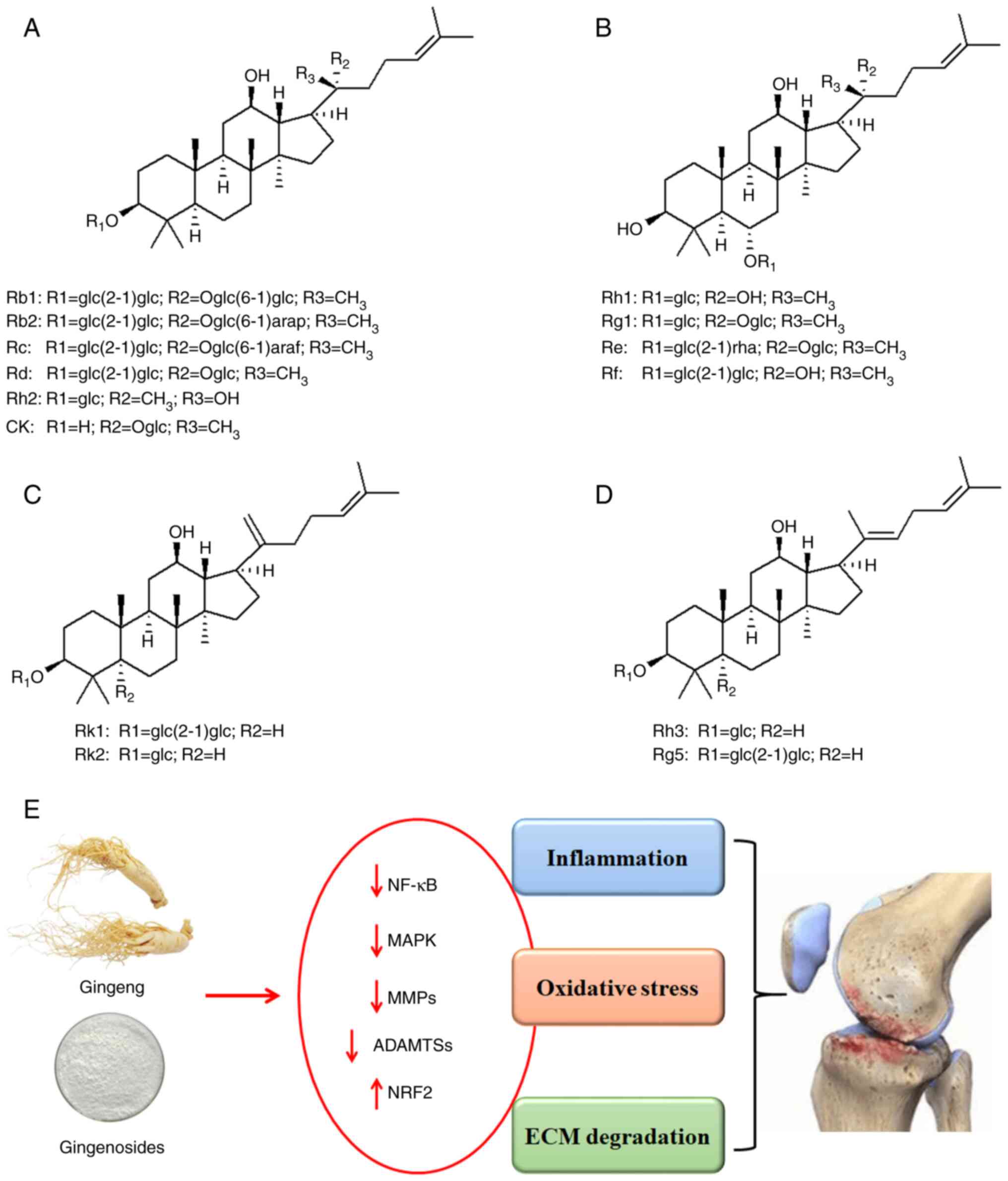
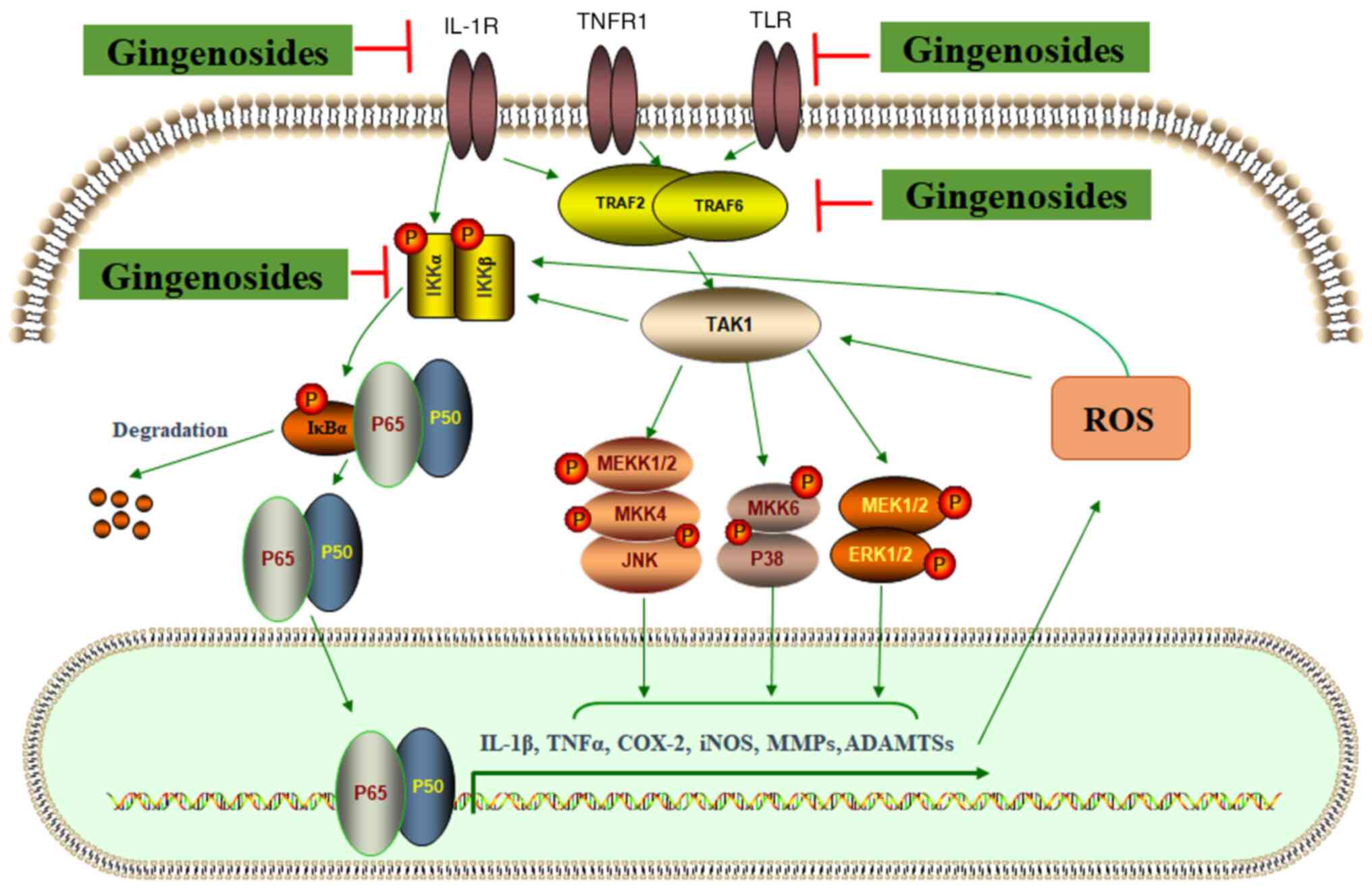
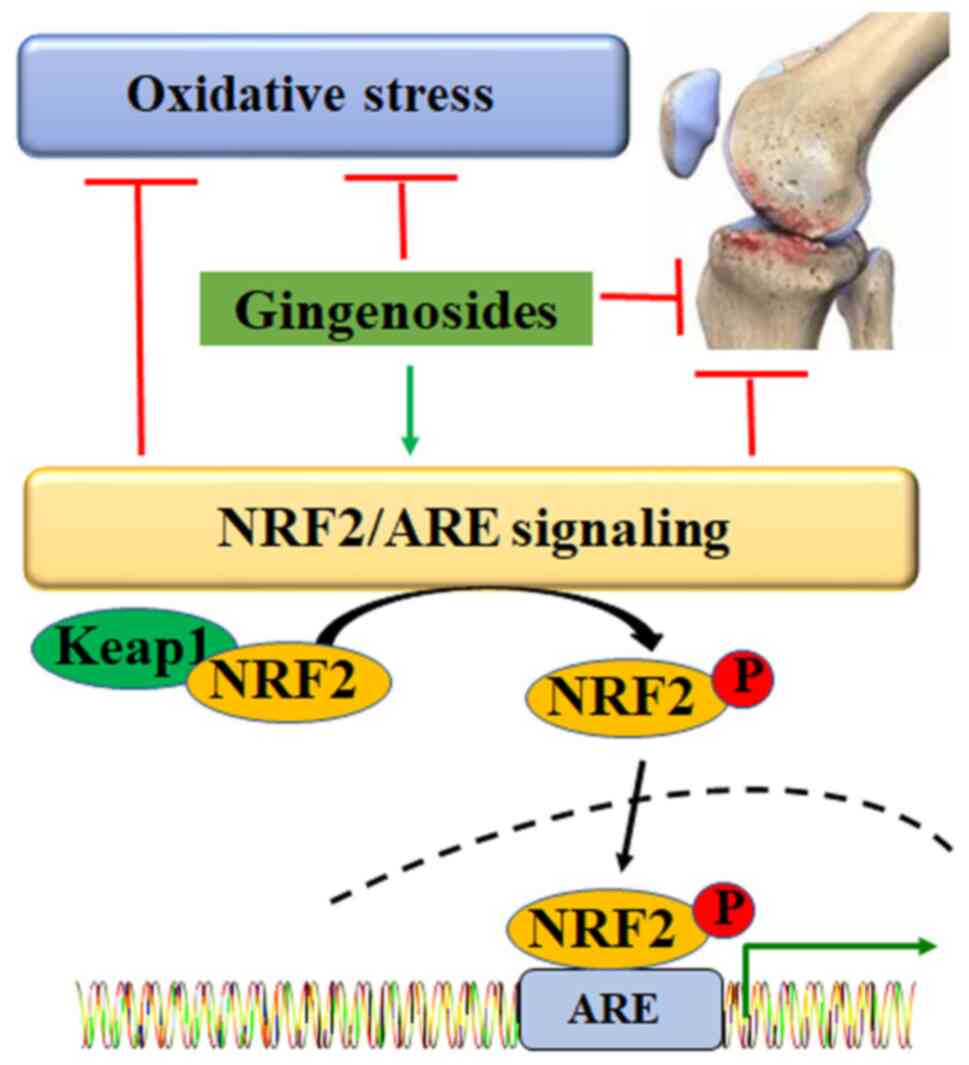
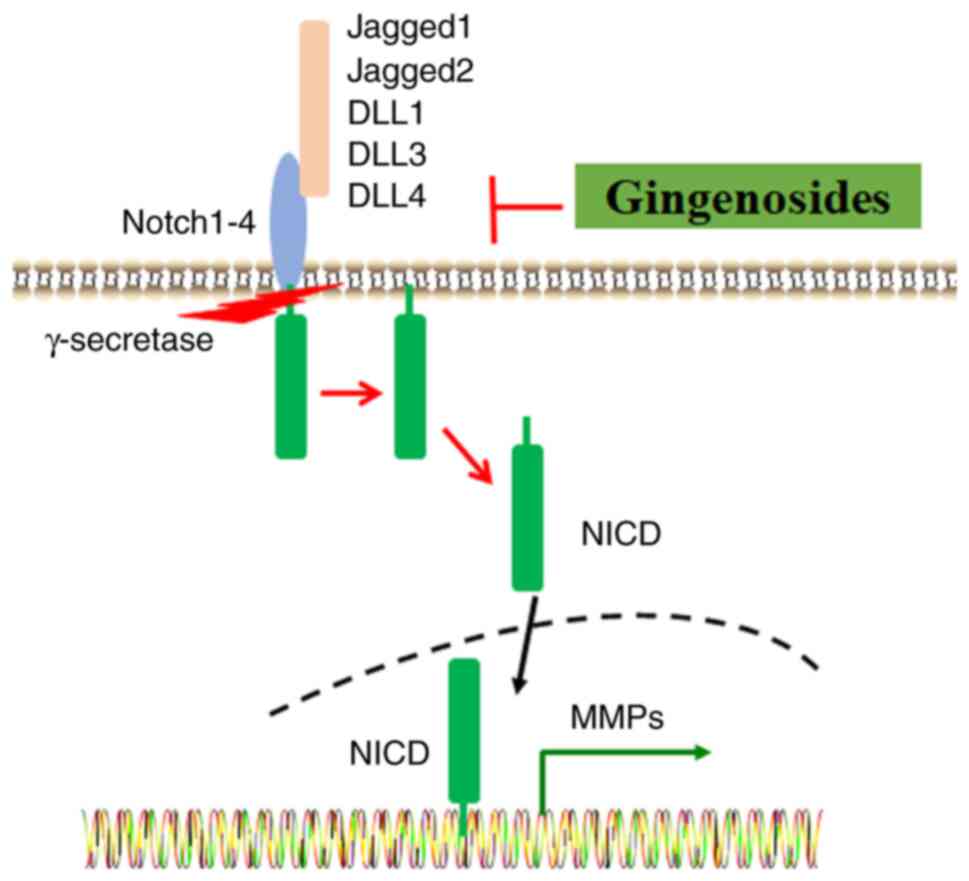
|
1
|
Wu SY, Lin CH, Chang NJ, Hu WL, Hung YC,
Tsao Y and Kuo CA: Combined effect of laser acupuncture and
electroacupuncture in knee osteoarthritis patients: A protocol for
a randomized controlled trial. Medicine (Baltimore).
99(e19541)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhang W, Ouyang H, Dass CR and Xu J:
Current research on pharmacologic and regenerative therapies for
osteoarthritis. Bone Res. 4(15040)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Jones IA, Togashi R, Wilson ML, Heckmann N
and Vangsness CT Jr: Intra-articular treatment options for knee
osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 15:77–90. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Charlesworth J, Fitzpatrick J, Perera NKP
and Orchard J: Osteoarthritis-a systematic review of long-term
