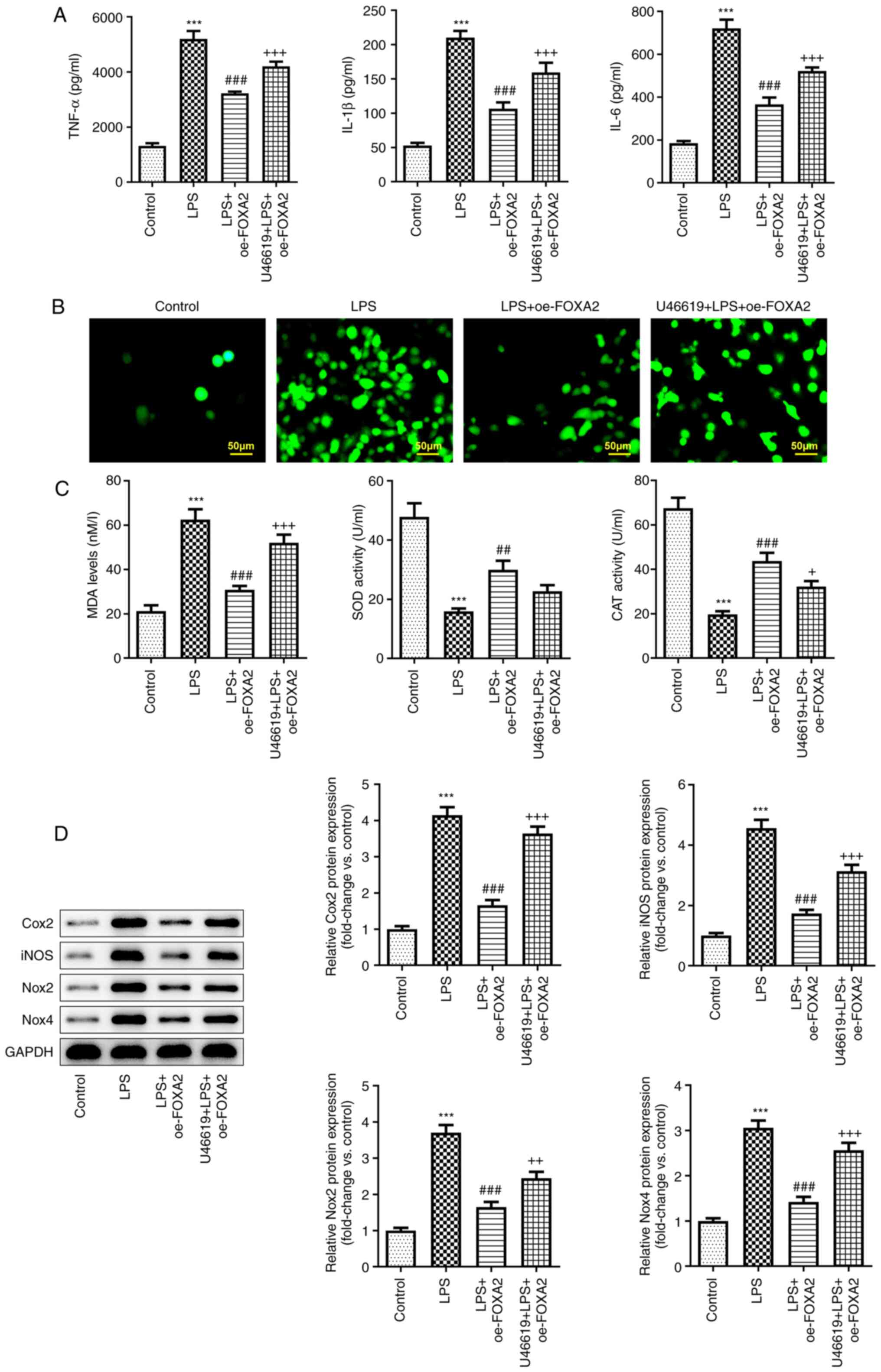
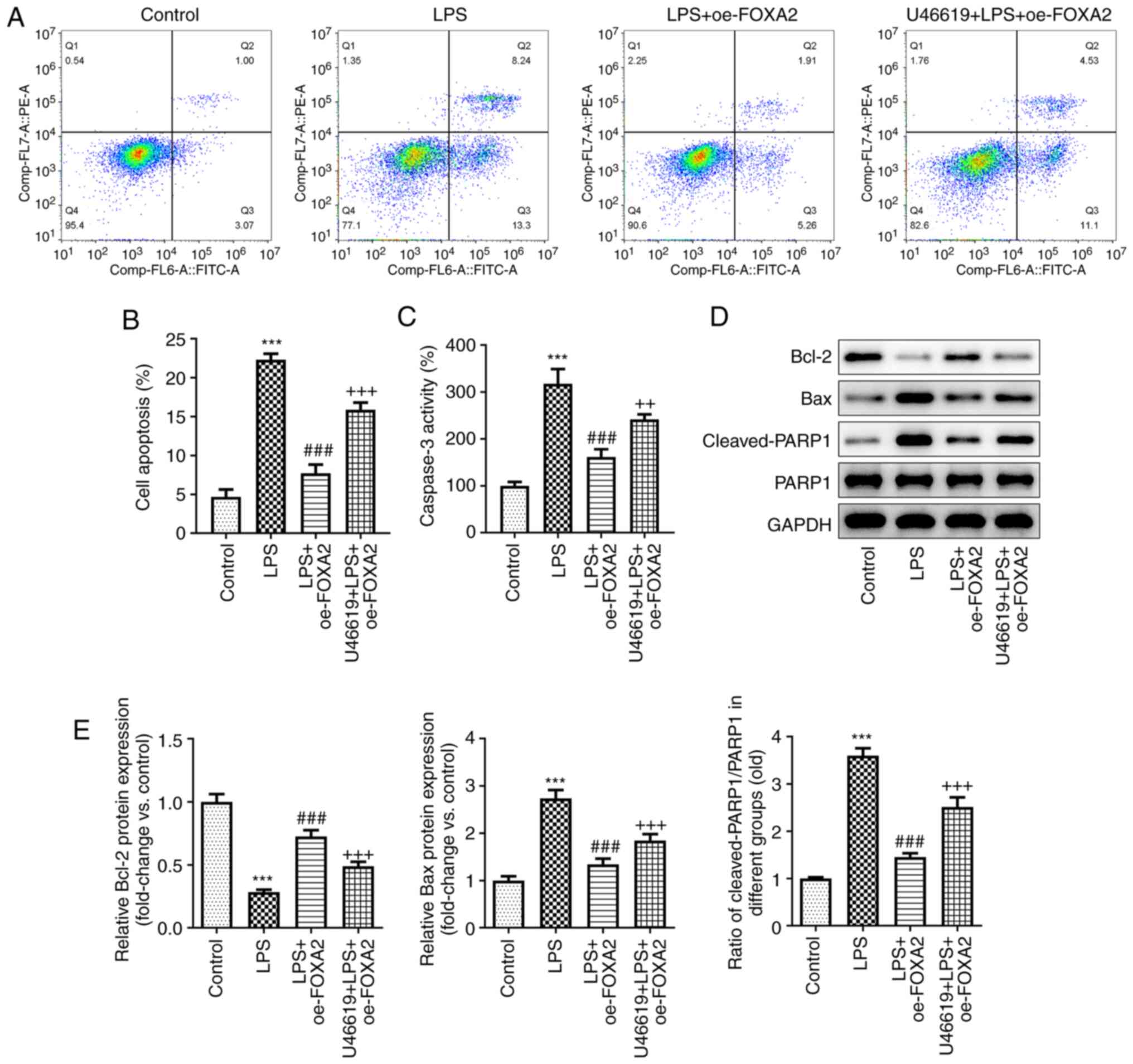
|
1
|
Kulkarni D, Wang X, Sharland E, Stansfield
D, Campbell H and Nair H: The global burden of hospitalisation due
to pneumonia caused by Staphylococcus aureus in the under-5
years children: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
EClinicalMedicine. 44(101267)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Liu L, Oza S, Hogan D, Chu Y, Perin J, Zhu
J, Lawn JE, Cousens S, Mathers C and Black RE: Global, regional,
and national causes of under-5 mortality in 2000-15: An updated
systematic analysis with implications for the sustainable
development goals. Lancet. 388:3027–3035. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Ma C, Zhang D, Ma Q, Liu Y and Yang Y:
Arbutin inhibits inflammation and apoptosis by enhancing autophagy
via SIRT1. Adv Clin Exp Med. 30:535–544. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Lee JK, Lee J, Park YS, Lee CH, Yim JJ,
Yoo CG, Kim YW, Han SK and Lee SM: Clinical manifestations of
pneumonia according to the causative organism in patients in the
intensive care unit. Korean J Intern Med. 30:829–836.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Calina D RL, Rosu AF, Ianoşi G, Ianoşi S,
Zlatian O, Mitruț R, Docea A, Rogoveanu O and Mitruț P: Etiological
diagnosis and pharmacotherapeutic management of parapneumonic
pleuresy. Farmacia. 64:946–952. 2016.
|
|
6
|
Carvalhaes CG, Sader HS, Rhomberg PR and
Mendes RE: Tedizolid activity against a multicentre worldwide
collection of Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pneumoniae
recovered from patients with pneumonia (2017-2019). Int J Infect
Dis. 107:92–100. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Fieldhouse JK, Toh TH, Lim WH, Ting J, Ha
SJ, Hii KC, Kong CI, Wong TM, Wong SC, Warkentien TE and Gray GC:
Surveillance for respiratory syncytial virus and parainfluenza
virus among patients hospitalized with pneumonia in Sarawak,
Malaysia. PLoS One. 13(e0202147)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Tanase A, Colita A, Ianosi G, Neagoe D,
Branisteanu DE, Calina D, Docea AO, Tsatsakis A and Ianosi SL: Rare
case of disseminated fusariosis in a young patient with graft vs.
host disease following an allogeneic transplant. Exp Ther Med.
