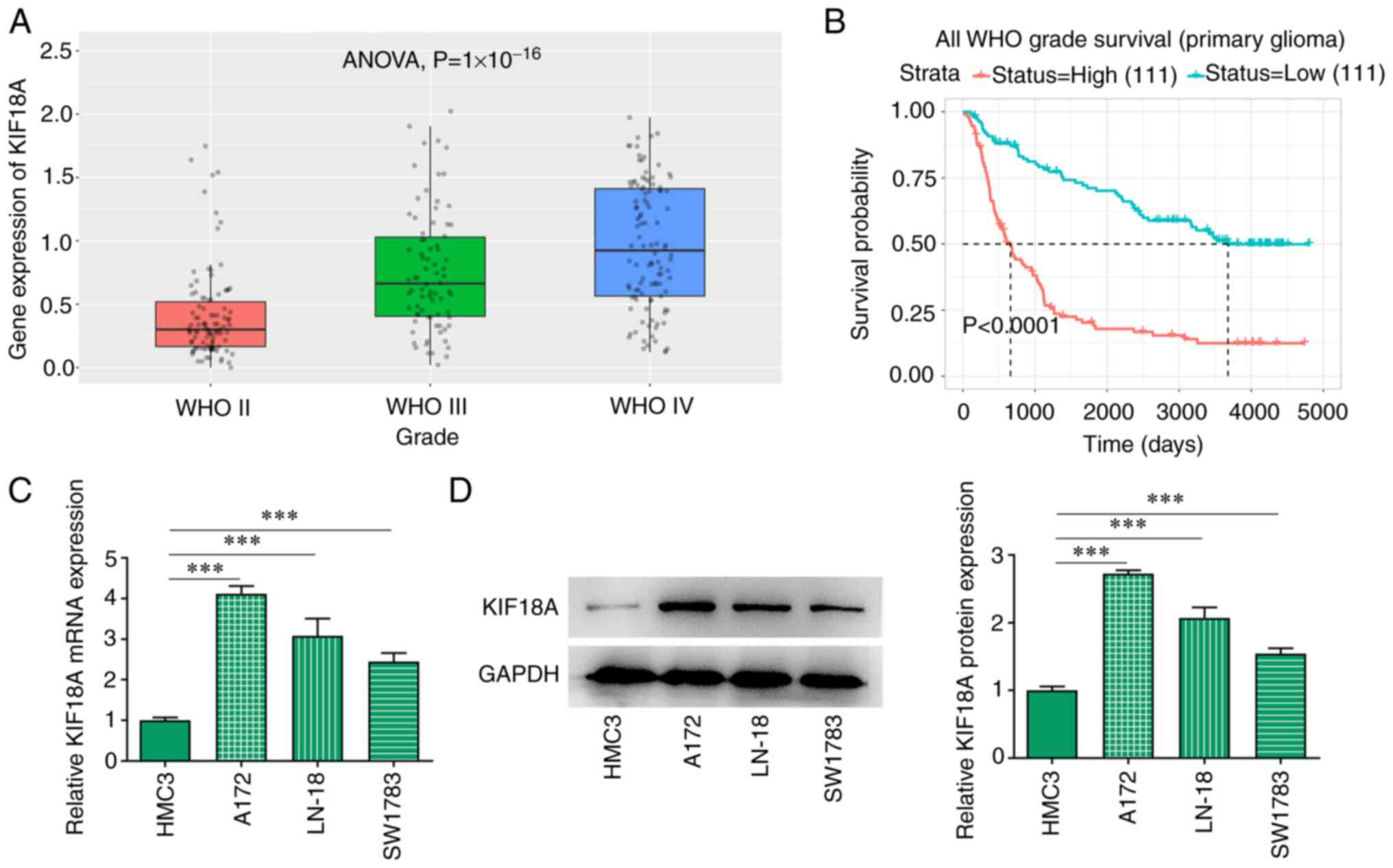
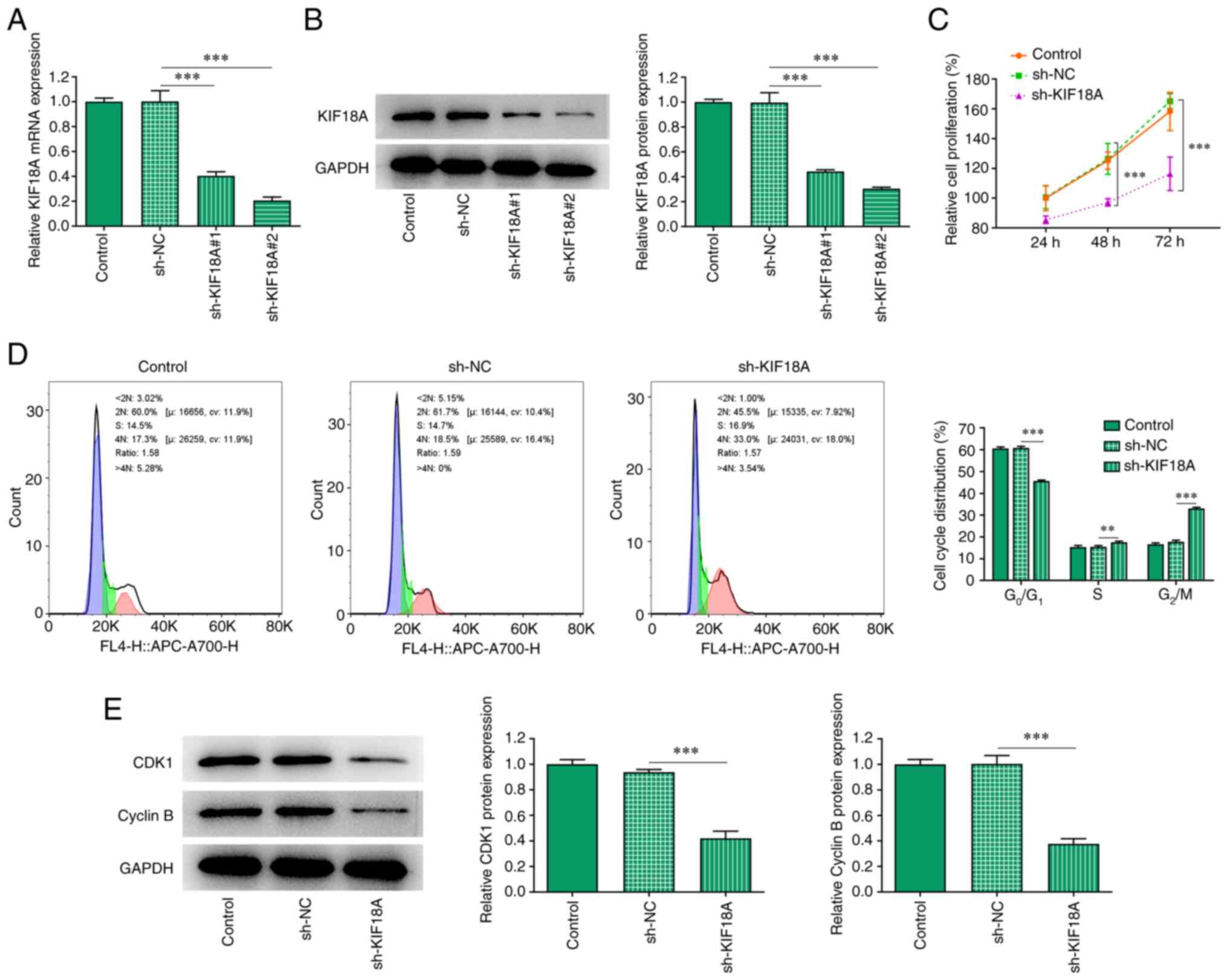
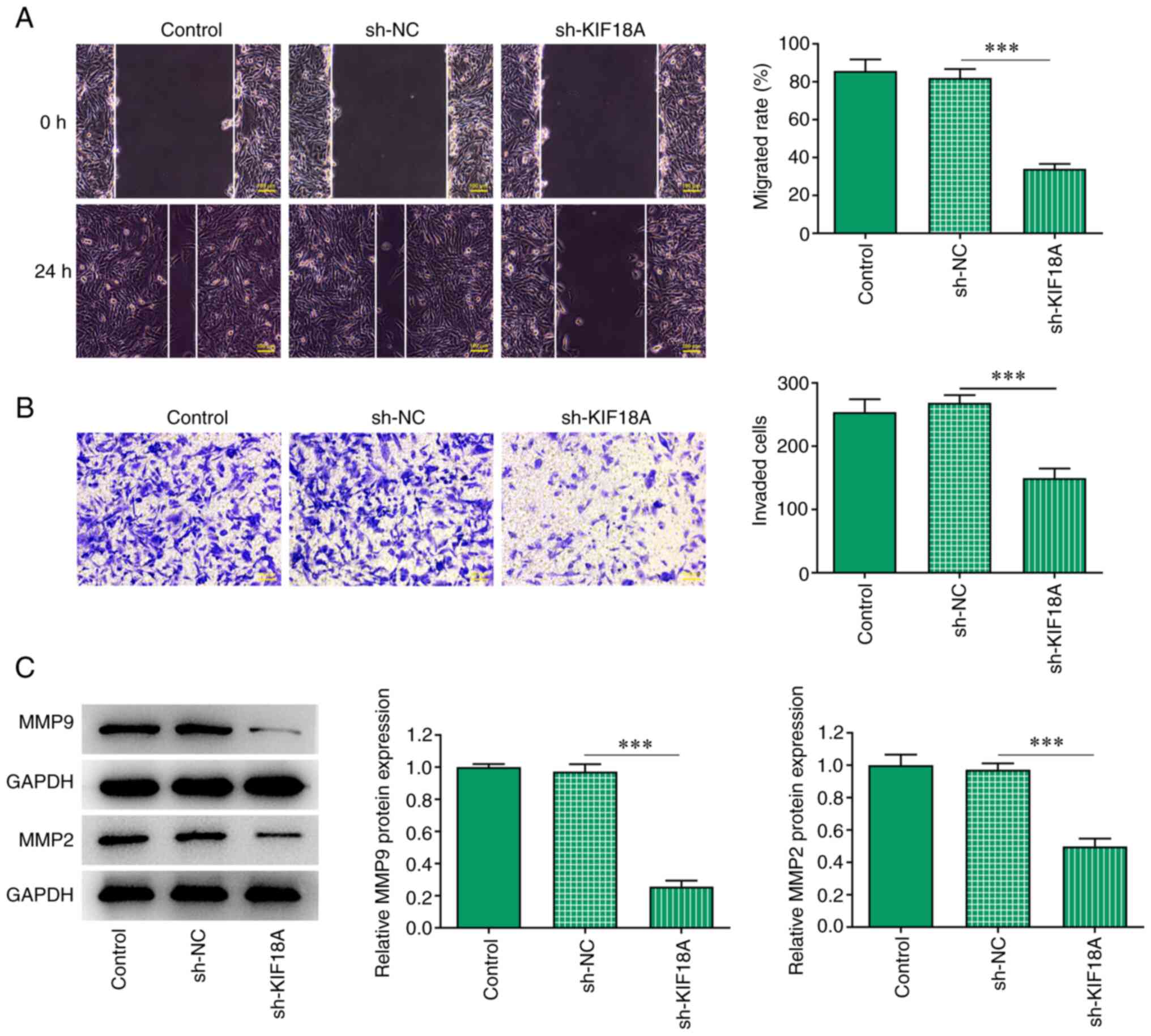
