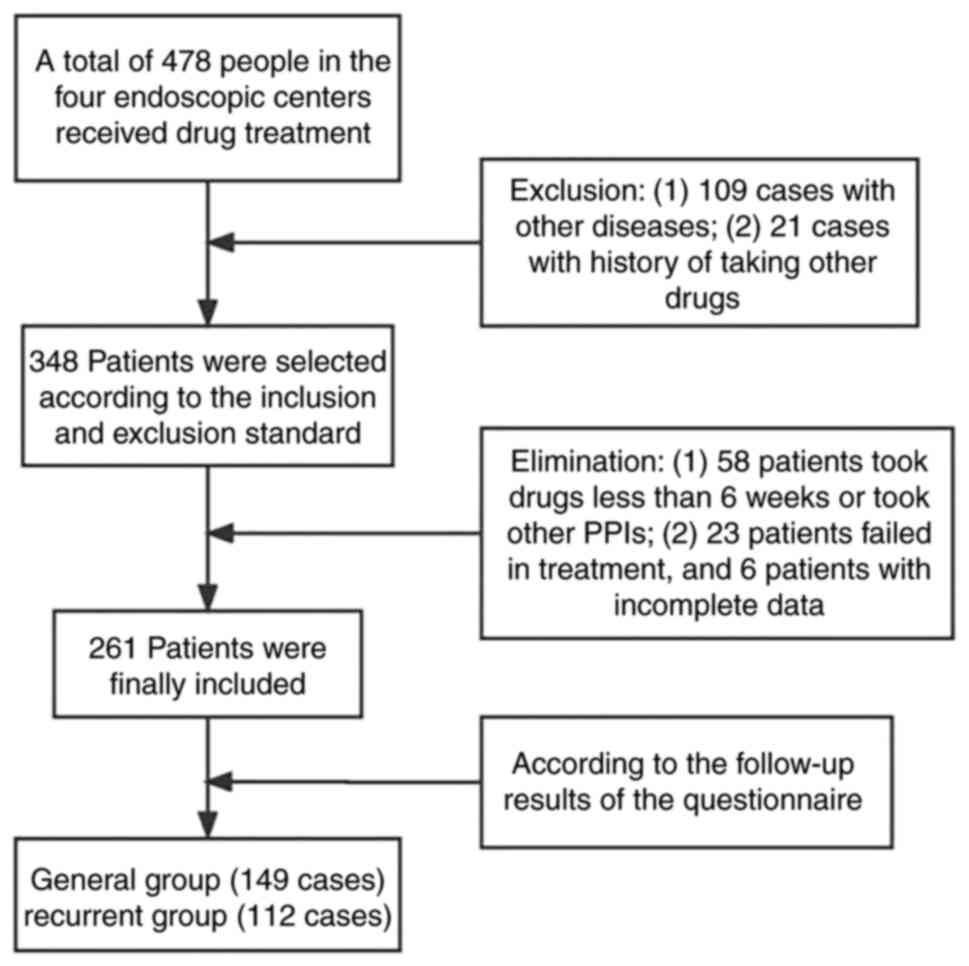
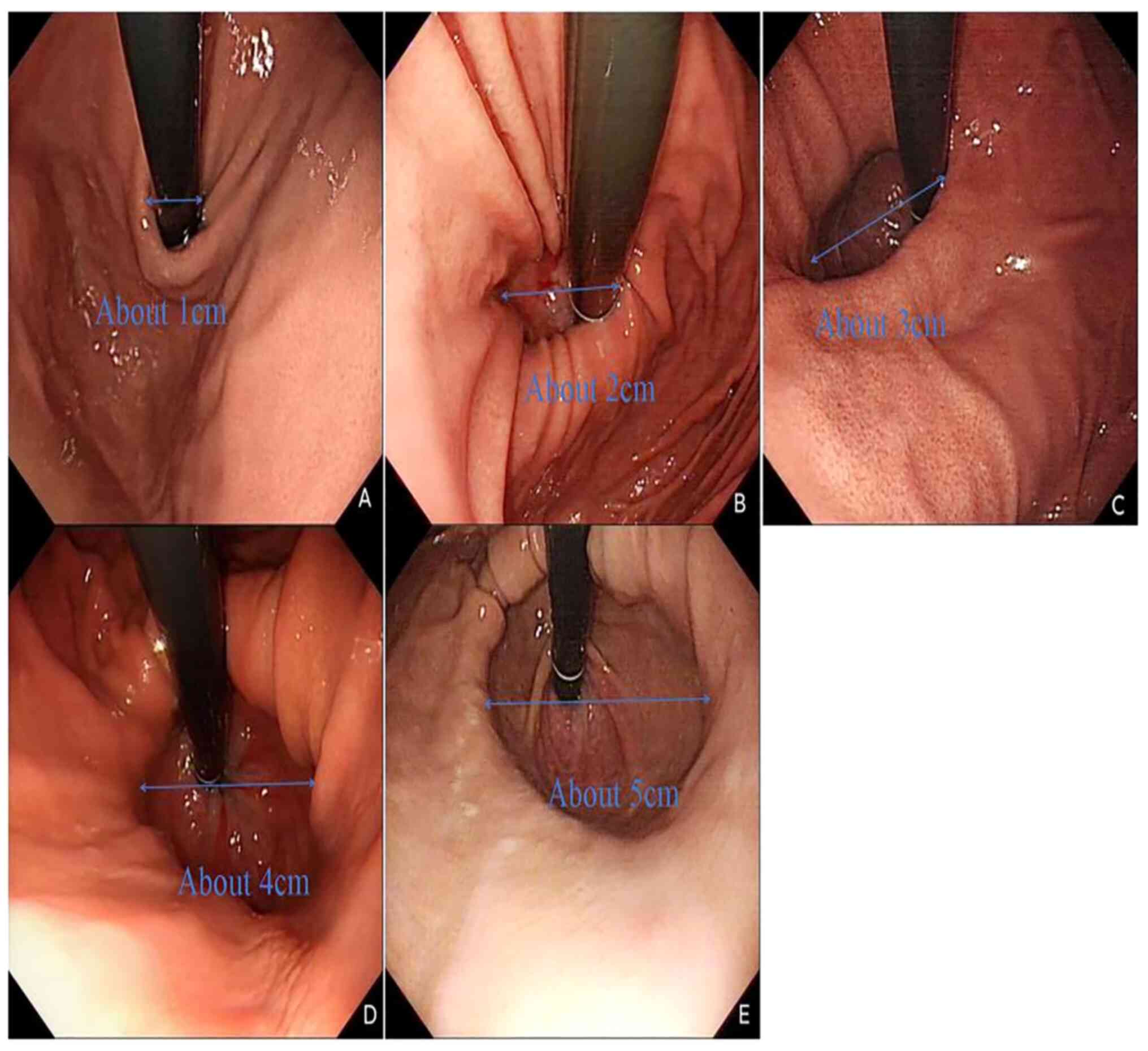
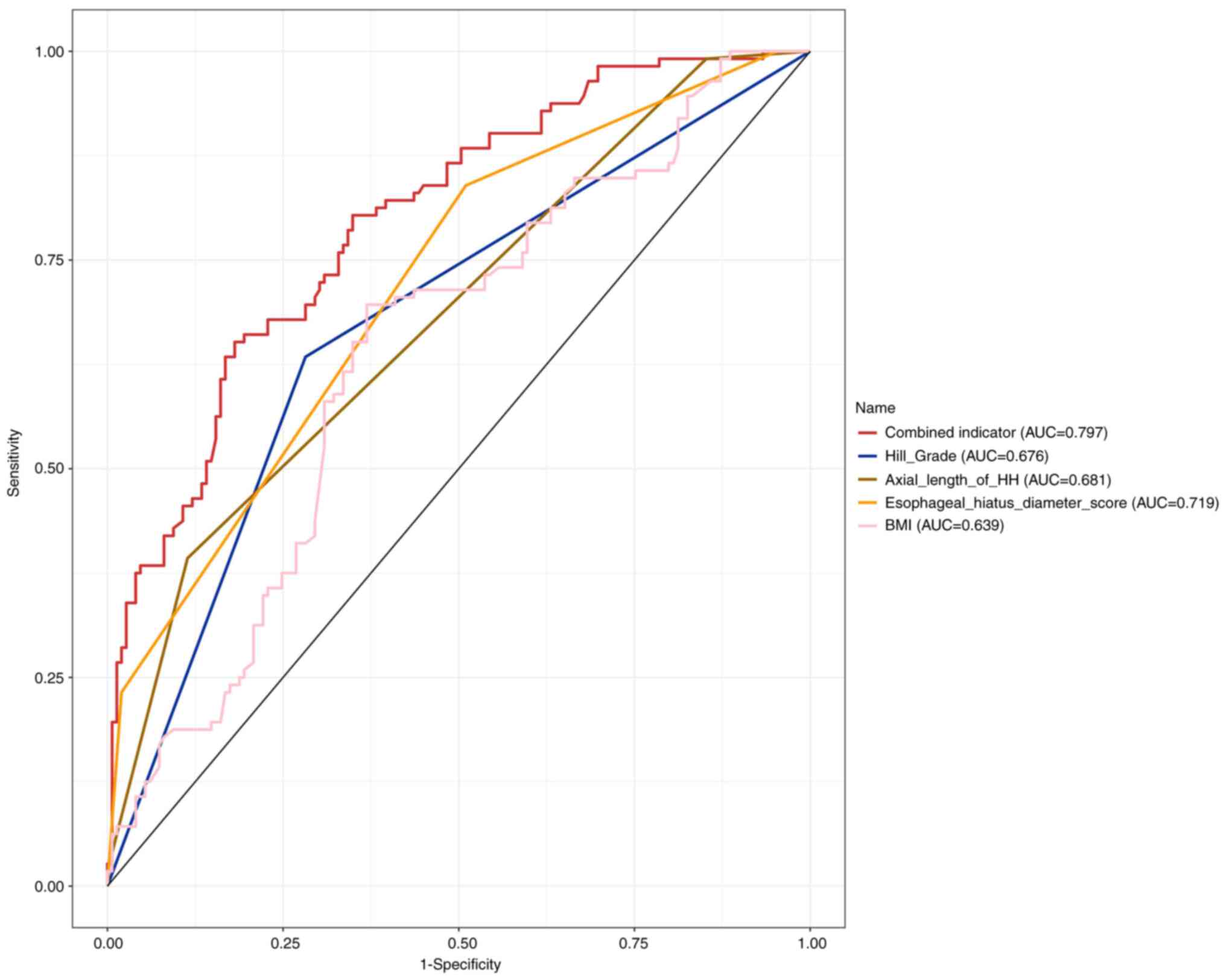
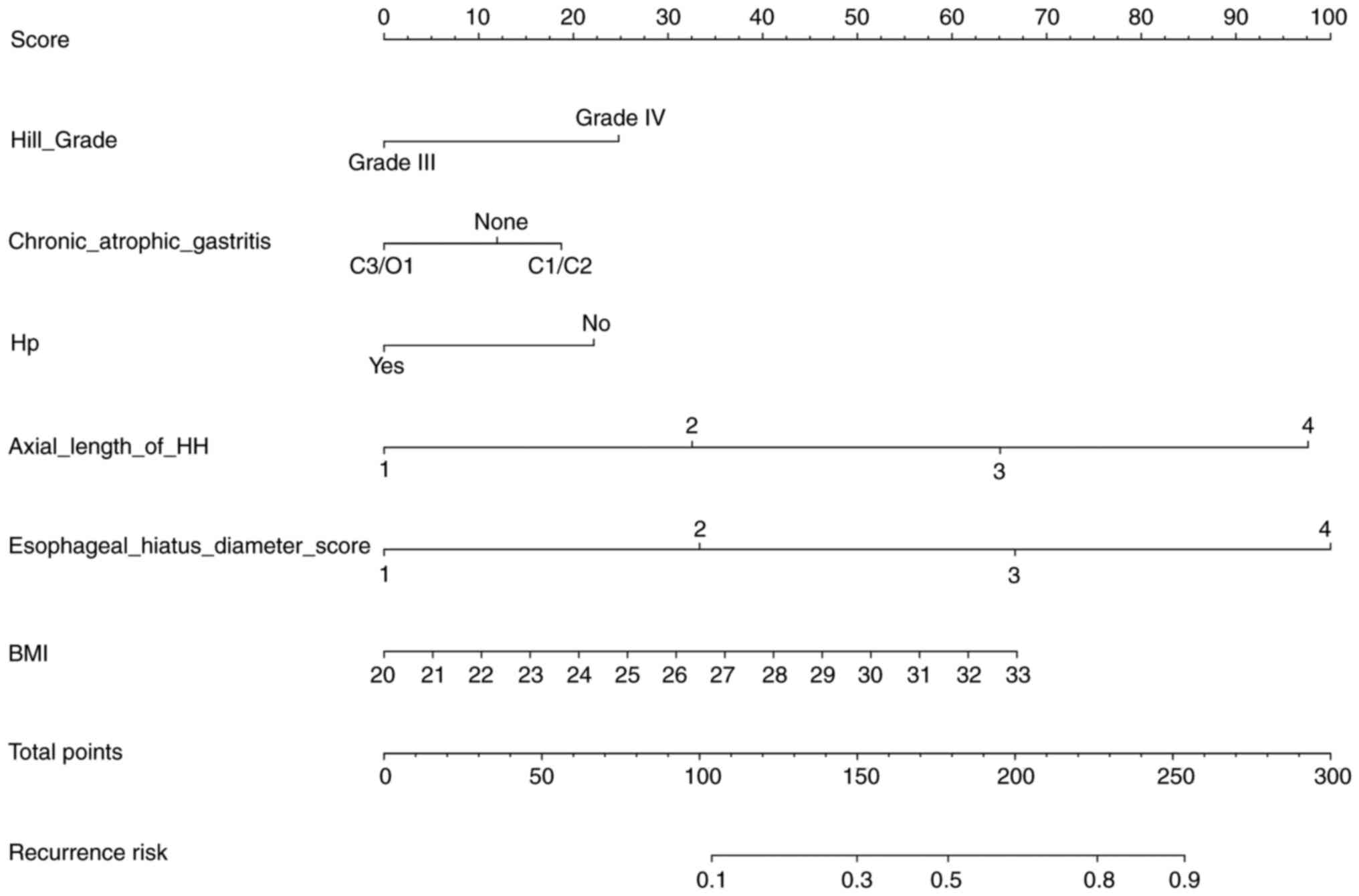
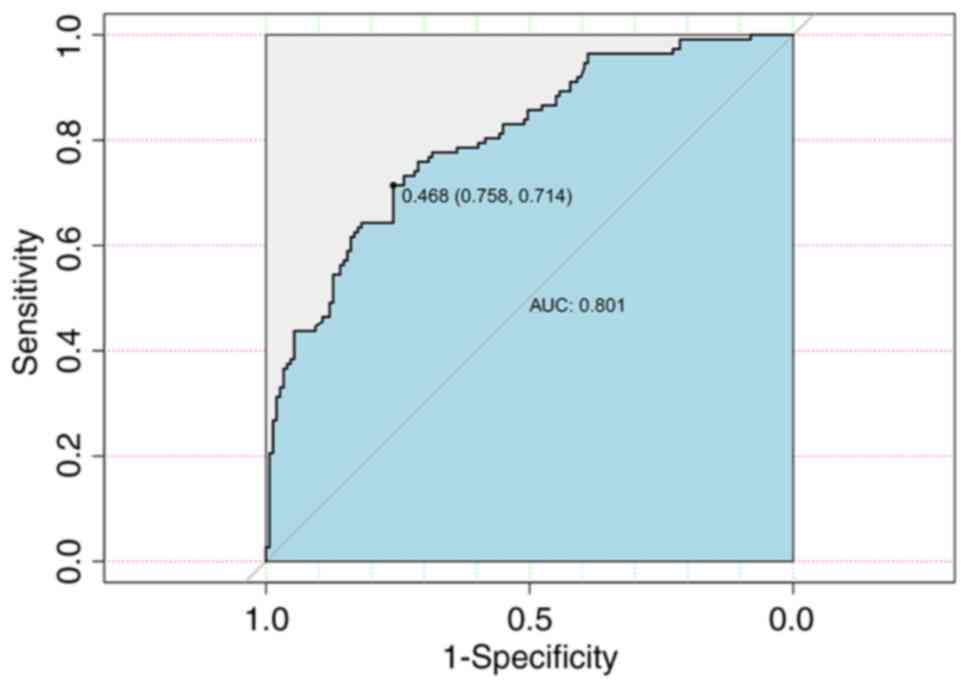
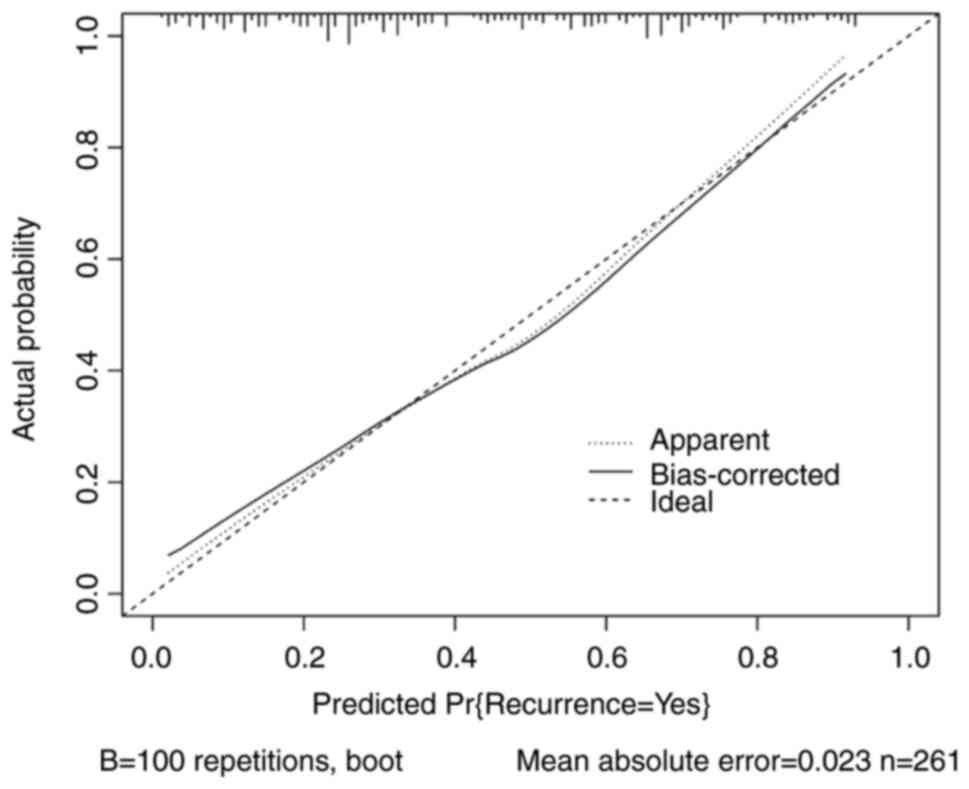
|
1
|
Fuchs KH, DeMeester TR, Otte F, Broderick
RC, Breithaupt W, Varga G and Musial F: Severity of GERD and
disease progression. Dis Esophagus. 34(doab006)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Li L, Gao H, Zhang C, Tu J, Geng X, Wang
J, Zhou X, Pan W and Jing J: Diagnostic value of X-ray, endoscopy,
