|
1
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Dobruch J, Daneshmand S, Fisch M, Lotan Y,
Noon AP, Resnick MJ, Shariat SF, Zlotta AR and Boorjian SA: Gender
and bladder cancer: A collaborative review of etiology, biology,
and outcomes. Eur Urol. 69:300–310. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Richters A, Aben KKH and Kiemeney LALM:
The global burden of urinary bladder cancer: An update. World J
Urol. 38:1895–1904. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
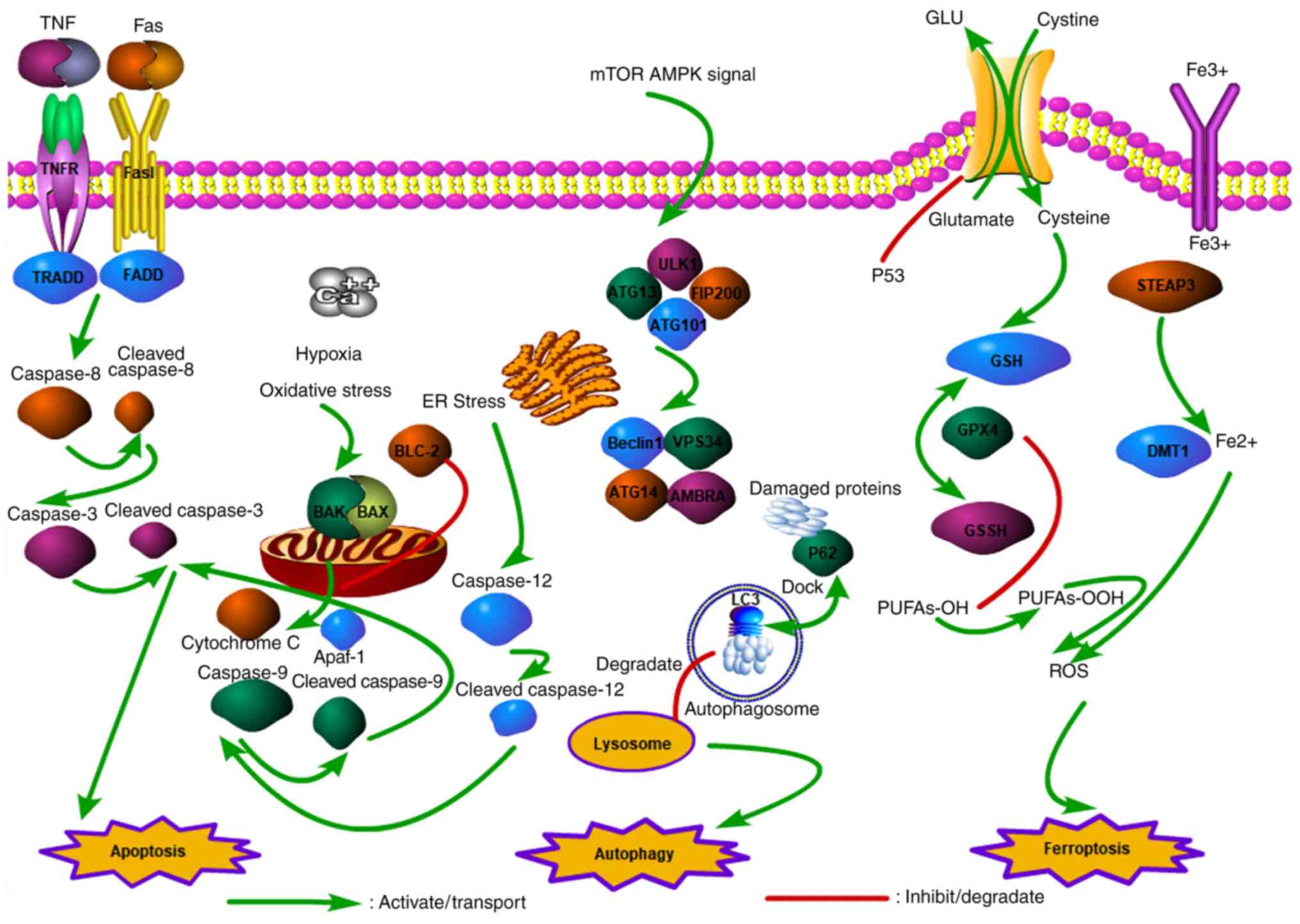
4
|
Xia Y, Chen R, Lu G, Li C, Lian S, Kang TW
and Jung YD: Natural phytochemicals in bladder cancer prevention
and therapy. Front Oncol. 11(652033)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Han J, Gu X, Li Y and Wu Q: Mechanisms of
BCG in the treatment of bladder cancer-current understanding and
the prospect. Biomed Pharmacother. 129(110393)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kimura T, Ishikawa H, Kojima T, Kandori S,
Kawahara T, Sekino Y, Sakurai H and Nishiyama H: Bladder
preservation therapy for muscle invasive bladder cancer: The past,
present and future. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 50:1097–1107. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tran L, Xiao JF, Agarwal N, Duex JE and
Theodorescu D: Advances in bladder cancer biology and therapy. Nat
Rev Cancer. 21:104–121. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
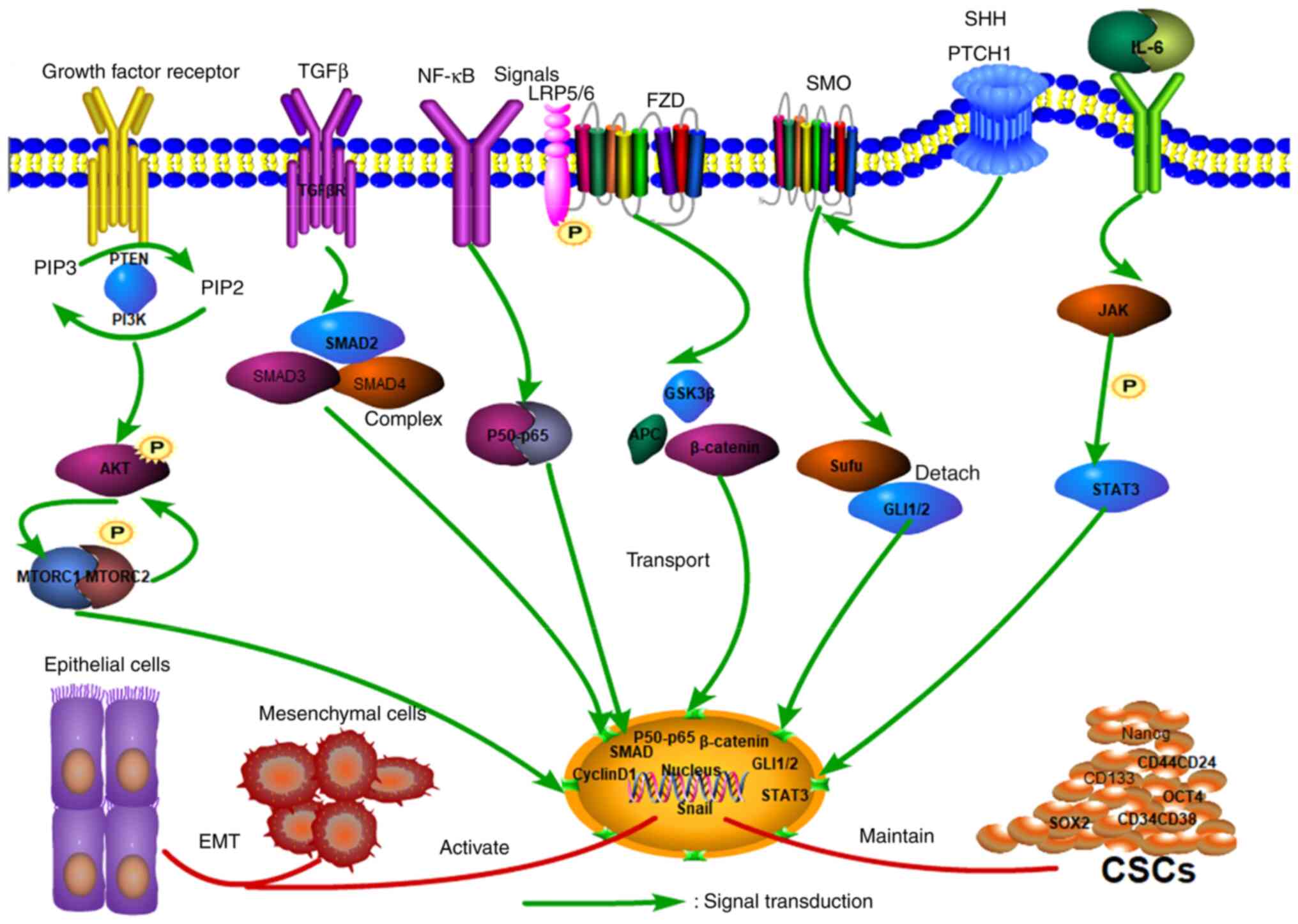
8
|
Bednova O and Leyton JV: Targeted
molecular therapeutics for bladder cancer-A new option beyond the
mixed fortunes of immune checkpoint inhibitors? Int J Mol Sci.
