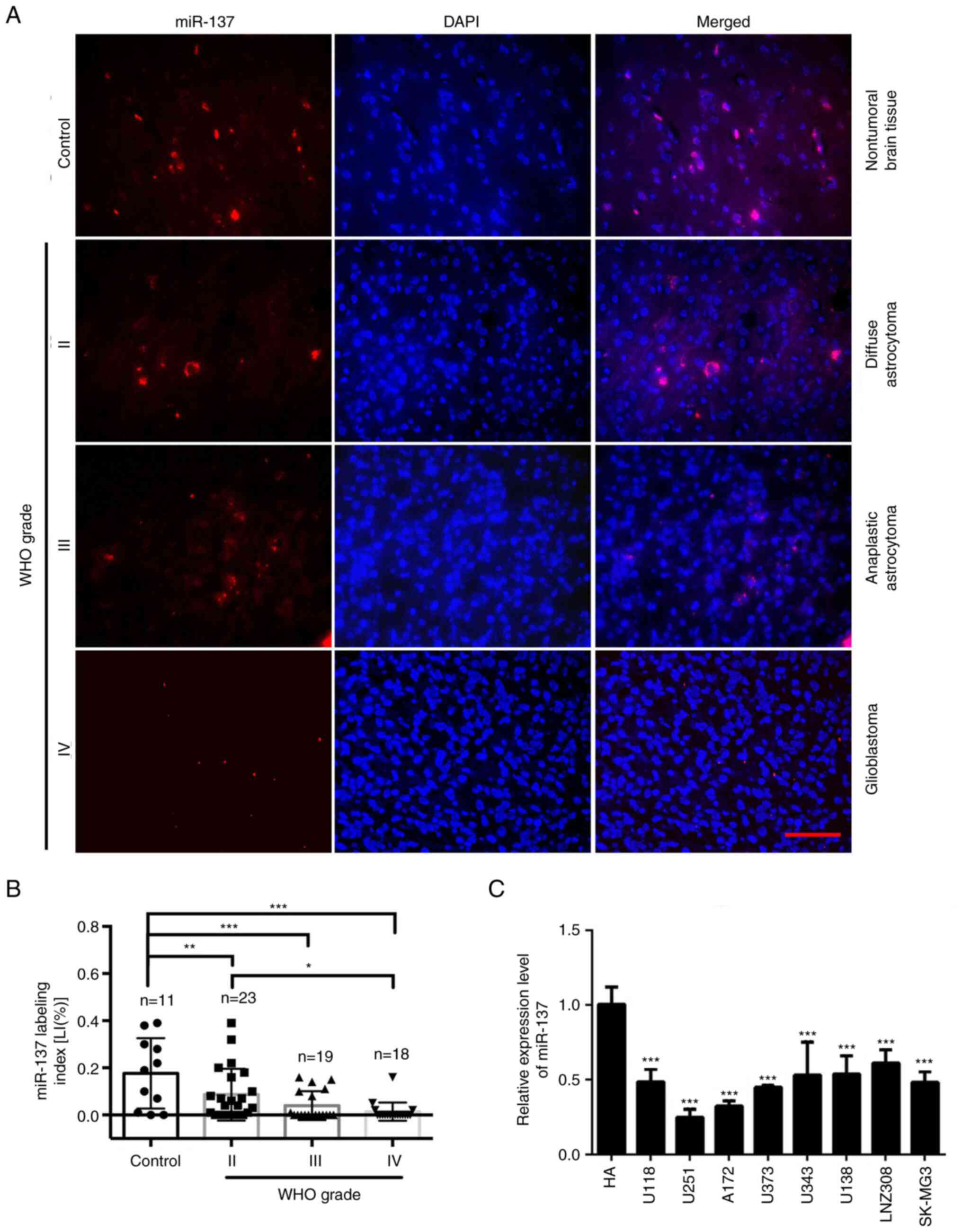
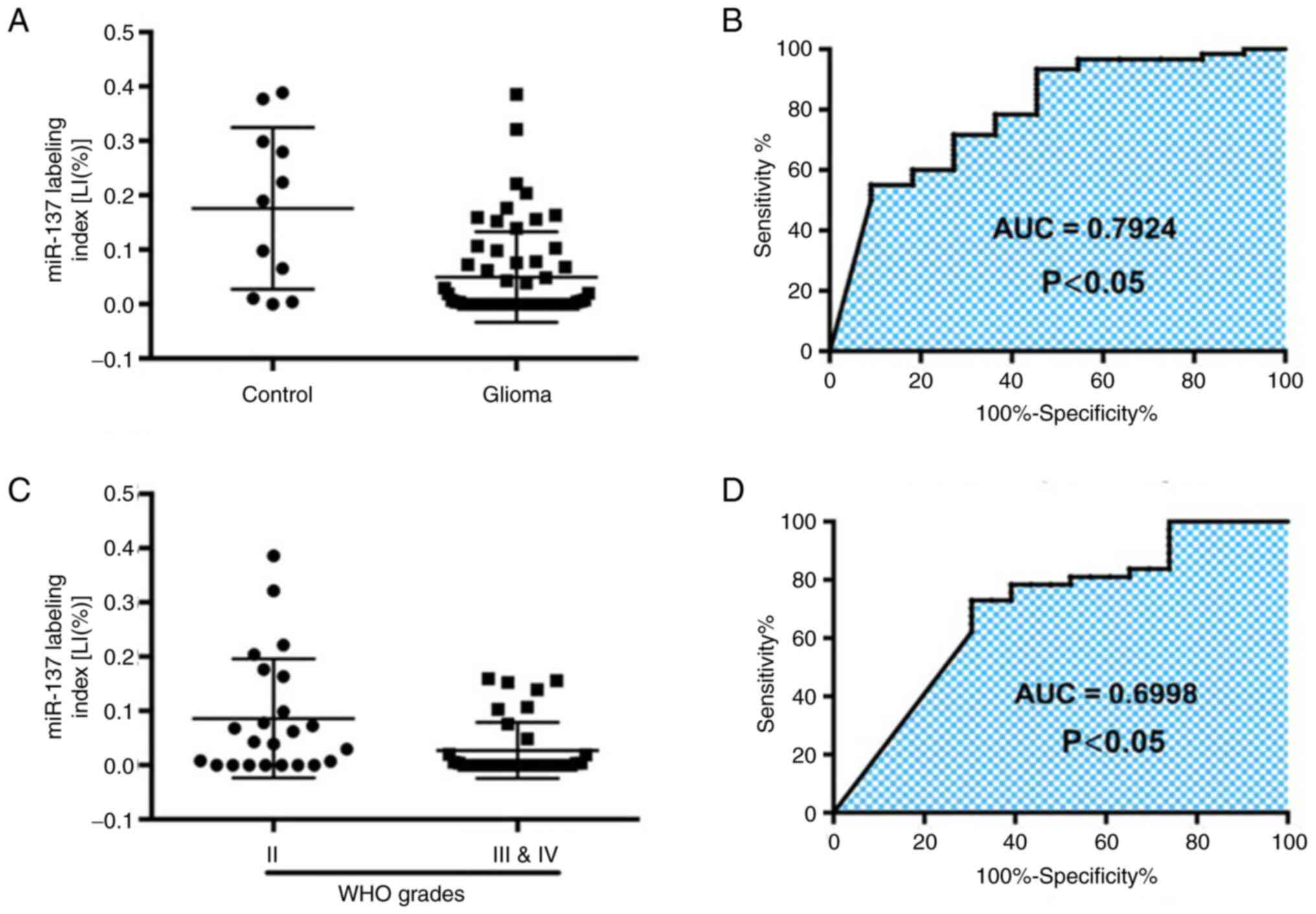
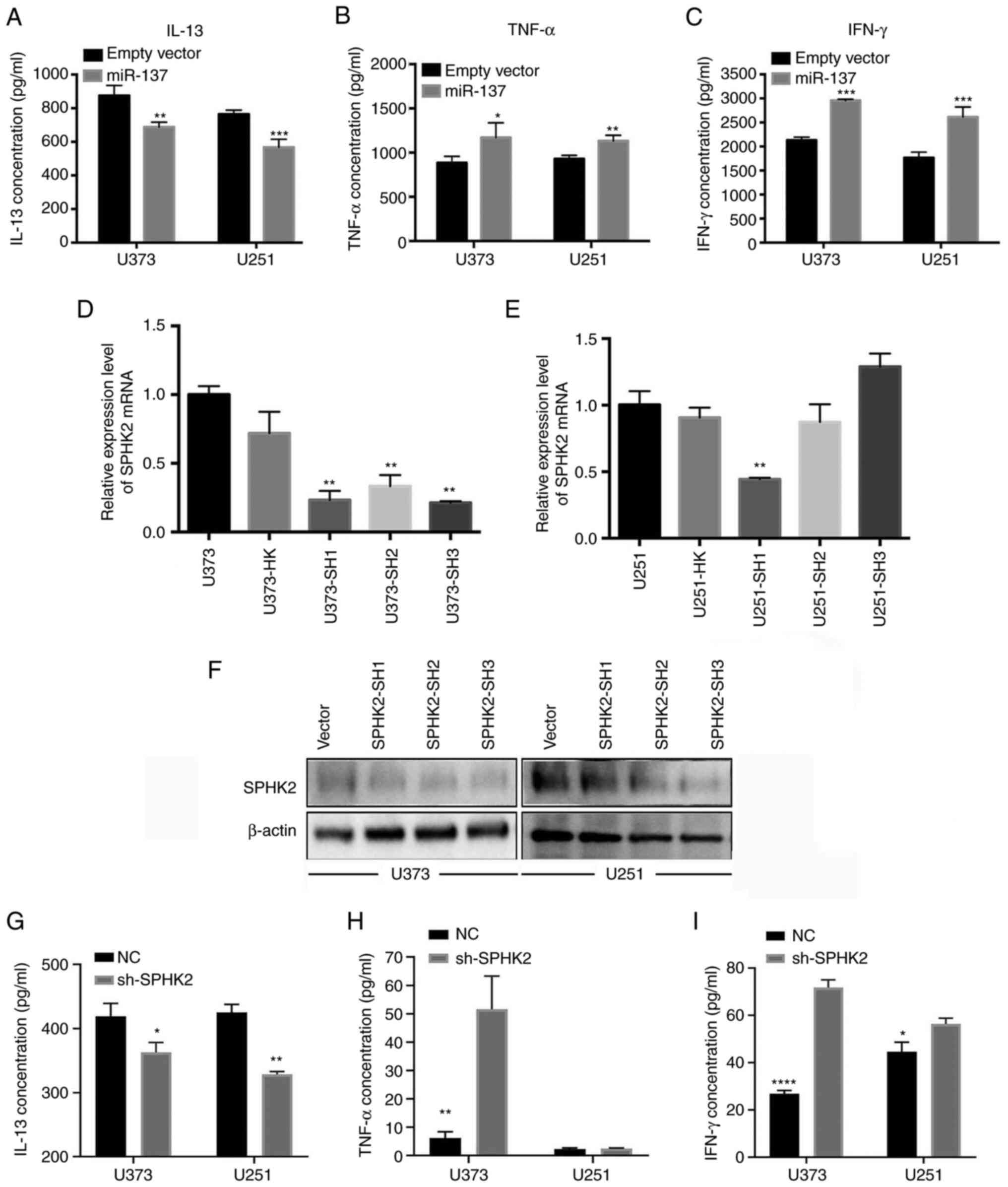
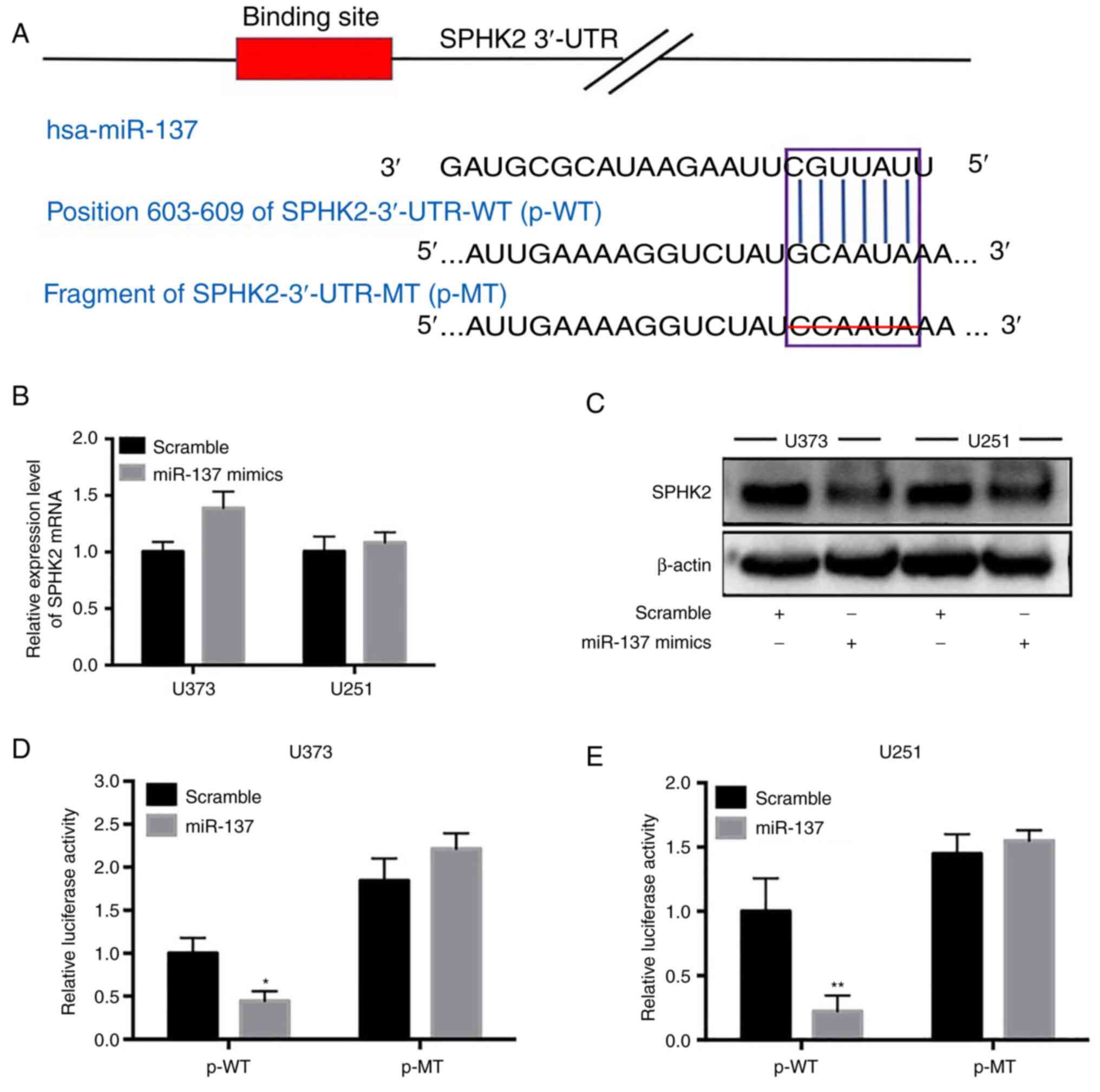
|
1
|
Ahmed R, Oborski MJ, Hwang M, Lieberman FS
and Mountz JM: Malignant gliomas: Current perspectives in
diagnosis, treatment, and early response assessment using advanced
quantitative imaging methods. Cancer Manag Res. 6:149–170.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Wen PY and Kesari S: Malignant gliomas in
adults. N Engl J Med. 359:492–507. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bastien JI, McNeill KA and Fine HA:
Molecular characterizations of glioblastoma, targeted therapy, and
