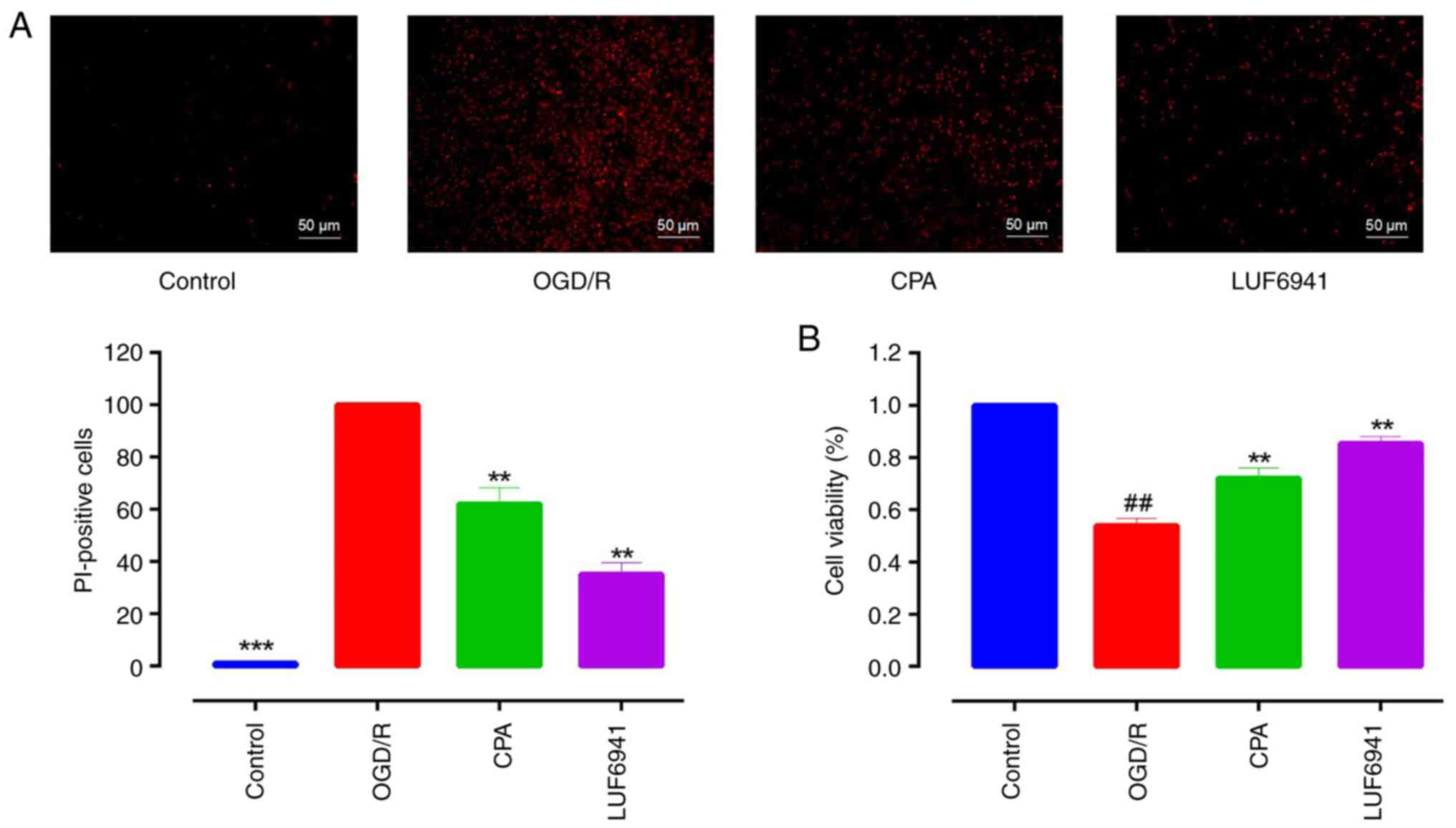
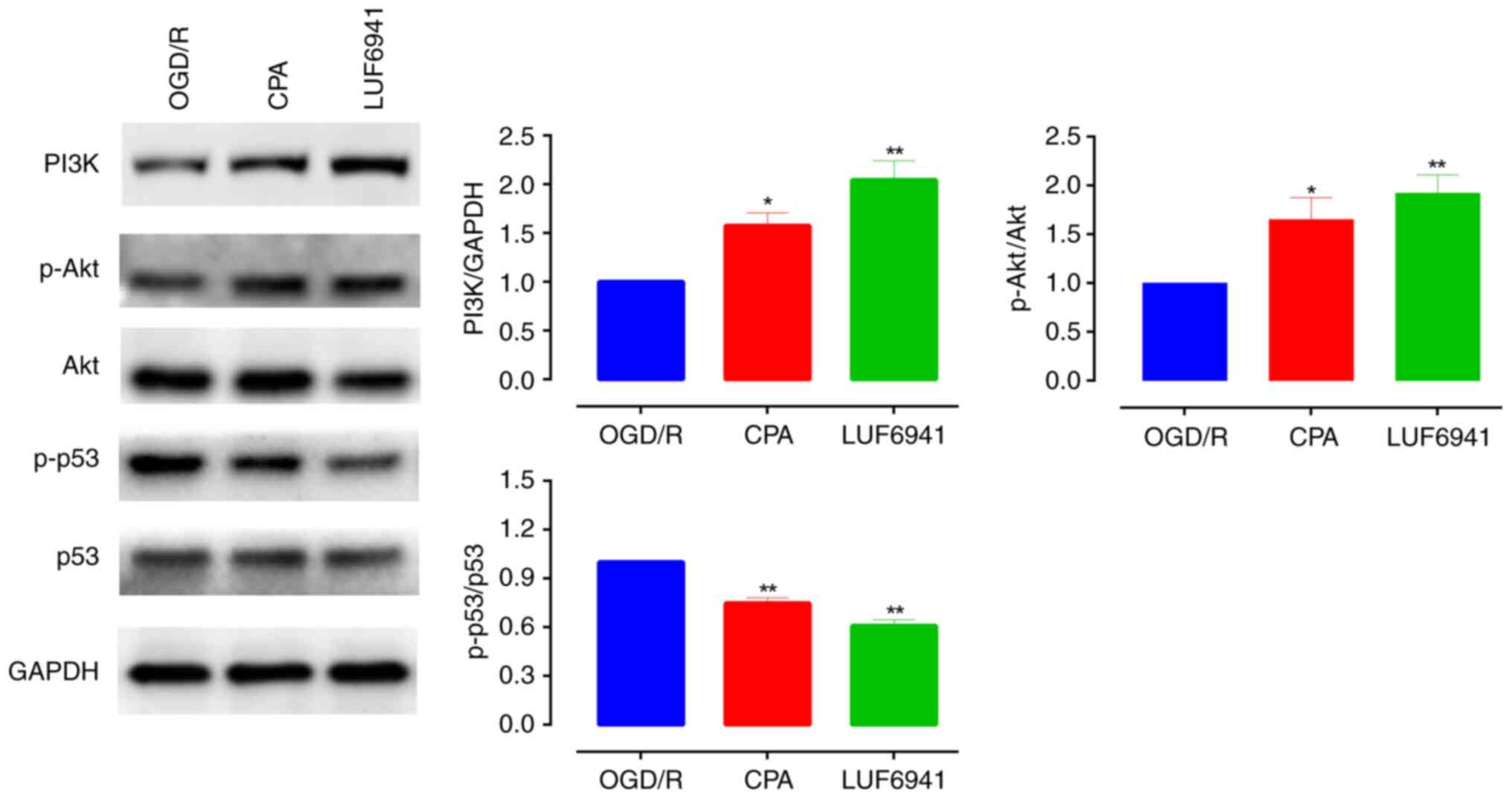
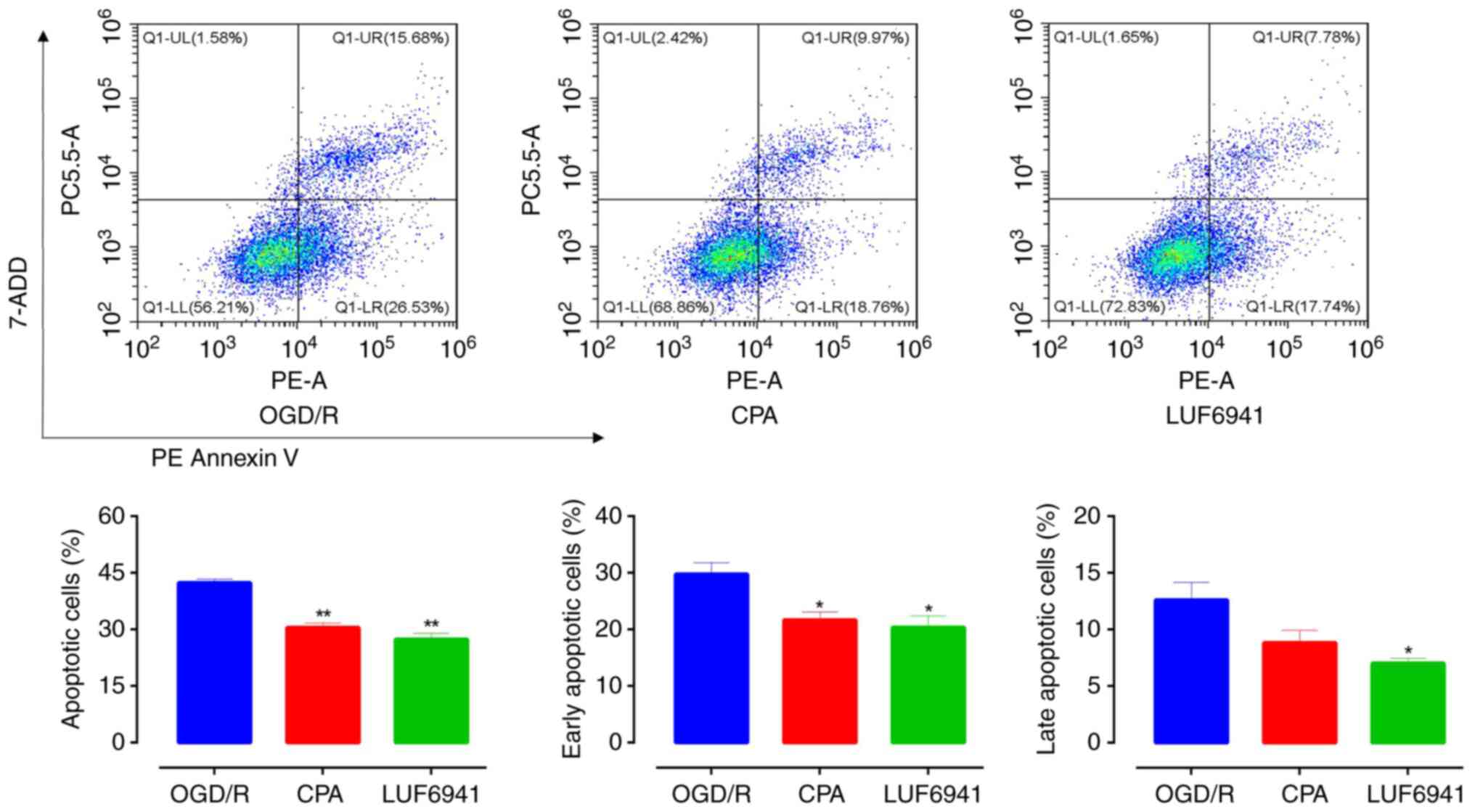
|
1
|
Barie PS: Schemes against ischemia;
solutions for reperfusion (injury)? Crit Care Med. 27:684–685.
1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Corcos O and Nuzzo A: Gastro-intestinal
vascular emergencies. Best Pract Res Clinl Gastroenterol.
27:709–725. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Schoenberg MH and Beger HG: Reperfusion
injury after intestinal ischemia. Crit Care Med. 21:1376–1386.
1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Horton JW and Walker PB: Oxygen radicals,
lipid peroxidation, and permeability changes after intestinal
ischemia and reperfusion. J Appl Physiol (1985). 74:1515–1520.
1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Taha MO, Fraga MM, Fagundes DJ, Jurkiewicz
A and Caricati-Neto A: Effect of allopurinol on autonomic
dysfunction in rat jejunal segments exposed to cold ischemic
preservation for transplantation. Transplant Proc. 36:293–295.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Taha MO, Fraga MM, Fagundes DJ, Jurkiewicz
A and Caricati-Neto A: Ascorbic acid prevents autonomic dysfunction
in rat jejunal submitted to cold ischemic preservation for
