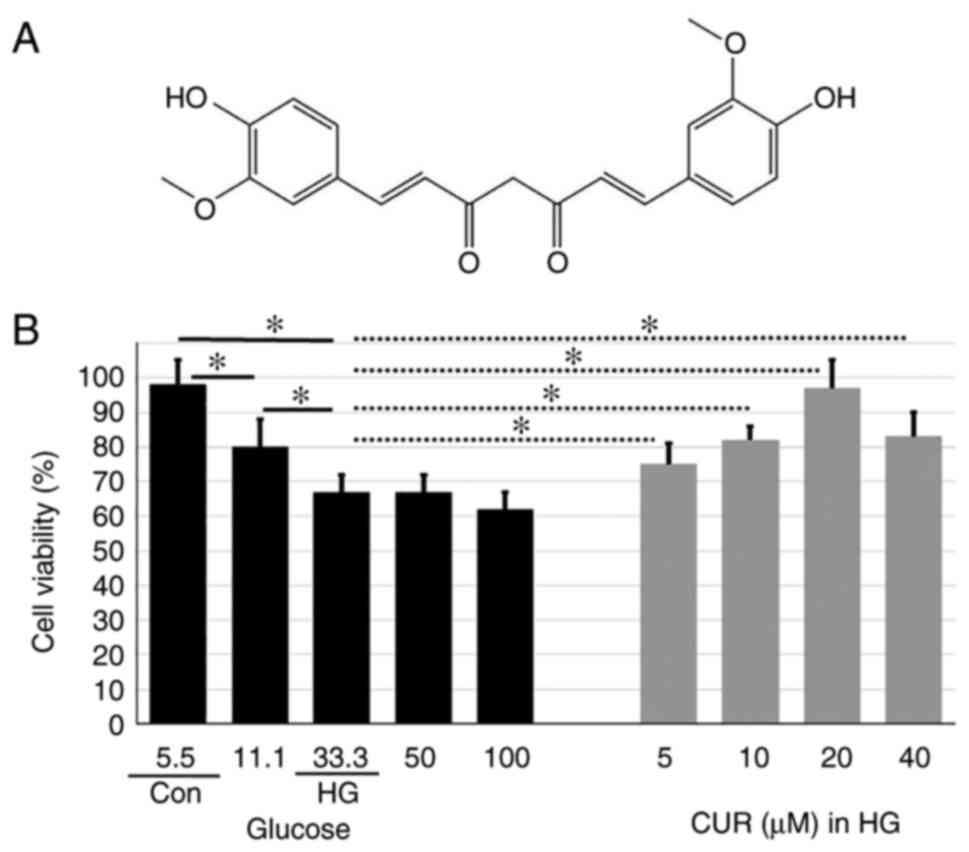
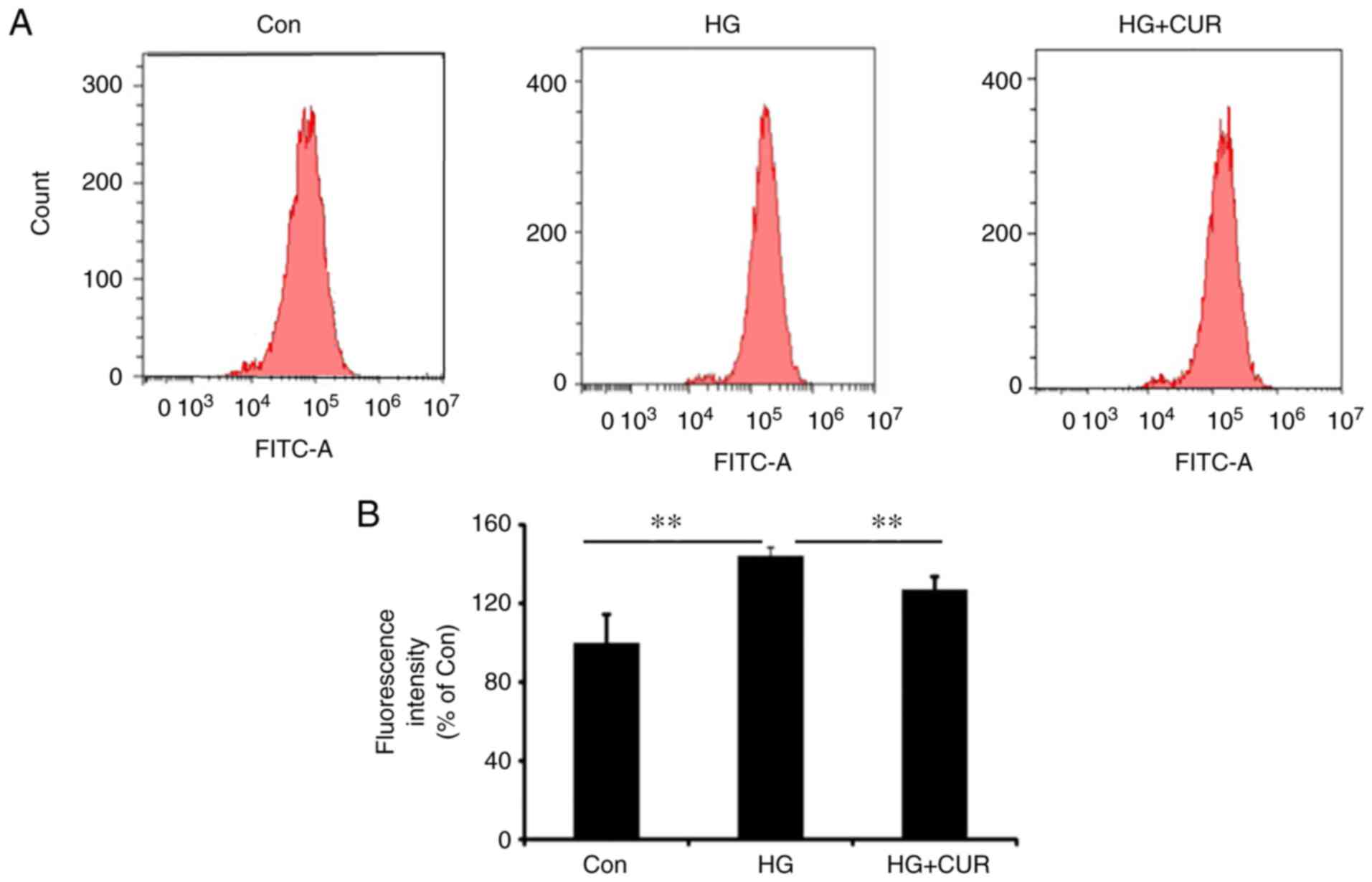
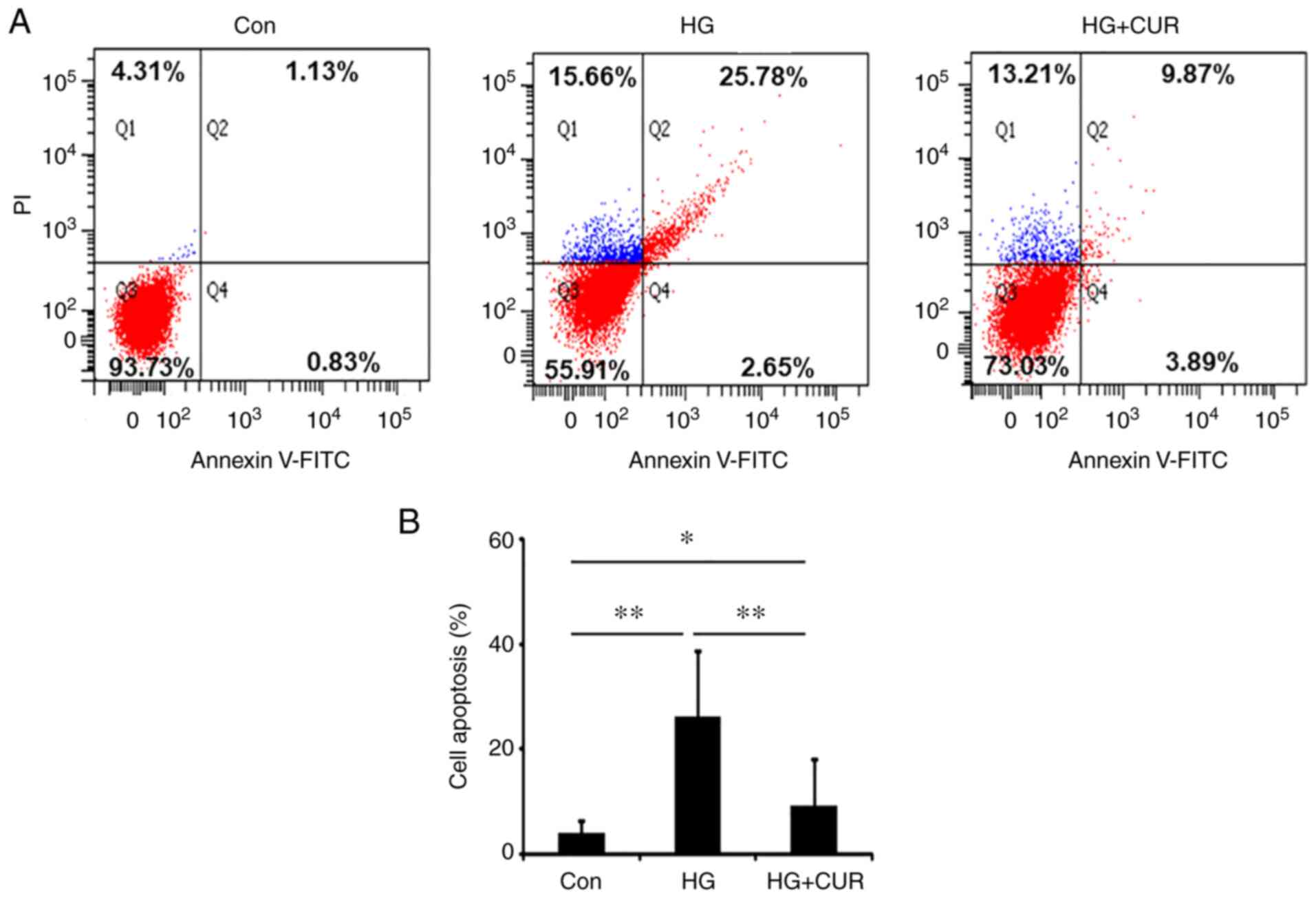
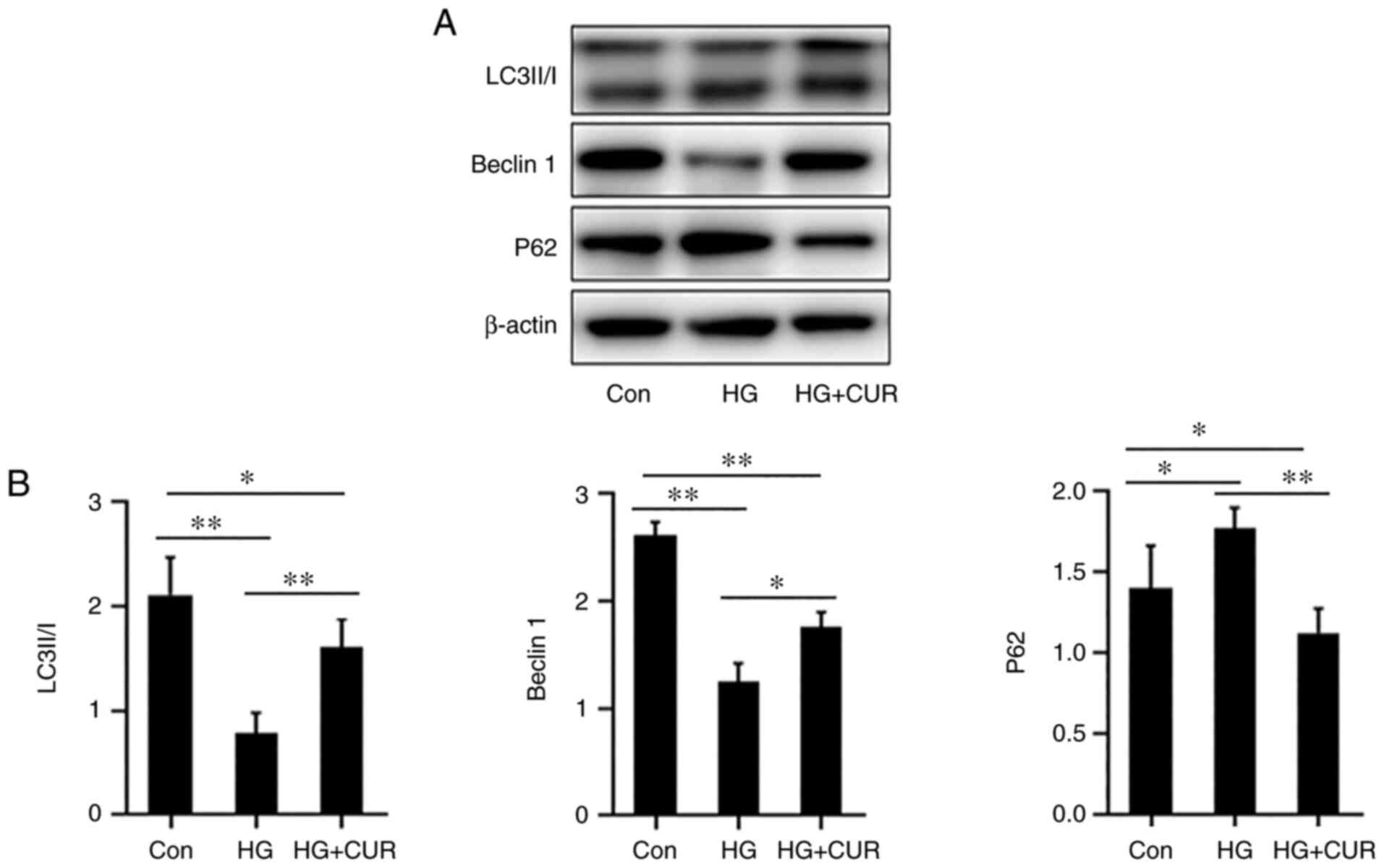
|
1
|
Zheng Y, Ley SH and Hu FB: Global
aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its
complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 14:88–98. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fowler MJ: Microvascular and macrovascular
complications of diabetes. Clin Diabetes. 26:77–82. 2008.
|
|
3
|
Popov D: Endothelial cell dysfunction in
hyperglycemia: Phenotypic change, intracellular signaling
modification, ultrastructural alteration, and potential clinical
outcomes. Int J Diabetes Mellitus. 2:189–195. 2010.
|
|
4
|
Giacco F and Brownlee M: Oxidative stress
and diabetic complications. Circ Res. 107:1058–1070.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang X, He N, Xing Y and Lu Y: Knockdown
