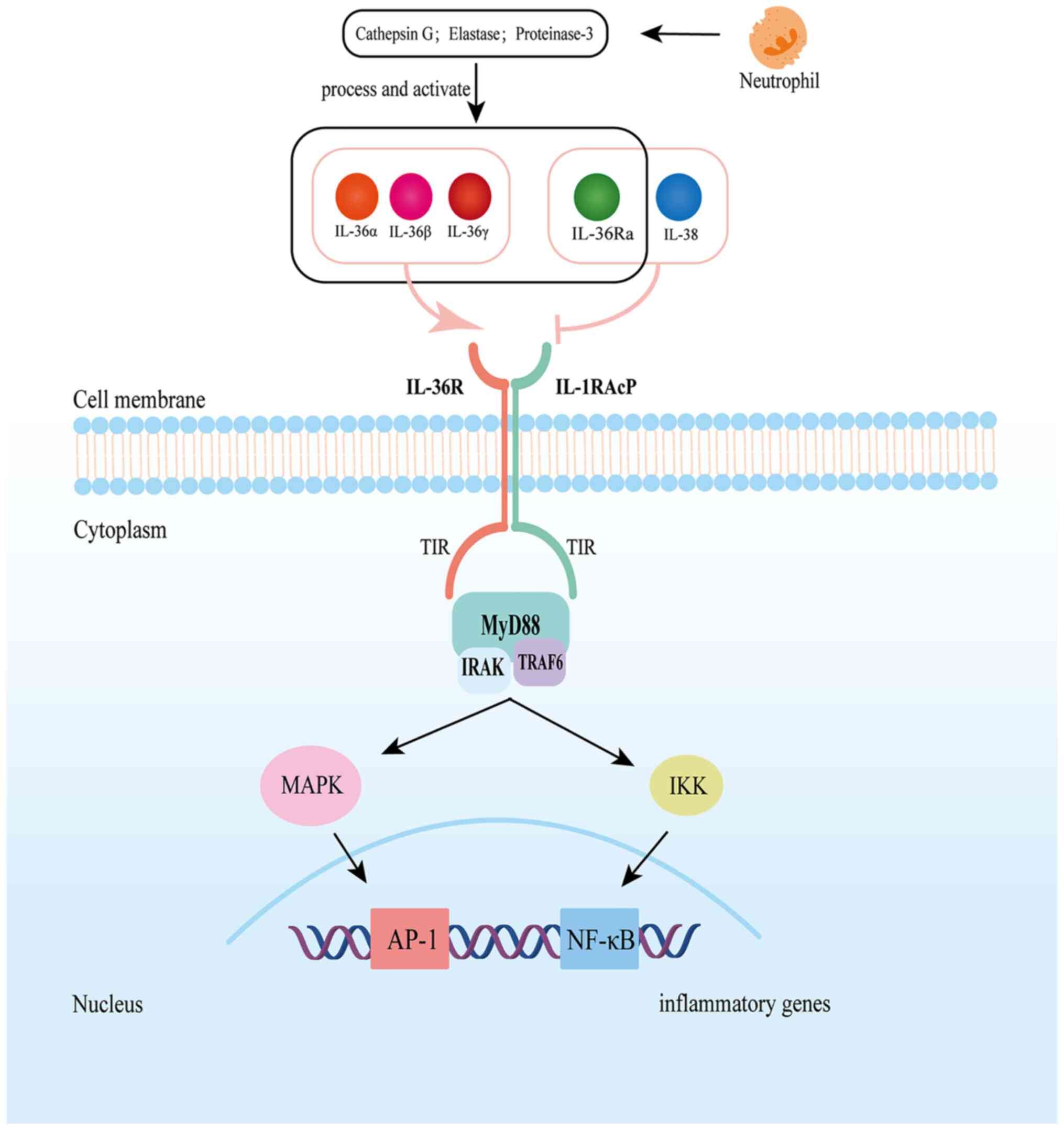
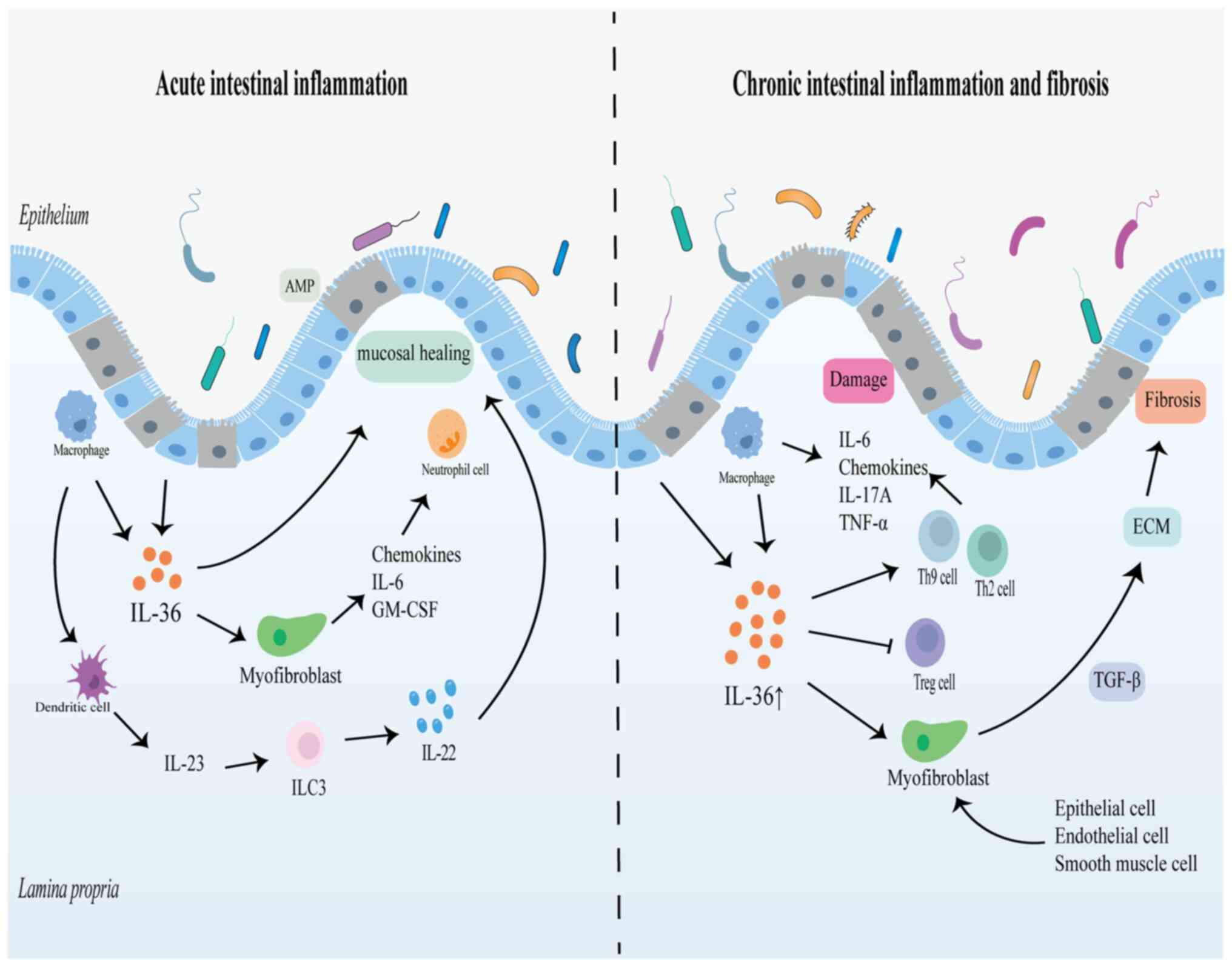
|
1
|
Taylor SL, Renshaw BR, Garka KE, Smith DE
and Sims JE: Genomic organization of the interleukin-1 locus.