clinical results to date. Cancer. 121:502–516. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Cohen AL and Colman H: Glioma biology and
molecular markers. Cancer Treat Res. 163:15–30. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Carthew RW and Sontheimer EJ: Origins and
mechanisms of miRNAs and siRNAs. Cell. 136:642–655. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Chipman LB and Pasquinelli AE: miRNA
targeting: Growing beyond the seed. Trends Genet. 35:215–222.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Esteller M: Non-coding RNAs in human
disease. Nat Rev Genet. 12:861–874. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Svoronos AA, Engelman DM and Slack FJ:
OncomiR or tumor suppressor? The duplicity of MicroRNAs in cancer.
Cancer Res. 76:3666–3670. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Nakamura K, Sawada K, Yoshimura A, Kinose
Y, Nakatsuka E and Kimura T: Clinical relevance of circulating
cell-free microRNAs in ovarian cancer. Mol Cancer.
15(48)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ji ZG, Jiang HT and Zhang PS: FOXK1
promotes cell growth through activating wnt/β-catenin pathway and
emerges as a novel target of miR-137 in glioma. Am J Transl Res.
10:1784–1792. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen L, Wang X, Wang H, Li Y, Yan W, Han
L, Zhang K, Zhang J, Wang Y, Feng Y, et al: miR-137 is frequently
down-regulated in glioblastoma and is a negative regulator of
Cox-2. Eur J Cancer. 48:3104–3111. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Xiao J, Peng F, Yu C, Wang M, Li X, Li Z,
Jiang J and Sun C: microRNA-137 modulates pancreatic cancer cells
tumor growth, invasion and sensitivity to chemotherapy. Int J Clin
Exp Pathol. 7:7442–7450. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wang L, Liu J, Zhong Z, Gong X, Liu W, Shi
L and Li X: PTP4A3 is a target for inhibition of cell proliferatin,
migration and invasion through Akt/mTOR signaling pathway in
glioblastoma under the regulation of miR-137. Brain Res.
