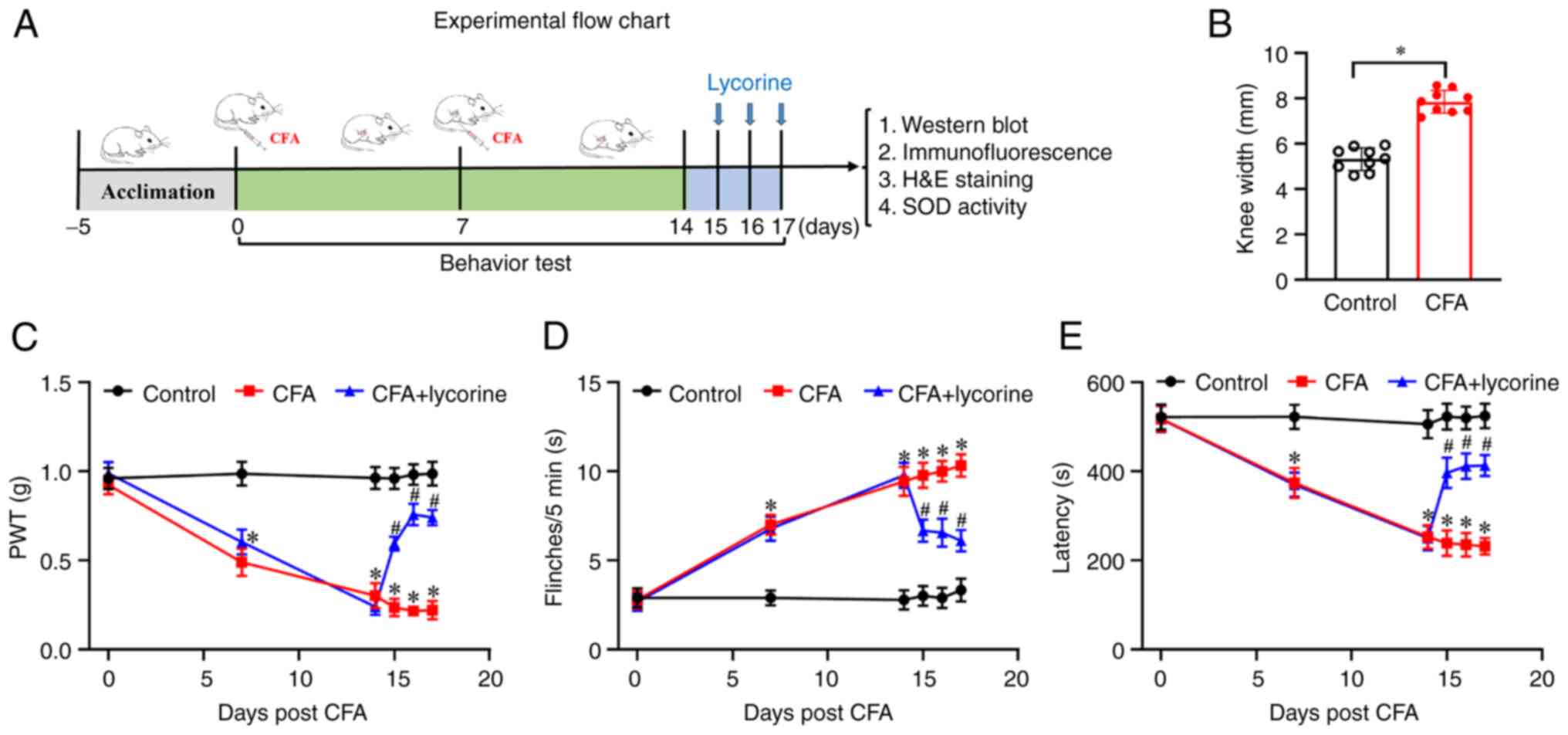
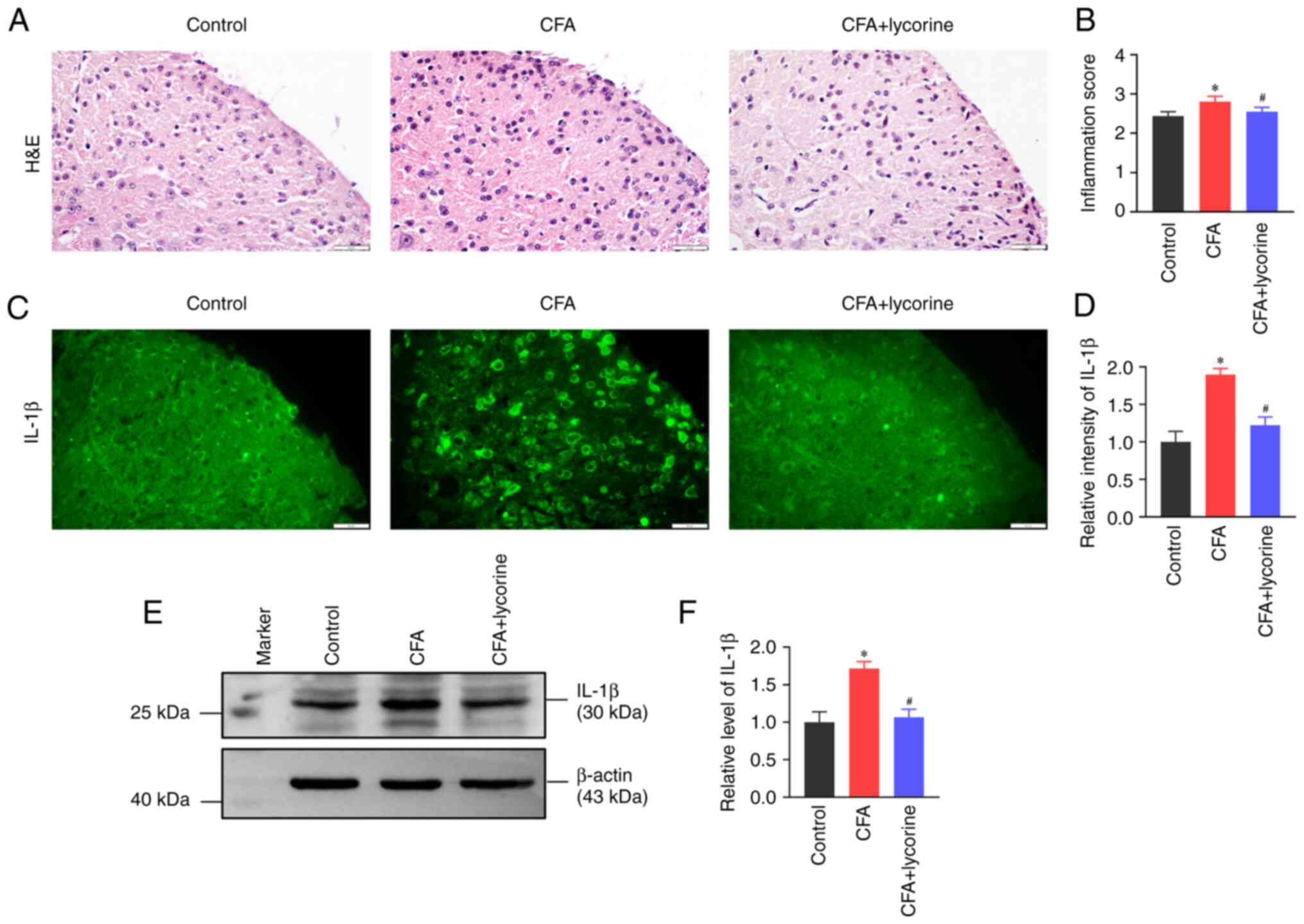
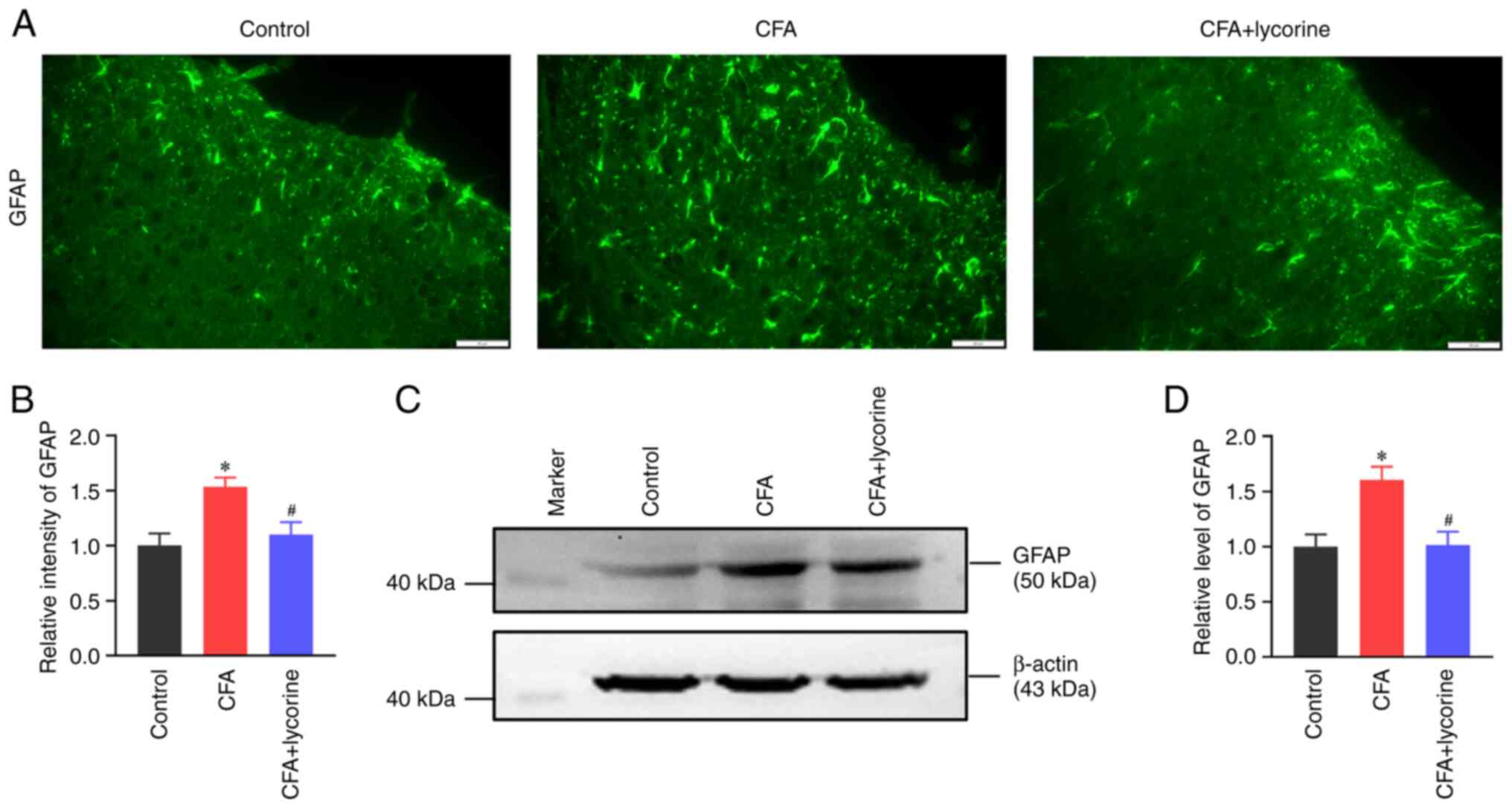
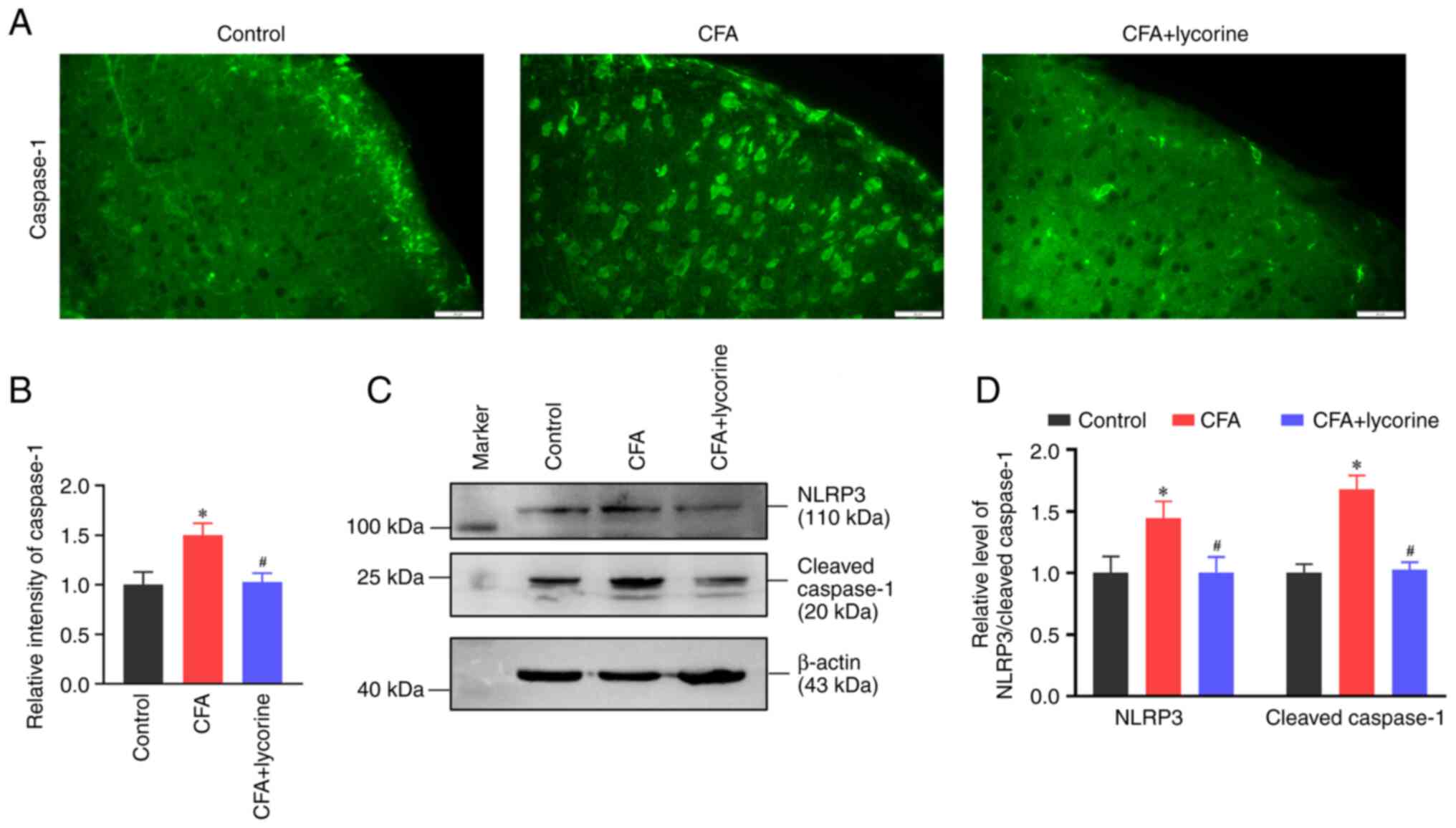
|
1
|
Xie SH, Wang Q, Wang LQ, Wang L, Song KP
and He CQ: Effect of internet-based rehabilitation programs on
improvement of pain and physical function in patients with knee