of GCN2 inhibits high glucose-induced oxidative stress and
apoptosis in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Clin Exp Pharmacol
Physiol. 47:591–598. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang J, Li G, Wang Z, Zhang X, Yao L, Wang
F, Liu S, Yin J, Ling EA, Wang L and Hao A: High glucose-induced
expression of inflammatory cytokines and reactive oxygen species in
cultured astrocytes. Neuroscience. 202:58–68. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Liu T, Gong J, Chen Y and Jiang S:
Periodic vs constant high glucose in inducing pro-inflammatory
cytokine expression in human coronary artery endothelial cells.
Inflamm Res. 62:697–701. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sweet IR, Gilbert M, Maloney E, Hockenbery
DM, Schwartz MW and Kim F: Endothelial inflammation induced by
excess glucose is associated with cytosolic glucose 6-phosphate but
not increased mitochondrial respiration. Diabetologia. 52:921–931.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Verma N and Manna SK: Advanced glycation
end products (AGE) potently induce autophagy through activation of
RAF protein kinase and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB). J Biol Chem.
291:1481–1491. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Xie Y, You SJ, Zhang YL, Han Q, Cao YJ, Xu
XS, Yang YP, Li J and Liu CF: Protective role of autophagy in
AGE-induced early injury of human vascular endothelial cells. Mol
Med Rep. 4:459–464. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ge D, Jing Q, Meng N, Su L, Zhang Y, Zhang
S, Miao J and Zhao J: Regulation of apoptosis and autophagy by
sphingosylphosphorylcholine in vascular endothelial cells. J Cell
Physiol. 226:2827–2833. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Allen DA, Yaqoob MM and Harwood SM:
Mechanisms of high glucose-induced apoptosis and its relationship
to diabetic complications. J Nutr Biochem. 16:705–713.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ao H, Li H, Zhao X, Liu B and Lu L: TXNIP
positively regulates the autophagy and apoptosis in the rat müller
cell of diabetic retinopathy. Life Sci. 267(118988)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li Q, Yin Y, Zheng Y, Chen F and Jin P:
Inhibition of autophagy promoted high glucose/ROS-mediated
apoptosis in ADSCs. Stem Cell Res Ther. 9(289)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liu H, Yu S, Zhang H and Xu J:
Angiogenesis impairment in diabetes: Role of methylglyoxal-induced
receptor for advanced glycation endproducts, autophagy and vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor 2. PLoS One.
