. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Spiga F, Zhao Z and Lightman SL: Prolonged
treatment with the synthetic glucocorticoid methylprednisolone
affects adrenal steroidogenic function and response to inflammatory
stress in the rat. Brain Behav Immun. 87:703–714. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shan LS, Liu X, Kang XY, Wang F, Han XH
and Shang YX: Effects of methylprednisolone or immunoglobulin when
added to standard treatment with intravenous azithromycin for
refractory Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia in children.
World J Pediatr. 13:321–327. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Pu M, Chen J, Tao Z, Miao L, Qi X, Wang Y
and Ren J: Regulatory network of miRNA on its target: coordination
between transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene
expression. Cell Mol Life Sci. 76:441–451. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ebrahimi A and Sadroddiny E: MicroRNAs in
lung diseases: Recent findings and their pathophysiological
implications. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 34:55–63. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zhao L, Wang B, Zhang W and Sun L: Effect
of miR-499a-5p on damage of cardiomyocyte induced by
hypoxia-reoxygenation via downregulating CD38 protein. J Cell
Biochem. 121:996–1004. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
He S, Li Z, Yu Y, Zeng Q, Cheng Y, Ji W,
Xia W and Lu S: Exosomal miR-499a-5p promotes cell proliferation,
migration and EMT via mTOR signaling pathway in lung
adenocarcinoma. Exp Cell Res. 379:203–213. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wang M, Yang C, Liu X, Zheng J, Xue Y,
Ruan X, Shen S, Wang D, Li Z, Cai H and Liu Y: An upstream open
reading frame regulates vasculogenic mimicry of glioma via
ZNRD1-AS1/miR-499a-5p/ELF1/EMI1 pathway. J Cell Mol Med.
24:6120–6136. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ozkul Y, Taheri S, Bayram KK, Sener EF,
Mehmetbeyoglu E, Öztop DB, Aybuga F, Tufan E, Bayram A, Dolu N, et
al: A heritable profile of six miRNAs in autistic patients and
mouse models. Sci Rep. 10(9011)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Singh AK, Rooge SB, Varshney A, Vasudevan
M, Bhardwaj A, Venugopal SK, Trehanpati N, Kumar M, Geffers R,
Kumar V and Sarin SK: Global microRNA expression profiling in the
liver biopsies of hepatitis B virus-infected patients suggests
specific microRNA signatures for viral persistence and
hepatocellular injury. Hepatology. 67:1695–1709. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhang W, Li J, Yao H and Li T: Restoring
microRNA-499-5p protects sepsis-induced lung injury mice via
targeting Sox6. Nanoscale Res Lett. 16(89)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jarret A, McFarland AP, Horner SM, Kell A,
Schwerk J, Hong M, Badil S, Joslyn RC, Baker DP, Carrington M, et
al: Hepatitis-C-virus-induced microRNAs dampen interferon-mediated
antiviral signaling. Nat Med. 22:1475–1481. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lin Y, Tan D, Kan Q, Xiao Z and Jiang Z:
The protective effect of Naringenin on airway remodeling after
Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection by inhibiting
autophagy-mediated lung inflammation and fibrosis. Mediators
Inflamm. 2018(8753894)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Liu F, Zhang X, Zhang B, Mao W, Liu T, Sun
M and Wu Y: TREM1: A positive regulator for inflammatory response
via NF-κB pathway in A549 cells infected with Mycoplasma
pneumoniae. Biomed Pharmacother. 107:1466–1472. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zerin T, Kim YS, Hong SY and Song HY:
Protective effect of methylprednisolone on paraquat-induced A549
cell cytotoxicity via induction of efflux transporter,
P-glycoprotein expression. Toxicol Lett. 208:101–107.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Kitsiouli E, Antoniou G, Gotzou H,
Karagiannopoulos M, Basagiannis D, Christoforidis S, Nakos G and
Lekka ME: Effect of azithromycin on the LPS-induced production and
secretion of phospholipase A2 in lung cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1852:1288–1297. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Shi S, Liu X and Li H: Downregulation of
caspase3 alleviates Mycoplasma pneumoniae induced apoptosis
in alveolar epithelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 16:9601–9606.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Segovia JA, Chang TH, Winter VT, Coalson
JJ, Cagle MP, Pandranki L, Bose S, Baseman JB and Kannan TR: NLRP3
is a critical regulator of inflammation and innate immune cell
response during Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Infect
Immun. 86:e00548–17. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu LQ, Wang ZH and Yao HY: Hepatocyte
growth factor can guide treatment of Mycoplasma pneumoniae
pneumonia in children. Exp Ther Med. 19:3432–3438. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Zhang C, Dong WB, Zhao S, Li QP, Kang L,
Lei XP, Guo L and Zhai XS: Construction of p66Shc gene interfering
lentivirus vectors and its effects on alveolar epithelial cells
apoptosis induced by hyperoxia. Drug Des Devel Ther. 10:2611–2622.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Sun G, Xu X, Wang Y, Shen X, Chen Z and
Yang J: Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection induces reactive
oxygen species and DNA damage in A549 human lung carcinoma cells.
Infect Immun. 76:4405–4413. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Gu X, Dong M, Liu Z, Yang J and Shi Y:
MiR-499a-5p inhibits proliferation, invasion, migration, and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition, and enhances radiosensitivity of
cervical cancer cells via targeting eIF4E. Onco Targets Ther.
13:2913–2924. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Guanizo AC, Fernando CD, Garama DJ and
Gough DJ: STAT3: A multifaceted oncoprotein. Growth Factors.
36:1–14. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Deverrière G, Lemée L, Grangé S, Boyer S,
Picard C, Fischer A and Marguet C: Life-threatening Pneumopathy and
U urealyticum in a STAT3-deficient hyper-IgE syndrome patient.
Pediatrics. 139(e20160845)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hao Y, Kuang Z, Jing J, Miao J, Mei LY,
Lee RJ, Kim S, Choe S, Krause DC and Lau GW: Mycoplasma
pneumoniae modulates STAT3-STAT6/EGFR-FOXA2 signaling to induce
overexpression of airway mucins. Infect Immun. 82:5246–5255.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Choi SY, Lim JW, Shimizu T, Kuwano K, Kim
JM and Kim H: Reactive oxygen species mediate Jak2/Stat3 activation
and IL-8 expression in pulmonary epithelial cells stimulated with
lipid-associated membrane proteins from Mycoplasma
pneumoniae. Inflamm Res. 61:493–501. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|