12:2078–2082. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Taheri Y, Jokovic N, Vitorovic J,
Grundmann O, Maroyi A and Calina D: The burden of the serious and
difficult-to-treat infections and a new antibiotic available:
Cefiderocol. Front Pharmacol. 11(578823)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ungureanu A, Zlatian O, Mitroi G, Drocas
A, Tirca T, Calina D, Dehelean C, Docea AO, Izotov BN, Rakitskii
VN, et al: Staphylococcus aureus colonisation in patients from a
primary regional hospital. Mol Med Rep. 16:8771–8780.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Zlatian O, Balasoiu AT, Balasoiu M,
Cristea O, Docea AO, Mitrut R, Spandidos DA, Tsatsakis AM, Bancescu
G and Calina D: Antimicrobial resistance in bacterial pathogens
among hospitalised patients with severe invasive infections. Exp
Ther Med. 16:4499–4510. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Islam MT, Nasiruddin M, Khan IN, Mishra
SK, Kudrat EZM, Riaz TA, Ali ES, Rahman MS, Mubarak MS, Martorell
M, et al: A perspective on emerging therapeutic interventions for
COVID-19. Front Public Health. 8(281)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Calina D, Sarkar C, Arsene AL, Salehi B,
Docea AO, Mondal M, Islam MT, Zali A and Sharifi-Rad J: Recent
advances, approaches and challenges in targeting pathways for
potential COVID-19 vaccines development. Immunol Res. 68:315–324.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Islam MT, Quispe C, Martorell M, Docea AO,
Salehi B, Calina D, Reiner Ž and Sharifi-Rad J: Dietary
supplements, vitamins and minerals as potential interventions
against viruses: Perspectives for COVID-19. Int J Vitam Nutr Res.
92:49–66. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
COVID-19 Excess Mortality Collaborators.
Estimating excess mortality due to the COVID-19 pandemic: A
systematic analysis of COVID-19-related mortality, 2020-21. Lancet.
399:1513–1536. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li J, Machado AC, Guo M, Sagendorf JM,
Zhou Z, Jiang L, Chen X, Wu D, Qu L, Chen Z, et al: Structure of
the forkhead domain of FOXA2 bound to a complete DNA consensus
site. Biochemistry. 56:3745–3753. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jackson DA, Rowader KE, Stevens K, Jiang
C, Milos P and Zaret KS: Modulation of liver-specific transcription
by interactions between hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 and nuclear
factor 1 binding DNA in close apposition. Mol Cell Biol.
13:2401–2410. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Orstad G, Fort G, Parnell TJ, Jones A,
Stubben C, Lohman B, Gillis KL, Orellana W, Tariq R, Klingbeil O,
et al: FoxA1 and FoxA2 control growth and cellular identity in
NKX2-1-positive lung adenocarcinoma. Dev Cell. 57:1866–1882 e10.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gao H, Yan Z, Sun H and Chen Y: FoXA2
promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma progression by ZEB2
activation. World J Surg Oncol. 19(286)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Connelly ZM, Jin R, Zhang J, Yang S, Cheng
S, Shi M, Cates JM, Shi R, DeGraff DJ, Nelson PS, et al: FOXA2
promotes prostate cancer growth in the bone. Am J Transl Res.
12:5619–5629. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Choi W, Choe S and Lau GW: Inactivation of
FOXA2 by respiratory bacterial pathogens and dysregulation of
pulmonary mucus homeostasis. Front Immunol. 11(515)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhou Y, Liu L, Tao S, Yao Y, Wang Y, Wei
Q, Shao A and Deng Y: Parthanatos and its associated components:
Promising therapeutic targets for cancer. Pharmacol Res.
163(105299)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bai D, Han A and Cong S: The effect of
down-regulation of CCL5 on lipopolysaccharide-induced WI-38
fibroblast injury: A potential role for infantile pneumonia. Iran J
Basic Med Sci. 21:449–454. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yu Y, Yang T, Ding Z and Cao Y:
Circ_0026579 alleviates LPS-induced WI-38 cells inflammation injury
in infantile pneumonia. Innate Immun. 28:37–48. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ren H, Meng Q, Yepuri N, Du X, Sarpong JO
and Cooney RN: Protective effects of glutathione on oxidative
injury induced by hydrogen peroxide in intestinal epithelial cells.