and high-resolution manometry for hiatal hernia: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 35:13–18.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Asaoka D, Takeda T, Sasaki H, Shimada Y,
Matsumoto K, Ueyama H, Matsumoto K, Izumi K, Komori H, Akazawa Y,
et al: Evaluation of symptomatic reflux esophagitis in proton pump
inhibitor users. Biomed Rep. 10:277–282. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
El-Serag H, Becher A and Jones R:
Systematic review: Persistent reflux symptoms on proton pump
inhibitor therapy in primary care and community studies. Aliment
Pharmacol Ther. 32:720–737. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Katz PO, Dunbar KB, Schnoll-Sussman FH,
Greer KB, Yadlapati R and Spechler SJ: ACG clinical guideline for
the diagnosis and management of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am
J Gastroenterol. 117:27–56. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Gyawali CP, Kahrilas PJ, Savarino E,
Zerbib F, Mion F, Smout AJPM, Vaezi M, Sifrim D, Fox MR, Vela MF,
et al: Modern diagnosis of GERD: The Lyon Consensus. Gut.
67:1351–1362. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Multidisciplinary Branch of
Gastroesophageal Reflux of China International Exchange and
Promotion Association for Medical and Healthcare. Consensus on
multidisciplinary diagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal
reflux disease in China. Chin J Gastroesophagol Reflux Dis
(Electronic Edition). 7:1–28. 2020.(In Chinese).
|
|
8
|
Dent J, Vakil N, Jones R, Bytzer P,
Schöning U, Halling K, Junghard O and Lind T: Accuracy of the
diagnosis of GORD by questionnaire, physicians and a trial of
proton pump inhibitor treatment: The Diamond Study. Gut.
59:714–721. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Value of reflux diagnostic questionnaire
in the diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Chin J Dig
Dis. 5:51–55. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Shaw MJ, Talley NJ, Beebe TJ, Rockwood T,
Carlsson R, Adlis S, Fendrick AM, Jones R, Dent J and Bytzer P:
Initial validation of a diagnostic questionnaire for
gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Gastroenterol. 96:52–57.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, Blum AL,
Armstrong D, Galmiche JP, Johnson F, Hongo M, Richter JE, Spechler
SJ, et al: Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: Clinical and
functional correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles
classification. Gut. 45:172–180. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Quach DT and Hiyama T: Assessment of
endoscopic gastric atrophy according to the kimura-takemoto
classification and its potential application in daily practice.
