|
1
|
Behl T, Upadhyay T, Singh S, Chigurupati
S, Alsubayiel AM, Mani V, Vargas-De-La-Cruz C, Uivarosan D, Bustea
C, Sava C, et al: Polyphenols targeting MAPK mediated oxidative
stress and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Molecules.
26(6570)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Dar WR, Mir IA, Siddiq S, Nadeem M and
Singh G: The assessment of fatigue in rheumatoid arthritis patients
and its impact on their quality of life. Clin Pract. 12:591–598.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Alturaiki W, Alhamad A, Alturaiqy M, Mir
SA, Iqbal D, Bin Dukhyil AA, Alaidarous M, Alshehri B, Alsagaby SA,
Almalki SG, et al: Assessment of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-8, and CCL
5 levels in newly diagnosed Saudi patients with rheumatoid
arthritis. Int J Rheum Dise. 25:1013–1019. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Wang X, Fan D, Cao X, Ye Q, Wang Q, Zhang
M and Xiao C: The role of reactive oxygen species in the rheumatoid
arthritis-associated synovial microenvironment. Antioxidants
(Basel). 11(1153)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mateen S, Zafar A, Moin S, Khan AQ and
Zubair S: Understanding the role of cytokines in the pathogenesis
of rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Chim Acta. 455:161–171.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zeng Y, Yi R and Cullen BR: MicroRNAs and
small interfering RNAs can inhibit mRNA expression by similar
mechanisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 100:9779–9784. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zeng Y, Wagner EJ and Cullen BR: Both
natural and designed micro RNAs can inhibit the expression of
cognate mRNAs when expressed in human cells. Mol Cell. 9:1327–1333.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Tomso DJ, Liu X and Bell DA:
Single nucleotide polymorphism in transcriptional regulatory
regions and expression of environmentally responsive genes. Toxicol
App Pharmacol. 207:84–90. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Jadidi N, Alesaeidi S, Arab F, Pakzad B,
Siasi E and Esmaeilzadeh E: MiRNA-binding site polymorphism in
IL-15RA gene in rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus
erythematosus: Correlation with disease risk and clinical
characteristics. Clin Rheumatol. 41:3487–3494. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Zeinalzadeh S, Kheradmand N, Rasouli G,
Esmaeilzadeh E, Pakzad B, Behroozi J, Chamanara M, Zoshk MY,
Ehtesham N and Sabet MN: Association of a miRNA-binding site
polymorphism in IL-16 gene with disease risk and clinical
characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus
erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. 41:2189–2196. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
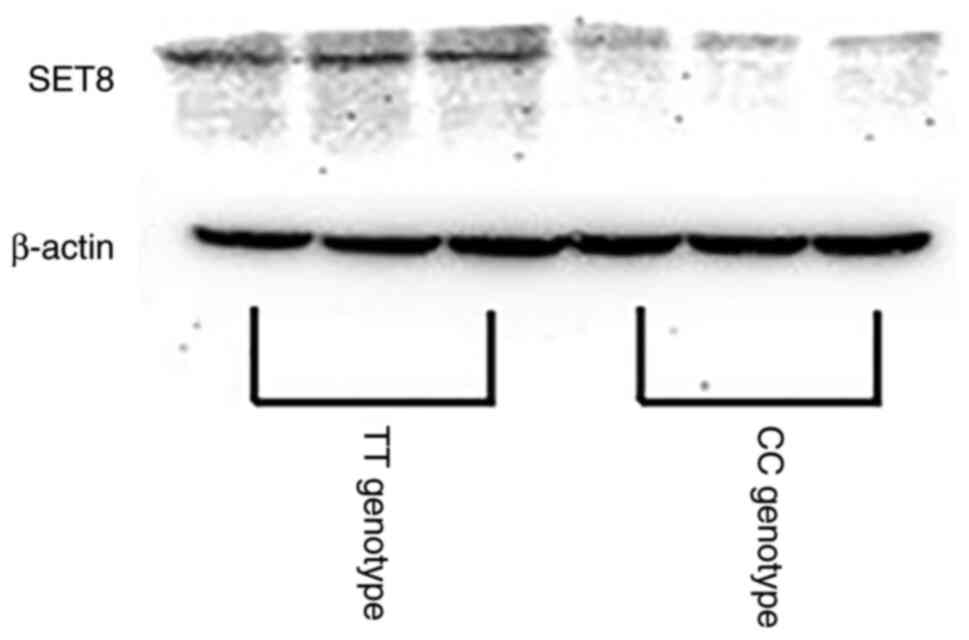
Chen X, Ding X, Wu Q, Qi J, Zhu M and Miao
C: Monomethyltransferase SET8 facilitates hepatocellular carcinoma
growth by enhancing aerobic glycolysis. Cell Death Dis.