21(7268)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
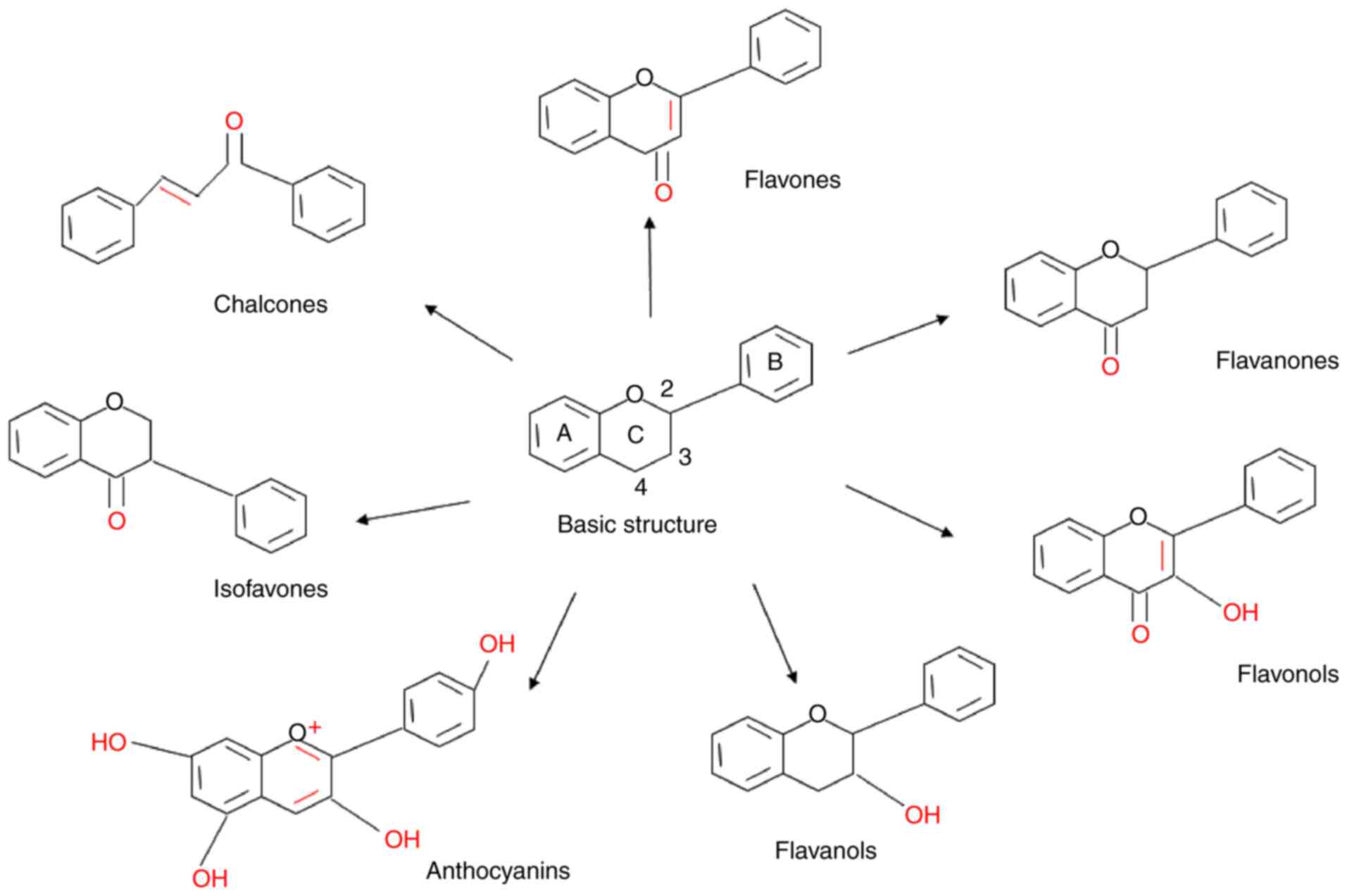
9
|
Rutz J, Janicova A, Woidacki K, Chun FK,
Blaheta RA and Relja B: Curcumin-A viable agent for better bladder
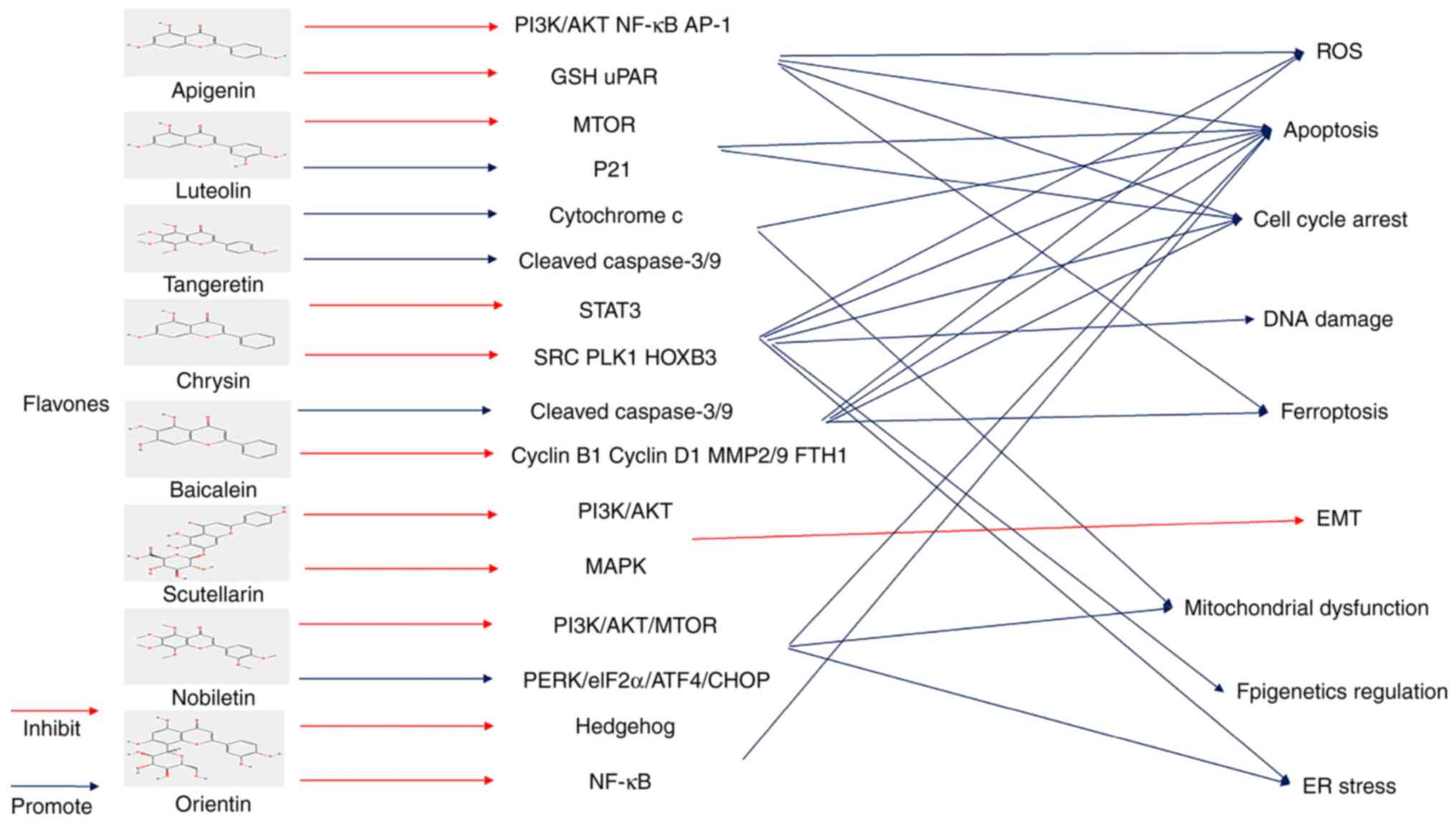
cancer treatment. Int J Mol Sci. 21(3761)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zanoaga O, Braicu C, Jurj A, Rusu A, Buiga
R and Berindan-Neagoe I: Progress in research on the role of
flavonoids in lung cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 20(4291)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Niedzwiecki A, Roomi MW, Kalinovsky T and
Rath M: Anticancer efficacy of polyphenols and their combinations.
Nutrients. 8(552)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kumar S and Pandey AK: Chemistry and
biological activities of flavonoids: An overview.