Clin Endosc. 52:321–327. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Sgouros SN, Mpakos D, Rodias M,
Vassiliades K, Karakoidas C, Andrikopoulos E, Stefanidis G and
Mantides A: Prevalence and axial length of hiatus hernia in
patients, with nonerosive reflux disease: A prospective study. J
Clin Gastroenterol. 41:814–818. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wallner B, Björ O, Andreasson A, Hellström
PM, Forsberg AM, Talley NJ and Agreus L: Identifying clinically
relevant sliding hiatal hernias: A population-based endoscopy
study. Scand J Gastroenterol. 53:657–660. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kaneyama H, Kaise M, Arakawa H, Arai Y,
Kanazawa K and Tajiri H: Gastroesophageal flap valve status
distinguishes clinical phenotypes of large hiatal hernia. World J
Gastroenterol. 16:6010–6015. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Peng S, Xiao YL, Cui Y, Lin JK, Zhang N,
Hu PJ and Chen MH: High-dose esomeprazole is required for
intraesophageal acid control in gastroesophageal reflux disease
patients with hiatus hernia. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 27:893–898.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Cheong JH, Kim GH, Lee BE, Choi MK, Moon
JY, Ryu DY, Kim DU and Song GA: Endoscopic grading of
gastroesophageal flap valve helps predict proton pump inhibitor
response in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Scand J
Gastroenterol. 46:789–796. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Watanabe A, Iwakiri R, Yamaguchi D,
Higuchi T, Tsuruoka N, Miyahara K, Akutagawa K, Sakata Y, Fujise T,
Oda Y, et al: Risk factors for resistance to proton pump inhibitor
maintenance therapy for reflux esophagitis in Japanese women over
60 years. Digestion. 86:323–331. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Pandolfino JE, El-Serag HB, Zhang Q, Shah
N, Ghosh SK and Kahrilas PJ: Obesity: A challenge to
esophagogastric junction integrity. Gastroenterology. 130:639–649.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hill LD, Kozarek RA, Kraemer SJ, Aye RW,
Mercer CD, Low DE and Pope CE II: The gastroesophageal flap valve:
In vitro and in vivo observations. Gastrointest Endosc. 44:541–547.
1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Osman A, Albashir MM, Nandipati K, Walters
RW and Chandra S: Esophagogastric junction morphology on Hill's
classification predicts gastroesophageal reflux with good accuracy
and consistency. Dig Dis Sci. 66:151–159. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Duranceau A: Massive hiatal hernia: A
review. Dis Esophagus. 29:350–366. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Schlottmann F, Andolfi C, Herbella FA,
Rebecchi F, Allaix ME and Patti MG: GERD: Presence and size of
hiatal hernia influence clinical presentation, esophageal function,
reflux profile, and degree of mucosal injury. Am Surg. 84:978–982.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hansdotter I, Björ O, Andreasson A, Agreus
L, Hellström P, Forsberg A, Talley NJ, Vieth M and Wallner B: Hill
classification is superior to the axial length of a hiatal hernia
for assessment of the mechanical anti-reflux barrier at the
gastroesophageal junction. Endosc Int Open. 4:E311–E317.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Richter JE and Rubenstein JH: Presentation
and epidemiology of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
Gastroenterology. 154:267–276. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Eusebi LH, Ratnakumaran R, Yuan Y,
Solaymani-Dodaran M, Bazzoli F and Ford AC: Global prevalence of,
and risk factors for, gastro-oesophageal reflux symptoms: A
meta-analysis. Gut. 67:430–440. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Han YM, Chung SJ, Yoo S, Yang JI, Choi JM,
Lee J and Kim JS: Inverse correlation between gastroesophageal
reflux disease and atrophic gastritis assessed by endoscopy and
serology. World J Gastroenterol. 28:853–867. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kim JY, Shin IS, Min YW, Kim K, Lee H, Min
BH, Lee JH, Kim JJ and Rhee PL: Endoscopic prediction for acid
reflux in patients without Hiatus Hernia. Korean J Gastroenterol.
76:134–141. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Xiao YL, Zhou LY, Hou XH, Li YQ, Zou DW
and Chen MH: Chinese Society of Gastroenterology. Chinese expert
consensus on gastroesophageal reflux disease in 2020. J Dig Dis.
22:376–389. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|