7(e46720)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tu Q, Li Y, Jin J, Jiang X, Ren Y and He
Q: Curcumin alleviates diabetic nephropathy via inhibiting podocyte
mesenchymal transdifferentiation and inducing autophagy in rats and
MPC5 cells. Pharm Biol. 57:778–786. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Wang L, Xiong X, Zhang X, Ye Y, Jian Z,
Gao W and Gu L: Sodium Tanshinone IIA sulfonate protects against
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting autophagy and
inflammation. Neuroscience. 441:46–57. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kelany ME, Hakami TM and Omar AH: Curcumin
improves the metabolic syndrome in high-fructose-diet-fed rats:
Role of TNF-α, NF-κB, and oxidative stress. Can J Physiol
Pharmacol. 95:140–150. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang Z and Li K: Curcumin attenuates high
glucose-induced inflammatory injury through the reactive oxygen
species-phosphoinositide 3-kinase/protein kinase B-nuclear
factor-κB signaling pathway in rat thoracic aorta endothelial
cells. J Diabetes Investig. 9:731–740. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Huang J, Fu J, Liu B, Wang R and You T: A
synthetic curcuminoid analog,
(2E,6E)-2,6-bis(2-(trifluoromethyl)benzylidene)cyclohexanone,
ameliorates impaired wound healing in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic mice by increasing miR-146a. Molecules.
25(920)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Shimizu K, Sunagawa Y, Funamoto M,
Wakabayashi H, Genpei M, Miyazaki Y, Katanasaka Y, Sari N, Shimizu
S, Katayama A, et al: The synthetic curcumin analogue GO-Y030
effectively suppresses the development of pressure overload-induced
heart failure in mice. Sci Rep. 10(7172)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Jin QH, Shen HX, Wang H, Shou QY and Liu
Q: Curcumin improves expression of SCF/c-kit through attenuating
oxidative stress and NF-κB activation in gastric tissues of
diabetic gastroparesis rats. Diabetol Metab Syndr.
5(12)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Han J, Pan XY, Xu Y, Xiao Y, An Y, Tie L,
Pan Y and Li XJ: Curcumin induces autophagy to protect vascular
endothelial cell survival from oxidative stress damage. Autophagy.
8:812–825. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yu W, Zha W, Ke Z, Min Q, Li C, Sun H and
Liu C: Curcumin protects neonatal rat cardiomyocytes against high
glucose-induced apoptosis via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. J
Diabetes Res. 2016(4158591)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Tu Y, Guo C, Song F, Huo Y, Geng Y, Guo M,
Bao H, Wu X and Fan W: Mild hypothermia alleviates diabetes
aggravated cerebral ischemic injury via activating autophagy and
inhibiting pyroptosis. Brain Res Bull. 150:1–12. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wei Y, Gao J, Qin L, Xu Y, Shi H, Qu L,
Liu Y, Xu T and Liu T: Curcumin suppresses AGEs induced apoptosis
in tubular epithelial cells via protective autophagy. Exp Ther Med.
14:6052–6058. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Guo S, Long M, Li X, Zhu S, Zhang M and
Yang Z: Curcumin activates autophagy and attenuates oxidative
damage in EA.hy926 cells via the Akt/mTOR pathway. Mol Med Rep.
13:2187–2193. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wang Y, Gao A, Xu X, Dang B, You W, Li H,
Yu Z and Chen G: The neuroprotection of lysosomotropic agents in
experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage probably involving the
apoptosis pathway triggering by cathepsins via chelating
intralysosomal iron. Mol Neurobiol. 52:64–77. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yan H, Ma Y, Li Y, Zheng X, Lv P, Zhang Y,
Li J, Ma M, Zhang L, Li C, et al: Insulin inhibits inflammation and
promotes atherosclerotic plaque stability via PI3K-Akt pathway
activation. Immunol Lett. 170:7–14. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Arshad L, Haque MA, Abbas Bukhari SN and
Jantan I: An overview of structure-activity relationship studies of
curcumin analogs as antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents.