safety implications for osteoarthritis of the knee. BMC
Musculoskelet Disord. 20(151)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Wang J, Li J, Song D, Ni J, Ding M, Huang
J and Yan M: AMPK: Implications in osteoarthritis and therapeutic
targets. Am J Transl Res. 12:7670–7681. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dilley JE, Bello MA, Roman N, McKinley T
and Sankar U: Post-traumatic osteoarthritis: A review of pathogenic
mechanisms and novel targets for mitigation. Bone Rep.
18(101658)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Goldring MB and Marcu KB: Cartilage
homeostasis in health and rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther.
11(224)2009.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Jiang J, Feng S, Li Z, Luo Y, Wang Z, Li M
and Wu G: The expression of MDM2 gene promoted chondrocyte
proliferation in rats with osteoarthritis via the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 67:236–241.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang Y, Zhao H, Jia S, Wang Q, Yao W, Yang
Y and Bai L: Senomorphic agent pterostilbene ameliorates
osteoarthritis through the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB axis: An in vitro and in
vivo study. Am J Transl Res. 14:5243–5262. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qiu J, Jiang T, Yang G, Gong Y, Zhang W,
Zheng X, Hong Z and Chen H: Neratinib exerts dual effects on
cartilage degradation and osteoclast production in Osteoarthritis
by inhibiting the activation of the MAPK/NF-κB signaling pathways.
Biochem Pharmacol. 205(115155)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Minguzzi M, Panichi V, D'Adamo S, Cetrullo
S, Cattini L, Flamigni F, Mariani E and Borzì RM: Pleiotropic roles
of NOTCH1 signaling in the loss of maturational arrest of human
osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Int J Mol Sci.