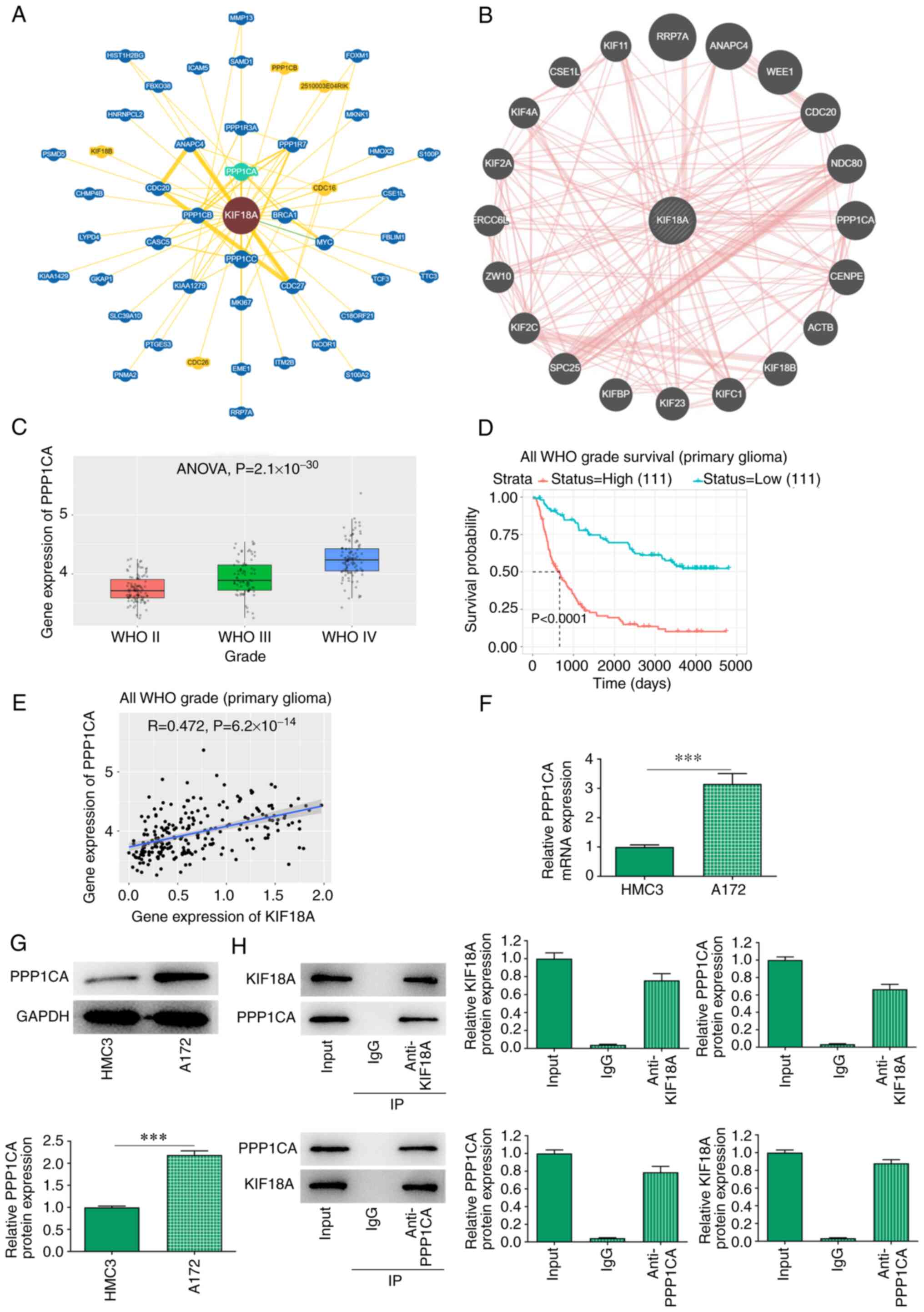
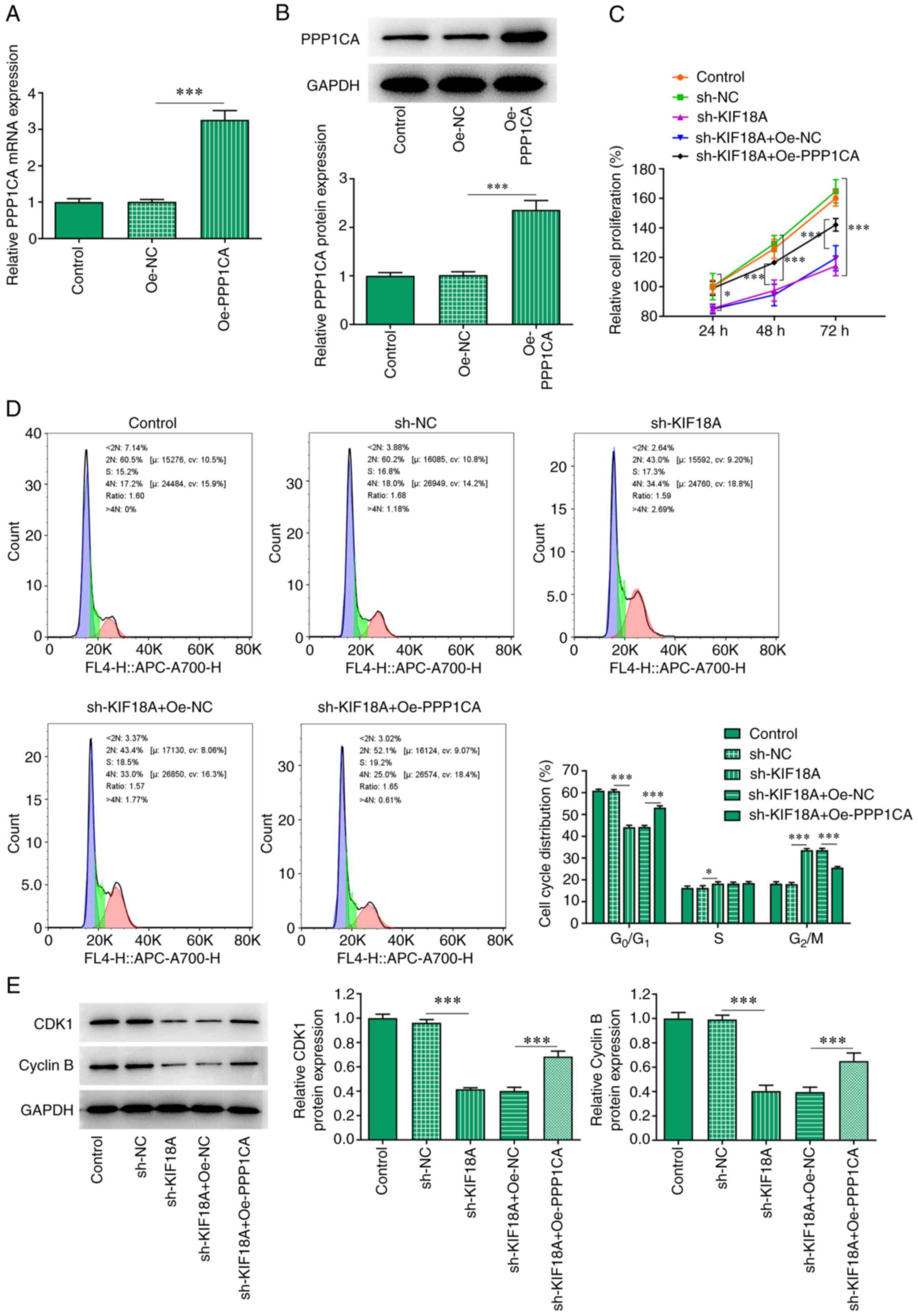
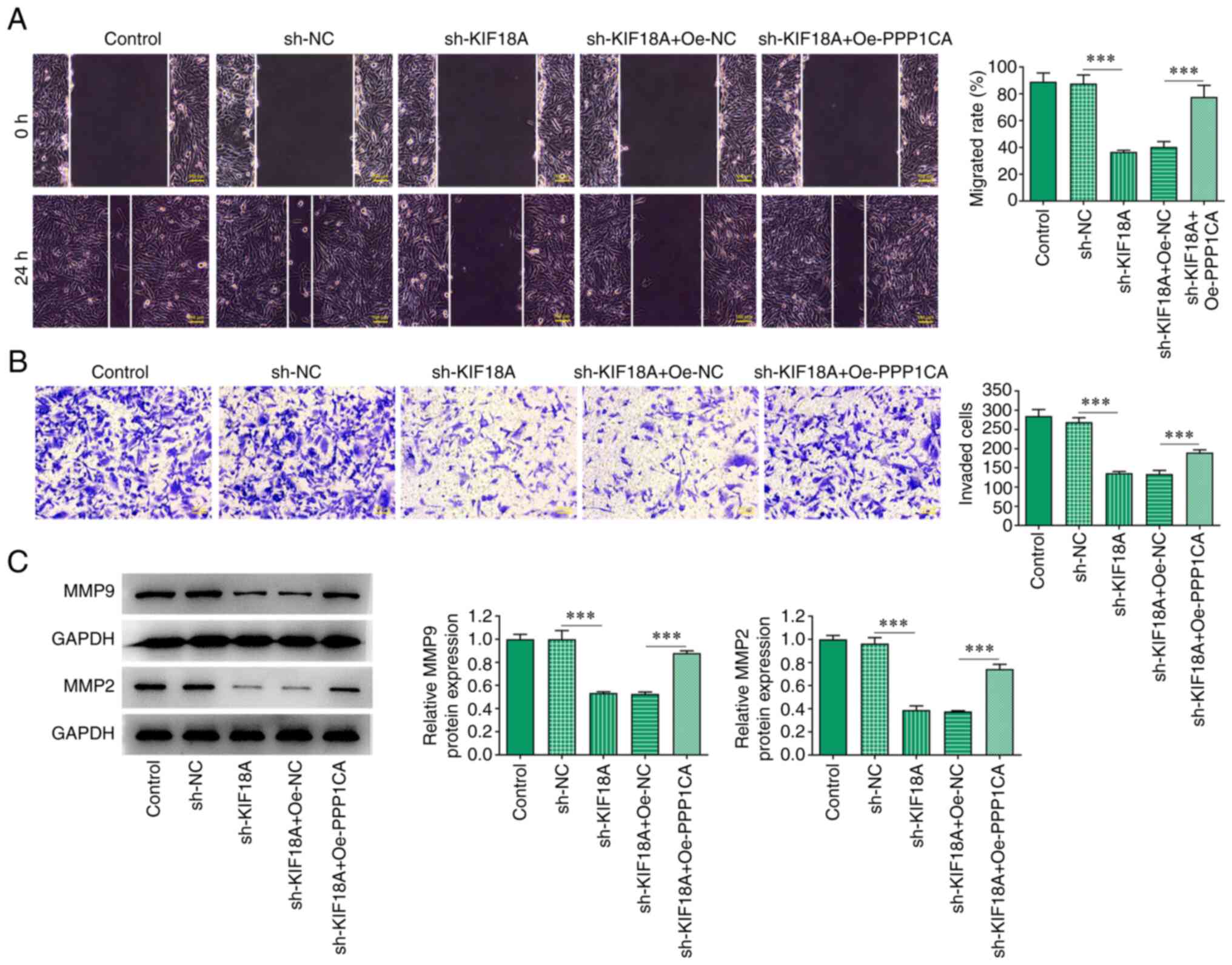
|
1
|
Davis ME: Epidemiology and overview of
gliomas. Semin Oncol Nurs. 34:420–429. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Preusser M, Lim M, Hafler DA, Reardon DA
and Sampson JH: Prospects of immune checkpoint modulators in the
treatment of glioblastoma. Nat Rev Neurol. 11:504–514.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chen R, Smith-Cohn M, Cohen AL and Colman
H: Glioma subclassifications and their clinical significance.