1646:441–450. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Li KK, Yang L, Pang JC, Chan AK, Zhou L,
Mao Y, Wang Y, Lau KM, Poon WS, Shi Z and Ng HK: MIR-137 suppresses
growth and invasion, is downregulated in oligodendroglial tumors
and targets CSE1L. Brain Pathol. 23:426–439. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ding F, Zhang S, Gao S, Shang J, Li Y, Cui
N and Zhao Q: MiR-137 functions as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic
cancer by targeting MRGBP. J Cell Biochem. 119:4799–4807.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li ZM, Zhang HY, Wang YX and Wang WB:
MicroRNA-137 is downregulated in human osteosarcoma and regulates
cell proliferation and migration through targeting FXYD6. J Drug
Target. 24:102–110. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zheng X, Dong J, Gong T, Zhang Z, Wang Y,
Li Y, Shang Y, Li K, Ren G, Feng B, et al: MicroRNA library-based
functional screening identified miR-137 as a suppresser of gastric
cancer cell proliferation. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 141:785–795.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kozaki K, Imoto I, Mogi S, Omura K and
Inazawa J: Exploration of tumor-suppressive microRNAs silenced by
DNA hypermethylation in oral cancer. Cancer Res. 68:2094–2105.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen W, Du J, Li X, Zhi Z and Jiang S:
microRNA-137 downregulates MCL1 in ovarian cancer cells and
mediates cisplatin-induced apoptosis. Pharmacogenomics. 21:195–207.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wu DC, Zhang MF, Su SG, Fang HY, Wang XH,
He D, Xie YY and Liu XH: HEY2, a target of miR-137, indicates poor
outcomes and promotes cell proliferation and migration in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget. 7:38052–38063.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chang TH, Tsai MF, Gow CH, Wu SG, Liu YN,
Chang YL, Yu SL, Tsai HC, Lin SW, Chen YW, et al: Upregulation of
microRNA-137 expression by Slug promotes tumor invasion and
metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer cells through suppression
of TFAP2C. Cancer Lett. 402:190–202. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Liu J, Zhou Q, Wu CP, Xu YW, Liu WL, Zhao
HF and Li WP: SPHK2 protein expression, Ki-67 index and
infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) in human
glioma. Histol Histopathol. 33:987–994. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Domingues P, González-Tablas M, Otero Á,
Pascual D, Miranda D, Ruiz L, Sousa P, Ciudad J, Goncalves JM,
Lopes MC, et al: Tumor infiltrating immune cells in gliomas and
meningiomas. Brain Behav Immun. 53:1–15. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Brouland JP and Hottinger AF: Revised WHO
classification 2016 of gliomas: What's new? Rev Med Suisse.
13:1805–1809. 2017.PubMed/NCBI(In French).
|
|
25
|
Zhu J, Cai Y, Liu P and Zhao W.: Frequent
Nek1 overexpression in human gliomas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
476:522–527. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Barrett JW, Alston LR, Wang F, Stanford
MM, Gilbert PA, Gao X, Jimenez J, Villeneuve D, Forsyth P and
McFadden G: Identification of host range mutants of myxoma virus
with altered oncolytic potential in human glioma cells. J
Neurovirol. 13:549–560. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Liu J, Yang J, Yu L, Rao C, Wang Q, Sun C,
Shi C, Hua D, Zhou X, Luo W, et al: miR-361-5p inhibits glioma
migration and invasion by targeting SND1. Onco Targets Ther.
11:5239–5252. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Orihuela R, McPherson CA and Harry GJ:
Microglial M1/M2 polarization and metabolic states. Br J Pharmacol.