transplantation. Transplant Proc. 36:289–292. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Abbracchio MP and Burnstock G: Purinergic
signalling: Pathophysiological roles. Jpn J Pharmacol. 78:113–145.
1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Burnstock G: Purinergic signaling. B J
Pharmacol. 147 (Suppl 1):S172–S181. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kaminski PM and Proctor KG: Attenuation of
no-reflow phenomenon, neutrophil activation, and reperfusion injury
in intestinal microcirculation by topical adenosine. Circ Res.
65:426–435. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ozacmak VH and Sayan H: Pretreatment with
adenosine and adenosine A1 receptor agonist protects against
intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat. World J
Gastroenterol. 13:538–547. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Magata S, Taniguchi M, Suzuki T, Shimamura
T, Fukai M, Furukawa H, Fujita M and Todo S: The effect of
antagonism of adenosine A1 receptor against ischemia and
reperfusion injury of the liver. J Surg Res. 139:7–14.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lee HT, Xu H, Nasr SH, Schnermann J and
Emala CW: A1 adenosine receptor knockout mice exhibit increased
renal injury following ischemia and reperfusion. Am J Physiol Renal
Physiol. 286:F298–F306. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Gazoni LM, Walters DM, Unger EB, Linden J,
Kron IL and Laubach VE: Activation of A1, A2A, or A3 adenosine
receptors attenuates lung ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 140:440–446. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yang Z, Cerniway RJ, Byford AM, Berr SS,
French BA and Matherne GP: Cardiac overexpression of A1-adenosine
receptor protects intact mice against myocardial infarction. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 282:H949–H955. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Shackelford RE, Alford PB, Xue Y, Thai SF,
Adams DO and Pizzo S: Aspirin inhibits tumor necrosis factor-α gene
expression in murine tissue macrophages. Mol Pharmacol. 52:421–429.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Jacobson KA and Gao ZG: Adenosine
receptors as therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:247–264.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Hausenloy DJ and Yellon DM: New directions
for protecting the heart against ischaemia-reperfusion injury:
Targeting the reperfusion injury salvage kinase (RISK)-pathway.
