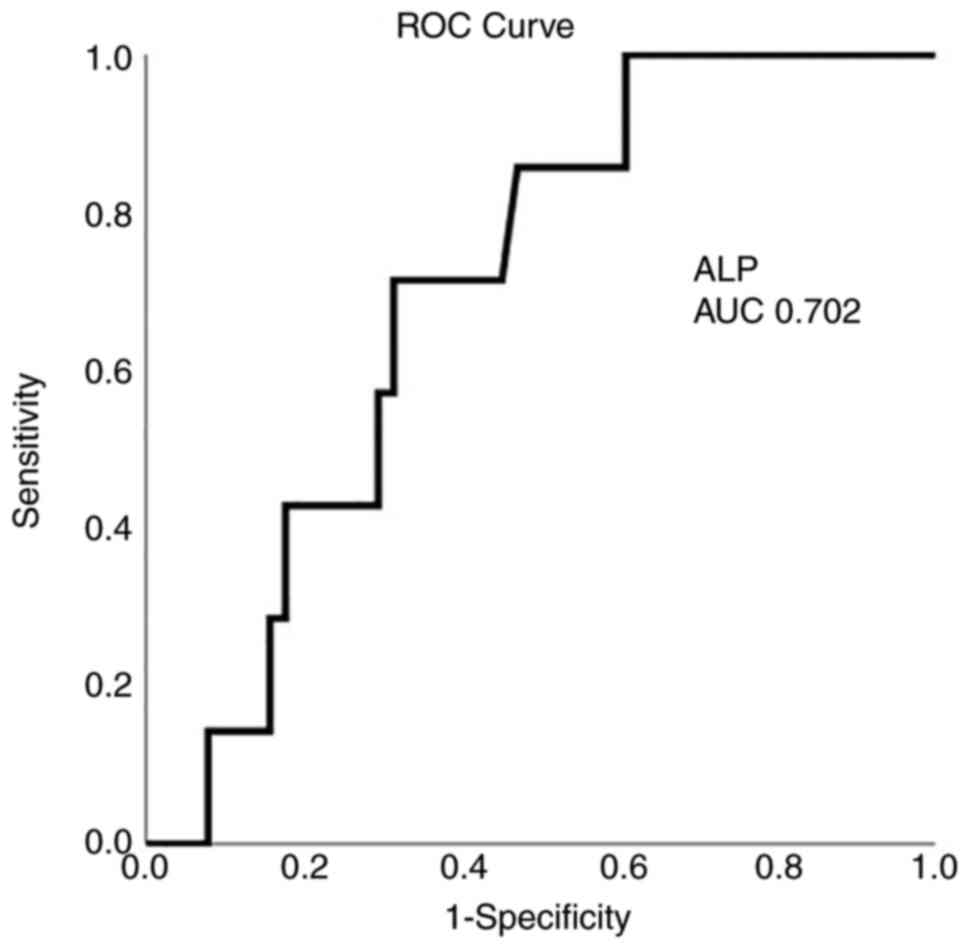
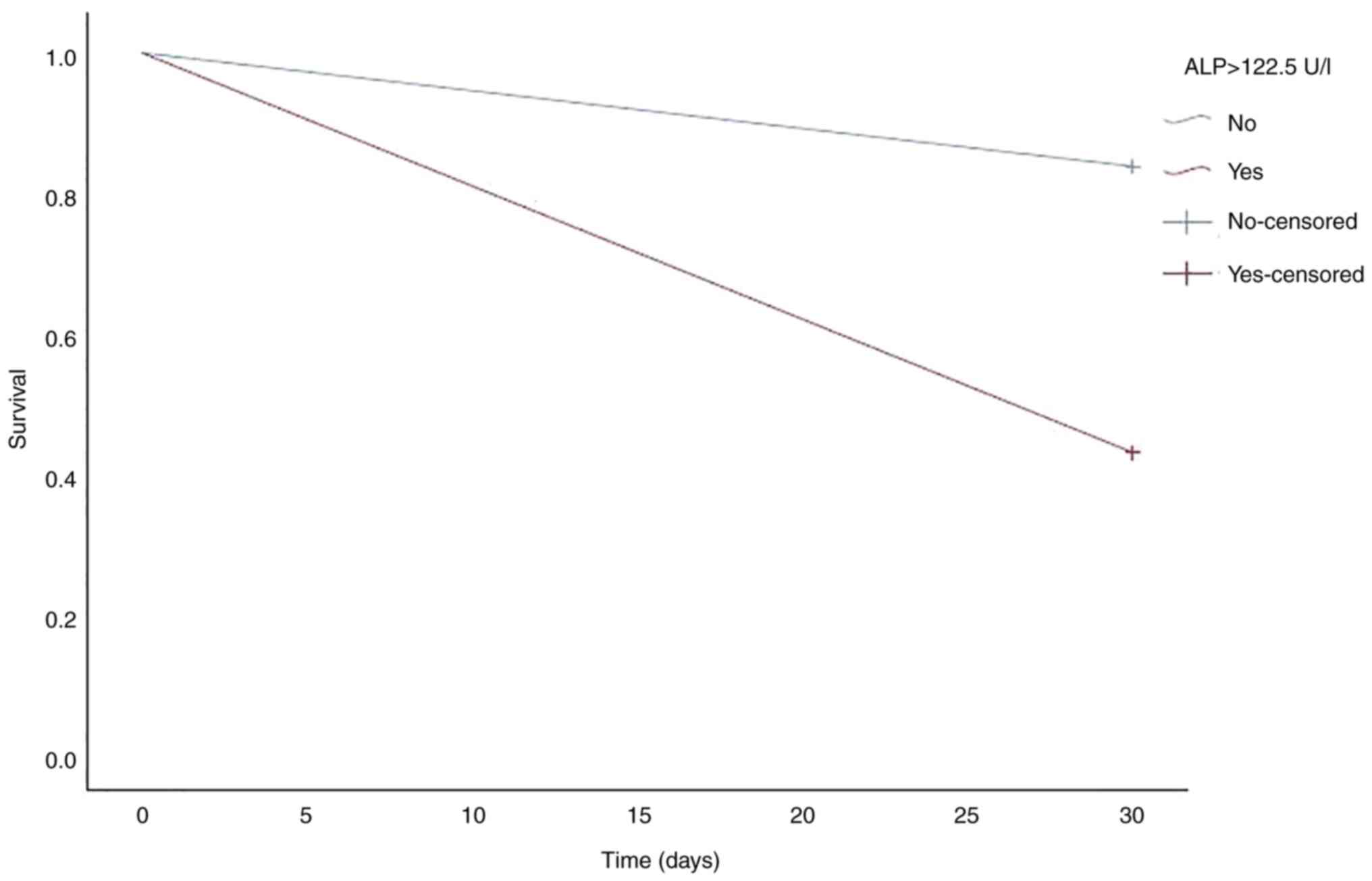
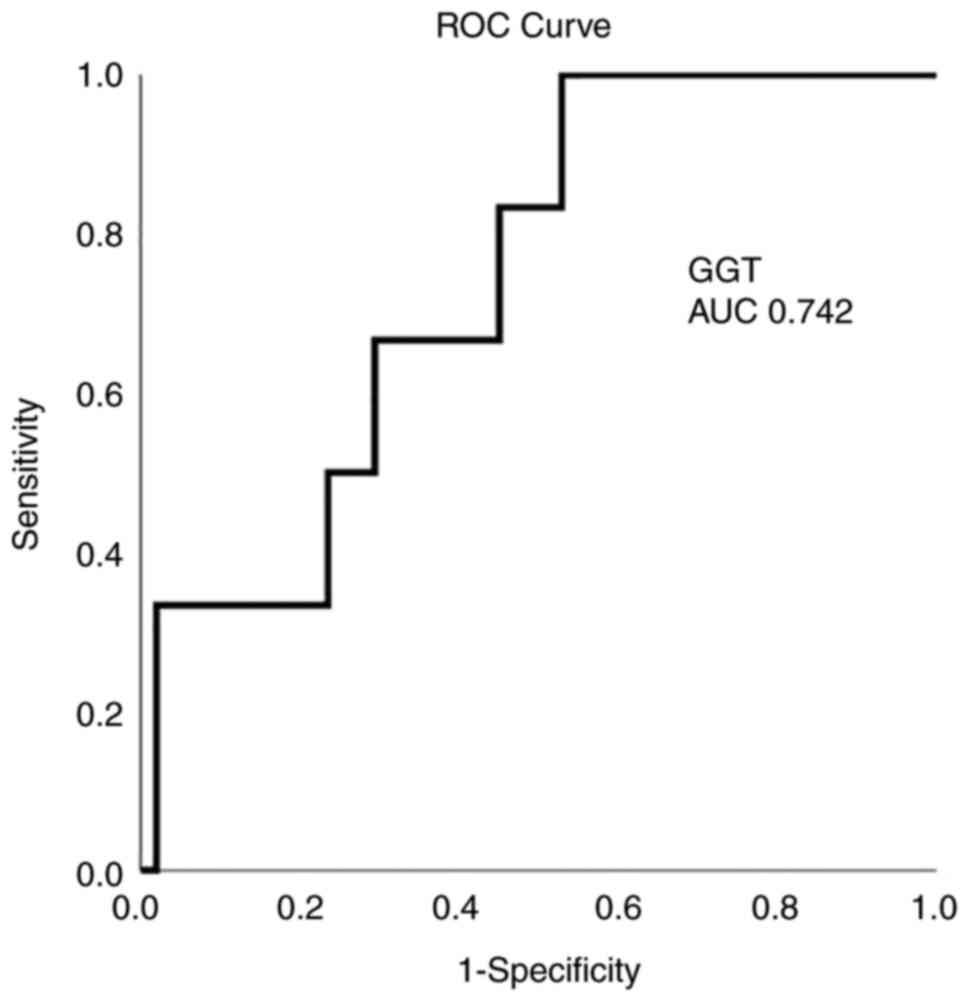
|
1
|
Axiotakis LG Jr, Youngerman BE, Casals RK,
Cooke TS, Winston GM, Chang CL, Boyett DM, Lalwani AK and McKhann
GM: Risk of acquiring perioperative COVID-19 during the initial
pandemic peak: A retrospective cohort study. Ann Surg. 273:41–48.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
COVIDSurg Collaborative: Elective surgery
cancellations due to the COVID-19 pandemic: Global predictive
modelling to inform surgical recovery plans. Br J Surg.
107:1440–1449. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Al-Jabir A, Kerwan A, Nicola M, Alsafi Z,
Khan M, Sohrabi C, O'Neill N, Iosifidis C, Griffin M, Mathew G and
Agha R: Impact of the Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic on surgical
practice-Part 1. Int J Surg. 79:168–179. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Knisely A, Zhou ZN, Wu J, Huang Y, Holcomb
K, Melamed A, Advincula AP, Lalwani A, Khoury-Collado F, Tergas AI,
et al: Perioperative morbidity and mortality of patients with
COVID-19 who undergo urgent and emergent surgical procedures. Ann
Surg. 273:34–40. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Heffernan DS, Evans HL, Huston JM,