22(12012)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yang M, Jiang L, Wang Q, Chen H and Xu G:
Traditional Chinese medicine for knee osteoarthritis: An overview
of systematic review. PLoS One. 12(e0189884)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kim JH: Pharmacological and medical
applications of Panax ginseng and ginsenosides: A review for
use in cardiovascular diseases. J Ginseng Res. 42:264–269.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kang OJ and Kim JS: Comparison of
ginsenoside contents in different parts of Korean ginseng (Panax
ginseng C.A. Meyer). Prev Nutr Food Sci. 21:389–392.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Fan M, Lan X, Wang Q, Shan M, Fang X,
Zhang Y, Wu D, Luo H, Gao W and Zhu D: Renal function protection
and the mechanism of ginsenosides: Current progress and future
perspectives. Front Pharmacol. 14(1070738)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhao T, Wang X, Liu Q, Yang T, Qu H and
Zhou H: Ginsenoside Rd promotes cardiac repair after myocardial
infarction by modulating monocytes/macrophages subsets conversion.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 16:2767–2782. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhou AF, Zhu K, Pu PM, Li ZY, Zhang YY,
Shu B, Cui XJ, Yao M and Wang YJ: Neuroprotective effect and
possible mechanisms of ginsenoside-Rd for cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion damage in experimental animal: A meta-analysis
and systematic review. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2022(7650438)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Liu Y, Liu N, Liu Y, He H, Luo Z, Liu W,
Song N and Ju M: Ginsenoside Rb1 reduces D-GalN/LPS-induced acute
liver injury by regulating TLR4/NF-κB signaling and NLRP3
inflammasome. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 10:474–485. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xue X, Liu Y, Qu L, Fan C, Ma X, Ouyang P
and Fan D: Ginsenoside Rh3 inhibits lung cancer metastasis by
targeting extracellular signal-regulated kinase: A network
pharmacology study. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 15(758)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Song B, Ding L, Zhang H, Chu Y, Chang Z,
Yu Y, Guo D, Zhang S and Liu X: Ginsenoside Rb1 increases insulin
sensitivity through suppressing 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase
type I. Am J Transl Res. 9:1049–1057. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song M, Cui Y, Wang Q, Zhang X, Zhang J,
Liu M and Li Y: Ginsenoside Rg3 alleviates aluminum
chloride-induced bone impairment in rats by activating the
TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway. J Agric Food Chem. 69:12634–12644.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Xu HL, Chen GH, Wu YT, Xie LP, Tan ZB, Liu
B, Fan HJ, Chen HM, Huang GQ, Liu M and Zhou YC: Ginsenoside Ro, an
oleanolic saponin of Panax ginseng, exerts an
anti-inflammatory effect by direct inhibiting toll-like receptor 4
signaling pathway. J Ginseng Res. 46:156–166. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Wu Z, Yang Z, Liu L and Xiao Y: Natural
compounds protect against the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis by
mediating the NRF2/ARE signaling. Front Pharmacol.
14(1188215)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Scanzello CR and Goldring SR: The role of
synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 51:249–257.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Di Nicola V: Degenerative osteoarthritis a
reversible chronic disease. Regen Ther. 15:149–160. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wojdasiewicz P, Poniatowski ŁA and
Szukiewicz D: The role of inflammatory and anti-inflammatory
cytokines in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm.
2014(561459)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Chow YY and Chin KY: The role of
inflammation in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Mediators
Inflamm. 2020(8293921)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Zahan OM, Serban O, Gherman C and Fodor D:
The evaluation of oxidative stress in osteoarthritis. Med Pharm
Rep. 93:12–22. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Wang H, Liao R, Tang W, Su W, Zeng M, Yang
J, Fan X, Xie J and Hu Y: Dietary inflammation index and
osteoarthritis in the elderly: Is there a mediating role of
physical activity? Br J Nutr. 128:2258–2266. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Zarezadeh M, Mahmoudinezhad M, Hosseini B,
Khorraminezhad L, Razaghi M, Alvandi E and Saedisomeolia A: Dietary
pattern in autism increases the need for probiotic supplementation:
A comprehensive narrative and systematic review on oxidative stress
hypothesis. Clin Nutr. 42:1330–1358. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ott M, Gogvadze V, Orrenius S and
Zhivotovsky B: Mitochondria, oxidative stress and cell death.
Apoptosis. 12:913–922. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sadasivam N, Kim YJ, Radhakrishnan K and
Kim DK: Oxidative stress, genomic integrity, and liver diseases.
Molecules. 27(3159)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Park J, Lee J and Choi C: Mitochondrial
network determines intracellular ROS dynamics and sensitivity to
oxidative stress through switching inter-mitochondrial messengers.
PLoS One. 6(e23211)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Youle RJ and Karbowski M: Mitochondrial
fission in apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 6:657–663.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sirše M: Effect of dietary polyphenols on
osteoarthritis-molecular mechanisms. Life (Basel).
12(436)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Baatar D, Siddiqi MZ, Im WT, Ul Khaliq N
and Hwang SG: Anti-inflammatory effect of ginsenoside
Rh2-Mix on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7
murine macrophage cells. J Med Food. 21:951–960. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Lee JH, Shehzad O, Ko SK, Kim YS and Kim
HP: Matrix metalloproteinase-13 downregulation and potential
cartilage protective action of the Korean red ginseng preparation.
J Ginseng Res. 39:54–60. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Jhun JY, Na HS, Shin JW, Jung KA, Seo HB,
Ryu JY, Choi JW, Moon SJ, Park HJ, Oh SW, et al: Notoginseng Radix
and Rehmanniae Radix Preparata extract combination (YH23537)
reduces pain and cartilage degeneration in rats with monosodium
iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. J Med Food. 21:745–754.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Xie JJ, Chen J, Guo SK, Gu YT, Yan YZ, Guo
WJ, Yao CL, Jin MY, Xie CL, Wang X, et al: Panax quinquefolium
saponin inhibits endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis and
the associated inflammatory response in chondrocytes and attenuates
the progression of osteoarthritis in rat. Biomed Pharmacother.