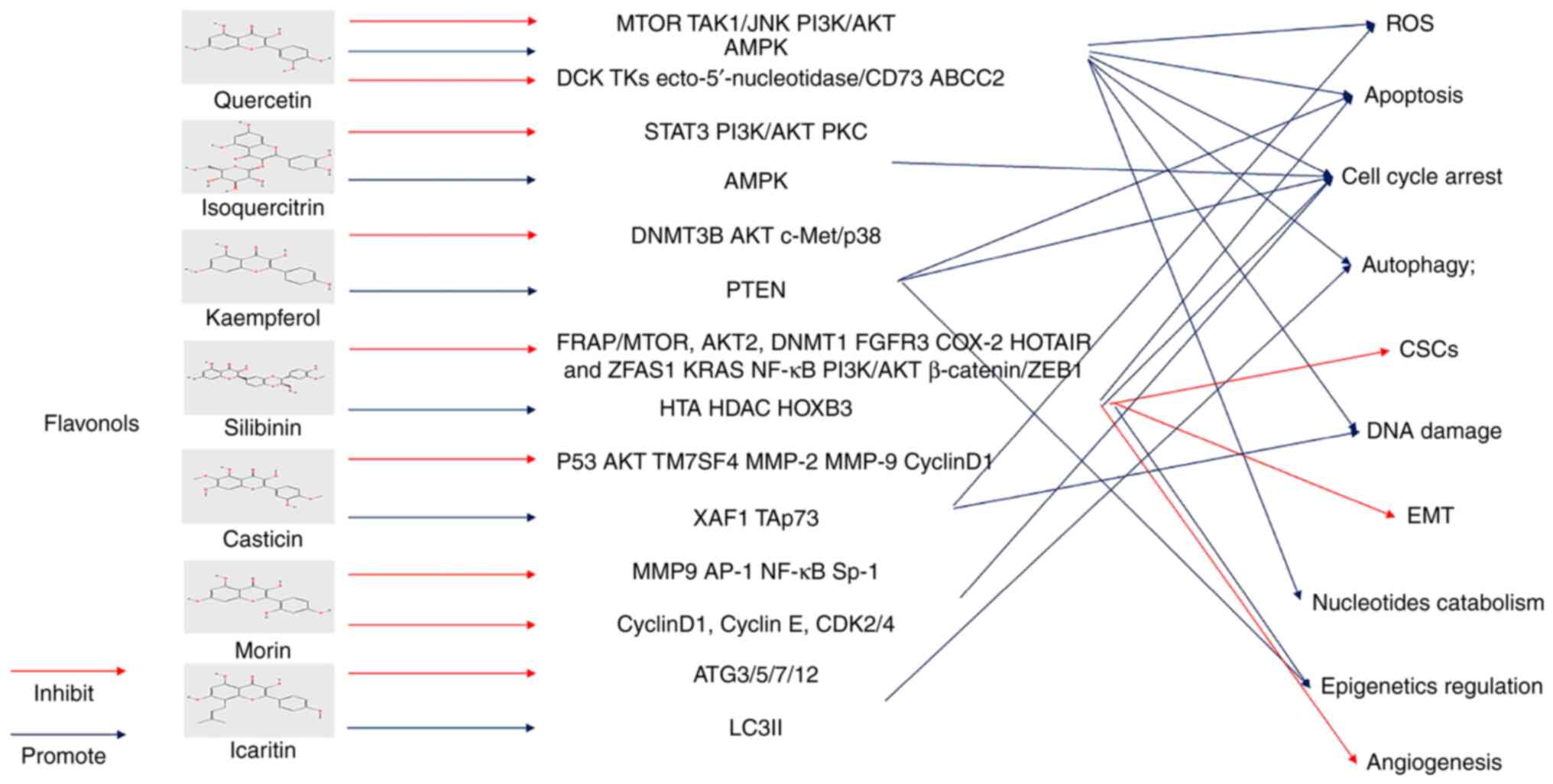
ScientificWorldJournal. 2013(162750)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Amawi H, Ashby CR Jr and Tiwari AK: Cancer
chemoprevention through dietary flavonoids: What's limiting? Chin J
Cancer. 36(50)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lama-Sherpa TD and Shevde LA: An emerging
regulatory role for the tumor microenvironment in the DNA damage
response to double-strand breaks. Mol Cancer Res. 18:185–193.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Srinivas US, Tan BWQ, Vellayappan BA and
Jeyasekharan AD: ROS and the DNA damage response in cancer. Redox
Biol. 25(101084)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Harashima H, Dissmeyer N and Schnittger A:
Cell cycle control across the eukaryotic kingdom. Trends Cell Biol.
23:345–356. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lim S and Kaldis P: Cdks, cyclins and
CKIs: Roles beyond cell cycle regulation. Development.
140:3079–3093. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
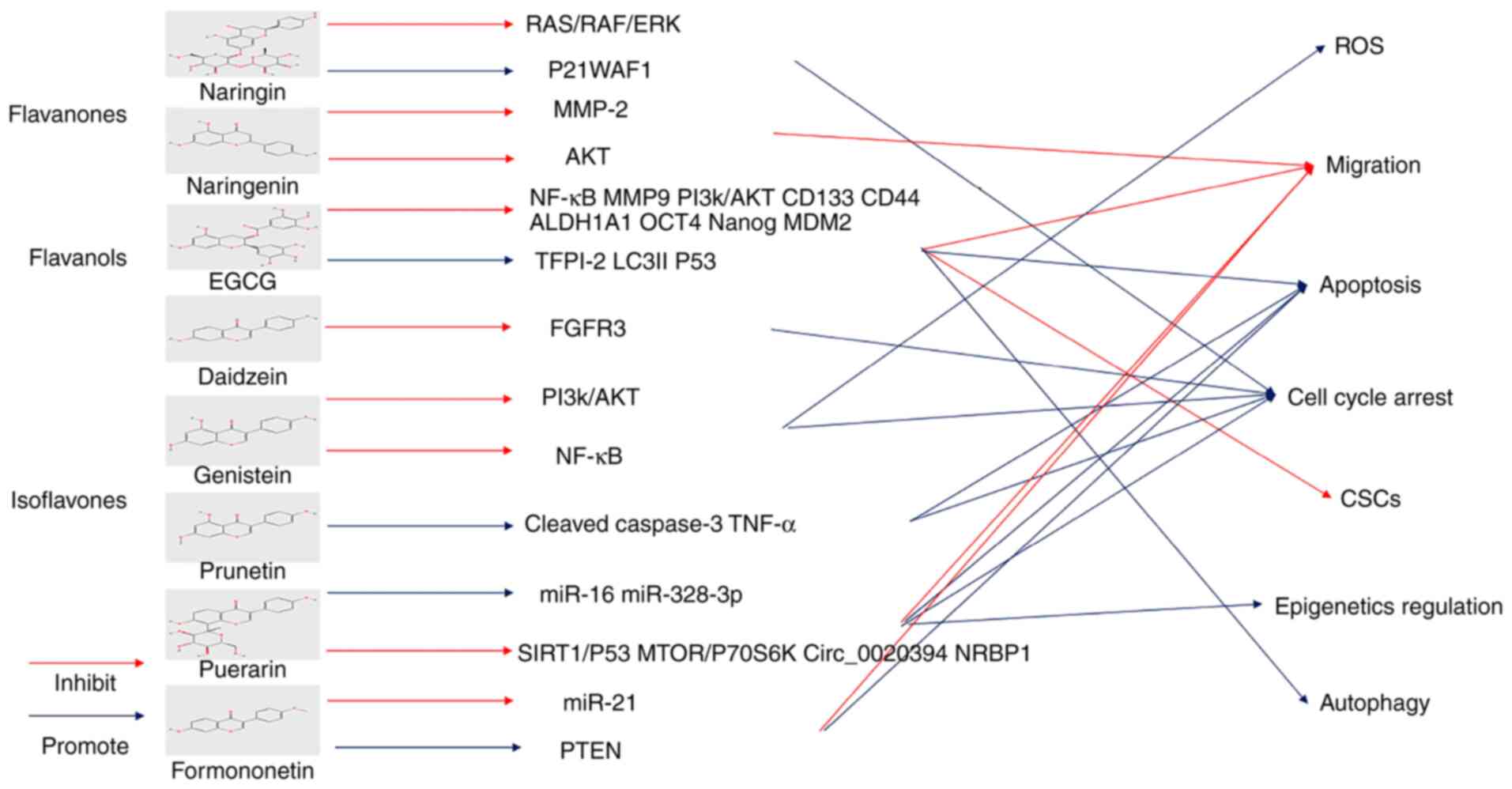
18
|
Carusillo A and Mussolino C: DNA Damage:
From threat to treatment. Cells. 9(1665)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Solier S, Zhang YW, Ballestrero A, Pommier
Y and Zoppoli G: DNA damage response pathways and cell cycle
checkpoints in colorectal cancer: Current concepts and future
perspectives for targeted treatment. Curr Cancer Drug Targets.