Claridge JA, Blake DP, May AK, Beilman GS, Barie PS and Kaplan LJ:
Surgical infection society guidance for operative and
peri-operative care of adult patients infected by the severe acute
respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2). Surg Infect
(Larchmt). 21:301–308. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
COVIDSurg Collaborative: Mortality and
pulmonary complications in patients undergoing surgery with
perioperative SARS-CoV-2 infection: An international cohort study.
Lancet. 396:27–38. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jonker PKC, van der Plas WY, Steinkamp PJ,
Poelstra R, Emous M, van der Meij W, Thunnissen F, Bierman WFW,
Struys MMRF, de Reuver PR, et al: Perioperative SARS-CoV-2
infections increase mortality, pulmonary complications, and
thromboembolic events: A Dutch, multicenter, matched-cohort
clinical study. Surgery. 169:264–274. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Doglietto F, Vezzoli M, Gheza F, Lussardi
GL, Domenicucci M, Vecchiarelli L, Zanin L, Saraceno G, Signorini
L, Panciani PP, et al: Factors associated with surgical mortality
and complications among patients with and without coronavirus
disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Italy. JAMA Surg. 155:691–702.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lei S, Jiang F, Su W, Chen C, Chen J, Mei
W, Zhan LY, Jia Y, Zhang L, Liu D, et al: Clinical characteristics
and outcomes of patients undergoing surgeries during the incubation
period of COVID-19 infection. EclinicalMedicine.
21(100331)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel:
Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Treatment Guidelines. National
Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, 2021. https://www.covid19treatmentguidelines.nih.gov/.
Accessed October 10, 2021.
|
|
11
|
Kader N, Clement ND, Patel VR, Caplan N,
Banaszkiewicz P and Kader D: The theoretical mortality risk of an
asymptomatic patient with a negative SARS-CoV-2 test developing
COVID-19 following elective orthopaedic surgery. Bone Joint J.
102-B:1256–1260. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Clement ND, Hall AJ, Makaram NS, Robinson
PG, Patton RFL, Moran M, Macpherson GJ, Duckworth AD and Jenkins
PJ: IMPACT-Restart: The influence of COVID-19 on postoperative
mortality and risk factors associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection
after orthopaedic and trauma surgery. Bone Joint J.
