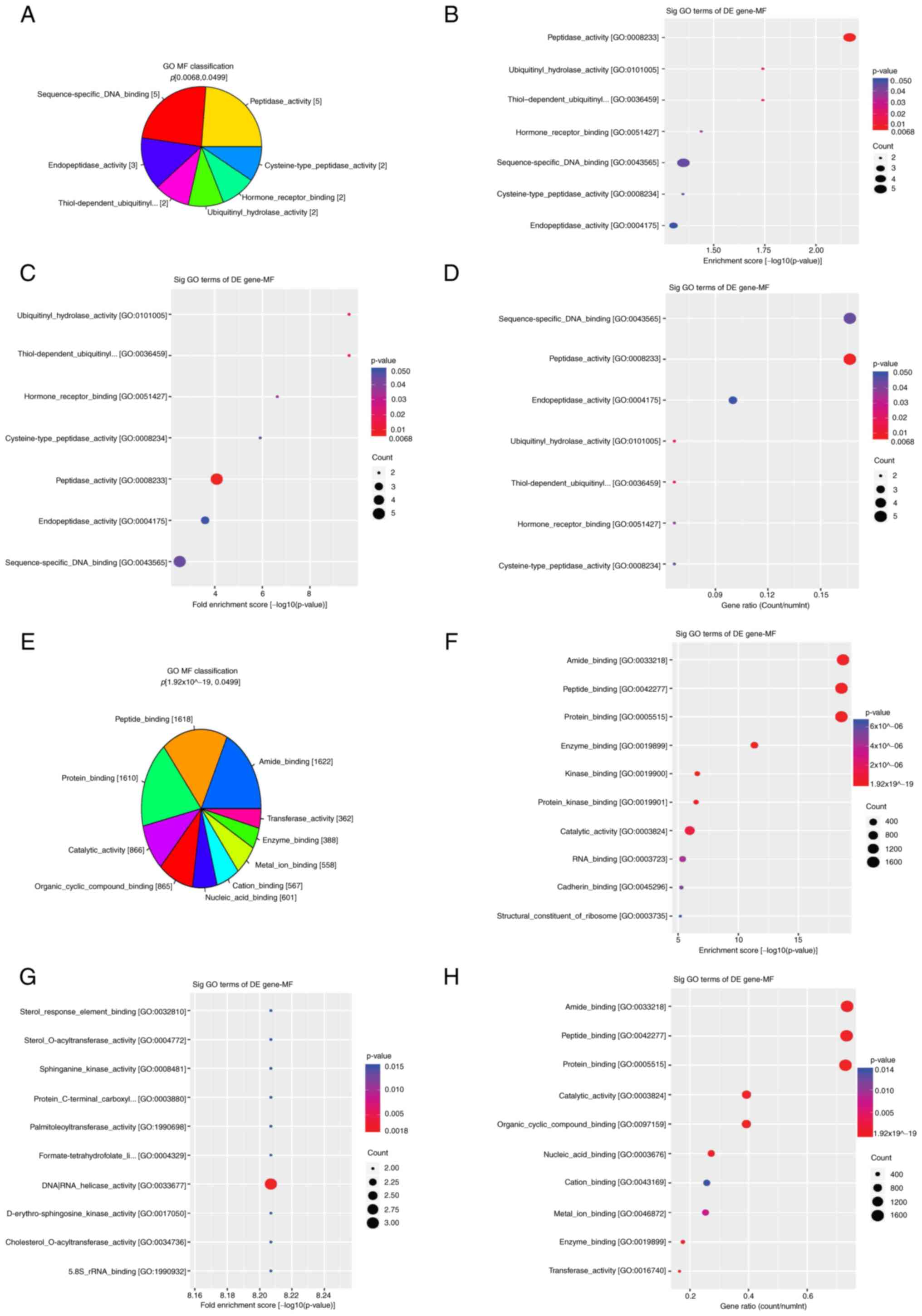
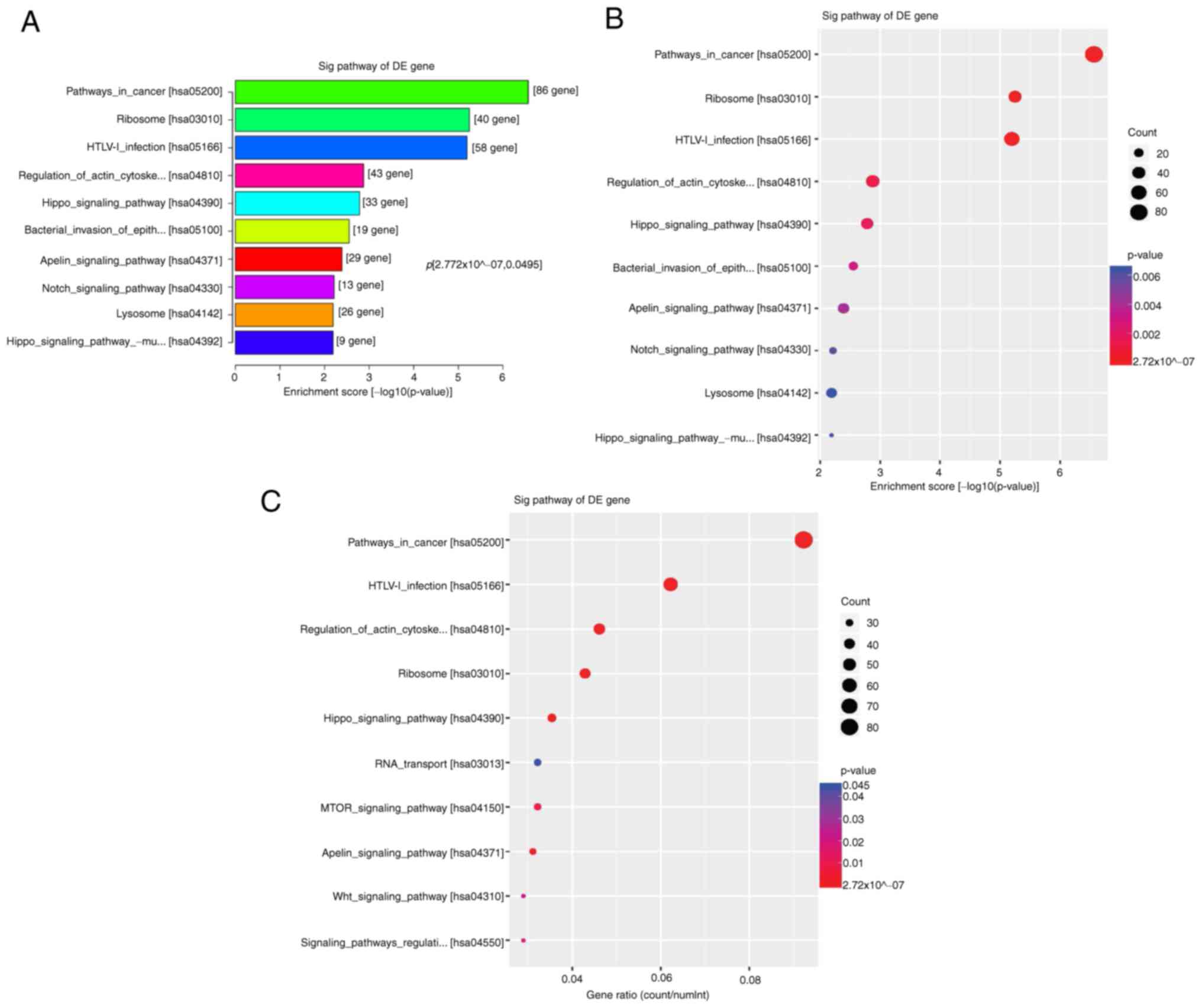
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Shapiro J, van Lanschot JJB, Hulshof MCCM,
van Hagen P, van Berge Henegouwen MI, Wijnhoven BPL, van Laarhoven
HWM, Nieuwenhuijzen GAP, Hospers GAP, Bonenkamp JJ, et al:
Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery versus surgery alone for
oesophageal or junctional cancer (CROSS): Long-term results of a
randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 16:1090–1098.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Li J, Zhao Q, Ge X, Song Y, Tian Y, Wang
S, Liu M and Qiao X: Neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy improves
survival in locally advanced adenocarcinoma of esophagogastric
junction compared with neoadjuvant chemotherapy: A propensity score
matching analysis. BMC Surg. 21(137)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yang Y, Zhu L, Cheng Y, Liu Z, Cai X, Shao
J, Zhang M, Liu J, Sun Y, Li Y, et al: Three-arm phase II trial
comparing camrelizumab plus chemotherapy versus camrelizumab plus
chemoradiation versus chemoradiation as preoperative treatment for
locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (NICE-2 study).