Genomics. 79:726–733. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Smith DE, Renshaw BR, Ketchem RR, Kubin M,
Garka KE and Sims JE: Four new members expand the interleukin-1
superfamily. J Biol Chem. 275:1169–1175. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Dunn E, Sims JE, Nicklin MJ and O'Neill
LA: Annotating genes with potential roles in the immune system: Six
new members of the IL-1 family. Trends Immunol. 22:533–536.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Dinarello C, Arend W, Sims J, Smith D,
Blumberg H, O'Neill L, Goldbach-Mansky R, Pizarro T, Hoffman H,
Bufler P, et al: IL-1 family nomenclature. Nat Immunol.
11(973)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sims JE, Nicklin MJ, Bazan JF, Barton JL,
Busfield SJ, Ford JE, Kastelein RA, Kumar S, Lin H, Mulero JJ, et
al: A new nomenclature for IL-1-family genes. Trends Immunol.
22:536–537. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Henry CM, Sullivan GP, Clancy DM, Afonina
IS, Kulms D and Martin SJ: Neutrophil-derived proteases escalate
inflammation through activation of IL-36 family cytokines. Cell
Rep. 14:708–722. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Macleod T, Doble R, McGonagle D, Wasson
CW, Alase A, Stacey M and Wittmann M: Neutrophil elastase-mediated
proteolysis activates the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-36 receptor
antagonist. Sci Rep. 6(24880)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bassoy EY, Towne JE and Gabay C:
Regulation and function of interleukin-36 cytokines. Immunol Rev.
281:169–178. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Gabay C and Towne JE: Regulation and
function of interleukin-36 cytokines in homeostasis and
pathological conditions. J Leukocyte Biol. 97:645–652.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Towne JE, Garka KE, Renshaw BR, Virca GD
and Sims JE: Interleukin (IL)-1F6, IL-1F8, and IL-1F9 signal
through IL-1Rrp2 and IL-1RAcP to activate the pathway leading to
NF-kappaB and MAPKs. J Biol Chem. 279:13677–13688. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Towne JE, Renshaw BR, Douangpanya J,
Lipsky BP, Shen M, Gabel CA and Sims JE: Interleukin-36 (IL-36)
ligands require processing for full agonist (IL-36α, IL-36β, and
IL-36γ) or antagonist (IL-36Ra) activity. J Biol Chem.
286:42594–42602. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Mullard A: FDA approves first anti-IL-36
receptor antibody for rare skin disease. Nat Rev Drug Discov.
21(786)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Ding L, Wang X, Hong X, Lu L and Liu D:
IL-36 cytokines in autoimmunity and inflammatory disease.
Oncotarget. 9:2895–2901. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Boutet MA, Bart G, Penhoat M, Amiaud J,
Brulin B, Charrier C, Morel F, Lecron JC, Rolli-Derkinderen M,
Bourreille A, et al: Distinct expression of interleukin (IL)-36α, β
and γ, their antagonist IL-36Ra and IL-38 in psoriasis, rheumatoid
arthritis and Crohn's disease. Clin Exp Immunol. 184:159–173.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Scheibe K, Kersten C, Schmied A, Vieth M,
Primbs T, Carlé B, Knieling F, Claussen J, Klimowicz AC, Zheng J,
et al: Inhibiting interleukin 36 receptor signaling reduces
fibrosis in mice with chronic intestinal inflammation.
Gastroenterology. 156:1082–1097.e11. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ngo VL, Abo H, Maxim E, Harusato A, Geem
D, Medina-Contreras O, Merlin D, Gewirtz AT, Nusrat A and Denning
TL: A cytokine network involving IL-36γ, IL-23, and IL-22 promotes
antimicrobial defense and recovery from intestinal barrier damage.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 115:E5076–E5085. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Queen D, Ediriweera C and Liu L: Function
and regulation of IL-36 signaling in inflammatory diseases and
cancer development. Front Cell Dev Biol. 7(317)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Xu P, Guan H, Xiao W and Sun L: The role
of IL-36 subfamily in intestinal disease. Biochem Soc Trans.