J Surg Res. 222:39–47. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hotamisligil GS and Davis RJ: Cell
signaling and stress responses. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
8(a006072)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Tang AC, Saferali A, He G, Sandford AJ,
Strug LJ and Turvey SE: Endoplasmic reticulum stress and chemokine
production in cystic fibrosis airway cells: Regulation by STAT3
modulation. J Infect Dis. 215:293–302. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Bjarnason A, Westin J, Lindh M, Andersson
LM, Kristinsson KG, Love A, Baldursson O and Gottfredsson M:
Incidence, etiology, and outcomes of community-acquired pneumonia:
A population-based study. Open Forum Infect Dis.
5(ofy010)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Liu Y, Bao C, Deng G and Ouyang Y:
Arid2-IR downregulates miR-132-3p through methylation to promote
LPS-induced ALI in pneumonia. Inhal Toxicol. 34:297–303.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
An X, Sun X, Hou Y, Yang X, Chen H, Zhang
P and Wu J: Protective effect of oxytocin on LPS-induced acute lung
injury in mice. Sci Rep. 9(2836)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Shi J, Wang H, Liu J, Zhang Y, Luo J, Li
Y, Yang C and Jiang J: Ganoderic acid B attenuates LPS-induced lung
injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 88(106990)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang S, Lu B, Liu J and Gu Y: TRIM27
suppresses inflammation injuries in pediatric pneumonia by
targeting TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Allergol Immunopathol
(Madr). 50:33–39. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Cao X and Wan H and Wan H: Urolithin A
induces protective autophagy to alleviate inflammation, oxidative
stress, and endoplasmic reticulum stress in pediatric pneumonia.
Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 50:147–153. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cui H, Zhang S, Wu Z, Xu C, Xu D and Jin
Z: Insulin-like growth factor-1 reduces hyperoxia-induced lung
inflammation and oxidative stress and inhibits cell apoptosis
through PERK/eIF2alpha/ATF4/CHOP signaling. Exp Lung Res.
48:187–197. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Xu C, Song L, Zhang W, Zou R and Zhu M:
6'-O-galloylpaeoniflorin alleviates inflammation and oxidative
stress in pediatric pneumonia through activating Nrf2 activation.
Allergol Immunopathol (Madr). 50:71–76. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yánez DC, Lau CI, Papaioannou E, Chawda
MM, Rowell J, Ross S, Furmanski A and Crompton T: The pioneer
transcription factor Foxa2 modulates T helper differentiation to
reduce mouse allergic airway disease. Front Immunol.
13(890781)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Mei M, Nie J, Sun H, Wang H and Rong L:
LncRNA-NEF regulated the hyperoxia-induced injury of lung
epithelial cells by FOXA2. Am J Transl Res. 12:5563–5574.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim HJ, Jeong JS, Kim SR, Park SY, Chae HJ
and Lee YC: Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress alleviates
lipopolysaccharide-induced lung inflammation through modulation of
NF-κB/HIF-1α signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 3(1142)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wang K, Brems JJ, Gamelli RL and Holterman
AX: Foxa2 may modulate hepatic apoptosis through the cIAP1 pathway.
Cell Signal. 25:867–874. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zou X and Blank M: Targeting p38 MAP
kinase signaling in cancer through post-translational
modifications. Cancer Lett. 384:19–26. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Santana FPR, da Silva RC, Ponci V,
Pinheiro A, Olivo CR, Caperuto LC, Arantes-Costa FM, Claudio SR,
Ribeiro DA, Tibério IFLC, et al: Dehydrodieugenol improved lung
inflammation in an asthma model by inhibiting the STAT3/SOCS3 and
MAPK pathways. Biochem Pharmacol. 180(114175)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Tolomeo M and Cascio A: The multifaced
role of STAT3 in cancer and its implication for anticancer therapy.
Int J Mol Sci. 22(603)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Cao L, Liu F, Liu Y, Liu T, Wu J, Zhao J,
Wang J, Li S, Xu J and Dong L: TSLP promotes asthmatic airway
remodeling via p38-STAT3 signaling pathway in human lung
fibroblast. Exp Lung Res. 44:288–301. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kim J, Lee HJ, Park JH, Cha BY and Hoe HS:
Nilotinib modulates LPS-induced cognitive impairment and
neuroinflammatory responses by regulating P38/STAT3 signaling. J
Neuroinflammation. 19(187)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Tao Y, Sun Y, Wu B, Xu D, Yang J, Gu L and
Du C: Overexpression of FOXA2 attenuates cigarette smoke-induced
cellular senescence and lung inflammation through inhibition of the
p38 and Erk1/2 MAPK pathways. Int Immunopharmacol.
94(107427)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|