97:886–894. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Zhang Y, Cai W, Han G, Zhou S, Li J, Chen
M and Li H: Panax notoginseng saponins prevent senescence and
inhibit apoptosis by regulating the PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway in
osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Int J Mol Med. 45:1225–1236.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Seo SK, Hong Y, Yun BH, Chon SJ, Jung YS,
Park JH, Cho S, Choi YS and Lee BS: Antioxidative effects of Korean
red ginseng in postmenopausal women: A double-blind randomized
controlled trial. J Ethnopharmacol. 154:753–757. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kim HI, Chon SJ, Seon KE, Seo SK and Choi
YR: Clinical effects of Korean red ginseng in postmenopausal women
with hand osteoarthritis: A double-blind, randomized controlled
trial. Front Pharmacol. 12(745568)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Zhu DC, Wang YH, Lin JH, Miao ZM, Xu JJ
and Wu YS: Maltol inhibits the progression of osteoarthritis via
the nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2/heme oxygenase-1
signal pathway in vitro and in vivo. Food Funct. 12:1327–1337.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Lu H, Fu C, Kong S, Wang X, Sun L, Lin Z,
Luo P and Jin H: Maltol prevents the progression of osteoarthritis
by targeting PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway: In vitro and in vivo studies.
J Cell Mol Med. 25:499–509. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Yang SM, Ka SM, Hua KF, Wu TH, Chuang YP,
Lin YW, Yang FL, Wu SH, Yang SS, Lin SH, et al: Antroquinonol
mitigates an accelerated and progressive IgA nephropathy model in
mice by activating the Nrf2 pathway and inhibiting T cells and
NLRP3 inflammasome. Free Radic Biol Med. 61:285–297.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Yi YS: Roles of ginsenosides in
inflammasome activation. J Ginseng Res. 43:172–178. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Kim J, Ahn H, Han BC, Lee SH, Cho YW, Kim
CH, Hong EJ, An BS, Jeung EB and Lee GS: Korean red ginseng
extracts inhibit NLRP3 and AIM2 inflammasome activation. Immunol
Lett. 158:143–150. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Gao Y, Li J, Wang J, Li X, Li J, Chu S, Li
L, Chen N and Zhang L: Ginsenoside Rg1 prevent and treat
inflammatory diseases: A review. Int Immunopharmacol.
87(106805)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Cheng W, Jing J, Wang Z, Wu D and Huang Y:
Chondroprotective effects of ginsenoside Rg1 in human
osteoarthritis chondrocytes and a rat model of anterior cruciate
ligament transection. Nutrients. 9(263)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Cho JY, Yoo ES, Baik KU, Park MH and Han
BH: In vitro inhibitory effect of protopanaxadiol ginsenosides on
tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha production and its modulation by
known TNF-alpha antagonists. Planta Med. 67:213–218.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Cheng W, Wu D, Zuo Q, Wang Z and Fan W:
Ginsenoside Rb1 prevents interleukin-1 beta induced inflammation
and apoptosis in human articular chondrocytes. Int Orthop.
37:2065–2070. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Kim MK, Kang H, Baek CW, Jung YH, Woo YC,
Choi GJ, Shin HY and Kim KS: Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory
effects of ginsenoside Rf in a rat model of incisional pain. J
Ginseng Res. 42:183–191. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Aravinthan A, Hossain MA, Kim B, Kang CW,
Kim NS, Hwang KC and Kim JH: Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits
monoiodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis in postmenopausal rats
through prevention of cartilage degradation. J Ginseng Res.
45:287–294. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Hung IH, Schoenwolf GC, Lewandoski M and
Ornitz DM: A combined series of Fgf9 and Fgf18 mutant alleles
identifies unique and redundant roles in skeletal development. Dev
Biol. 411:72–84. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Ellsworth JL, Berry J, Bukowski T, Claus
J, Feldhaus A, Holderman S, Holdren MS, Lum KD, Moore EE, Raymond
F, et al: Fibroblast growth factor-18 is a trophic factor for
mature chondrocytes and their progenitors. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 10:308–320. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Luan J, Che G, Man G and Xiao F:
Ginsenoside Rb1 from Panax ginseng attenuates
monoiodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis by inhibiting
miR-21-5p/FGF18-mediated inflammation. J Food Biochem.
46(e14340)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Shared principles
in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 132:344–362. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Yu Q, Zeng KW, Ma XL, Jiang Y, Tu PF and
Wang XM: Ginsenoside Rk1 suppresses pro-inflammatory responses in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 cells by inhibiting the
Jak2/Stat3 pathway. Chin J Nat Med. 15:751–757. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Saba E, Jeong D, Irfan M, Lee YY, Park SJ,
Park CK and Rhee MH: Anti-inflammatory activity of Rg3-enriched
korean red ginseng extract in murine model of sepsis. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2018(6874692)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Olivotto E, Borzi RM, Vitellozzi R, Pagani
S, Facchini A, Battistelli M, Penzo M, Li X, Flamigni F, Li J, et
al: Differential requirements for IKKalpha and IKKbeta in the
differentiation of primary human osteoarthritic chondrocytes.