osteoarthritis: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials. J Med Internet Res. 23(e21542)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Malfait AM, Miller RE and Miller RJ: Basic
Mechanisms of pain in osteoarthritis: Experimental observations and
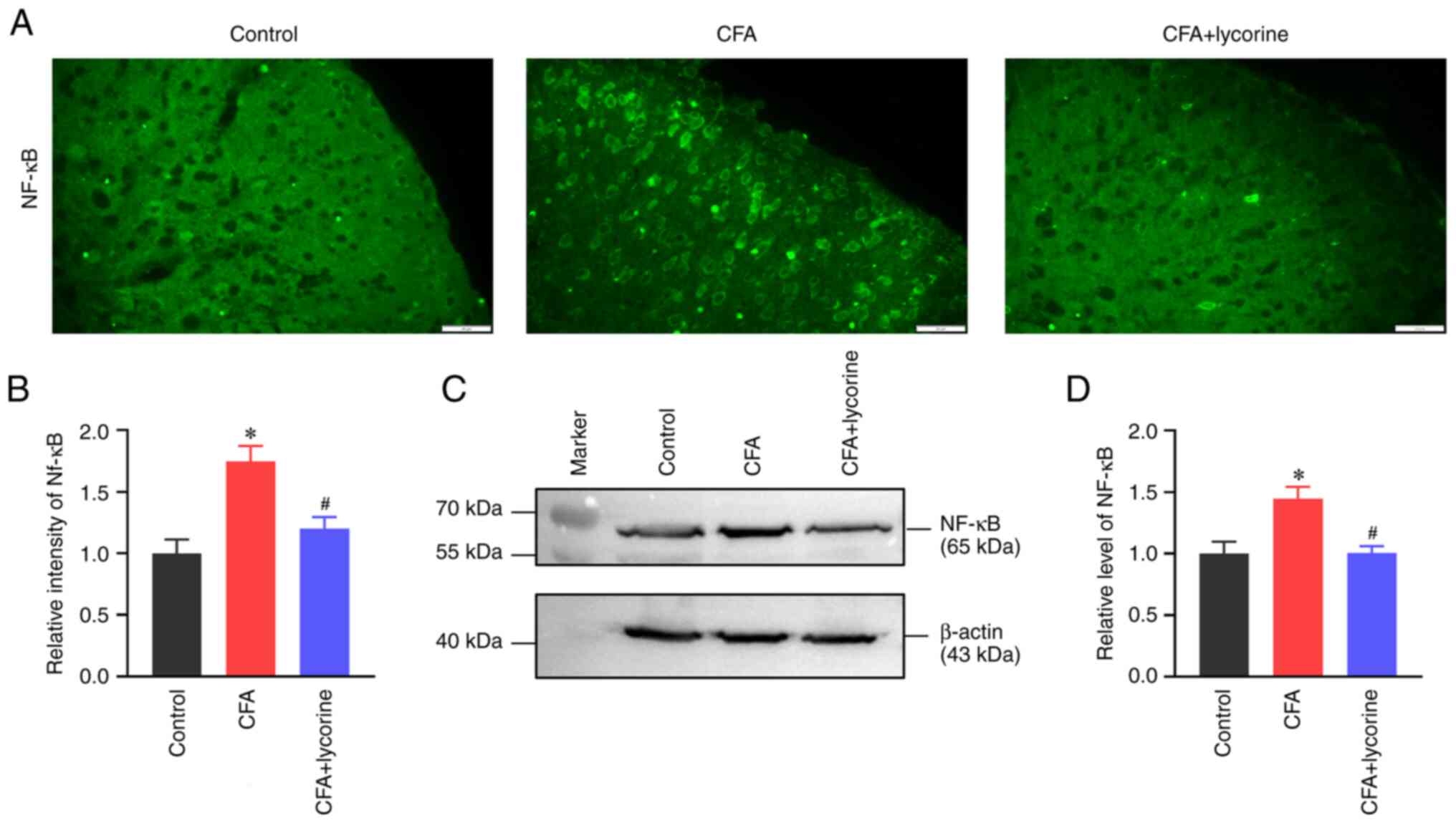
new perspectives. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 47:165–180.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Rajamäki TJ Jr, Puolakka PA, Hietaharju A,
Moilanen T and Jämsen E: Use of prescription analgesic drugs before
and after hip or knee replacement in patients with osteoarthritis.
BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 20(427)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
D'Arcy Y, Mantyh P, Yaksh T, Donevan S,
Hall J, Sadrarhami M and Viktrup L: Treating osteoarthritis pain:
Mechanisms of action of acetaminophen, nonsteroidal
anti-inflammatory drugs, opioids, and nerve growth factor
antibodies. Postgrad Med. 133:879–894. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Schaible HG, König C and Ebersberger A:
Spinal pain processing in arthritis: Neuron and glia
(inter)actions. J Neurochem: Dec 15, 2022 (Epub ahead of
print).