BMC Cancer. 22(506)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Liu J, Yang Y, Liu Z, Fu X, Cai X, Li H,
Zhu L, Shen Y, Zhang H, Sun Y, et al: Multicenter, single-arm,
phase II trial of camrelizumab and chemotherapy as neoadjuvant
treatment for locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
J Immunother Cancer. 10(e004291)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Yang H, Liu H, Chen Y, Zhu C, Fang W, Yu
Z, Mao W, Xiang J, Han Y, Chen Z, et al: Long-term efficacy of
neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy plus surgery for the treatment of
locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: The
NEOCRTEC5010 randomized clinical trial. JAMA Surg. 156:721–729.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Yang P, Zhou X, Yang X, Wang Y, Sun T,
Feng S and Ma X: Neoadjuvant camrelizumab plus chemotherapy in
treating locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
patients: A pilot study. World J Surg Oncol. 19(333)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Liu J, Li J, Lin W, Shao D, Depypere L,
Zhang Z, Li Z, Cui F, Du Z, Zeng Y, et al: Neoadjuvant camrelizumab
plus chemotherapy for resectable, locally advanced esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma (NIC-ESCC2019): A multicenter, phase 2
study. Int J Cancer. 151:128–137. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Shang X, Zhang W, Zhao G, Liang F, Zhang
C, Yue J, Duan X, Ma Z, Chen C, Pang Q, et al: Pembrolizumab
combined with neoadjuvant chemotherapy versus neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy followed by surgery for locally advanced
oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Protocol for a multicentre,
prospective, randomized-controlled, phase III clinical study
(Keystone-002). Front Oncol. 12(831345)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Huang RW, Chao YK, Wen YW, Chang HK, Tseng
CK, Chan SC and Liu YH: Predictors of pathological complete
response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for esophageal squamous
cell carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol. 12(170)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang X, Wang H, Wang H, Huang J, Wang X,
Jiang Z, Tan L, Jiang D and Hou Y: Prognostic value of visual
residual tumour cells (VRTC) for patients with esophageal squamous
cell carcinomas after neoadjuvant therapy followed by surgery. BMC
Cancer. 21(111)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lin D, Chen X and Tan L: The predictive
value of microRNAs for pathological response after neoadjuvant
treatment in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A systematic
review. Ann Transl Med. 9(420)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Niwa Y, Yamada S, Sonohara F, Kurimoto K,
Hayashi M, Tashiro M, Iwata N, Kanda M, Tanaka C, Kobayashi D, et
al: Identification of a serum-based miRNA signature for response of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma to neoadjuvant chemotherapy. J
Transl Med. 17(1)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wen J, Luo K, Liu H, Liu S, Lin G, Hu Y,
Zhang X, Wang G, Chen Y, Chen Z, et al: MiRNA expression analysis
of pretreatment biopsies predicts the pathological response of
esophageal squamous cell carcinomas to neoadjuvant
chemoradiotherapy. Ann Surg. 263:942–948. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Slotta-Huspenina J, Drecoll E, Feith M,
Habermehl D, Combs S, Weichert W, Bettstetter M, Becker K and
Langer R: MicroRNA expression profiling for the prediction of
resistance to neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy in squamous cell
carcinoma of the esophagus. J Transl Med. 16(109)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Shekhawat J, Gauba K, Gupta S, Choudhury
B, Purohit P, Sharma P and Banerjee M: Ten-eleven translocase: Key
regulator of the methylation landscape in cancer. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 147:1869–1879. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bachman M, Uribe-Lewis S, Yang X, Williams
M, Murrell A and Balasubramanian S: 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine is a
predominantly stable DNA modification. Nat Chem. 6:1049–1055.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Pfeifer GP, Xiong W, Hahn MA and Jin SG:
The role of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in human cancer. Cell Tissue
Res. 356:631–641. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
He B, Zhang C, Zhang X, Fan Y, Zeng H, Liu
J, Meng H, Bai D, Peng J, Zhang Q, et al: Tissue-specific
5-hydroxymethylcytosine landscape of the human genome. Nat Commun.
12(4249)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tian X, Sun B, Chen C, Gao C, Zhang J, Lu
X, Wang L, Li X, Xing Y, Liu R, et al: Circulating tumor DNA
5-hydroxymethylcytosine as a novel diagnostic biomarker for
esophageal cancer. Cell Res. 28:597–600. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Jin N, George TL, Otterson GA,
Verschraegen C, Wen H, Carbone D, Herman J, Bertino EM and He K:
Advances in epigenetic therapeutics with focus on solid tumors.
Clin Epigenetics. 13(83)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Lin L, Cheng X and Yin D: Aberrant DNA
methylation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Biological and
clinical implications. Front Oncol. 10(549850)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Grady WM, Yu M and Markowitz SD:
Epigenetic alterations in the gastrointestinal tract: Current and
emerging use for biomarkers of cancer. Gastroenterology.