12:356–371. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Kastan MB and Bartek J: Cell-cycle
checkpoints and cancer. Nature. 432:316–323. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
de Sá Junior PL, Câmara DAD, Porcacchia
AS, Fonseca PMM, Jorge SD, Araldi RP and Ferreira AK: The roles of
ROS in cancer heterogeneity and therapy. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2017(2467940)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Aggarwal V, Tuli HS, Varol A, Thakral F,
Yerer MB, Sak K, Varol M, Jain A, Khan MA and Sethi G: Role of
reactive oxygen species in cancer progression: Molecular mechanisms
and recent advancements. Biomolecules. 9(735)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Perillo B, Di Donato M, Pezone A, Di Zazzo
E, Giovannelli P, Galasso G, Castoria G and Migliaccio A: ROS in
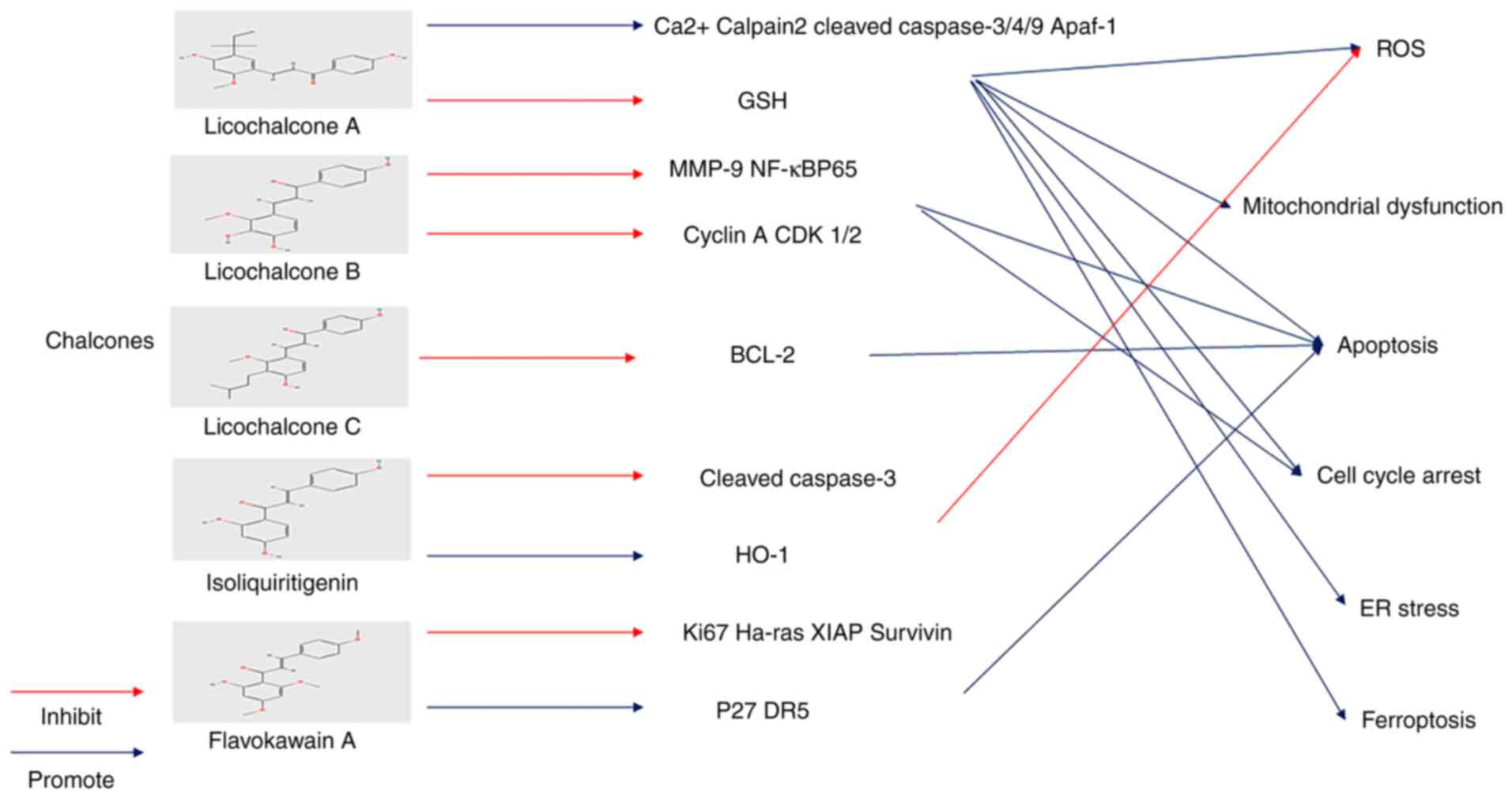
cancer therapy: the bright side of the moon. Exp Mol Med.
52:192–203. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xu X, Lai Y and Hua ZC: Apoptosis and
apoptotic body: Disease message and therapeutic target potentials.
Biosci Rep. 39(BSR20180992)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Hengartner MO: Apoptosis: Corralling the
corpses. Cell. 104:325–328. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Schneider P and Tschopp J: Apoptosis
induced by death receptors. Pharm Acta Helv. 74:281–286.
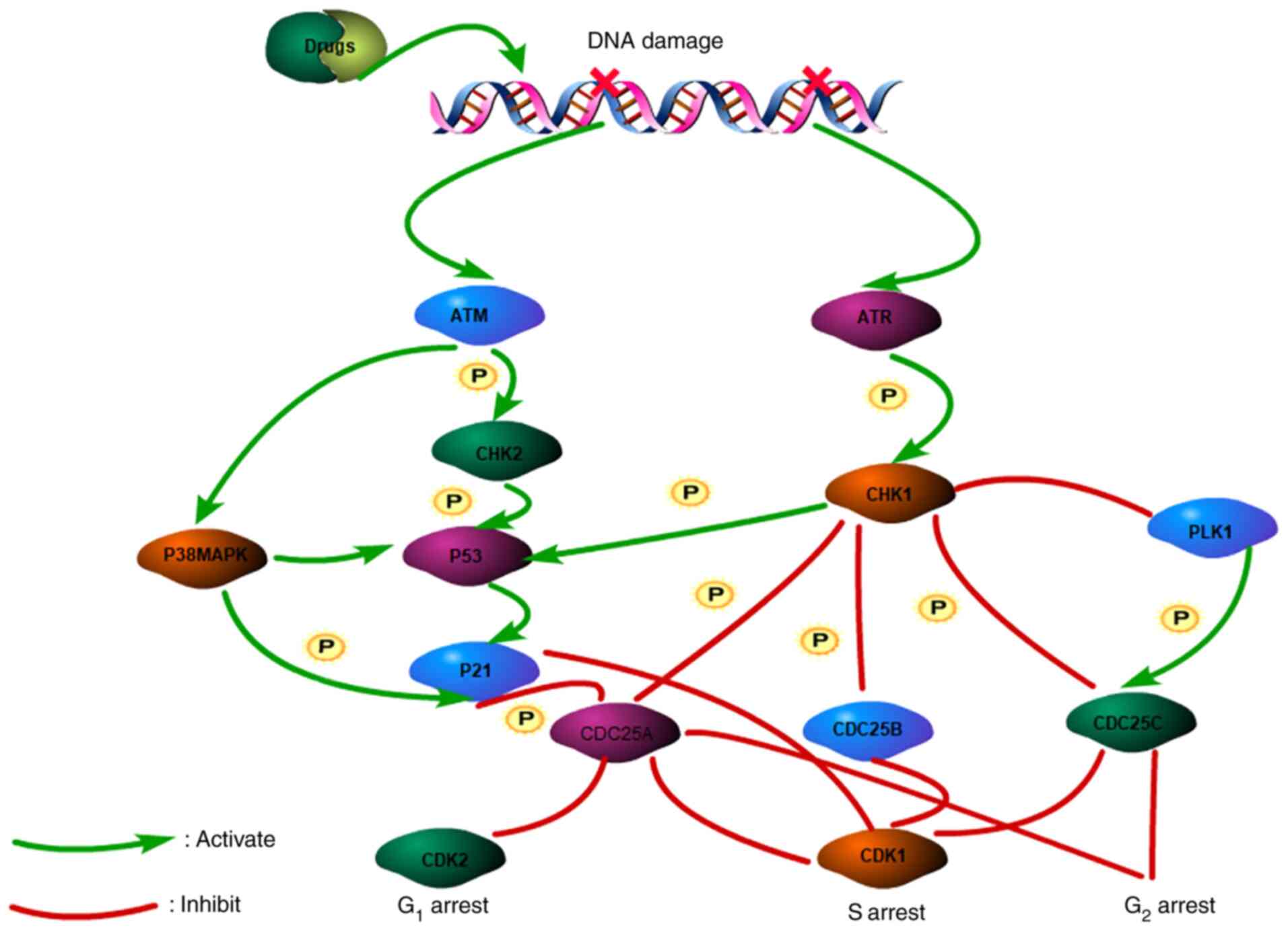
2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Indran IR, Tufo G, Pervaiz S and Brenner
C: Recent advances in apoptosis, mitochondria and drug resistance
in cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1807:735–745.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Bertheloot D, Latz E and Franklin BS:
Necroptosis, pyroptosis and apoptosis: An intricate game of cell
death. Cell Mol Immunol. 18:1106–1121. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wong RS: Apoptosis in cancer: From
pathogenesis to treatment. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
30(87)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Szegezdi E, Fitzgerald U and Samali A:
Caspase-12 and ER-stress-mediated apoptosis: The story so far. Ann
N Y Acad Sci. 1010:186–194. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Levy JMM, Towers CG and Thorburn A:
Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 17:528–542.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Amaravadi RK, Kimmelman AC and Debnath J:
Targeting autophagy in cancer: Recent advances and future
directions. Cancer Discov. 9:1167–1181. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
White E, Mehnert JM and Chan CS:
Autophagy, metabolism, and cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 21:5037–5046.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Amaravadi R, Kimmelman AC and White E:
Recent insights into the function of autophagy in cancer. Genes
Dev. 30:1913–1930. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mou Y, Wang J, Wu J, He D, Zhang C, Duan C
and Li B: Ferroptosis, a new form of cell death: Opportunities and
challenges in cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 12(34)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Xu T, Ding W, Ji X, Ao X, Liu Y, Yu W and
Wang J: Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and its role in cancer
therapy. J Cell Mol Med. 23:4900–4912. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bebber CM, Müller F, Prieto Clemente L,
Weber J and von Karstedt S: Ferroptosis in cancer cell biology.