|
|
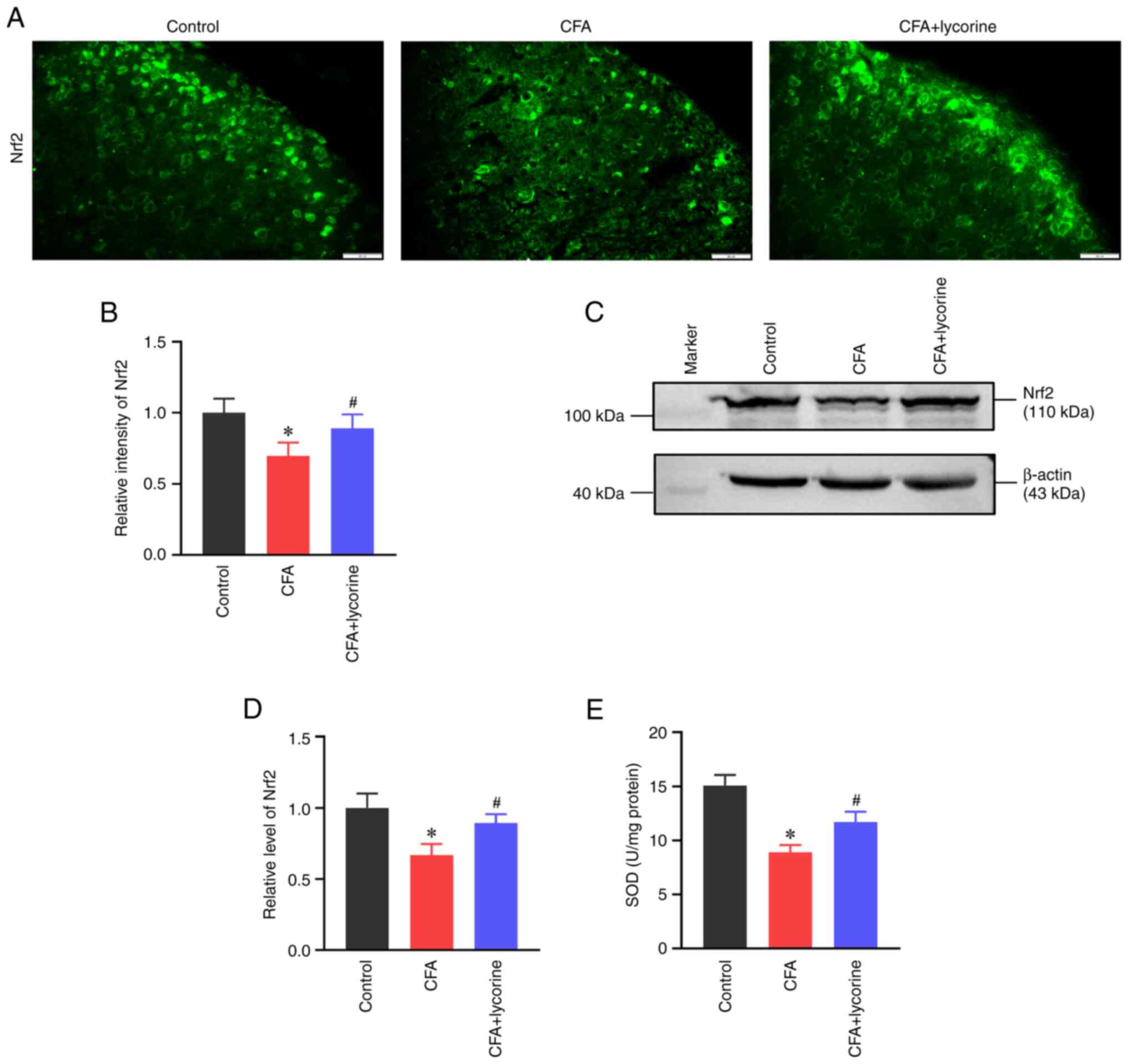
6
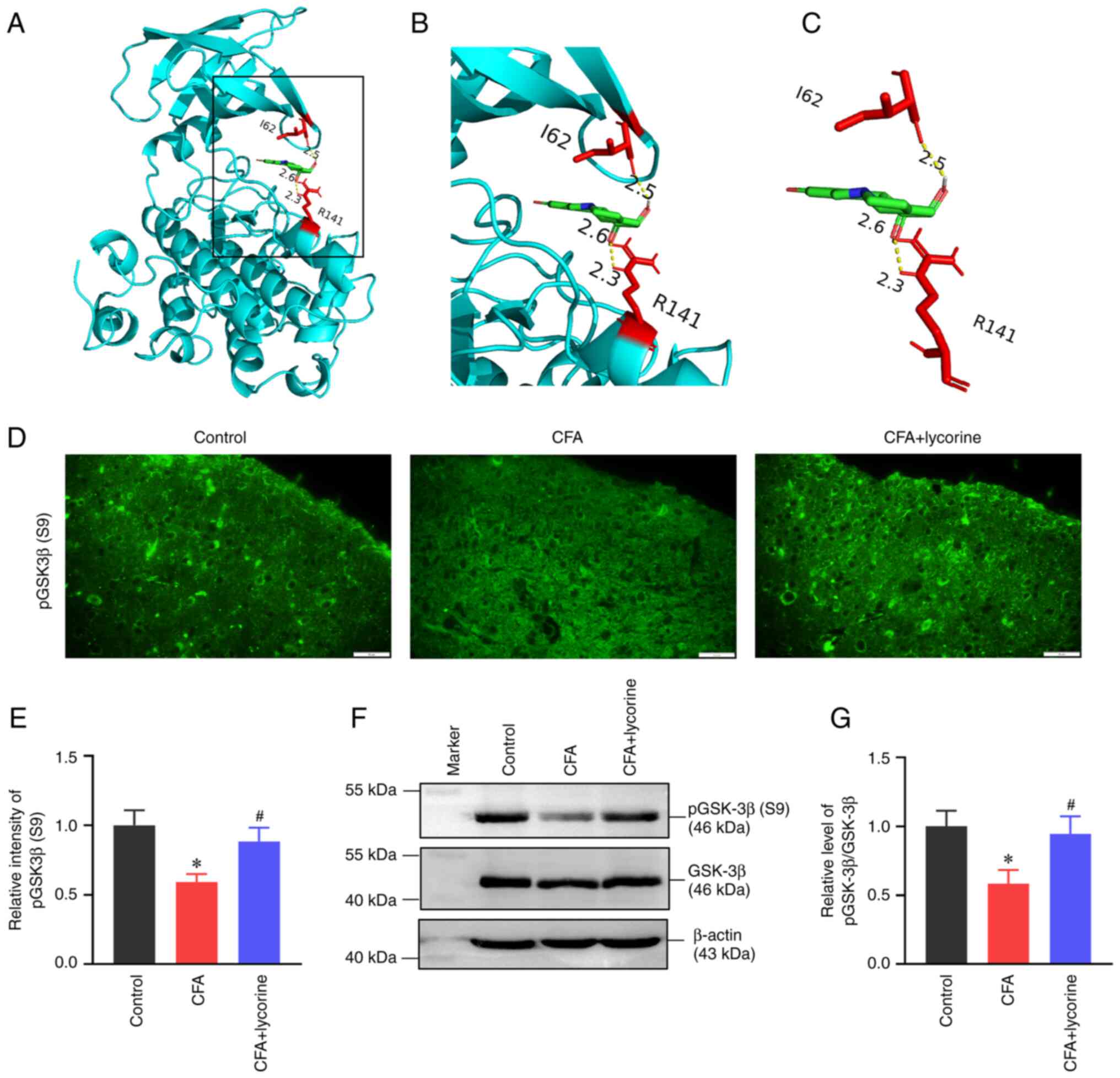
|
Leuchtweis J, Segond von Banchet G, Eitner
A, Ebbinghaus M and Schaible HG: Pain-related behaviors associated
with persistence of mechanical hyperalgesia after antigen-induced
arthritis in rats. Pain. 161:1571–1583. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Adami G, Gerratana E, Atzeni F, Benini C,
Vantaggiato E, Rotta D, Idolazzi L, Rossini M, Gatti D and Fassio
A: Is central sensitization an important determinant of functional
disability in patients with chronic inflammatory arthritides? Ther
Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 13(1759720X21993252)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Woolf CJ: Central sensitization:
Implications for the diagnosis and treatment of pain. Pain. 152
(Suppl 3):S2–S15. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Amodeo G, Franchi S, Galimberti G, Comi L,
D'Agnelli S, Baciarello M, Bignami EG and Sacerdote P:
Osteoarthritis pain in old mice aggravates neuroinflammation and
frailty: The positive effect of morphine treatment. Biomedicines.
10(2847)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kwon HS and Koh SH: Neuroinflammation in
neurodegenerative disorders: The roles of microglia and astrocytes.
Transl Neurodegener. 9(42)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pfyffer D, Wyss PO, Huber E, Curt A,
Henning A and Freund P: Metabolites of neuroinflammation relate to
neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. Neurology. 95:e805–e814.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Albrecht DS, Ahmed SU, Kettner NW, Borra
RJH, Cohen-Adad J, Deng H, Houle TT, Opalacz A, Roth SA, Melo MFV,
et al: Neuroinflammation of the spinal cord and nerve roots in
chronic radicular pain patients. Pain. 159:968–977. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Im HJ, Kim JS, Li X, Kotwal N, Sumner DR,
van Wijnen AJ, Davis FJ, Yan D, Levine B, Henry JL, et al:
Alteration of sensory neurons and spinal response to an
experimental osteoarthritis pain model. Arthritis Rheum.
62:2995–3005. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Matsushita T, Otani K, Oto Y, Takahashi Y,
Kurosaka D and Kato F: Sustained microglial activation in the area
postrema of collagen-induced arthritis mice. Arthritis Res Ther.
23(273)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Li Y, Yang Y, Guo J, Guo X, Feng Z and
Zhao X: Spinal NF-kB upregulation contributes to hyperalgesia in a
rat model of advanced osteoarthritis. Mol Pain.
16(1744806920905691)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ansari MY, Ahmad N and Haqqi TM: Oxidative
stress and inflammation in osteoarthritis pathogenesis: Role of
polyphenols. Biomed Pharmacother. 129(110452)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Quiñonez-Flores CM, González-Chávez SA,
Del Río Nájera D and Pacheco-Tena C: Oxidative stress relevance in
the pathogenesis of the rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review.
Biomed Res Int. 2016(6097417)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Ediz L, Hiz O, Ozkol H, Gulcu E, Toprak M
and Ceylan MF: Relationship between anti-CCP antibodies and oxidant
and anti-oxidant activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Int J Med Sci. 8:139–147. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Poulet B and Beier F: Targeting oxidative
stress to reduce osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther.
18(32)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen L, Tian Q, Shi Z, Qiu Y, Lu Q and Liu
C: Melatonin alleviates cardiac function in sepsis-caused
myocarditis via maintenance of mitochondrial function. Front Nutr.
8(754235)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dong D, Wu J, Sheng L, Gong X, Zhang Z and
Yu C: FUNDC1 induces apoptosis and autophagy under oxidative stress
via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in cataract lens cells. Curr Eye Res.