Cardiovasc Res. 61:448–460. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ma XJ, Yin HJ, Guo CY, Jiang YR, Wang JS
and Shi DZ: Ischemic postconditioning through percutaneous
transluminal coronary angioplasty in pigs: Roles of PI3K
activation. Coron Artery Dis. 23:245–250. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Copeland RA, Pompliano DL and Meek TD:
Drug-target residence time and its implications for lead
optimization. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 5:730–739. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yun Y, Chen J, Liu R, Chen W, Liu C, Wang
R, Hou Z, Yu Z, Sun Y, IJzerman AP, et al: Long residence time
adenosine A1 receptor agonists produce sustained
wash-resistant antilipolytic effect in rat adipocytes. Biochem
Pharmacol. 164:45–52. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Guo D, Heitman LH and IJzerman AP: The
added value of assessing ligand-receptor binding kinetics in drug
discovery. ACS Med Chem Lett. 7:819–821. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sun S, Hu F, Wu J and Zhang S: Cannabidiol
attenuates OGD/R-induced damage by enhancing mitochondrial
bioenergetics and modulating glucose metabolism via
pentose-phosphate pathway in hippocampal neurons. Redox Biol.
11:577–585. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Lu Y, An J, Liu Y, Ren L and Zhang L: MMP9
is involved in HO-1-mediated upregulation of apical junctional
complex in Caco-2 cells under oxygen-glucose deprivation. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 498:125–131. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Maggirwar SB, Dhanraj DN, Somani SM and
Ramkumar V: Adenosine acts as an endogenous activator of the
cellular antioxidant defense system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
201:508–515. 1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Copeland RA: The drug-target residence
time model: A 10-year retrospective. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 15:87–95.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Vauquelin G, Bostoen S, Vanderheyden P and
Seeman P: Clozapine, atypical antipsychotics, and the benefits of
fast-off D2 dopamine receptor antagonism. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch
Pharmacol. 385:337–372. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Vauquelin G and Charlton SJ: Long-lasting
target binding and rebinding as mechanisms to prolong in vivo drug
action. Br J Pharmacol. 161:488–508. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Harnois C, Demers MJ and Vachon PH, Vallée
K, Gagné D, Fujita N, Tsuruo T, Vézina A, Beaulieu JF, Côté A and
Vachon PH: Human intestinal epithelial crypt cell survival and
death: Complex modulations of Bcl-2 homologs by Fak, PI3-K/Akt-1,
MEK/Erk, and p38 signaling pathways. J Cell Physiol. 198:209–222.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Baines CP, Wang L, Cohen MV and Downey JM:
Myocardial protection by insulin is dependent on
phospatidylinositol 3-kinase but not protein kinase C or KATP
channels in the isolated rabbit heart. Basic Res Cardiol.
94:188–198. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Yano S, Morioka M, Fukunaga K, Kawano T,
Hara T, Kai Y, Hamada J, Miyamoto E and Ushio Y: Activation of
Akt/protein kinase B contributes to induction of ischemic tolerance
in the CA1 subfield of gerbil hippocampus. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 21:351–360. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ikeda H, Suzuki Y, Suzuki M, Koike M,
Tamura J, Tong J, Nomura M and Itoh G: Apoptosis is a major mode of
cell death caused by ischaemia and ischaemia/reperfusion injury to
the rat intestinal epithelium. Gut. 42:530–537. 1998.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Fang L, Li G, Liu G, Lee SW and Aaronson
SA: p53 induction of heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor
counteracts p53 growth suppression through activation of MAPK and
PI3K/Akt signaling cascades. EMBO J. 20:1931–1939. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Taha MO, Miranda-Ferreira R, Simões RS,
Abrão MS, Oliveira-Junior IS, Monteiro HP, Santos JM, Rodrigues PH,
Rodrigues JV, Alves AE, et al: Role of adenosine on intestinal
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rabbits. Transplant Proc. 4:454–456.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Mandl M and Depping R: Hypoxia-inducible
aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator (ARNT) (HIF-1β): Is
it a rare exception? Mol Med. 20:215–220. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|