173:649–665. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Batra R, Suh MK, Carson JS, Dale MA,
Meisinger TM, Fitzgerald M, Opperman PJ, Luo J, Pipinos II, Xiong W
and Baxter BT: IL-1β (interleukin-1β) and TNF-α (tumor necrosis
factor-α) impact abdominal aortic aneurysm formation by
differential effects on macrophage polarization. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 38:457–463. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Berindan-Neagoe I and Calin GA: Molecular
pathways: microRNAs, cancer cells, and microenvironment. Clin
Cancer Res. 20:6247–6253. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Zheng Y, Bao J, Zhao Q, Zhou T and Sun X:
A spatio-temporal model of macrophage-mediated drug resistance in
glioma immunotherapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 17:814–824. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Khan S, Mittal S, McGee K, Alfaro-Munoz
KD, Majd N, Balasubramaniyan V and de Groot JF: Role of neutrophils
and myeloid-derived suppressor cells in glioma progression and
treatment resistance. Int J Mol Sci. 21(1954)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hambardzumyan D, Gutmann DH and Kettenmann
H: The role of microglia and macrophages in glioma maintenance and
progression. Nat Neurosci. 19:20–27. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Zheng X, Li W, Ren L, Liu J, Pang X, Chen
X, Kang D, Wang J and Du G: The sphingosine
kinase-1/sphingosine-1-phosphate axis in cancer: Potential target
for anticancer therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 195:85–99. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Weigert A, Schiffmann S, Sekar D, Ley S,
Menrad H, Werno C, Grosch S, Geisslinger G and Brüne B: Sphingosine
kinase 2 deficient tumor xenografts show impaired growth and fail
to polarize macrophages towards an anti-inflammatory phenotype. Int
J Cancer. 125:2114–2121. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Hatoum D, Haddadi N, Lin Y, Nassif NT and
McGowan EM: Mammalian sphingosine kinase (SphK) isoenzymes and
isoform expression: Challenges for SphK as an oncotarget.
Oncotarget. 8:36898–36929. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Liu H, Ma Y, He HW, Zhao WL and Shao RG:
SPHK1 (sphingosine kinase 1) induces epithelial-mesenchymal
transition by promoting the autophagy-linked lysosomal degradation
of CDH1/E-cadherin in hepatoma cells. Autophagy. 13:900–913.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Nemoto S, Nakamura M, Osawa Y, Kono S,
Itoh Y, Okano Y, Murate T, Hara A, Ueda H, Nozawa Y and Banno Y:
Sphingosine kinase isoforms regulate oxaliplatin sensitivity of
human colon cancer cells through ceramide accumulation and Akt
activation. J Biol Chem. 284:10422–10432. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Dai L, Smith CD, Foroozesh M, Miele L and
Qin Z: The sphingosine kinase 2 inhibitor ABC294640 displays
anti-non-small cell lung cancer activities in vitro and in vivo.
Int J Cancer. 142:2153–2162. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Xiao G, Wang Q, Li B, Wu X, Liao H, Ren Y
and Ai N: MicroRNA-338-3p suppresses proliferation of human liver
cancer cells by targeting SphK2. Oncol Res. 26:1183–1189.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wang W, Hind T, Lam BWS and Herr DR:
Sphingosine 1-phosphate signaling induces SNAI2 expression to
promote cell invasion in breast cancer cells. FASEB J.
33:7180–7191. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Qiu W, Yang Z, Fan Y and Zheng Q:
MicroRNA-613 inhibits cell growth, migration and invasion of
papillary thyroid carcinoma by regulating SphK2. Oncotarget.
7:39907–39915. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Hait NC, Sarkar S, Le Stunff H, Mikami A,
Maceyka M, Milstien S and Spiegel S: Role of sphingosine kinase 2
in cell migration toward epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem.
280:29462–29469. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Squadrito ML, Etzrodt M, De Palma M and
Pittet MJ: MicroRNA-mediated control of macrophages and its
implications for cancer. Trends Immunol. 34:350–359.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yin R, Zhu X, Wang J, Yang S, Ma A, Xiao
Q, Song J and Pan X: MicroRNA-155 promotes the ox-LDL-induced
activation of NLRP3 inflammasomes via the ERK1/2 pathway in THP-1
macrophages and aggravates atherosclerosis in ApoE-/-mice. Ann
Palliat Med. 8:676–689. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Zhang L, Fu Y, Wang H, Guan Y, Zhu W, Guo
M, Zheng N and Wu Z: Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome
virus-induced macrophage differentiation is regulated by miR-146.
Front Immunol. 10(1095)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Ji J, Wang J, Yang J, Wang XP, Huang JJ,
Xue TF and Sun XL: The intra-nuclear SphK2-S1P axis facilitates
M1-to-M2 shift of microglia via suppressing HDAC1-mediated KLF4
deacetylation. Front Immunol. 10(1241)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|