50:223–230. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen F, Qu M, Zhang F, Tan Z, Xia Q,
Hambly BD, Bao S and Tao K: IL-36 s in the colorectal cancer: Is
interleukin 36 good or bad for the development of colorectal
cancer? Bmc Cancer. 20(92)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Bao S, Hu R and Hambly BD: IL-34, IL-36
and IL-38 in colorectal cancer-key immunoregulators of
carcinogenesis. Biophys Rev. 12:925–930. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Byrne J, Baker K, Houston A and Brint E:
IL-36 cytokines in inflammatory and malignant diseases: Not the new
kid on the block anymore. Cell Mol Life Sci. 78:6215–6227.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhou L and Todorovic V: Interleukin-36:
Structure, signaling and function. Adv Exp Med Biol. 21:191–210.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Namba T, Ichii O, Nakamura T, Masum MA,
Otani Y, Hosotani M, Elewa YHA and Kon Y: Compartmentalization of
interleukin 36 subfamily according to inducible and constitutive
expression in the kidneys of a murine autoimmune nephritis model.
Cell Tissue Res. 386:59–77. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Buhl AL and Wenzel J: Interleukin-36 in
infectious and inflammatory skin diseases. Front Immunol.
10(1162)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Mai SZ, Li CJ, Xie XY, Xiong H, Xu M, Zeng
FQ, Guo Q and Han YF: Increased serum IL-36α and IL-36γ levels in
patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: Association with
disease activity and arthritis. Int Immunopharmacol. 58:103–108.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chen WJ, Yu X, Yuan XR, Chen BJ, Cai N,
Zeng S, Sun YS and Li HW: The role of IL-36 in the
pathophysiological processes of autoimmune diseases. Front
Pharmacol. 12(727956)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Dinarello CA: The IL-1 family of cytokines
and receptors in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 15:612–632.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Vigne S, Palmer G, Lamacchia C, Martin P,
Talabot-Ayer D, Rodriguez E, Ronchi F, Sallusto F, Dinh H, Sims JE
and Gabay C: IL-36R ligands are potent regulators of dendritic and
T cells. Blood. 118:5813–5823. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Foster AM, Baliwag J, Chen CS, Guzman AM,
Stoll SW, Gudjonsson JE, Ward NL and Johnston A: IL-36 promotes
myeloid cell infiltration, activation, and inflammatory activity in
skin. J Immunol. 192:6053–6061. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Carrier Y, Ma HL, Ramon HE, Napierata L,
Small C, O'Toole M, Young DA, Fouser LA, Nickerson-Nutter C,
Collins M, et al: Inter-regulation of Th17 cytokines and the IL-36
cytokines in vitro and in vivo: implications in psoriasis
pathogenesis. J Invest Dermatol. 131:2428–2437. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Catapano M, Vergnano M, Romano M, Mahil
SK, Choon SE, Burden AD, Young HS, Carr IM, Lachmann HJ, Lombardi
G, et al: IL-36 promotes systemic IFN-I responses in severe forms
of psoriasis. J Invest Dermatol. 140:816–826. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Baker KJ, Brint E and Houston A:
Transcriptomic and functional analyses reveal a tumour-promoting
role for the IL-36 receptor in colon cancer and crosstalk between
IL-36 signalling and the IL-17/ IL-23 axis. Brit J Cancer.