Future Med Chem. 9:605–626. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Parsamanesh N, Moossavi M, Bahrami A,
Butler AF and Sahebkar A: Therapeutic potential of Curcumin in
diabetic complications. Pharmacol Res. 136:181–193. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Yao Q, Ke ZQ, Guo S, Yang XS, Zhang FX,
Liu XF, Chen X, Chen HG, Ke HY and Liu C: Curcumin protects against
diabetic cardiomyopathy by promoting autophagy and alleviating
apoptosis. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 124:26–34. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhang X, Li ZL, Crane JA, Jordan KL, Pawar
AS, Textor SC, Lerman A and Lerman LO: Valsartan regulates
myocardial autophagy and mitochondrial turnover in experimental
hypertension. Hypertension. 64:87–93. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wu S, Lu Q, Ding Y, Wu Y, Qiu Y, Wang P,
Mao X, Huang K, Xie Z and Zou MH: Hyperglycemia-driven inhibition
of AMP-activated protein kinase α2 induces diabetic cardiomyopathy
by promoting mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum
membranes in vivo. Circulation. 139:1913–1936. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Yu W, Gao B, Li N, Wang J, Qiu C, Zhang G,
Liu M, Zhang R, Li C, Ji G and Zhang Y: Sirt3 deficiency
exacerbates diabetic cardiac dysfunction: Role of
Foxo3A-Parkin-mediated mitophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis
Dis. 1863:1973–1983. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Ihnat MA, Thorpe JE, Kamat CD, Szabó C,
Green DE, Warnke LA, Lacza Z, Cselenyák A, Ross K, Shakir S, et al:
Reactive oxygen species mediate a cellular ‘memory’ of high glucose
stress signalling. Diabetologia. 50:1523–1531. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Quagliaro L, Piconi L, Assaloni R,
Martinelli L, Motz E and Ceriello A: Intermittent high glucose
enhances apoptosis related to oxidative stress in human umbilical
vein endothelial cells: The role of protein kinase C and
NAD(P)H-oxidase activation. Diabetes. 52:2795–2804. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ortiz-Cordero C, Bincoletto C, Dhoke NR,
Selvaraj S, Magli A, Zhou H, Kim DH, Bang AG and Perlingeiro RC:
Defective autophagy and increased apoptosis contribute toward the
pathogenesis of FKRP-associated muscular dystrophies. Stem Cell
Reports. 16:2752–2767. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Xu J, Kitada M, Ogura Y, Liu H and Koya D:
Dapagliflozin restores impaired autophagy and suppresses
inflammation in high glucose-treated HK-2 cells. Cells.
10(1457)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang Z, Zhang S, Wang Y, Yang M, Zhang N,
Jin Z, Ding L, Jiang W, Yang J, Sun Z, et al: Autophagy inhibits
high glucose induced cardiac microvascular endothelial cells
apoptosis by mTOR signal pathway. Apoptosis. 22:1510–1523.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Rezabakhsh A, Ahmadi M, Khaksar M,
Montaseri A, Malekinejad H, Rahbarghazi R and Garjani A: Rapamycin
inhibits oxidative/nitrosative stress and enhances angiogenesis in
high glucose-treated human umbilical vein endothelial cells: Role
of autophagy. Biomed Pharmacother. 93:885–894. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Hou G, Zhao H, Teng H, Li P, Xu W, Zhang
J, Lv L, Guo Z, Wei L, Yao H and Xu Y: N-Cadherin attenuates high
glucose-induced nucleus pulposus cell senescence through regulation
of the ROS/NF-κB pathway. Cell Physio Biochem. 47:257–265.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Cao G, Fan J, Yu H and Chen Z: Resveratrol
attenuates high glucose-induced cardiomyocytes injury via
interfering ROS-MAPK-NF-κB signaling pathway. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 11:48–57. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Teng JF, Mei QB, Zhou XG, Tang Y, Xiong R,
Qiu WQ, Pan R, Law BY, Wong VK, Yu CL, et al: Polyphyllin VI
induces Caspase-1-mediated pyroptosis via the Induction of
ROS/NF-κB/NLRP3/GSDMD signal axis in non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 12(193)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Ma B, Wang X, Zhang R, Niu S, Rong Z, Ni
L, Di X, Han Q and Liu C: Cigarette smoke extract stimulates PCSK9
production in HepG2 cells via ROS/NF-κB signaling. Mol Med Rep.
23(331)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Morgan MJ and Liu Z: Crosstalk of reactive
oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 21:103–115.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Xu X, Huang X, Zhang L, Huang X, Qin Z and
Hua F: Adiponectin protects obesity-related glomerulopathy by
inhibiting ROS/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammation pathway. BMC Nephrol.
22(218)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|