10(312)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Fang J, Feng Q, Ketel CS, Wang H, Cao R,
Xia L, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Simon JA and Zhang Y:
Purification and functional characterization of SET8, a nucleosomal
histone H4-lysine 20-specific methyltransferase. Curr Biol.
12:1086–1099. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Nishioka K, Rice JC, Sarma K,
Erdjument-Bromage H, Werner J, Wang Y, Chuikov S, Valenzuela P,
Tempst P, Steward R, et al: PR-Set7 is a nucleosome-specific
methyltransferase that modifies lysine 20 of histone H4 and is
associated with silent chromatin. Mol Cell. 9:1201–1213.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wu S, Wang W, Kong X, Congdon LM, Yokomori
K, Kirschner MW and Rice JC: Dynamic regulation of the PR-Set7
histone methyltransferase is required for normal cell cycle
progression. Genes Dev. 24:2531–2542. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Singh V, Prakhar P, Rajmani RS, Mahadik K,
Borbora SM and Balaji KN: Histone methyltransferase SET8
epigenetically reprograms host immune responses to assist
mycobacterial survival. J Infect Dis. 216:477–488. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang XP, Cheng QY, Gu MM, Leng RX, Fan YG,
Li BZ and Ye DQ: Diagnostic accuracy of anti-keratin antibody for
rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol.
38:1841–1849. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Moll R, Divo M and Langbein L: The human
keratins: Biology and pathology. Histochem Cell Biol. 129:705–733.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sha Z, Lai R, Zhang X, Zhao Y, Wu J, Geng
C and Guo Z: A polymorphism at the microRNA binding Site in the 3'
untranslated region of KRT81 is associated with breast cancer. DNA
and Cell Biol. 39:1886–1894. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Zhang K, Liang Y, Zhang W, Zeng N, Tang S
and Tian R: KRT81 knockdown inhibits malignant progression of
melanoma through regulating interleukin-8. DNA Cell Biol.
40:1290–1297. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J,
Felson DT, Bingham CO III, Birnbaum NS, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP,
Cohen MD, et al: 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria:
An American college of rheumatology/European league against
rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 62:2569–2581.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fransen J and van Riel PL: The disease
activity score and the EULAR response criteria. Rheum Dis Clin
North Am. 35:745–757, vii-viii. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
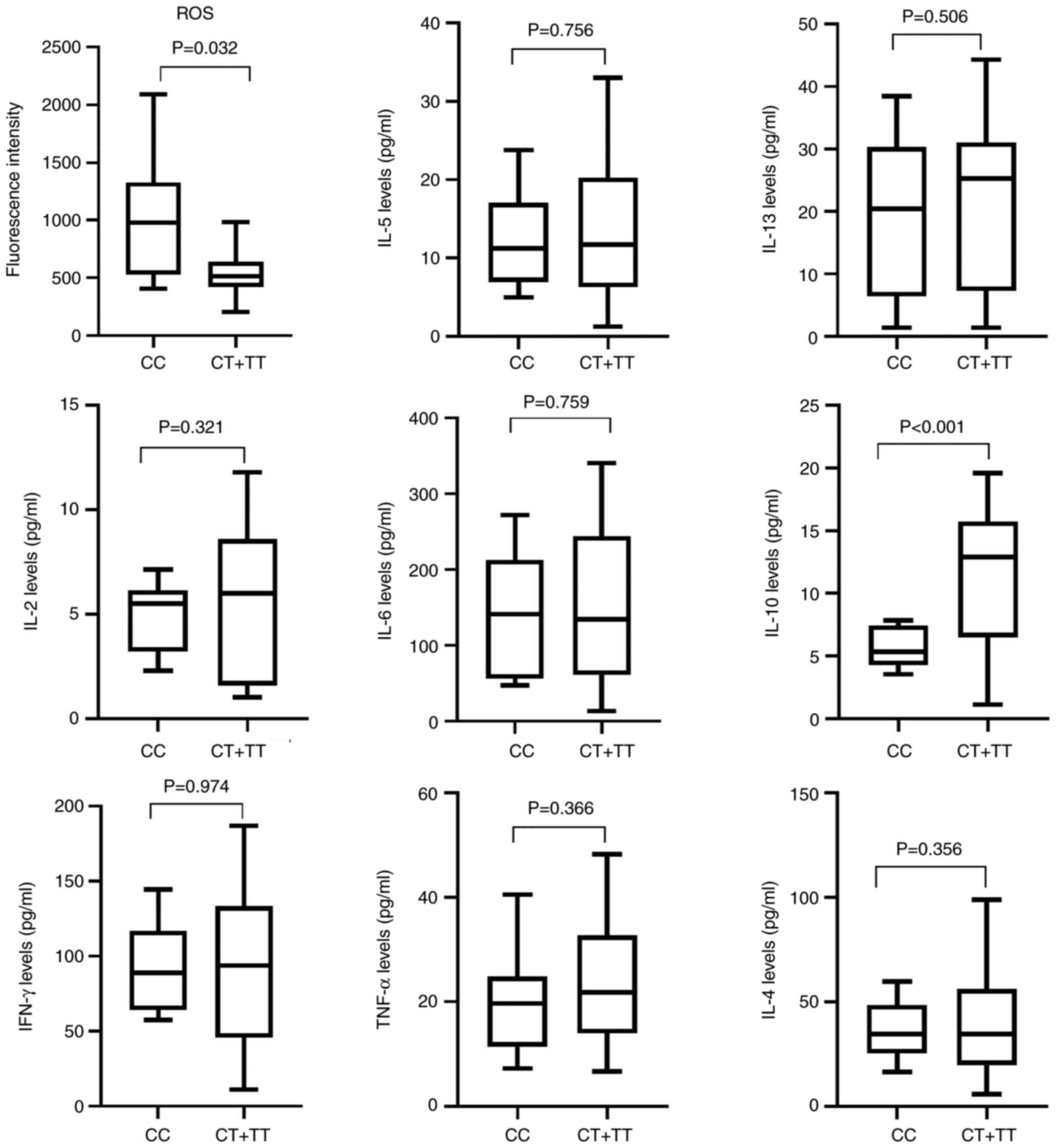
Mukhopadhyay K, De S, Kundu S, Ghosh P,
Chatterjee S and Chatterjee M: Evaluation of levels of oxidative
stress as a potential biomarker in patients with rheumatoid
arthritis. J Family Med Prim Care. 10:1981–1986. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mateen S, Moin S, Khan AQ, Zafar A and