Cancers (Basel). 12(164)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Li J, Cao F, Yin HL, Huang ZJ, Lin ZT, Mao
N, Sun B and Wang G: Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell
Death Dis. 11(88)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Tiffon C: The impact of nutrition and
environmental epigenetics on human health and disease. Int J Mol
Sci. 19(3425)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Margueron R and Reinberg D: Chromatin
structure and the inheritance of epigenetic information. Nat Rev
Genet. 11:285–296. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Mahmoud AM and Ali MM: Methyl donor
micronutrients that modify DNA methylation and cancer outcome.
Nutrients. 11(608)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Jasek K, Kubatka P, Samec M, Liskova A,
Smejkal K, Vybohova D, Bugos O, Biskupska-Bodova K, Bielik T, Zubor
P, et al: DNA methylation status in cancer disease: Modulations by
plant-derived natural compounds and dietary interventions.
Biomolecules. 9(289)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Huang Z, Huang Q, Ji L, Wang Y, Qi X, Liu
L, Liu Z and Lu L: Epigenetic regulation of active Chinese herbal
components for cancer prevention and treatment: A follow-up review.
Pharmacol Res. 114:1–12. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Qin J, Wen B, Liang Y, Yu W and Li H:
Histone modifications and their role in colorectal cancer (Review).
Pathol Oncol Res. 26:2023–2033. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Audia JE and Campbell RM: Histone
modifications and cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
8(a019521)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Lee YS and Dutta A: MicroRNAs in cancer.
Annu Rev Pathol. 4:199–227. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ali Syeda Z, Langden SSS, Munkhzul C, Lee
M and Song SJ: Regulatory mechanism of MicroRNA expression in
cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 21(1723)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Tay Y, Rinn J and Pandolfi PP: The
multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature.
505:344–352. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Hanahan D and Folkman J: Patterns and
emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis.
Cell. 86:353–364. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Koch AE and Distler O: Vasculopathy and
disordered angiogenesis in selected rheumatic diseases: Rheumatoid
arthritis and systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res Ther. 9 (Suppl
2)(S3)2007.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Ramjiawan RR, Griffioen AW and Duda DG:
Anti-angiogenesis for cancer revisited: Is there a role for
combinations with immunotherapy? Angiogenesis. 20:185–204.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Rajabi M and Mousa SA: The role of
angiogenesis in cancer treatment. Biomedicines.
5(34)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Pan G, Liu Y, Shang L, Zhou F and Yang S:
EMT-associated microRNAs and their roles in cancer stemness and
drug resistance. Cancer Commun (Lond). 41:199–217. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Eun K, Ham SW and Kim H: Cancer stem cell
heterogeneity: Origin and new perspectives on CSC targeting. BMB
Rep. 50:117–125. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Barzegar Behrooz A, Syahir A and Ahmad S:
CD133: Beyond a cancer stem cell biomarker. J Drug Target.
27:257–269. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Huang T, Song X, Xu D, Tiek D, Goenka A,
Wu B, Sastry N, Hu B and Cheng SY: Stem cell programs in cancer
initiation, progression, and therapy resistance. Theranostics.
10:8721–8743. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Du B and Shim JS: Targeting
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) to overcome drug resistance
in cancer. Molecules. 21(965)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Lehman HL, Kidacki M and Stairs DB: Twist2
is NFkB-responsive when p120-catenin is inactivated and EGFR is
overexpressed in esophageal keratinocytes. Sci Rep.
10(18829)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Luongo F, Colonna F, Calapà F, Vitale S,
Fiori ME and De Maria R: PTEN tumor-suppressor: The dam of stemness
in cancer. Cancers (Basel). 11(1076)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Kopustinskiene DM, Jakstas V, Savickas A
and Bernatoniene J: Flavonoids as anticancer agents. Nutrients.
12(457)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Abotaleb M, Samuel SM, Varghese E,
Varghese S, Kubatka P, Liskova A and Büsselberg D: Flavonoids in
cancer and apoptosis. Cancers (Basel). 11(28)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Panche AN, Diwan AD and Chandra SR:
Flavonoids: An overview. J Nutr Sci. 5(e47)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Hostetler GL, Ralston RA and Schwartz SJ:
Flavones: Food sources, bioavailability, metabolism, and
bioactivity. Adv Nutr. 8:423–435. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Shi MD, Shiao CK, Lee YC and Shih YW:
Apigenin, a dietary flavonoid, inhibits proliferation of human
bladder cancer T-24 cells via blocking cell cycle progression and
inducing apoptosis. Cancer Cell Int. 15(33)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Zhu Y, Mao Y, Chen H, Lin Y, Hu Z, Wu J,
Xu X, Xu X, Qin J and Xie L: Apigenin promotes apoptosis, inhibits
invasion and induces cell cycle arrest of T24 human bladder cancer
cells. Cancer Cell Int. 13(54)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Xia Y, Yuan M, Li S, Thuan UT, Nguyen TT,
Kang TW, Liao W, Lian S and Jung YD: Apigenin Suppresses the
IL-1β-induced expression of the urokinase-type plasminogen
activator receptor by inhibiting MAPK-Mediated AP-1 and NF-κB
signaling in human bladder cancer T24 cells. J Agric Food Chem.
66:7663–7673. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Lin Y, Shi R, Wang X and Shen HM:
Luteolin, a flavonoid with potential for cancer prevention and
therapy. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:634–646. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Kilani-Jaziri S, Frachet V, Bhouri W,
Ghedira K, Chekir-Ghedira L and Ronot X: Flavones inhibit the
proliferation of human tumor cancer cell lines by inducing
apoptosis. Drug Chem Toxicol. 35:1–10. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Iida K, Naiki T, Naiki-Ito A, Suzuki S,
Kato H, Nozaki S, Nagai T, Etani T, Nagayasu Y, Ando R, et al:
Luteolin suppresses bladder cancer growth via regulation of
mechanistic target of rapamycin pathway. Cancer Sci. 111:1165–1179.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Yang G, Wang Z, Wang W, Zhou X, Hu X and
Yang J: Anticancer activity of Luteolin and its synergism effect
with BCG on human bladder cancer cell line BIU-87. Zhong Nan Da Xue
Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 39:371–378. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
72
|
Lin JJ, Huang CC, Su YL, Luo HL, Lee NL,
Sung MT and Wu YJ: Proteomics analysis of tangeretin-induced
apoptosis through mitochondrial dysfunction in bladder cancer
cells. Int J Mol Sci. 20(1017)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Mani R and Natesan V: Chrysin: Sources,
beneficial pharmacological activities, and molecular mechanism of
action. Phytochemistry. 145:187–196. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Xu Y, Tong Y, Ying J, Lei Z, Wan L, Zhu X,
Ye F, Mao P, Wu X, Pan R, et al: Chrysin induces cell growth
arrest, apoptosis, and ER stress and inhibits the activation of
STAT3 through the generation of ROS in bladder cancer cells. Oncol
Lett. 15:9117–9125. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Lima APB, Almeida TC, Barros TMB, Rocha
LCM, Garcia CCM and da Silva GN: Toxicogenetic and
antiproliferative effects of chrysin in urinary bladder cancer
cells. Mutagenesis: Aug 13, 2020 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
76
|
Yang Y, Liu K, Yang L and Zhang G: Bladder
cancer cell viability inhibition and apoptosis induction by
baicalein through targeting the expression of anti-apoptotic genes.
Saudi J Biol Sci. 25:1478–1482. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Choi EO, Park C, Hwang HJ, Hong SH, Kim
GY, Cho EJ, Kim WJ and Choi YH: Baicalein induces apoptosis via
ROS-dependent activation of caspases in human bladder cancer 5637
cells. Int J Oncol. 49:1009–1018. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Li HL, Zhang S, Wang Y, Liang RR, Li J, An
P, Wang ZM, Yang J and Li ZF: Baicalein induces apoptosis via a
mitochondrial-dependent caspase activation pathway in T24 bladder
cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 7:266–270. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Kong N, Chen X, Feng J, Duan T, Liu S, Sun
X, Chen P, Pan T, Yan L, Jin T, et al: Baicalin induces ferroptosis
in bladder cancer cells by downregulating FTH1. Acta Pharm Sin B.