Arthritis Rheum. 58:227–239. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Xing L, Jiang M, Dong L, Gao J, Hou Y, Bai
G and Luo G: Cardioprotective effects of the YiQiFuMai injection
and isolated compounds on attenuating chronic heart failure via
NF-κB inactivation and cytokine suppression. J Ethnopharmacol.
148:239–245. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Zhang XH, Xu XX and Xu T: Ginsenoside Ro
suppresses interleukin-1β-induced apoptosis and inflammation in rat
chondrocytes by inhibiting NF-κB. Chin J Nat Med. 13:283–289.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Braicu C, Buse M, Busuioc C, Drula R,
Gulei D, Raduly L, Rusu A, Irimie A, Atanasov AG, Slaby O, et al: A
comprehensive review on MAPK: A promising therapeutic target in
cancer. Cancers (Basel). 11(1618)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Chen Y, Shou K, Gong C, Yang H, Yang Y and
Bao T: Anti-inflammatory effect of geniposide on osteoarthritis by
suppressing the activation of p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Biomed
Res Int. 2018(8384576)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Arafa EA, Refaey MS, Abd El-Ghafar OAM,
Hassanein EHM and Sayed AM: The promising therapeutic potentials of
ginsenosides mediated through p38 MAPK signaling inhibition.
Heliyon. 7(e08354)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Joh EH, Lee IA, Jung IH and Kim DH:
Ginsenoside Rb1 and its metabolite compound K inhibit IRAK-1
activation-the key step of inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol.
82:278–286. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
Hossain MA, Alam MJ, Kim B, Kang CW and
Kim JH: Ginsenoside-Rb1 prevents bone cartilage destruction through
down-regulation of p-Akt, p-P38, and p-P65 signaling in rabbit.
Phytomedicine. 100(154039)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Cui T, Lan Y, Lu Y, Yu F, Lin S, Fu Y, Qiu
J and Niu G: Isoorientin ameliorates
H2O2-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress
in chondrocytes by regulating MAPK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Aging
(Albany NY). 15:4861–4874. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Nuttall ME, Nadeau DP, Fisher PW, Wang F,
Keller PM, DeWolf WE Jr, Goldring MB, Badger AM, Lee D, Levy MA, et
al: Inhibition of caspase-3-like activity prevents apoptosis while
retaining functionality of human chondrocytes in vitro. J Orthop
Res. 18:356–363. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Na JY, Kim S, Song K, Lim KH, Shin GW, Kim
JH, Kim B, Kwon YB and Kwon J: Anti-apoptotic activity of
ginsenoside Rb1 in hydrogen peroxide-treated chondrocytes:
Stabilization of mitochondria and the inhibition of caspase-3. J
Ginseng Res. 36:242–247. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Kim S, Na JY, Song KB, Choi DS, Kim JH,
Kwon YB and Kwon J: Protective effect of ginsenoside rb1 on
hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in rat articular
chondrocytes. J Ginseng Res. 36:161–168. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Huang Y, Wu D and Fan W: Protection of
ginsenoside Rg1 on chondrocyte from IL-1β-induced
mitochondria-activated apoptosis through PI3K/Akt signaling. Mol
Cell Biochem. 392:249–257. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Xu Z, Li X, Shen G, Zou Y, Zhang H, Yang K
and Zhu Y: The protective effect of ginsenoside Rg1 on apoptosis in
human ankle joint traumatic arthritis chondrocytes. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2022(6798377)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Ma CH, Chou WC, Wu CH, Jou IM, Tu YK,
Hsieh PL and Tsai KL: Ginsenoside Rg3 attenuates TNF-α-induced
damage in chondrocytes through regulating SIRT1-mediated
anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory mechanisms. Antioxidants
(Basel). 10(1972)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Zhang J, Xu HX, Zhu JQ, Dou YX, Xian YF
and Lin ZX: Natural Nrf2 inhibitors: A review of their potential
for cancer treatment. Int J Biol Sci. 19:3029–3041. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Bellezza I, Giambanco I, Minelli A and
Donato R: Nrf2-Keap1 signaling in oxidative and reductive stress.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1865:721–733. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
77
|
Dong C, Liu P, Wang H, Dong M, Li G and Li
Y: Ginsenoside Rb1 attenuates diabetic retinopathy in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats1. Acta Cir Bras.
34(e201900201)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
78
|
Yang Q, Lin J, Zhang H, Liu Y, Kan M, Xiu
Z, Chen X, Lan X, Li X, Shi X, et al: Ginsenoside compound K
regulates amyloid β via the Nrf2/Keap1 signaling pathway in mice
with scopolamine hydrobromide-induced memory impairments. J Mol
Neurosci. 67:62–71. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
79
|
Hwang YP and Jeong HG: Ginsenoside Rb1
protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative stress by
increasing heme oxygenase-1 expression through an estrogen
receptor-related PI3K/Akt/Nrf2-dependent pathway in human
dopaminergic cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 242:18–28.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
80
|
Vincent TL, McClurg O and Troeberg L: The
extracellular matrix of articular cartilage controls the
bioavailability of pericellular matrix-bound growth factors to
drive tissue homeostasis and repair. Int J Mol Sci.
23(6003)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
81
|
Hu Q and Ecker M: Overview of MMP-13 as a
promising target for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Int J Mol
Sci. 22(1742)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
82
|
Yang CY, Chanalaris A and Troeberg L:
ADAMTS and ADAM metalloproteinases in osteoarthritis-looking beyond
the ‘usual suspects’. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 25:1000–1009.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Lee JH, Lim H, Shehzad O, Kim YS and Kim
HP: Ginsenosides from Korean red ginseng inhibit matrix
metalloproteinase-13 expression in articular chondrocytes and
prevent cartilage degradation. Eur J Pharmacol. 724:145–151.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
84
|
Shin JS, Park N, Ra J, Kim Y, Shin M, Hong
M, Kim SH, Kwon HJ, Hong SP, Kim J and Bae H: Panax ginseng C.A.