Fatima N: Increased reactive oxygen species formation and oxidative
stress in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One.
11(e0152925)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531.
2004.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Gene. 12:861–874. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zhou M, Jiang B, Xiong M and Zhu X: An
updated meta-analysis of the associations between microRNA
polymorphisms and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis. Front
Physiol. 9(1604)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Papathanasiou I, Mourmoura E, Balis C and
Tsezou A: Impact of miR-SNP rs2910164 on miR-146a expression in
osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Adv Med Sci. 65:78–85. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Song F, Zheng H, Liu B, Wei S, Dai H,
Zhang L, Calin GA, Hao X, Wei Q, Zhang W and Chen K: An
miR-502-binding site single-nucleotide polymorphism in the
3'-untranslated region of the SET8 gene is associated with early
age of breast cancer onset. Clin Cancer Res. 15:6292–6300.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chen X, Wu Q, Jiang H, Wang J, Zhao Y, Xu
Y and Zhu M: SET8 is involved in the regulation of hyperglycemic
memory in human umbilical endothelial cells. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin(Shanghai). 50:635–642. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Balogh E, Veale DJ, McGarry T, Orr C,
Szekanecz Z, Ng CT, Fearon U and Biniecka M: Oxidative stress
impairs energy metabolism in primary cells and synovial tissue of
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arth Res Ther.
20(95)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Mateen S, Moin S, Zafar A and Khan AQ:
Redox signaling in rheumatoid arthritis and the preventive role of
polyphenols. Clin Chim Acta. 463:4–10. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Bauerová K and Bezek A: Role of reactive
oxygen and nitrogen species in etiopathogenesis of rheumatoid
arthritis. Gen Physiol Biophys. 18:15–20. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Broeren MG, de Vries M, Bennink MB, Arntz
OJ, Blom AB, Koenders MI, van Lent PL, van der Kraan PM, van den
Berg WB and van de Loo FA: Disease-regulated gene therapy with
anti-inflammatory interleukin-10 under the control of the CXCL10
promoter for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Gene Ther.
27:244–254. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Tian S, Yan Y, Qi X, Li X and Li Z:
Treatment of type II collagen-induced rat rheumatoid arthritis
model by interleukin 10 (IL10)-mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs). Med
Sci Monit. 25:2923–2934. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Henningsson L, Eneljung T, Jirholt P,
Tengvall S, Lidberg U, van den Berg WB, van de Loo FA and Gjertsson
I: Disease-dependent local IL-10 production ameliorates collagen
induced arthritis in mice. PLoS One. 7(e49731)2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|