47:547–554. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Shen J, Zhang T, Cheng Z, Zhu N, Wang H,
Lin L, Wang Z, Yi H and Hu M: Lycorine inhibits glioblastoma
multiforme growth through EGFR suppression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
37(157)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xiao H, Xu X, Du L, Li X, Zhao H, Wang Z,
Zhao L, Yang Z, Zhang S, Yang Y and Wang C: Lycorine and organ
protection: Review of its potential effects and molecular
mechanisms. Phytomedicine. 104(154266)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Roy M, Liang L, Xiao X, Feng P, Ye M and
Liu J: Lycorine: A prospective natural lead for anticancer drug
discovery. Biomed Pharmacother. 107:615–624. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Liu J, Li Y, Tang LJ, Zhang GP and Hu WX:
Treatment of lycorine on SCID mice model with human APL cells.
Biomed Pharmacother. 61:229–234. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Çitoğlu GS, Acikara OB, Yilmaz BS and
Ozbek H: Evaluation of analgesic, anti-inflammatory and
hepatoprotective effects of lycorine from Sternbergia fisheriana
(Herbert) Rupr. Fitoterapia. 83:81–87. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang G, Huang K, Dong Y, Chen S, Zhang J,
Wang J, Xie Z, Lin X, Fang X and Fan S: Lycorine suppresses
endplate-chondrocyte degeneration and prevents intervertebral disc
degeneration by inhibiting NF-κB signalling pathway. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 45:1252–1269. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liang Q, Cai W, Zhao Y, Xu H, Tang H, Chen
D, Qian F and Sun L: Lycorine ameliorates bleomycin-induced
pulmonary fibrosis via inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation and
pyroptosis. Pharmacol Res. 158(104884)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wu J, Fu Y, Wu YX, Wu ZX, Wang ZH and Li
P: Lycorine ameliorates isoproterenol-induced cardiac dysfunction
mainly via inhibiting inflammation, fibrosis, oxidative stress and
apoptosis. Bioengineered. 12:5583–5594. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Parvathy SS and Masocha W: Gait analysis
of C57BL/6 mice with complete Freund's adjuvant-induced arthritis
using the CatWalk system. BMC Musculoskelet Disord.
14(14)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chen S, Gu Y, Dai Q, He Y and Wang J:
Spinal miR-34a regulates inflammatory pain by targeting SIRT1 in
complete Freund's adjuvant mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
516:1196–1203. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kumar VL and Roy S: Calotropis procera
latex extract affords protection against inflammation and oxidative
stress in Freund's complete adjuvant-induced monoarthritis in rats.
Mediators Inflamm. 2007(47523)2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Xu SF, Du GH, Abulikim K, Cao P and Tan
HB: Verification and defined dosage of sodium pentobarbital for a
urodynamic study in the possibility of survival experiments in
female rat. Biomed Res Int. 2020(6109497)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Laferriere CA, Leung VS and Pang DS:
Evaluating intrahepatic and intraperitoneal sodium pentobarbital or
ethanol for mouse euthanasia. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 59:264–268.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zatroch KK, Knight CG, Reimer JN and Pang
DS: Refinement of intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital
for euthanasia in laboratory rats (Rattus norvegicus). BMC Vet Res.
13(60)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Robledo-González LE, Martínez-Martínez A,
Vargas-Muñoz VM, Acosta-González RI, Plancarte-Sánchez R,
Anaya-Reyes M, Fernández Del Valle-Laisequilla C, Reyes-García JG
and Jiménez-Andrade JM: Repeated administration of mazindol reduces
spontaneous pain-related behaviors without modifying bone density
and microarchitecture in a mouse model of complete Freund's
adjuvant-induced knee arthritis. J Pain Res. 10:1777–1786.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Chen S, Fang XQ, Zhang JF, Ma Y, Tang XZ,
Zhou ZJ, Wang JY, Qin A and Fan SW: Lycorine protects cartilage
through suppressing the expression of matrix metalloprotenases in
rat chondrocytes and in a mouse osteoarthritis model. Mol Med Rep.
14:3389–3396. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Luo H, Liu L, Zhao JJ, Mi XF, Wang QJ and
Yu M: Effects of oxaliplatin on inflammation and intestinal floras
in rats with colorectal cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
24:10542–10549. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Hao M, Tang Q, Wang B, Li Y, Ding J, Li M,
Xie M and Zhu H: Resveratrol suppresses bone cancer pain in rats by
attenuating inflammatory responses through the AMPK/Drp1 signaling.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 52:231–240. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Mao Y, Wang C, Tian X, Huang Y, Zhang Y,
Wu H, Yang S, Xu K, Liu Y, Zhang W, et al: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress contributes to nociception via neuroinflammation in a murine
bone cancer pain model. Anesthesiology. 132:357–372.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Shi X, Bai H, Wang J, Wang J, Huang L, He
M, Zheng X, Duan Z, Chen D, Zhang J, et al: Behavioral assessment
of sensory, motor, emotion, and cognition in rodent models of
intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Neurol. 12(667511)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Chatterjee P, Pedrini S, Stoops E, Goozee
K, Villemagne VL, Asih PR, Verberk IMW, Dave P, Taddei K, Sohrabi
HR, et al: Plasma glial fibrillary acidic protein is elevated in
cognitively normal older adults at risk of Alzheimer's disease.
