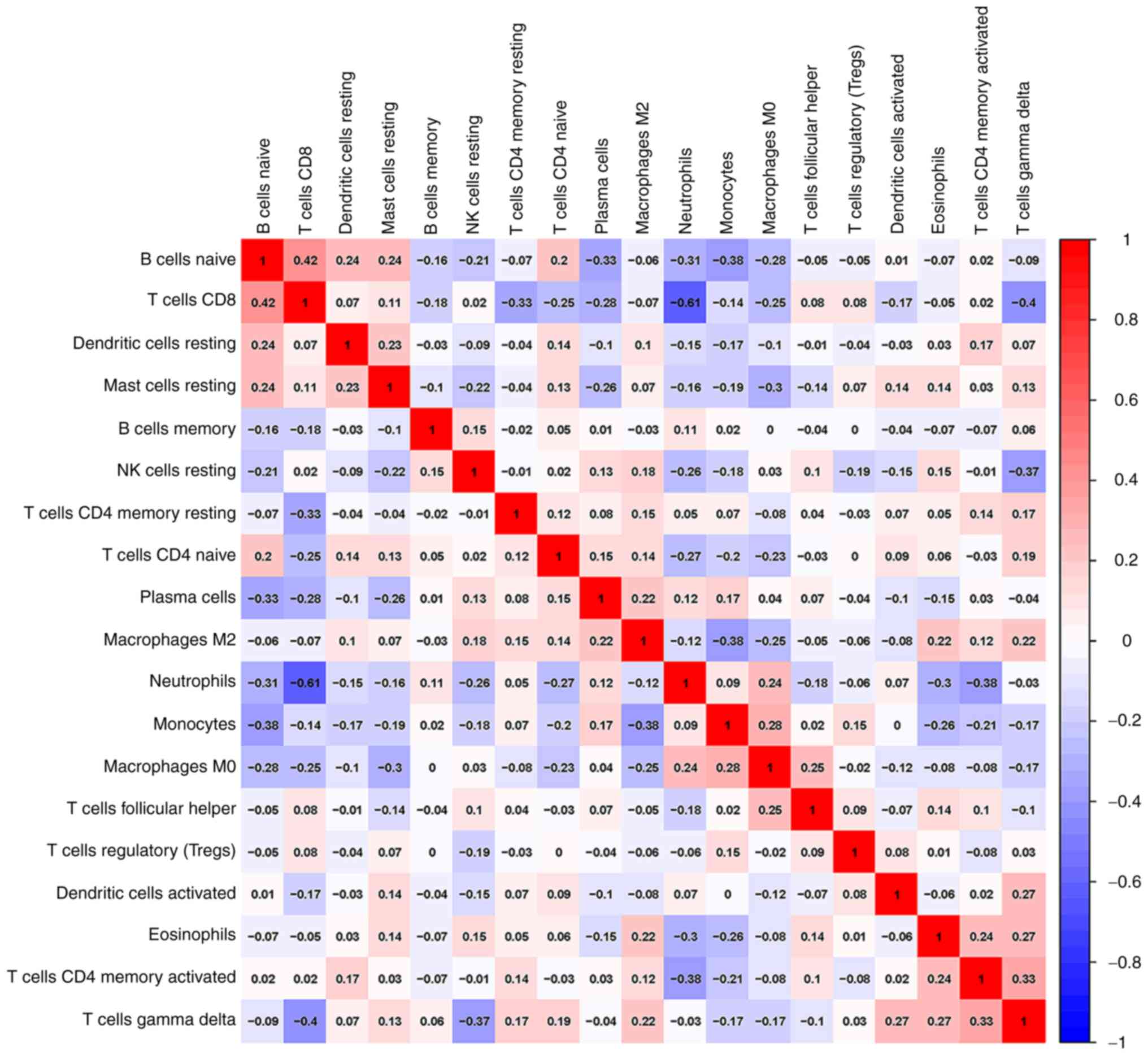
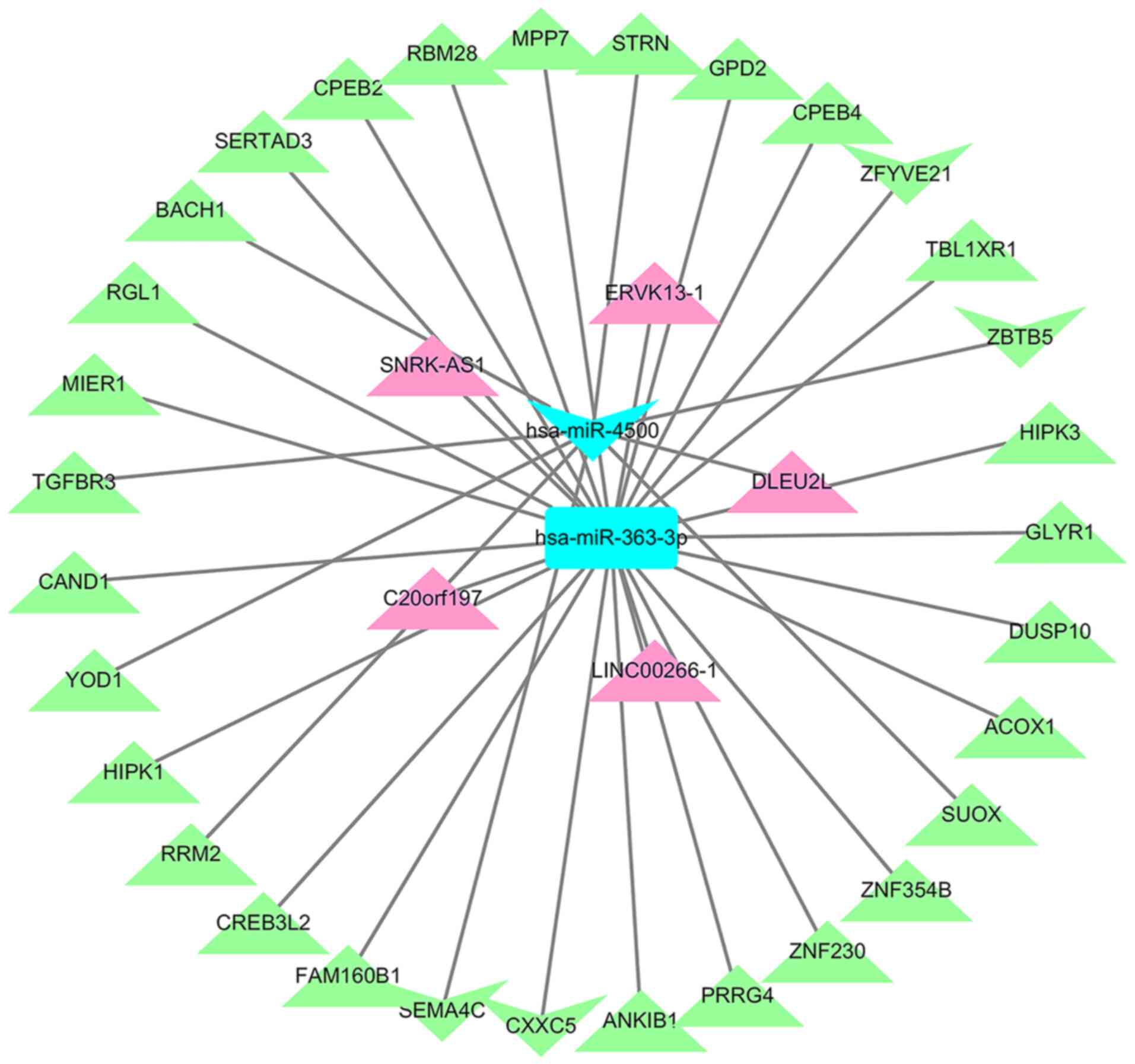
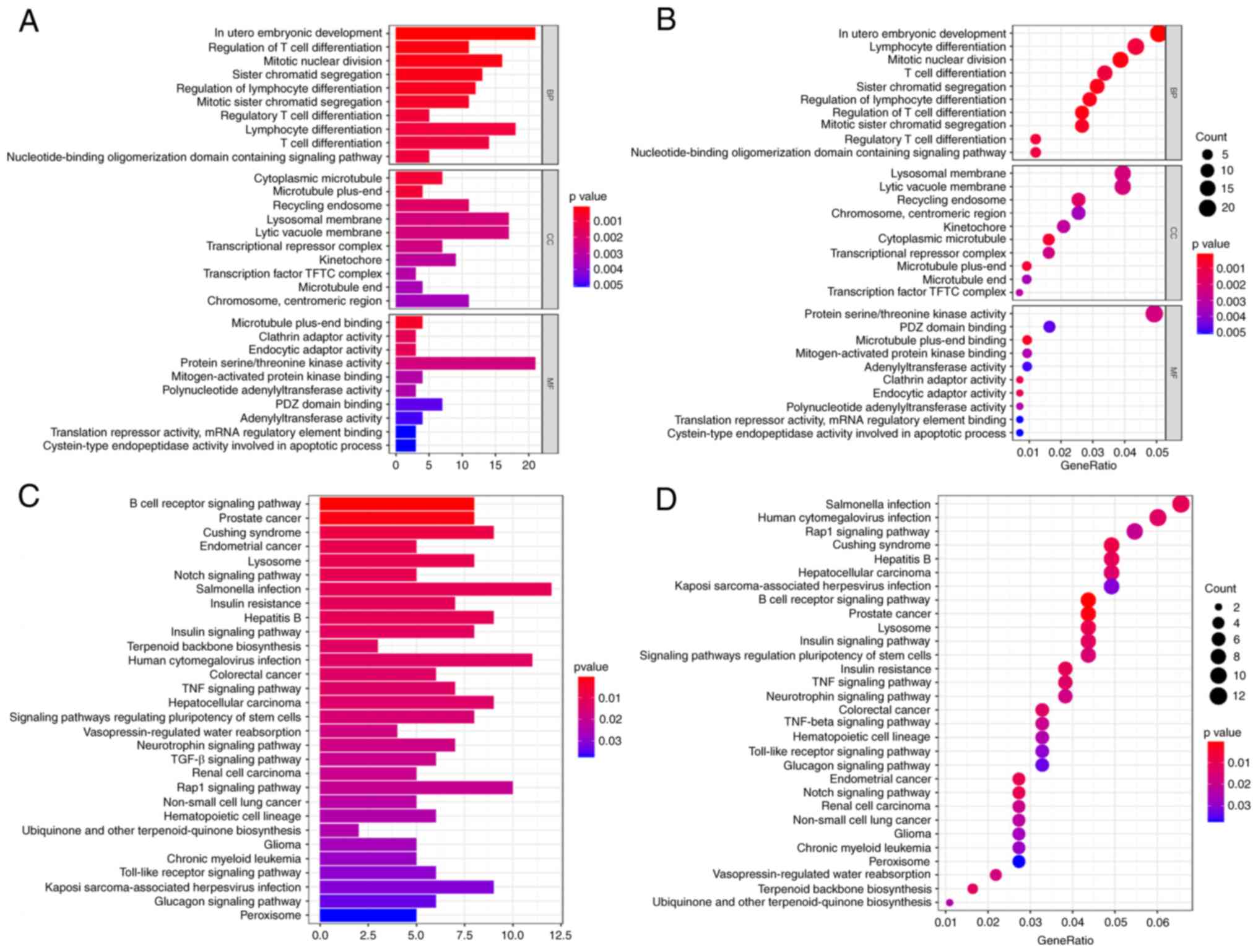
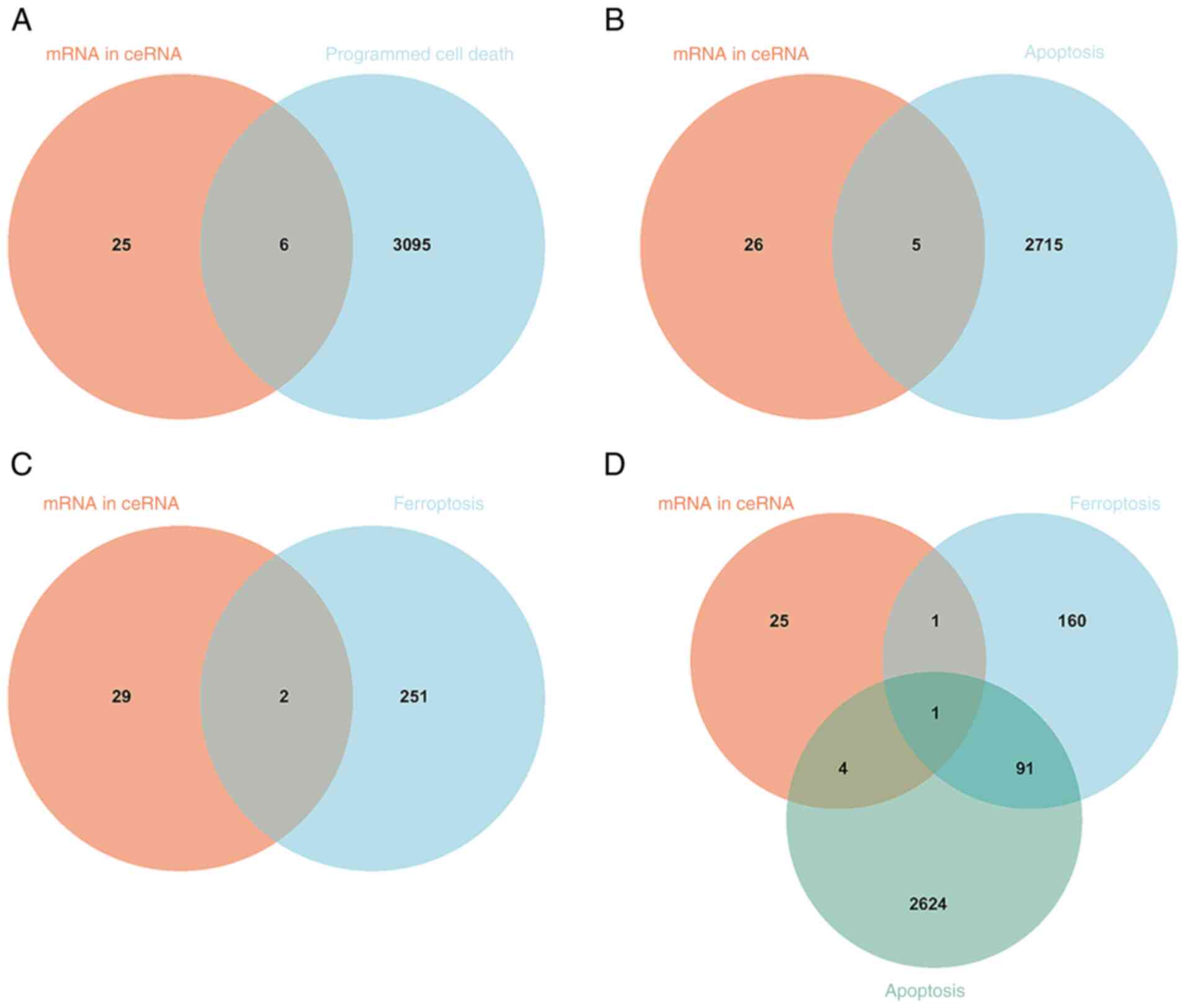
|
1
|
Feske SK: Ischemic stroke. Am J Med.
134:1457–1464. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Blakeley JO and Llinas RH: Thrombolytic
therapy for acute ischemic stroke. J Neurol Sci. 261:55–62.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Kyzar EJ, Bohnsack JP and Pandey SC:
Current and future perspectives of noncoding RNAs in brain function
and neuropsychiatric disease. Biol Psychiatry. 91:183–193.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kimura T, Horikoshi Y, Kuriyagawa C and
Niiyama Y: Rho/ROCK pathway and noncoding RNAs: Implications in
ischemic stroke and spinal cord injury. Int J Mol Sci.
22(11573)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gugliandolo A, Silvestro S, Sindona C,
Bramanti P and Mazzon E: MiRNA: Involvement of the MAPK pathway in
ischemic stroke. A promising therapeutic target. Medicina (Kaunas).
57(1053)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bulygin KV, Beeraka NM, Saitgareeva AR,
Nikolenko VN, Gareev I, Beylerli O, Akhmadeeva LR, Mikhaleva LM,
Torres Solis LF, Solís Herrera A, et al: Can miRNAs be considered
as diagnostic and therapeutic molecules in ischemic stroke
pathogenesis?-Current status. Int J Mol Sci.