128:735–747. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Aoyagi T, Newstead MW, Zeng X, Nanjo Y,
Peters-Golden M, Kaku M and Standiford TJ: Interleukin-36γ and
IL-36 receptor signaling mediate impaired host immunity and lung
injury in cytotoxic Pseudomonas aeruginosa pulmonary infection:
Role of prostaglandin E2. PLoS Pathog. 13(e1006737)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gao Y, Wen Q, Hu S, Zhou X, Xiong W, Du X,
Zhang L, Fu Y, Yang J, Zhou C, et al: IL-36γ promotes killing of
mycobacterium tuberculosis by macrophages via WNT5A-induced
noncanonical WNT signaling. J Immunol. 203:922–935. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kovach MA, Singer B, Martinez-Colon G,
Newstead MW, Zeng X, Mancuso P, Moore TA, Kunkel SL, Peters-Golden
M, Moore BB and Standiford TJ: IL-36γ is a crucial proximal
component of protective type-1-mediated lung mucosal immunity in
Gram-positive and -negative bacterial pneumonia. Mucosal Immunol.
10:1320–1334. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yi G, Ybe JA, Saha SS, Caviness G, Raymond
E, Ganesan R, Mbow ML and Kao CC: Structural and functional
attributes of the interleukin-36 receptor. J Biol Chem.
291:16597–16609. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Zarezadeh Mehrabadi A, Aghamohamadi N,
Khoshmirsafa M, Aghamajidi A, Pilehforoshha M, Massoumi R and Falak
R: The roles of interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein in certain
inflammatory conditions. Immunology. 166:38–46. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Zhou L, Todorovic V, Kakavas S, Sielaff B,
Medina L, Wang L, Sadhukhan R, Stockmann H, Richardson PL,
DiGiammarino E, et al: Quantitative ligand and receptor binding
studies reveal the mechanism of interleukin-36 (IL-36) pathway
activation. J Biol Chem. 293:403–411. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ganesan R, Raymond EL, Mennerich D, Woska
JR Jr, Caviness G, Grimaldi C, Ahlberg J, Perez R, Roberts S, Yang
D, et al: Generation and functional characterization of anti-human
and anti-mouse IL-36R antagonist monoclonal antibodies. MAbs.
9:1143–1154. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Onoufriadis A, Simpson MA, Pink AE, Di
Meglio P, Smith CH, Pullabhatla V, Knight J, Spain SL, Nestle FO,
Burden AD, et al: Mutations in IL36RN/IL1F5 are associated with the
severe episodic inflammatory skin disease known as generalized
pustular psoriasis. Am J Hum Genet. 89:432–437. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
van de Veerdonk FL, Stoeckman AK, Wu G,
Boeckermann AN, Azam T, Netea MG, Joosten LA, van der Meer JW, Hao
R, Kalabokis V and Dinarello CA: IL-38 binds to the IL-36 receptor
and has biological effects on immune cells similar to IL-36
receptor antagonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 109:3001–3005.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Li JM, Lu R, Zhang Y, Lin J, Hua X,
Pflugfelder SC and Li DQ: IL-36α/IL-36RA/IL-38 signaling mediates
inflammation and barrier disruption in human corneal epithelial
cells under hyperosmotic stress. Ocul Surf. 22:163–171.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Ngo VL, Kuczma M, Maxim E and Denning TL:
IL-36 cytokines and gut immunity. Immunology. 163:145–154.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Han Y, Huard A, Mora J, da Silva P, Brüne
B and Weigert A: IL-36 family cytokines in protective versus
destructive inflammation. Cell Signal. 75(109773)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Verstak B, Nagpal K, Bottomley SP,
Golenbock DT, Hertzog PJ and Mansell A: MyD88 adapter-like
(Mal)/TIRAP interaction with TRAF6 is critical for TLR2- and
TLR4-mediated NF-kappaB proinflammatory responses. J Biol Chem.
284:24192–24203. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Swindell WR, Beamer MA, Sarkar MK, Loftus
S, Fullmer J, Xing X, Ward NL, Tsoi LC, Kahlenberg MJ, Liang Y and
Gudjonsson JE: RNA-Seq analysis of IL-1B and IL-36 responses in
epidermal keratinocytes identifies a shared MyD88-dependent gene
signature. Front Immunol. 9(80)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Nishida A, Hidaka K, Kanda T, Imaeda H,
Shioya M, Inatomi O, Bamba S, Kitoh K, Sugimoto M and Andoh A:
Increased expression of interleukin-36, a member of the
interleukin-1 cytokine family, in inflammatory bowel disease.