Transl Psychiatry. 11(27)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kelley N, Jeltema D, Duan Y and He Y: The
NLRP3 inflammasome: An overview of mechanisms of activation and
regulation. Int J Mol Sci. 20(3328)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lee MJ, Agrahari G, Kim HY, An EJ, Chun
KH, Kang H, Kim YS, Bang CW, Tak LJ and Kim TY: Extracellular
superoxide dismutase prevents skin aging by promoting collagen
production through the activation of AMPK and Nrf2/HO-1 cascades. J
Invest Dermatol. 141:2344–2353.e7. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Chen Y, Maejima Y, Shirakabe A, Yamamoto
T, Ikeda Y, Sadoshima J and Zhai P: Ser9 phosphorylation of GSK-3β
promotes aging in the heart through suppression of autophagy. J
Cardiovasc Aging. 1(9)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yuan L, Liu C, Wan Y, Yan H and Li T:
Effect of HDAC2/Inpp5f on neuropathic pain and cognitive function
through regulating PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signal pathway in rats with
neuropathic pain. Exp Ther Med. 18:678–684. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Xu W, Zhu M, Yuan S and Yu W: Spinal CXCL5
contributes to nerve injury-induced neuropathic pain via modulating
GSK-3β phosphorylation and activity in rats. Neurosci Lett.
634:52–59. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Rashvand M, Danyali S and Manaheji H: The
potential role of glycogen synthase kinase-3β in neuropathy-induced
apoptosis in spinal cord. Basic Clin Neurosci. 11:15–30.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Peng Z, Zha L, Yang M, Li Y, Guo X and
Feng Z: Effects of ghrelin on pGSK-3β and β-catenin expression when
protects against neuropathic pain behavior in rats challenged with
chronic constriction injury. Sci Rep. 9(14664)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Yang HY, Zhang F, Cheng ML, Wu J, Xie M,
Yu LZ, Liu L, Xiong J and Zhu HL: Glycogen synthase kinase-3β
inhibition decreases inflammation and relieves cancer induced bone
pain via reducing Drp1-mediated mitochondrial damage. J Cell Mol
Med. 26:3965–3976. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Shu Z, Miao X, Tang T, Zhan P, Zeng L and
Jiang Y: The GSK-3β/β-catenin signaling pathway is involved in
HMGB1-induced chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage matrix
degradation. Int J Mol Med. 45:769–778. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Shin D, Lee SC, Heo YS, Lee WY, Cho YS,
Kim YE, Hyun YL, Cho JM, Lee YS and Ro S: Design and synthesis of
7-hydroxy-1H-benzoimidazole derivatives as novel inhibitors of
glycogen synthase kinase-3beta. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 17:5686–5689.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Dutta M, Tareq AM, Rakib A, Mahmud S, Sami
SA, Mallick J, Islam MN, Majumder M, Uddin MZ, Alsubaie A, et al:
Phytochemicals from leucas zeylanica targeting main protease of
SARS-CoV-2: Chemical profiles, molecular docking, and molecular
dynamics simulations. Biology (Basel). 10(789)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Li H, Zhang W, Lou Q, Chang Y, Lin Z and
Lou L: XueFu ZhuYu Decoction alleviates cardiopulmonary
bypass-induced NLRP3 inflammasome-dependent pyroptosis by
inhibiting IkB-α/NF-κB pathway in acute lung injury rats. Evid
Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022(6248870)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Lee KM, Kang BS, Lee HL, Son SJ, Hwang SH,
Kim DS, Park JS and Cho HJ: Spinal NF-kB activation induces COX-2
upregulation and contributes to inflammatory pain hypersensitivity.
Eur J Neurosci. 19:3375–3381. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Liu J, Sun S, Zhou C, Sun Z, Wang Q and
Sun C: In vitro and in vivo anticancer activity of Lycorine in
prostate cancer by inhibiting NF-κB signaling pathway. J Cancer.
13:3151–3159. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Ge X, Meng X, Fei D, Kang K, Wang Q and
Zhao M: Lycorine attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury through the HMGB1/TLRs/NF-κB pathway. 3 Biotech.
10(369)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Steinbrecher KA, Wilson W III, Cogswell PC
and Baldwin AS: Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta functions to specify
gene-specific, NF-kappaB-dependent transcription. Mol Cell Biol.
25:8444–8455. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Medunjanin S, Schleithoff L, Fiegehenn C,
Weinert S, Zuschratter W and Braun-Dullaeus RC: GSK-3β controls
NF-kappaB activity via IKKγ/NEMO. Sci Rep. 6(38553)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Rada P, Rojo AI, Chowdhry S, McMahon M,
Hayes JD and Cuadrado A: SCF/{beta}-TrCP promotes glycogen synthase
kinase 3-dependent degradation of the Nrf2 transcription factor in
a Keap1-independent manner. Mol Cell Biol. 31:1121–1133.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Chen X, Liu Y, Zhu J, Lei S, Dong Y, Li L,
Jiang B, Tan L, Wu J, Yu S and Zhao Y: GSK-3β downregulates Nrf2 in
cultured cortical neurons and in a rat model of cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion. Sci Rep. 6(20196)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Arendt-Nielsen L, Morlion B, Perrot S,
Dahan A, Dickenson A, Kress HG, Wells C, Bouhassira D and Drewes
AM: Assessment and manifestation of central sensitisation across
different chronic pain conditions. Eur J Pain. 22:216–241.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Lluch E, Nijs J, Courtney CA, Rebbeck T,
Wylde V, Baert I, Wideman TH, Howells N and Skou ST: Clinical
descriptors for the recognition of central sensitization pain in
patients with knee osteoarthritis. Disabil Rehabil. 40:2836–2845.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Pan TT, Pan F, Gao W, Hu SS and Wang D:
Involvement of macrophages and spinal microglia in osteoarthritis
pain. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 23(29)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|