11:4045–4054. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Wu JY, Tsai KW, Li YZ, Chang YS, Lai YC,
Laio YH, Wu JD and Liu YW: Anti-bladder-tumor effect of baicalein
from scutellaria baicalensis georgi and its application in vivo.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013(579751)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Peng L, Wen L, Shi QF, Gao F, Huang B,
Meng J, Hu CP and Wang CM: Scutellarin ameliorates pulmonary
fibrosis through inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3-mediated
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and inflammation. Cell Death Dis.
11(978)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Lv WL, Liu Q, An JH and Song XY:
Scutellarin inhibits hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal
transition in bladder cancer cells. J Cell Physiol.
234:23169–23175. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Ashrafizadeh M, Zarrabi A, Saberifar S,
Hashemi F, Hushmandi K, Hashemi F, Moghadam ER, Mohammadinejad R,
Najafi M and Garg M: Nobiletin in cancer therapy: How this plant
derived-natural compound targets various oncogene and
onco-suppressor pathways. Biomedicines. 8(110)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Goan YG, Wu WT, Liu CI, Neoh CA and Wu YJ:
Involvement of mitochondrial dysfunction, endoplasmic reticulum
stress, and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in nobiletin-induced
apoptosis of human bladder cancer cells. Molecules.
24(2881)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Tian F, Tong M, Li Z, Huang W, Jin Y, Cao
Q, Zhou X and Tong G: The effects of orientin on proliferation and
apoptosis of T24 human bladder carcinoma cells occurs through the
inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB and the hedgehog signaling
pathway. Med Sci Monit. 25:9547–9554. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Stavric B: Quercetin in our diet: From
potent mutagen to probable anticarcinogen. Clin Biochem.
27:245–248. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Rauf A, Imran M, Khan IA, Ur-Rehman M,
Gilani SA, Mehmood Z and Mubarak MS: Anticancer potential of
quercetin: A comprehensive review. Phytother Res. 32:2109–2130.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Adami BS, Diz FM, Oliveira Gonçalves GP,
Reghelin CK, Scherer M, Dutra AP, Papaléo RM, de Oliveira JR,
Morrone FB, Wieck A and Xavier LL: Morphological and mechanical
changes induced by quercetin in human T24 bladder cancer cells.
Micron. 151(103152)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Oršolić N, Karač I, Sirovina D, Kukolj M,
Kunštić M, Gajski G, Garaj-Vrhovac V and Štajcar D:
Chemotherapeutic potential of quercetin on human bladder cancer
cells. J Environ Sci Health A Tox Hazard Subst Environ Eng.
51:776–781. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Su Q, Peng M, Zhang Y, Xu W, Darko KO, Tao
T, Huang Y, Tao X and Yang X: Quercetin induces bladder cancer
cells apoptosis by activation of AMPK signaling pathway. Am J
Cancer Res. 6:498–508. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Wei L, Liu JJ, Cao J, Du NC, Ji LN and
Yang XL: Role of autophagy in quercetin-induced apoptosis in human
bladder carcinoma BIU-87 cells. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi.
34:414–418. 2012.PubMed/NCBI(In Chinese).
|
|
92
|
Tan DQ and Liu XH: Mechanism in growth
inhibition of quercetin on human bladder cancer cell line. Zhongguo
Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 42:1742–1746. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
93
|
Rockenbach L, Bavaresco L, Fernandes
Farias P, Cappellari AR, Barrios CH, Bueno Morrone F and Oliveira
Battastini AM: Alterations in the extracellular catabolism of
nucleotides are involved in the antiproliferative effect of
quercetin in human bladder cancer T24 cells. Urol Oncol.
31:1204–1211. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Berger SI and Iyengar R: Network analyses
in systems pharmacology. Bioinformatics. 25:2466–2472.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Dong Y, Hao L, Fang K, Han XX, Yu H, Zhang
JJ, Cai LJ, Fan T, Zhang WD, Pang K, et al: A network pharmacology
perspective for deciphering potential mechanisms of action of
Solanum nigrum L. in bladder cancer. BMC Complement Med Ther.
21(45)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Cho CJ, Yu CP, Wu CL, Ho JY, Yang CW and
Yu DS: Decreased drug resistance of bladder cancer using
phytochemicals treatment. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 37:128–135.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Oršolić N, Odeh D, Jembrek MJ, Knežević J
and Kučan D: Interactions between cisplatin and quercetin at
physiological and hyperthermic conditions on cancer cells in vitro
and in vivo. Molecules. 25(3271)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Lee YH and Tuyet PT: Synthesis and
biological evaluation of quercetin-zinc (II) complex for
anti-cancer and anti-metastasis of human bladder cancer cells. In
Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 55:395–404. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Tao T, He C, Deng J, Huang Y, Su Q, Peng
M, Yi M, Darko KO, Zou H and Yang X: A novel synthetic derivative
of quercetin,
8-trifluoromethyl-3,5,7,3',4'-O-pentamethyl-quercetin, inhibits
bladder cancer growth by targeting the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway.
Oncotarget. 8:71657–71671. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Alban L, Monteiro WF, Diz FM, Miranda GM,
Scheid CM, Zotti ER, Morrone FB and Ligabue R: New quercetin-coated
titanate nanotubes and their radiosensitization effect on human
bladder cancer. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.
110(110662)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Shui L, Wang W, Xie M, Ye B, Li X, Liu Y
and Zheng M: Isoquercitrin induces apoptosis and autophagy in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells via AMPK/mTOR/p70S6K signaling
pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 12:24318–24332. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Chen F, Chen X, Yang D, Che X, Wang J, Li
X, Zhang Z, Wang Q, Zheng W, Wang L, et al: Isoquercitrin inhibits
bladder cancer progression in vivo and in vitro by regulating the
PI3K/Akt and PKC signaling pathways. Oncol Rep. 36:165–172.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Wu P, Liu S, Su J, Chen J, Li L, Zhang R
and Chen T: Apoptosis triggered by isoquercitrin in bladder cancer
cells by activating the AMPK-activated protein kinase pathway. Food
Funct. 8:3707–3722. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Ran J, Wang Y, Zhang W, Ma M and Zhang H:
Research on the bioactivity of isoquercetin extracted from
marestail on bladder cancer EJ cell and the mechanism of its
occurrence. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 44:859–864.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
105
|
Imran M, Salehi B, Sharifi-Rad J, Aslam
Gondal T, Saeed F, Imran A, Shahbaz M, Tsouh Fokou PV, Umair Arshad
M, Khan H, et al: Kaempferol: A key emphasis to its anticancer
potential. Molecules. 24(2277)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Qiu W, Lin J, Zhu Y, Zhang J, Zeng L, Su M
and Tian Y: Kaempferol modulates DNA methylation and downregulates
DNMT3B in bladder cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem. 41:1325–1335.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Wu P, Meng X, Zheng H, Zeng Q, Chen T,
Wang W, Zhang X and Su J: Kaempferol attenuates ROS-Induced
hemolysis and the molecular mechanism of its induction of apoptosis
on bladder cancer. Molecules. 23(2592)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Dang Q, Song W, Xu D, Ma Y, Li F, Zeng J,
Zhu G, Wang X, Chang LS, He D and Li L: Kaempferol suppresses
bladder cancer tumor growth by inhibiting cell proliferation and
inducing apoptosis. Mol Carcinog. 54:831–840. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Xie F, Su M, Qiu W, Zhang M, Guo Z, Su B,
Liu J, Li X and Zhou L: Kaempferol promotes apoptosis in human
bladder cancer cells by inducing the tumor suppressor, PTEN. Int J
Mol Sci. 14:21215–21226. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
DE Oliveira DT, Savio AL, Marcondes JP,
Barros TM, Barbosa LC, Salvadori DM and DA Silva GN: Cytotoxic and
toxicogenomic effects of silibinin in bladder cancer cells with
different TP53 status. J Biosci. 42:91–101. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Barros TMB, Lima APB, Almeida TC and da
Silva GN: Inhibition of urinary bladder cancer cell proliferation
by silibinin. Environ Mol Mutagen. 61:445–455. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Li F, Sun Y, Jia J, Yang C, Tang X, Jin B,
Wang K, Guo P, Ma Z, Chen Y, et al: Silibinin attenuates
TGF-β1-induced migration and invasion via EMT suppression and is
associated with COX-2 downregulation in bladder transitional cell
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 40:3543–3550. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Wu K, Ning Z, Zeng J, Fan J, Zhou J, Zhang
T, Zhang L, Chen Y, Gao Y, Wang B, et al: Silibinin inhibits
β-catenin/ZEB1 signaling and suppresses bladder cancer metastasis
via dual-blocking epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness.