102-B:1774–1781. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Clement ND, Hall AJ and Kader N: IMPACT
Restart Collaboration. Ollivere B, Oussedik S, Kader DF, Deehan DJ
and Duckworth AD: The rate of COVID-19 and associated mortality
after elective hip and knee arthroplasty prior to cessation of
elective services in UK. Bone Joint J. 103-B:681–688.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Al Masri E, Redwan B, Thiel B, Ellger B,
Begher C, Biancosino C and Kösek V: Clinical outcome in patients
with nosocomial COVID-19 infection after thoracic surgery. Adv Exp
Med Biol. 1374:33–40. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Uysal A, Erturk E, Abacilar AF, Duman U
and Dogan OF: The outcomes of patients incidentally confirmed with
Covid-19 after cardiac surgery. Heart Surg Forum. 24:E940–E946.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tabourin T, Sarfati J, Pinar U, Beaud N,
Parra J, Vaessen C, Gomez F, Benamran D, Canlorbe G, Belghiti J, et
al: Postoperative assessment of nosocomial transmission of COVID-19
after robotic surgical procedures during the pandemic. Urol Oncol.
39:298.e7–e11. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bacalbasa N and Balescu I: The Impact of
COVID-19 infection during the postoperative period after surgery
for ovarian cancer. In Vivo. 36:1337–1341. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Prasad NK, Lake R, Englum BR, Turner DJ,
Siddiqui T, Mayorga-Carlin M, Sorkin JD and Lal BK: Increased
complications in patients who test COVID-19 positive after elective
surgery and implications for pre and postoperative screening. Am J
Surg. 223:380–387. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Canet J, Gallart L, Gomar C, Paluzie G,
Vallès J, Castillo J, Sabaté S, Mazo V, Briones Z and Sanchis J:
ARISCAT Group. Prediction of postoperative pulmonary complications
in a population-based surgical cohort. Anesthesiology.
113:1338–1350. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Georgakopoulou VE, Gkoufa A, Garmpis N,
Makrodimitri S, Papageorgiou CV, Barlampa D, Garmpi A, Chiapoutakis
S, Sklapani P, Trakas N and Damaskos C: COVID-19 and acute
pancreatitis: A systematic review of case reports and case series.
Ann Saudi Med. 42:276–287. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Georgakopoulou VE, Gkoufa A, Damaskos C,
Papalexis P, Pierrakou A, Makrodimitri S, Sypsa G, Apostolou A,
Asimakopoulou S, Chlapoutakis S, et al: COVID-19-associated acute
appendicitis in adults. A report of five cases and a review of the
literature. Exp Ther Med. 24(482)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Siafarikas C, Stafylidis C, Tentolouris A,
Samara S, Eliadi I, Makrodimitri S, Spandidos DA, Mathioudakis N,
Karamichalos P, Papalexis P, et al: Radiologically suspected
COVID-19-associated organizing pneumonia responding well to
corticosteroids: A report of two cases and a review of the
literature. Exp Ther Med. 24(453)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Georgakopoulou VE, Avramopoulos P,
Papalexis P, Bitsani A, Damaskos C, Garmpi A, Venetikou MS,
Paramythiotis D, Karlafti E, Sklapani P, et al: COVID-19 induced
hypoparathyroidism: A case report. Exp Ther Med.
23(346)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bzeizi K, Abdulla M, Mohammed N, Alqamish
J, Jamshidi N and Broering D: Effect of COVID-19 on liver
abnormalities: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep.
11(10599)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Krishnan A, Prichett L, Tao X, Alqahtani
SA, Hamilton JP, Mezey E, Strauss AT, Kim A, Potter JJ, Chen PH and
Woreta TA: Abnormal liver chemistries as a predictor of COVID-19
severity and clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients. World J
Gastroenterol. 28:570–587. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Del Zompo F, De Siena M, Ianiro G,
Gasbarrini A, Pompili M and Ponziani FR: Prevalence of liver injury
and correlation with clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19:
Systematic review with meta-analysis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
24:13072–13088. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu J, Yu C, Yang Q, Yuan X, Yang F, Li P,
Chen G, Liang W and Yang Y: The clinical implication of
gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase in COVID-19. Liver Res. 5:209–216.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Cholongitas E, Bali T, Georgakopoulou VE,
Giannakodimos A, Gyftopoulos A, Georgilaki V, Gerogiannis D,
Basoulis D, Eliadi I, Karamanakos G, et al: Prevalence of abnormal
liver biochemistry and its impact on COVID-19 patients' outcomes: A
single-center Greek study. Ann Gastroenterol. 35:290–296.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|