Inflamm Bowel Dis. 22:303–314. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Fonseca-Camarillo G, Furuzawa-Carballeda
J, Iturriaga-Goyon E and Yamamoto-Furusho JK: Differential
expression of IL-36 family members and IL-38 by immune and
nonimmune cells in patients with active inflammatory bowel disease.
Biomed Res Int. 2018(5140691)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Scheibe K, Backert I, Wirtz S, Hueber A,
Schett G, Vieth M, Probst HC, Bopp T, Neurath MF and Neufert C:
IL-36R signalling activates intestinal epithelial cells and
fibroblasts and promotes mucosal healing in vivo. Gut. 66:823–838.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Russell SE, Horan RM, Stefanska AM, Carey
A, Leon G, Aguilera M, Statovci D, Moran T, Fallon PG, Shanahan F,
et al: IL-36α expression is elevated in ulcerative colitis and
promotes colonic inflammation. Mucosal Immunol. 9:1193–1204.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Harusato A, Abo H, Ngo VL, Yi SW,
Mitsutake K, Osuka S, Kohlmeier JE, Li JD, Gewirtz AT, Nusrat A and
Denning TL: IL-36γ signaling controls the induced regulatory T
cell-Th9 cell balance via NFκB activation and STAT transcription
factors. Mucosal Immunol. 10:1455–1467. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Kanda T, Nishida A, Takahashi K, Hidaka K,
Imaeda H, Inatomi O, Bamba S, Sugimoto M and Andoh A:
Interleukin(IL)-36α and IL-36γ induce proinflammatory mediators
from human colonic subepithelial myofibroblasts. Front Med
(Lausanne). 2(69)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Zhu J, Xu Y, Li Z, Liu S, Fu W and Wei Y:
Interleukin-36β exacerbates DSS-induce acute colitis via inhibiting
Foxp3+ regulatory T cell response and increasing Th2
cell response. Int Immunopharmacol. 108(108762)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Xie C, Yan W, Quan R, Chen C, Tu L, Hou X
and Fu Y: Interleukin-38 is elevated in inflammatory bowel diseases
and suppresses intestinal inflammation. Cytokine.
127(154963)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Sonnenberg GF, Fouser LA and Artis D:
Border patrol: Regulation of immunity, inflammation and tissue
homeostasis at barrier surfaces by IL-22. Nat Immunol. 12:383–390.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Longman RS, Diehl GE, Victorio DA, Huh JR,
Galan C, Miraldi ER, Swaminath A, Bonneau R, Scherl EJ and Littman
DR: CX3CR1+ mononuclear phagocytes support
colitis-associated innate lymphoid cell production of IL-22. J Exp
Med. 211:1571–1583. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Medina-Contreras O, Harusato A, Nishio H,
Flannigan KL, Ngo V, Leoni G, Neumann PA, Geem D, Lili LN, Ramadas
RA, et al: Cutting edge: IL-36 receptor promotes resolution of
intestinal damage. J Immunol. 196:34–38. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Parkos CA: Neutrophil-Epithelial
Interactions: A Double-Edged Sword. Am J Pathol. 186:1404–1416.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Luissint AC, Parkos CA and Nusrat A:
Inflammation and the intestinal barrier: Leukocyte-epithelial cell
interactions, cell junction remodeling, and mucosal repair.