21(6728)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Chi NF, Chiou HY, Chou SY, Hu CJ, Chen KY,
Chang CF and Hsieh YC: Hyperglycemia-related FAS gene and
hsa-let-7b-5p as markers of poor outcomes for ischaemic stroke. Eur
J Neurol. 27:1647–1655. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhang X, Tang X, Liu K, Hamblin MH and Yin
KJ: Long noncoding RNA Malat1 regulates cerebrovascular pathologies
in ischemic stroke. J Neurosci. 37:1797–1806. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Yan H, Yuan J, Gao L, Rao J and Hu J: Long
noncoding RNA MEG3 activation of p53 mediates ischemic neuronal
death in stroke. Neuroscience. 337:191–199. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang J, Zhao H, Fan Z, Li G, Ma Q, Tao Z,
Wang R, Feng J and Luo Y: Long noncoding RNA H19 promotes
neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke by driving histone deacetylase
1-dependent M1 microglial polarization. Stroke. 48:2211–2221.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tay Y, Rinn J and Pandolfi PP: The
multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature.
505:344–352. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sen R, Ghosal S, Das S, Balti S and
Chakrabarti J: Competing endogenous RNA: The key to
posttranscriptional regulation. ScientificWorldJournal.
2014(896206)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Duris K, Splichal Z and Jurajda M: The
role of inflammatory response in stroke associated programmed cell
death. Curr Neuropharmacol. 16:1365–1374. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Sun Y, Wang J, Han B, Meng K, Han Y and
Ding Y: Elucidating the molecular mechanism of ischemic stroke
using integrated analysis of miRNA, mRNA, and lncRNA expression
profiles. Front Integr Neurosci. 15(638114)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Liu F, Cheng X, Zhong S, Liu C, Jolkkonen
J, Zhang X, Liang Y, Liu Z and Zhao C: Communications between
peripheral and the brain-resident immune system in neuronal
regeneration after stroke. Front Immunol. 11(1931)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zheng Y, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Dang Y, Cheng
Y, Hua W, Teng M, Wang S and Lu X: Novel lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA
competing endogenous RNA triple networks associated programmed cell
death in heart failure. Front Cardiovasc Med.
8(747449)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang L, Liu B, Han J, Wang T and Han L:
Competing endogenous RNA network analysis for screening
inflammation-related long non-coding RNAs for acute ischemic
stroke. Mol Med Rep. 22:3081–3094. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Stamova B, Jickling GC, Ander BP, Zhan X,
Liu D, Turner R, Ho C, Khoury JC, Bushnell C, Pancioli A, et al:
Gene expression in peripheral immune cells following cardioembolic
stroke is sexually dimorphic. PLoS One. 9(e102550)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jickling GC, Ander BP, Zhan X, Noblett D,
Stamova B and Liu D: microRNA expression in peripheral blood cells
following acute ischemic stroke and their predicted gene targets.
PLoS One. 9(e99283)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43(e47)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
R Core Team: R: A language and environment
for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing,
Vienna, Austria. ISBN 3-900051-07-0, 2012.
|
|
22
|
Zou JB, Chai HB, Zhang XF, Guo DY, Tai J,
Wang Y, Liang YL, Wang F, Cheng JX, Wang J and Shi YJ:
Reconstruction of the lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA network based on
competitive endogenous RNA reveal functional lncRNAs in Cerebral
Infarction. Sci Rep. 9(12176)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Vejnar CE and Zdobnov EM: MiRmap:
Comprehensive prediction of microRNA target repression strength.
Nucleic Acids Res. 40:11673–11683. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Betel D, Wilson M, Gabow A, Marks DS and
Sander C: The microRNA.org resource. Targets and
expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 36 (Database Issue):D149–D153.
2008.
|
|
25
|
Wong N and Wang X: miRDB: An online
resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43 (Database Issue):D146–D152. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Agarwal V, Bell GW, Nam JW and Bartel DP:
Predicting effective microRNA target sites in mammalian mRNAs.
Elife. 4(e05005)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chou CH, Shrestha S, Yang CD, Chang NW,
Lin YL, Liao KW, Huang WC, Sun TH, Tu SJ, Lee WH, et al: miRTarBase
update 2018: A resource for experimentally validated
microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 46 (D1):D296–D302.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Li JH, Liu S, Zhou H, Qu LH and Yang JH:
starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA
interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids
Res. 42 (Database Issue):D92–D97. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Uematsu M, Takasawa M, Hosoi R and Inoue
O: Uncoupling of flow and metabolism by chloral hydrate: A rat
in-vivo autoradiographic study. Neuroreport. 20:219–222.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wang K, Liu CY, Zhou LY, Wang JX, Wang M,
Zhao B, Zhao WK, Xu SJ, Fan LH, Zhang XJ, et al: APF lncRNA
regulates autophagy and myocardial infarction by targeting
miR-188-3p. Nat Commun. 6(6779)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Huang Y: The novel regulatory role of
lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA axis in cardiovascular diseases. J Cell Mol Med.