Cell Signal. 25:2625–2633. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Imai-Sumida M, Chiyomaru T, Majid S, Saini
S, Nip H, Dahiya R, Tanaka Y and Yamamura S: Silibinin suppresses
bladder cancer through down-regulation of actin cytoskeleton and
PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Oncotarget. 8:92032–92042.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Sun Y, Guan Z, Zhao W, Jiang Y, Li Q,
Cheng Y and Xu Y: Silibinin suppresses bladder cancer cell
malignancy and chemoresistance in an NF-κB signal-dependent and
signal-independent manner. Int J Oncol. 51:1219–1226.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Prack Mc Cormick B, Langle Y, Belgorosky
D, Vanzulli S, Balarino N, Sandes E and Eiján AM: Flavonoid silybin
improves the response to radiotherapy in invasive bladder cancer. J
Cell Biochem. 119:5402–5412. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Gándara L, Sandes E, Di Venosa G, Prack Mc
Cormick B, Rodriguez L, Mamone L, Batlle A, Eiján AM and Casas A:
The natural flavonoid silybin improves the response to Photodynamic
Therapy of bladder cancer cells. J Photochem Photobiol B.
133:55–64. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Ramchandani S, Naz I, Lee JH, Khan MR and
Ahn KS: An Overview of the potential antineoplastic effects of
casticin. Molecules. 25(1287)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Xu H, Shi HL, Hao JW, Shu KP, Zhang YT and
Hou TQ: Casticin inhibits the proliferation, migration and invasion
of bladder cancer cells by inhibition of TM7SF4 expression.
Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 44:334–340. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
120
|
Huang AC, Cheng YD, Huang LH, Hsiao YT,
Peng SF, Lu KW, Lien JC, Yang JL, Lin TS and Chung JG: Casticin
induces DNA damage and impairs DNA repair in human bladder cancer
TSGH-8301 cells. Anticancer Res. 39:1839–1847. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Chung YH and Kim D: RIP kinase-mediated
ROS production triggers XAF1 expression through activation of TAp73
in casticin-treated bladder cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 36:1135–1142.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Gao X, Xu J, Jiang L, Liu W, Hong H, Qian
Y, Li S, Huang W, Zhao H, Yang Z, et al: Morin alleviates aflatoxin
B1-induced liver and kidney injury by inhibiting heterophil
extracellular traps release, oxidative stress and inflammatory
responses in chicks. Poult Sci. 100(101513)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Shin SS, Won SY, Noh DH, Hwang B, Kim WJ
and Moon SK: Morin inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion
of bladder cancer EJ cells via modulation of signaling pathways,
cell cycle regulators, and transcription factor-mediated MMP-9
expression. Drug Dev Res. 78:81–90. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Pan XW, Li L, Huang Y, Huang H, Xu DF, Gao
Y, Chen L, Ren JZ, Cao JW, Hong Y and Cui XG: Icaritin acts
synergistically with epirubicin to suppress bladder cancer growth
through inhibition of autophagy. Oncol Rep. 35:334–342.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Stevens Y, Rymenant EV, Grootaert C, Camp
JV, Possemiers S, Masclee A and Jonkers D: The intestinal fate of
citrus flavanones and their effects on gastrointestinal health.
Nutrients. 11(1464)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
126
|
Kim DI, Lee SJ, Lee SB, Park K, Kim WJ and
Moon SK: Requirement for Ras/Raf/ERK pathway in naringin-induced
G1-cell-cycle arrest via p21WAF1 expression. Carcinogenesis.
29:1701–1709. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
127
|
Liao AC, Kuo CC, Huang YC, Yeh CW, Hseu
YC, Liu JY and Hsu LS: Naringenin inhibits migration of bladder
cancer cells through downregulation of AKT and MMP-2. Mol Med Rep.
10:1531–1536. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
128
|
Juhem A, Boumendjel A, Touquet B, Guillot
A, Popov A, Ronot X and Martel-Frachet V: AG11, a novel
dichloroflavanone derivative with anti-mitotic activity towards
human bladder cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 33:4445–4452.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Khan N, Afaq F and Mukhtar H: Cancer
chemoprevention through dietary antioxidants: Progress and promise.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 10:475–510. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
130
|
Khan N and Mukhtar H: Tea polyphenols in
promotion of human health. Nutrients. 11(39)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
131
|
Bernatoniene J and Kopustinskiene DM: The
role of catechins in cellular responses to oxidative stress.
Molecules. 23(965)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Khan N, Afaq F, Saleem M, Ahmad N and
Mukhtar H: Targeting multiple signaling pathways by green tea
polyphenol (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate. Cancer Res.
66:2500–2505. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
133
|
Yasuda T, Miyata Y, Nakamura Y, Sagara Y,
Matsuo T, Ohba K and Sakai H: High Consumption of Green tea
suppresses urinary tract recurrence of urothelial cancer via
down-regulation of human antigen-R expression in never smokers. In
Vivo. 32:721–729. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
134
|
Matsuo T, Miyata Y, Asai A, Sagara Y,
Furusato B, Fukuoka J and Sakai H: Green tea polyphenol induces
changes in cancer-related factors in an animal model of bladder
cancer. PLoS One. 12(e0171091)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
135
|
Chen Z, Yu T, Zhou B, Wei J, Fang Y, Lu J,
Guo L, Chen W, Liu ZP and Luo J: Mg(II)-Catechin nanoparticles
delivering siRNA targeting EIF5A2 inhibit bladder cancer cell
growth in vitro and in vivo. Biomaterials. 81:125–134.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Jankun J, Keck RW and Selman SH:
Epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents tumor cell implantation/growth
in an experimental rat bladder tumor model. Int J Oncol.
44:147–152. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
137
|
Lee HY, Chen YJ, Chang WA, Li WM, Ke HL,
Wu WJ and Kuo PL: Effects of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) on
urinary bladder urothelial carcinoma-next-generation sequencing and
bioinformatics approaches. Medicina (Kaunas).
55(768)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
138
|
Luo KW, Wei Chen, Lung WY, Wei XY, Cheng
BH, Cai ZM and Huang WR: EGCG inhibited bladder cancer SW780 cell
proliferation and migration both in vitro and in vivo via
down-regulation of NF-κB and MMP-9. J Nutr Biochem. 41:56–64.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
139
|
Luo KW, Lung WY, Chun-Xie Luo XL and Huang
WR: EGCG inhibited bladder cancer T24 and 5637 cell proliferation
and migration via PI3K/AKT pathway. Oncotarget. 9:12261–12272.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Qin J, Wang Y, Bai Y, Yang K, Mao Q, Lin
Y, Kong D, Zheng X and Xie L: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits
bladder cancer cell invasion via suppression of NF-κB-mediated
matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression. Mol Med Rep. 6:1040–1044.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
141
|
Feng C, Ho Y, Sun C, Xia G, Ding Q and Gu
B: Epigallocatechin gallate inhibits the growth and promotes the
apoptosis of bladder cancer cells. Exp Ther Med. 14:3513–3518.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
142
|
Yin Z, Li J, Kang L, Liu X, Luo J, Zhang
L, Li Y and Cai J: Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces
autophagy-related apoptosis associated with LC3B II and Beclin
expression of bladder cancer cells. J Food Biochem.
45(e13758)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
143
|
Sun X, Song J, Li E, Geng H, Li Y, Yu D
and Zhong C: (-)-Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits bladder cancer
stem cells via suppression of sonic hedgehog pathway. Oncol Rep.
42:425–435. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
144
|
Luo KW, Zhu XH, Zhao T, Zhong J, Gao HC,
Luo XL and Huang WR: EGCG enhanced the anti-tumor effect of
doxorubicine in bladder cancer via NF-κB/MDM2/p53 pathway. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 8(606123)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
145
|
Mottaghipisheh J, Doustimotlagh AH, Irajie
C, Tanideh N, Barzegar A and Iraji A: The promising therapeutic and
preventive properties of anthocyanidins/anthocyanins on prostate
cancer. Cells. 11(1070)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
146
|
Alappat B and Alappat J: Anthocyanin
pigments: Beyond aesthetics. Molecules. 25(5500)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
147
|
Higgins JA, Zainol M, Brown K and Jones
GD: Anthocyans as tertiary chemopreventive agents in bladder
cancer: Anti-oxidant mechanisms and interaction with mitomycin C.
Mutagenesis. 29:227–235. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
148
|
Li WL, Ji GH, Zhang XZ and Yu HY: The
influence and mechanisms of purple sweet potato anthocyanins on the
growth of bladder cancer BIU87 cell. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi.
98:457–459. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar : (In Chinese).
|
|
149
|
Li WL, Yu HY, Zhang XJ, Ke M and Hong T:
Purple sweet potato anthocyanin exerts antitumor effect in bladder
cancer. Oncol Rep. 40:73–82. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
150
|
Yang N, Gao J, Hou R, Xu X, Yang N and
Huang S: Grape seed proanthocyanidins inhibit migration and
invasion of bladder cancer cells by reversing EMT through
suppression of TGF-β signaling pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2021(5564312)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
151
|
Fishman AI, Johnson B, Alexander B, Won J,
Choudhury M and Konno S: Additively enhanced antiproliferative
effect of interferon combined with proanthocyanidin on bladder
cancer cells. J Cancer. 3:107–112. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Liu J, Zhang WY, Kong ZH and Ding DG:
Induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by grape seed
procyanidin extract in human bladder cancer BIU87 cells. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 20:3282–3291. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Křížová L, Dadáková K, Kašparovská J and
Kašparovský T: Isoflavones. Molecules. 24(1076)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
154
|
He Y, Wu X, Cao Y, Hou Y, Chen H, Wu L, Lu
L, Zhu W and Gu Y: Daidzein exerts anti-tumor activity against
bladder cancer cells via inhibition of FGFR3 pathway. Neoplasma.