Gastroenterology. 151:616–632. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Peterson LW and Artis D: Intestinal
epithelial cells: Regulators of barrier function and immune
homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:141–153. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Melton E and Qiu H: Interleukin-36
cytokine/receptor signaling: A new target for tissue fibrosis. Int
J Mol Sci. 21(6458)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Yun SM, Kim SH and Kim EH: The molecular
mechanism of transforming growth factor-β signaling for intestinal
fibrosis: A mini-review. Front Pharmacol. 10(162)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
D'Alessio S, Ungaro F, Noviello D, Lovisa
S, Peyrin-Biroulet L and Danese S: Revisiting fibrosis in
inflammatory bowel disease: The gut thickens. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 19:169–184. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Elias M, Zhao S, Le HT, Wang J, Neurath
MF, Neufert C, Fiocchi C and Rieder F: IL-36 in chronic
inflammation and fibrosis-bridging the gap? J Clin Invest.
131(e144336)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Chi HH, Hua KF, Lin YC, Chu CL, Hsieh CY,
Hsu YJ, Ka SM, Tsai YL, Liu FC and Chen A: IL-36 signaling
facilitates activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome and IL-23/IL-17
axis in renal inflammation and fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol.
28:2022–2037. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Sommerfeld SD, Cherry C, Schwab RM, Chung
L, Maestas DR Jr, Laffont P, Stein JE, Tam A, Ganguly S, Housseau
F, et al: Interleukin-36γ-producing macrophages drive
IL-17-mediated fibrosis. Sci Immunol. 4(eaax4783)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Nishida A, Inatomi O, Fujimoto T, Imaeda
H, Tani M and Andoh A: Interleukin-36α induces inflammatory
mediators from human pancreatic myofibroblasts via a MyD88
dependent pathway. Pancreas. 46:539–548. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Santacroce G, Lenti MV and Di Sabatino A:
Therapeutic targeting of intestinal fibrosis in Crohn's disease.
Cells. 11(429)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Wang J, Lin S, Brown JM, van Wagoner D,
Fiocchi C and Rieder F: Novel mechanisms and clinical trial
endpoints in intestinal fibrosis. Immunol Rev. 302:211–227.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Takahashi K, Nishida A, Shioya M, Imaeda
H, Bamba S, Inatomi O, Shimizu T, Kitoh K and Andoh A: Interleukin
(IL)-1β is a strong inducer of IL-36γ expression in human colonic
myofibroblasts. PLoS One. 10(e138423)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Shah SC and Itzkowitz SH: Colorectal
cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: Mechanisms and management.
Gastroenterology. 162:715–730.e3. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Hirano T, Hirayama D, Wagatsuma K,
Yamakawa T, Yokoyama Y and Nakase H: Immunological mechanisms in
inflammation-associated colon carcinogenesis. Int J Mol Sci.
21(3062)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Wang ZS, Cong ZJ, Luo Y, Mu YF, Qin SL,
Zhong M and Chen JJ: Decreased expression of interleukin-36α
predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. Int J Clin
Exp Patho. 7:8077–8081. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhao X, Chen X, Shen X, Tang P, Chen C,
Zhu Q, Li M, Xia R, Yang X, Feng C, et al: IL-36β promotes
CD8+ T cell activation and antitumor immune responses by
activating mTORC1. Front Immunol. 10(1803)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Pan QZ, Pan K, Zhao JJ, Chen JG, Li JJ, Lv
L, Wang DD, Zheng HX, Jiang SS, Zhang XF and Xia JC: Decreased
expression of interleukin-36α correlates with poor prognosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy.
62:1675–1685. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Wei X, Yao Y, Wang X, Sun J, Zhao W, Qiu
L, Zhai W, Qi Y, Gao Y and Wu Y: Interleukin-36α inhibits
colorectal cancer metastasis by enhancing the infiltration and
activity of CD8+ T lymphocytes. Int Immunopharmacol.
100(108152)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Wang X, Zhao X, Feng C, Weinstein A, Xia
R, Wen W, Lv Q, Zuo S, Tang P, Yang X, et al: IL-36γ transforms the
tumor microenvironment and promotes type 1 lymphocyte-mediated
antitumor immune responses. Cancer Cell. 28:296–306.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Stolk D, van der Vliet HJ, de Gruijl TD,
van Kooyk Y and Exley MA: Positive & negative roles of innate
effector cells in controlling cancer progression. Front Immunol.