22:5768–5775. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Schmitz SU, Grote P and Herrmann BG:
Mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function in development and
disease. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:2491–2509. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chen F, Zhang L, Wang E, Zhang C and Li X:
LncRNA GAS5 regulates ischemic stroke as a competing endogenous RNA
for miR-137 to regulate the Notch1 signaling pathway. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 496:184–190. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Lv L, Xi HP, Huang JC and Zhou XY: LncRNA
SNHG1 alleviated apoptosis and inflammation during ischemic stroke
by targeting miR-376a and modulating CBS/H2S pathway.
Int J Neurosci. 131:1162–1172. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Xu F, Wu H, Xiong J and Peng T: Long
non-coding RNA DLEU2L targets miR-210-3p to suppress gemcitabine
resistance in pancreatic cancer cells via BRCA2 regulation. Front
Mol Biosci. 8(645365)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zheng S, Wan L, Ge D, Jiang F, Qian Z,
Tang J, Yang J, Yao Y, Yan J, Zhao L, et al:
LINC00266-1/miR-548c-3p/SMAD2 feedback loop stimulates the
development of osteosarcoma. Cell Death Dis. 11(576)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Datta A, Sarmah D, Mounica L, Kaur H,
Kesharwani R, Verma G, Veeresh P, Kotian V, Kalia K, Borah A, et
al: Cell death pathways in ischemic stroke and targeted
pharmacotherapy. Transl Stroke Res. 11:1185–1202. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Bedoui S, Herold MJ and Strasser A:
Emerging connectivity of programmed cell death pathways and its
physiological implications. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 21:678–695.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Yu S, Zhai J, Yu J, Yang Q and Yang J:
Downregulation of BACH1 Protects AGAINST cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury through the functions of HO-1 and NQO1.
Neuroscience. 436:154–166. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Wang Y, Zhao R, Liu W, Wang Z, Rong J,
Long X, Liu Z, Ge J and Shi B: Exosomal circHIPK3 released from
hypoxia-pretreated cardiomyocytes regulates oxidative damage in
cardiac microvascular endothelial cells via the miR-29a/IGF-1
pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019(7954657)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Wu X, Li Y, Zhang S and Zhou X:
Ferroptosis as a novel therapeutic target for cardiovascular
disease. Theranostics. 11:3052–3059. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Ren JX, Li C, Yan XL, Qu Y, Yang Y and Guo
ZN: Crosstalk between oxidative stress and ferroptosis/oxytosis in
ischemic stroke: Possible targets and molecular mechanisms. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2021(6643382)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Liu Y, Fang Y, Zhang Z, Luo Y, Zhang A,
Lenahan C and Chen S: Ferroptosis: An emerging therapeutic target
in stroke. J Neurochem. 160:64–73. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Weiland A, Wang Y, Wu W, Lan X, Han X, Li
Q and Wang J: Ferroptosis and its role in diverse brain diseases.
Mol Neurobiol. 56:4880–4893. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Yang Y, Lin J, Guo S, Xue X, Wang Y, Qiu
S, Cui J, Ma L, Zhang X and Wang J: RRM2 protects against
ferroptosis and is a tumor biomarker for liver cancer. Cancer Cell
Int. 20(587)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Nishizawa H, Matsumoto M, Shindo T,
Saigusa D, Kato H, Suzuki K, Sato M, Ishii Y, Shimokawa H and
Igarashi K: Ferroptosis is controlled by the coordinated
transcriptional regulation of glutathione and labile iron
metabolism by the transcription factor BACH1. J Biol Chem.
295:69–82. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Igarashi K, Nishizawa H, Saiki Y and
Matsumoto M: The transcription factor BACH1 at the crossroads of
cancer biology: From epithelial-mesenchymal transition to
ferroptosis. J Biol Chem. 297(101032)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Yu Z, He H, Chen Y, Ji Q and Sun M: A
novel ferroptosis related gene signature is associated with
prognosis in patients with ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma. Sci
Rep. 11(11486)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|