160:690–709. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Buza N and Hui P: Characteristics of HER2
gene amplification by fluorescence in situ hybridization in
endometrial serous carcinoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
146(0)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Dagogo-Jack I and Shaw AT: Tumour
heterogeneity and resistance to cancer therapies. Nat Rev Clin
Oncol. 15:81–94. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Arnold M, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J and
Forman D: Global incidence of oesophageal cancer by histological
subtype in 2012. Gut. 64:381–387. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Mori T, Kumagai K, Nasu K, Yoshizawa T,
Kuwano K, Hamada Y, Kanazawa H and Suzuki R: Clonal expansion of
tumor-infiltrating T cells and analysis of the tumor
microenvironment within esophageal squamous cell carcinoma relapsed
after definitive chemoradiation therapy. Int J Mol Sci.
22(1098)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Schneider PM, Metzger R, Schaefer H,
Baumgarten F, Vallbohmer D, Brabender J, Wolfgarten E,
Bollschweiler E, Baldus SE, Dienes HP and Hoelscher AH: Response
evaluation by endoscopy, rebiopsy, and endoscopic ultrasound does
not accurately predict histopathologic regression after neoadjuvant
chemoradiation for esophageal cancer. Ann Surg. 248:902–908.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hoshimoto S, Takeuchi H, Ono S, Sim MS,
Huynh JL, Huang SK, Marzese DM, Kitagawa Y and Hoon DS: Genome-wide
hypomethylation and specific tumor-related gene hypermethylation
are associated with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma outcome. J
Thorac Oncol. 10:509–517. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network;
Analysis Working Group: Asan University; BC Cancer Agency; Brigham
and Women's Hospital; Broad Institute; Brown University; Case
Western Reserve University; Dana-Farber Cancer Institute; Duke
University et al. Integrated genomic characterization of
oesophageal carcinoma. Nature. 541:169–175. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Chen X, Cai S, Li B, Zhang X, Li W, Linag
H and Cao X: Identification of key genes and pathways for
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by bioinformatics analysis. Exp
Ther Med. 16:1121–1130. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhou M, Hou P, Yan C, Chen L, Li K, Wang
Y, Zhao J, Su J and Sun J: Cell-free DNA 5-hydroxymethylcytosine
profiles of long non-coding RNA genes enable early detection and
progression monitoring of human cancers. Clin Epigenetics.
13(197)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Xing J, Zhai R, Wang C, Liu H, Zeng J,
Zhou D, Zhang M, Wang L, Wu Q, Gu Y and Zhang Y: DiseaseMeth
version 3.0: A major expansion and update of the human disease
methylation database. Nucleic Acids Res. 50 (D1):D1208–D1215.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Peng D, Belkhiri A, Hu T, Chaturvedi R,
Asim M, Wilson KT, Zaika A and El-Rifai W: Glutathione peroxidase 7
protects against oxidative DNA damage in oesophageal cells. Gut.
61:1250–1260. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Peng DF, Razvi M, Chen H, Washington K,
Roessner A, Schneider-Stock R and El-Rifai W: DNA hypermethylation
regulates the expression of members of the Mu-class glutathione
S-transferases and glutathione peroxidases in Barrett's
adenocarcinoma. Gut. 58:5–15. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Qu X, Davison J, Du L, Storer B, Stirewalt
DL, Heimfeld S, Estey E, Appelbaum FR and Fang M: Identification of
differentially methylated markers among cytogenetic risk groups of
acute myeloid leukemia. Epigenetics. 10:526–535. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
de Klerk LK, Goedegebuure RSA, van Grieken
NCT, van Sandick JW, Cats A, Stiekema J, van der Kaaij RT, Farina
Sarasqueta A, van Engeland M, Jacobs MAJM, et al: Molecular
profiles of response to neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy in
oesophageal cancers to develop personalized treatment strategies.
Mol Oncol. 15:901–914. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Iwabu J, Yamashita S, Takeshima H, Kishino
T, Takahashi T, Oda I, Koyanagi K, Igaki H, Tachimori Y, Daiko H,
et al: FGF5 methylation is a sensitivity marker of esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma to definitive chemoradiotherapy. Sci Rep.
9(13347)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Coscia F, Lengyel E, Duraiswamy J,
Ashcroft B, Bassani-Sternberg M, Wierer M, Johnson A, Wroblewski K,
Montag A, Yamada SD, et al: Multi-level proteomics identifies CT45
as a chemosensitivity mediator and immunotherapy target in ovarian
cancer. Cell. 175:159–170.e16. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zhang W, Barger CJ, Link PA,
Mhawech-Fauceglia P, Miller A, Akers SN, Odunsi K and Karpf AR: DNA
hypomethylation-mediated activation of cancer/testis antigen 45
(CT45) genes is associated with disease progression and reduced
survival in epithelial ovarian cancer. Epigenetics. 10:736–748.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Martinez-Useros J, Martin-Galan M,
Florez-Cespedes M and Garcia-Foncillas J: Epigenetics of most
aggressive solid tumors: Pathways, targets and treatments. Cancers
(Basel). 13(3209)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|