Neurotherapeutics. 14:284–297. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Malaby HL, Lessard DV, Berger CL and
Stumpff J: KIF18A's neck linker permits navigation of
microtubule-bound obstacles within the mitotic spindle. Life Sci
Alliance. 2(e201800169)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tao BY, Liu YY, Liu HY, Zhang ZH, Guan YQ,
Wang H, Shi Y and Zhang J: Prognostic biomarker KIF18A and its
correlations with immune infiltrates and mitosis in glioma. Front
Genet. 13(852049)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Marquis C, Fonseca CL, Queen KA, Wood L,
Vandal SE, Malaby HLH, Clayton JE and Stumpff J: Chromosomally
unstable tumour cells specifically require KIF18A for
proliferation. Nat Commun. 12(1213)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Sepaniac LA, Martin W, Dionne LA, Stearns
TM, Reinholdt LG and Stumpff J: Micronuclei in Kif18a mutant mice
form stable micronuclear envelopes and do not promote
tumorigenesis. J Cell Biol. 220(e202101165)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Qian LX, Cao X, Du MY, Ma CX, Zhu HM, Peng
Y, Hu XY, He X and Yin L: KIF18A knockdown reduces proliferation,
migration, invasion and enhances radiosensitivity of oesophageal
cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 557:192–198. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Stangeland B, Mughal AA, Grieg Z, Sandberg
CJ, Joel M, Nygard S, Meling T, Murrell W, Vik Mo EO and Langmoen
IA: Combined expressional analysis, bioinformatics and targeted
proteomics identify new potential therapeutic targets in
glioblastoma stem cells. Oncotarget. 6:26192–26215. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang LB, Zhang XB, Liu J and Liu QJ: The
proliferation of glioblastoma is contributed to kinesin family
member 18A and medical data analysis of GBM. Front Genet.
13(858882)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sun H, Ou B, Zhao S, Liu X, Song L, Liu X,
Wang R and Peng Z: USP11 promotes growth and metastasis of
colorectal cancer via PPP1CA-mediated activation of ERK/MAPK
signalling pathway. EBioMedicine. 48:236–247. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Xie W, Sun Y, Zeng Y, Hu L, Zhi J, Ling H,
Zheng X, Ruan X and Gao M: Comprehensive analysis of PPPCs family
reveals the clinical significance of PPP1CA and PPP4C in breast
cancer. Bioengineered. 13:190–205. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Shastry AH, Thota B, Srividya MR,
Arivazhagan A and Santosh V: Nuclear Protein Phosphatase 1 α (PP1A)
expression is associated with poor prognosis in p53 expressing
glioblastomas. Pathol Oncol Res. 22:287–292. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hombach-Klonisch S, Mehrpour M, Shojaei S,
Harlos C, Pitz M, Hamai A, Siemianowicz K, Likus W, Wiechec E,
Toyota BD, et al: Glioblastoma and chemoresistance to alkylating
agents: Involvement of apoptosis, autophagy, and unfolded protein
response. Pharmacol Ther. 184:13–41. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller
M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn
U, et al: Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide
for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 352:987–996. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Luo W, Liao M, Liao Y, Chen X, Huang C,
Fan J and Liao W: The role of kinesin KIF18A in the invasion and
metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Surg Oncol.
16(36)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang H, Shen T, Zhang Z, Li Y and Pan Z:
Expression of KIF18A is associated with increased tumor stage and
cell proliferation in prostate cancer. Med Sci Monit. 25:6418–6428.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hang J, Lau SY, Yin R, Zhu L, Zhou S, Yuan
X and Wu L: The role of phosphoprotein phosphatases catalytic
subunit genes in pancreatic cancer. Biosci Rep.
41(BSR20203282)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Nohata N, Hanazawa T, Kikkawa N, Sakurai
D, Fujimura L, Chiyomaru T, Kawakami K, Yoshino H, Enokida H,
Nakagawa M, et al: Tumour suppressive microRNA-874 regulates novel
cancer networks in maxillary sinus squamous cell carcinoma. Br J
Cancer. 105:833–841. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Verdugo-Sivianes EM, Navas L,
Molina-Pinelo S, Ferrer I, Quintanal-Villalonga A, Peinado J,
Garcia-Heredia JM, Felipe-Abrio B, Muñoz-Galvan S, Marin JJ, et al:
Coordinated downregulation of Spinophilin and the catalytic
subunits of PP1, PPP1CA/B/C, contributes to a worse prognosis in
lung cancer. Oncotarget. 8:105196–105210. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|