Meyer modulates the levels of MMP3 in S12 murine articular
cartilage cell line. J Ethnopharmacol. 124:397–403. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
So MW, Lee EJ, Lee HS, Koo BS, Kim YG, Lee
CK and Yoo B: Protective effects of ginsenoside Rg3 on human
osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Mod Rheumatol. 23:104–111.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Chen Y, Lin S, Sun Y, Pan X, Xiao L, Zou
L, Ho KW and Li G: Translational potential of ginsenoside Rb1 in
managing progression of osteoarthritis. J Orthop Translat. 6:27–33.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
87
|
Lee SY: Anti-metastatic and
anti-inflammatory effects of matrix metalloproteinase inhibition by
ginsenosides. Biomedicines. 9(198)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
88
|
Lee SY: Ginsenoside Rg1 drives
stimulations of timosaponin AIII-induced anticancer effects in
human osteosarcoma cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2020(8980124)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
89
|
Young DA, Barter MJ and Wilkinson DJ:
Recent advances in understanding the regulation of
metalloproteinases. F1000Res. 8(F1000 Faculty
Rev-195)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
90
|
Zhang P: Ginsenoside-Rg5 treatment
inhibits apoptosis of chondrocytes and degradation of cartilage
matrix in a rat model of osteoarthritis. Oncol Rep. 37:1497–1502.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Deshotels L, Safa FM and Saba NS: NOTCH
signaling in mantle cell lymphoma: Biological and clinical
implications. Int J Mol Sci. 24(10280)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Wang H, Tian Y, Wang J, Phillips KLE,
Binch ALA, Dunn S, Cross A, Chiverton N, Zheng Z, Shapiro IM, et
al: Inflammatory cytokines induce NOTCH signaling in nucleus
pulposus cells: Implications in intervertebral disc degeneration. J
Biol Chem. 288:16761–16774. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
93
|
Wang W, Zeng L, Wang ZM, Zhang S, Rong XF
and Li RH: Ginsenoside Rb1 inhibits matrix metalloproteinase 13
through down-regulating Notch signaling pathway in osteoarthritis.
Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 240:1614–1621. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
94
|
Jallali N, Ridha H, Thrasivoulou C,
Underwood C, Butler PEM and Cowen T: Vulnerability to ROS-induced
cell death in ageing articular cartilage: The role of antioxidant
enzyme activity. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 13:614–622.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
95
|
Kim JK, Choi MS, Jeung W, Ra J, Yoo HH and
Kim DH: Effects of gut microbiota on the pharmacokinetics of
protopanaxadiol ginsenosides Rd, Rg3, F2, and compound K in healthy
volunteers treated orally with red ginseng. J Ginseng Res.
44:611–618. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
96
|
Kim DH: Gut microbiota-mediated
pharmacokinetics of ginseng saponins. J Ginseng Res. 42:255–263.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
97
|
Kim HJ, Oh TK, Kim YH, Lee J, Moon JM,
Park YS and Sung CM: Pharmacokinetics of ginsenoside Rb1, Rg3, Rk1,
Rg5, F2, and compound K from red ginseng extract in healthy korean
volunteers. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2022(8427519)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
98
|
Wang W, Wang GJ, Xie HT, Sun JG, Zhao S,
Jiang XL, Li H, Lv H, Xu MJ and Wang R: Determination of
ginsenoside Rd in dog plasma by liquid chromatography-mass
spectrometry after solid-phase extraction and its application in
dog pharmacokinetics studies. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed
Life Sci. 852:8–14. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Zeng X, Deng Y, Feng Y, Liu Y, Yang L,
Huang Y, Sun J, Liang W and Guan Y: Pharmacokinetics and safety of
ginsenoside Rd following a single or multiple intravenous dose in
healthy Chinese volunteers. J Clin Pharmacol. 50:285–292.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
100
|
Gao XY, Liu GC, Zhang JX, Wang LH, Xu C,
Yan ZA, Wang A, Su YF, Lee JJ, Piao GC and Yuan HD: Pharmacological
properties of ginsenoside Re. Front Pharmacol.
13(754191)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Joo KM, Lee JH, Jeon HY, Park CW, Hong DK,
Jeong HJ, Lee SJ, Lee SY and Lim KM: Pharmacokinetic study of
ginsenoside Re with pure ginsenoside Re and ginseng berry extracts
in mouse using ultra performance liquid chromatography/mass
spectrometric method. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 51:278–283.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
102
|
Zhao J, Su C, Yang C, Liu M, Tang L, Su W
and Liu Z: Determination of ginsenosides Rb1, Rb2, and Rb3 in rat
plasma by a rapid and sensitive liquid chromatography tandem mass
spectrometry method: Application in a pharmacokinetic study. J
Pharm Biomed Anal. 64-65:94–97. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
103
|
Miao L, Yang Y, Li Z, Fang Z, Zhang Y and
Han CC: Ginsenoside Rb2: A review of pharmacokinetics and
pharmacological effects. J Ginseng Res. 46:206–213. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
104
|
Xie F, Li S, Cheng Z, Liu X, Zhang H, Li
P, Liu Z, Guo X and Yu P: Determination of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol in
human plasma by HPLC-MS/MS: Application to a pharmacokinetic study.