63:523–531. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
155
|
Russo M, Russo GL, Daglia M, Kasi PD, Ravi
S, Nabavi SF and Nabavi SM: Understanding genistein in cancer: The
‘good’ and the ‘bad’ effects: A review. Food Chem. 196:589–600.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
156
|
Park C, Cha HJ, Lee H, Hwang-Bo H, Ji SY,
Kim MY, Hong SH, Jeong JW, Han MH, Choi SH, et al: Induction of
G2/M cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by genistein in human bladder
cancer T24 cells through Inhibition of the ROS-Dependent PI3k/Akt
signal transduction pathway. Antioxidants (Basel).
8(327)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
157
|
Wang Y, Wang H, Zhang W, Shao C, Xu P, Shi
CH, Shi JG, Li YM, Fu Q, Xue W, et al: Genistein sensitizes bladder
cancer cells to HCPT treatment in vitro and in vivo via
ATM/NF-κB/IKK pathway-induced apoptosis. PLoS One.
8(e50175)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
158
|
Köksal Karayildirim Ç, Nalbantsoy A and
Karabay Yavaşoğlu NU: Prunetin inhibits nitric oxide activity and
induces apoptosis in urinary bladder cancer cells via CASP3 and
TNF-α genes. Mol Biol Rep. 48:7251–7259. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Zhou YX, Zhang H and Peng C: Puerarin: A
review of pharmacological effects. Phytother Res. 28:961–975.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
160
|
Jiang K, Chen H, Tang K, Guan W, Zhou H,
Guo X, Chen Z, Ye Z and Xu H: Puerarin inhibits bladder cancer cell
proliferation through the mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway. Oncol
Lett. 15:167–174. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
161
|
Ye G, Kan S, Chen J and Lu X: Puerarin in
inducing apoptosis of bladder cancer cells through inhibiting
SIRT1/p53 pathway. Oncol Lett. 17:195–200. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
162
|
Jiang QQ, Liu B and Yuan T: MicroRNA-16
inhibits bladder cancer proliferation by targeting Cyclin D1. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:4127–4130. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
163
|
Liu X, Li S, Li Y, Cheng B, Tan B and Wang
G: Puerarin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis by
upregulation of miR-16 in bladder cancer cell line T24. Oncol Res.
26:1227–1234. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
164
|
Du L, Zhang L and Sun F: Puerarin inhibits
the progression of bladder cancer by regulating
circ_0020394/miR-328-3p/NRBP1 axis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm.
37:435–450. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
165
|
Wu Y, Zhang X, Li Z, Yan H, Qin J and Li
T: Formononetin inhibits human bladder cancer cell proliferation
and invasiveness via regulation of miR-21 and PTEN. Food Funct.
8:1061–1066. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
166
|
Ouyang Y, Li J, Chen X, Fu X, Sun S and Wu
Q: Chalcone derivatives: Role in anticancer therapy. Biomolecules.
11(894)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
167
|
Yuan X, Li D, Zhao H, Jiang J, Wang P, Ma
X, Sun X and Zheng Q: Licochalcone A-induced human bladder cancer
T24 cells apoptosis triggered by mitochondria dysfunction and
endoplasmic reticulum stress. Biomed Res Int.
2013(474272)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
168
|
Yang X, Jiang J, Yang X, Han J and Zheng
Q: Licochalcone A induces T24 bladder cancer cell apoptosis by
increasing intracellular calcium levels. Mol Med Rep. 14:911–919.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
169
|
Jiang J, Yuan X, Zhao H, Yan X, Sun X and
Zheng Q: Licochalcone A inhibiting proliferation of bladder cancer
T24 cells by inducing reactive oxygen species production. Biomed
Mater Eng. 24:1019–1025. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
170
|
Hong SH, Cha HJ, Hwang-Bo H, Kim MY, Kim
SY, Ji SY, Cheong J, Park C, Lee H, Kim GY, et al:
Anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effects of licochalcone A
through ROS-Mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human
bladder cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 20(3820)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Zhao H, Yuan X, Jiang J, Wang P, Sun X,
Wang D and Zheng Q: Antimetastatic effects of licochalcone B on
human bladder carcinoma T24 by inhibition of matrix
metalloproteinases-9 and NF-кB activity. Basic Clin Pharmacol
Toxicol. 115:527–533. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Yuan X, Li T, Xiao E, Zhao H, Li Y, Fu S,
Gan L and Wang Z, Zheng Q and Wang Z: Licochalcone B inhibits
growth of bladder cancer cells by arresting cell cycle progression
and inducing apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol. 65:242–251.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
173
|
Wang P, Yuan X, Wang Y, Zhao H, Sun X and
Zheng Q: Licochalcone C induces apoptosis via B-cell lymphoma 2
family proteins in T24 cells. Mol Med Rep. 12:7623–7628.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
174
|
Wang KL, Yu TC and Hsia SM: Perspectives
on the role of isoliquiritigenin in cancer. Cancers (Basel).
13(115)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
175
|
Patricia Moreno-Londoño A, Bello-Alvarez C
and Pedraza-Chaverri J: Isoliquiritigenin pretreatment attenuates
cisplatin induced proximal tubular cells (LLC-PK1) death and
enhances the toxicity induced by this drug in bladder cancer T24
cell line. Food Chem Toxicol. 109(Pt 1):143–154. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Li X, Xu X, Ji T, Liu Z, Gu M, Hoang BH
and Zi X: Dietary feeding of Flavokawain A, a Kava chalcone,
exhibits a satisfactory safety profile and its association with
enhancement of phase II enzymes in mice. Toxicol Rep. 1:2–11.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
177
|
Liu Z, Xu X, Li X, Liu S, Simoneau AR, He
F, Wu XR and Zi X: Kava chalcone, flavokawain A, inhibits
urothelial tumorigenesis in the UPII-SV40T transgenic mouse model.
Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 6:1365–1375. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
178
|
Liu Z, Song L, Xie J, Simoneau AR, Uchio E
and Zi X: Chemoprevention of urothelial cell carcinoma
tumorigenesis by dietary flavokawain A in UPII-Mutant Ha-ras
transgenic mice. Pharmaceutics. 14(496)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
179
|
Wu CM, Lin KW, Teng CH, Huang AM, Chen YC,
Yen MH, Wu WB, Pu YS and Lin CN: Chalcone derivatives inhibit human
platelet aggregation and inhibit growth in human bladder cancer
cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 37:1191–1198. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
180
|
Martel-Frachet V, Keramidas M, Nurisso A,
DeBonis S, Rome C, Coll JL, Boumendjel A, Skoufias DA and Ronot X:
IPP51, a chalcone acting as a microtubule inhibitor with in vivo
antitumor activity against bladder carcinoma. Oncotarget.
6:14669–14686. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
181
|
Martel-Frachet V, Areguian J, Blanc M,
Touquet B, Lamarca A, Ronot X and Boumendjel A: Investigation of a
new 1,3-diarylpropenone as a potential antimitotic agent targeting
bladder carcinoma. Anticancer Drugs. 20:469–476. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
182
|
Desilets A, Adam JP and Soulières D:
Management of cisplatin-associated toxicities in bladder cancer
patients. Curr Opin Support Palliat Care. 14:286–292.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
183
|
Cai Z, Zhang F, Chen W, Zhang J and Li H:
MiRNAs: A promising target in the chemoresistance of bladder
cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 12:11805–11816. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
184
|
Dobrzynska M, Napierala M and Florek E:
Flavonoid nanoparticles: A promising approach for cancer therapy.
Biomolecules. 10(1268)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
185
|
Sun T, Zhang YS, Pang B, Hyun DC, Yang M
and Xia Y: Engineered nanoparticles for drug delivery in cancer
therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 53:12320–12364. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
186
|
Kim S, Chen J, Cheng T, Gindulyte A, He J,
He S, Li Q, Shoemaker BA, Thiessen PA, Yu B, et al: PubChem in
2021: New data content and improved web interfaces. Nucleic Acids
Res. 49(D1):D1388–D1395. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
187
|
Patil M, Pabla N and Dong Z: Checkpoint
kinase 1 in DNA damage response and cell cycle regulation. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 70:4009–4021. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
188
|
Schmitt E, Paquet C, Beauchemin M and
Bertrand R: DNA-damage response network at the crossroads of
cell-cycle checkpoints, cellular senescence and apoptosis. J
Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 8:377–397. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
189
|
Yang L, Shi P, Zhao G, Xu J, Peng W, Zhang
J, Zhang G, Wang X, Dong Z, Chen F and Cui H: Targeting cancer stem
cell pathways for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
5(8)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|