9(1990)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Uzhachenko RV and Shanker A:
CD8+ T lymphocyte and NK cell network: Circuitry in the
cytotoxic domain of immunity. Front Immunol.
10(1906)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Weinstein AM, Chen L, Brzana EA, Patil PR,
Taylor JL, Fabian KL, Wallace CT, Jones SD, Watkins SC, Lu B, et
al: Tbet and IL-36γ cooperate in therapeutic DC-mediated promotion
of ectopic lymphoid organogenesis in the tumor microenvironment.
Oncoimmunology. 6(e1322238)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Lei X, Lei Y, Li JK, Du WX, Li RG, Yang J,
Li J, Li F and Tan HB: Immune cells within the tumor
microenvironment: Biological functions and roles in cancer
immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 470:126–133. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Schumacher TN and Thommen DS: Tertiary
lymphoid structures in cancer. Science.
375(eabf9419)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Weinstein AM, Giraldo NA, Petitprez F,
Julie C, Lacroix L, Peschaud F, Emile JF, Marisa L, Fridman WH,
Storkus WJ and Sautès-Fridman C: Association of IL-36γ with
tertiary lymphoid structures and inflammatory immune infiltrates in
human colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 68:109–120.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Yang M, Giehl E, Feng C, Feist M, Chen H,
Dai E, Liu Z, Ma C, Ravindranathan R, Bartlett DL, et al:
IL-36γ-armed oncolytic virus exerts superior efficacy through
induction of potent adaptive antitumor immunity. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 70:2467–2481. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Weinstein AM and Storkus WJ: Therapeutic
lymphoid organogenesis in the tumor microenvironment. Adv Cancer
Res. 128:197–233. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Yang W, Dong HP, Wang P, Xu ZG, Xian J,
Chen J, Wu H, Lou Y, Lin D and Zhong B: IL-36γ and IL-36Ra
reciprocally regulate colon inflammation and tumorigenesis by
modulating the cell-matrix adhesion network and Wnt signaling. Adv
Sci (Weinh). 9(e2103035)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Baker K, O'Donnell C, Bendix M, Keogh S,
Byrne J, O'Riordain M, Neary P, Houston A and Brint E: IL-36
signalling enhances a pro-tumorigenic phenotype in colon cancer
cells with cancer cell growth restricted by administration of the
IL-36R antagonist. Oncogene. 41:2672–2684. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Kaushik I, Ramachandran S, Zabel C,
Gaikwad S and Srivastava SK: The evolutionary legacy of immune
checkpoint inhibitors. Semin Cancer Biol. 86:491–498.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Wei SC, Duffy CR and Allison JP:
Fundamental mechanisms of immune checkpoint blockade therapy.
Cancer Discov. 8:1069–1086. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Peña-Asensio J, Calvo H, Torralba M,
Miquel J, Sanz-de-Villalobos E and Larrubia JR: Anti-PD-1/PD-L1
based combination immunotherapy to boost antigen-specific
CD8+ T cell response in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancers (Basel). 13(1922)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Hewitt SL, Bai A, Bailey D, Ichikawa K,
Zielinski J, Karp R, Apte A, Arnold K, Zacharek SJ, Iliou MS, et
al: Durable anticancer immunity from intratumoral administration of
IL-23, IL-36γ, and OX40L mRNAs. Sci Transl Med.
11(eaat9143)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Bachelez H, Choon SE, Marrakchi S, Burden
AD, Tsai TF, Morita A, Navarini AA, Zheng M, Xu J, Turki H, et al:
Trial of spesolimab for generalized pustular psoriasis. New Engl J
Med. 385:2431–2440. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Ferrante M, Irving PM, Selinger CP,
D'Haens G, Kuehbacher T, Seidler U, Gropper S, Haeufel T, Forgia S,
Danese S, et al: Safety and tolerability of spesolimab in patients
with ulcerative colitis. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 22:141–152.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|