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B. 3:385–391. 2013.
|
|
105
|
Li L, Chen X, Li D and Zhong D:
Identification of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol metabolites in human liver
microsomes and human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos. 39:472–483.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
106
|
Ren HC, Sun JG, Wang GJ, A JY, Xie HT, Zha
WB, Yan B, Sun FZ, Hao HP, Gu SH, et al: Sensitive determination of
20(S)-protopanaxadiol in rat plasma using HPLC-APCI-MS: Application
of pharmacokinetic study in rats. J Pharm Biomed Anal.
48:1476–1480. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Kim H, Lee JH, Kim JE, Kim YS, Ryu CH, Lee
HJ, Kim HM, Jeon H, Won HJ, Lee JY and Lee J: Micro-/nano-sized
delivery systems of ginsenosides for improved systemic
bioavailability. J Ginseng Res. 42:361–369. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
108
|
Wang H, Zheng Y, Sun Q, Zhang Z, Zhao M,
Peng C and Shi S: Ginsenosides emerging as both bifunctional drugs
and nanocarriers for enhanced antitumor therapies. J
Nanobiotechnology. 19(322)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Yang L, Zhang Z, Hou J, Jin X, Ke Z, Liu
D, Du M, Jia X and Lv H: Targeted delivery of ginsenoside compound
K using TPGS/PEG-PCL mixed micelles for effective treatment of lung
cancer. Int J Nanomedicine. 12:7653–7667. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
110
|
Dong Y, Fu R, Yang J, Ma P, Liang L, Mi Y
and Fan D: Folic acid-modified ginsenoside Rg5-loaded bovine serum
albumin nanoparticles for targeted cancer therapy in vitro and in
vivo. Int J Nanomedicine. 14:6971–6988. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
111
|
Liu Y, Zhu H, Zhou W and Ye Q:
Anti-inflammatory and anti-gouty-arthritic effect of free
ginsenoside Rb1 and nano ginsenoside Rb1 against MSU induced gouty
arthritis in experimental animals. Chem Biol Interact.
332(109285)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
112
|
Singh H, Du J, Singh P, Mavlonov GT and Yi
TH: Development of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles via
direct conjugation with ginsenosides and its in-vitro study. J
Photochem Photobiol B. 185:100–110. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Liu X, Tang I, Wainberg ZA and Meng H:
Safety considerations of cancer nanomedicine-A key step toward
translation. Small. 16(e2000673)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
114
|
Wu B, Yang L, Chen L, Ma L and Guo Y:
Traditional Chinese medicine therapies for patients with knee
osteoarthritis: A protocol for systematic review and network
meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 101(e29404)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
115
|
Ju L, Hu P, Chen P, Xue X, Li Z, He F, Qiu
Z, Cheng J and Huang F: Huoxuezhitong capsule ameliorates
MIA-induced osteoarthritis of rats through suppressing
PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway. Biomed Pharmacother.
129(110471)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
116
|
Liu T, Zhu L and Wang L: A narrative
review of the pharmacology of ginsenoside compound K. Ann Transl
Med. 10(234)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
117
|
Chen L, Zhou L, Wang Y, Yang G, Huang J,
Tan Z, Wang Y, Zhou G, Liao J and Ouyang D: Food and sex-related
impacts on the pharmacokinetics of a single-dose of ginsenoside
compound K in healthy subjects. Front Pharmacol.
8(636)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
118
|
Liu Y, Perumalsamy H, Kang CH, Kim SH,
Hwang JS, Koh SC, Yi TH and Kim YJ: Intracellular synthesis of gold
nanoparticles by Gluconacetobacter liquefaciens for delivery of
peptide CopA3 and ginsenoside and anti-inflammatory effect on
lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages. Artif Cells Nanomed
Biotechnol. 48:777–788. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
119
|
Kang S, Siddiqi MH, Yoon SJ, Ahn S, Noh
HY, Kumar NS, Kim YJ and Yang DC: Therapeutic potential of compound
K as an IKK inhibitor with implications for osteoarthritis
prevention: An in silico and in vitro study. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol
Anim. 52:895–905. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
120
|
Hassamal S: Chronic stress,
neuroinflammation, and depression: An overview of
pathophysiological mechanisms and emerging anti-inflammatories.
Front Psychiatry. 14(1130989)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Schaaf MJ and Cidlowski JA: Molecular
mechanisms of glucocorticoid action and resistance. J Steroid
Biochem Mol Biol. 83:37–48. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
122
|
Bannuru RR, Osani MC, Vaysbrot EE, Arden
NK, Bennell K, Bierma-Zeinstra SMA, Kraus VB, Lohmander LS, Abbott
JH, Bhandari M, et al: OARSI guidelines for the non-surgical
management of knee, hip, and polyarticular osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 27:1578–1589. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Guermazi A, Neogi T, Katz JN, Kwoh CK,
Conaghan PG, Felson DT and Roemer FW: Intra-articular
corticosteroid injections for the treatment of hip and knee
osteoarthritis-related pain: Considerations and controversies with
a focus on imaging-radiology scientific expert panel. Radiology.
297:503–512. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
124
|
Li J, Du J, Liu D, Cheng B, Fang F, Weng
L, Wang C and Ling C: Ginsenoside Rh1 potentiates dexamethasone's
anti-inflammatory effects for chronic inflammatory disease by
reversing dexamethasone-induced resistance. Arthritis Res Ther.
16(R106)2014.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
125
|
Barnes PJ and Adcock IM: Glucocorticoid
resistance in inflammatory diseases. Lancet. 373:1905–1917.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|