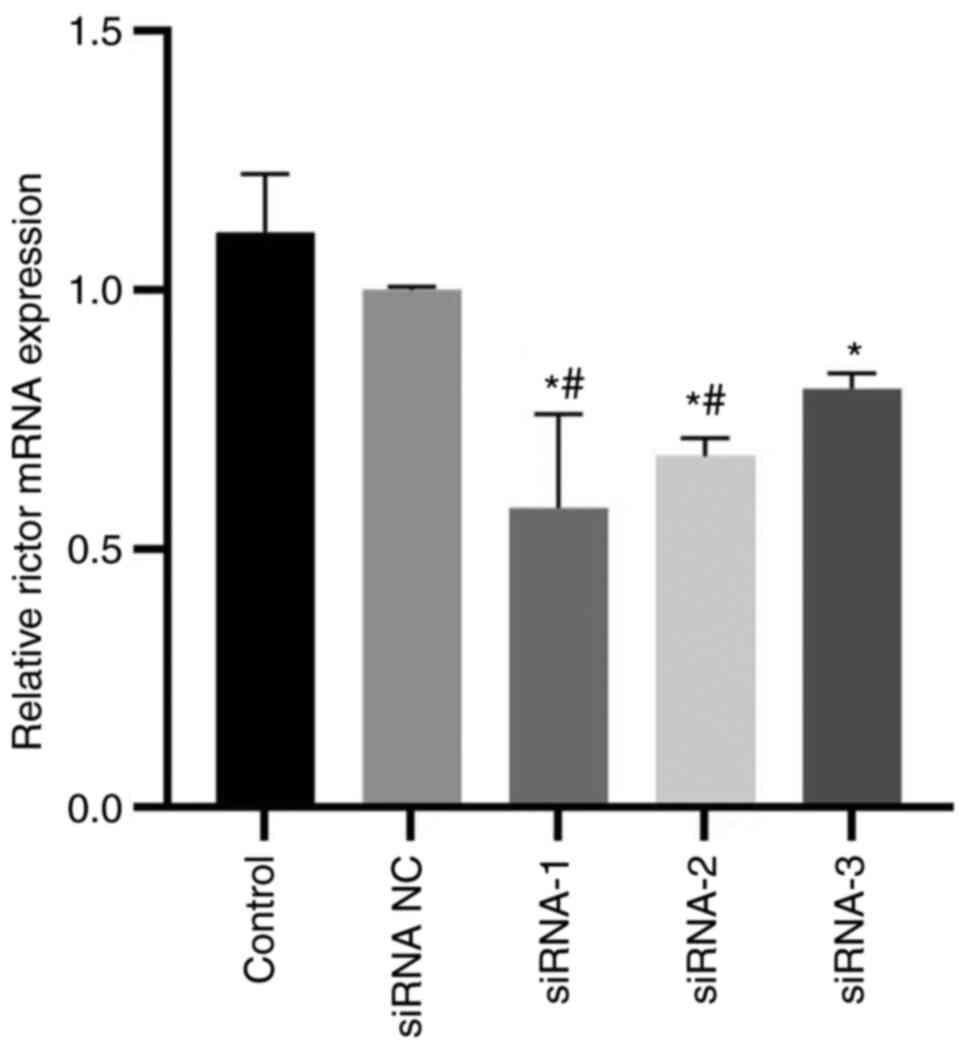
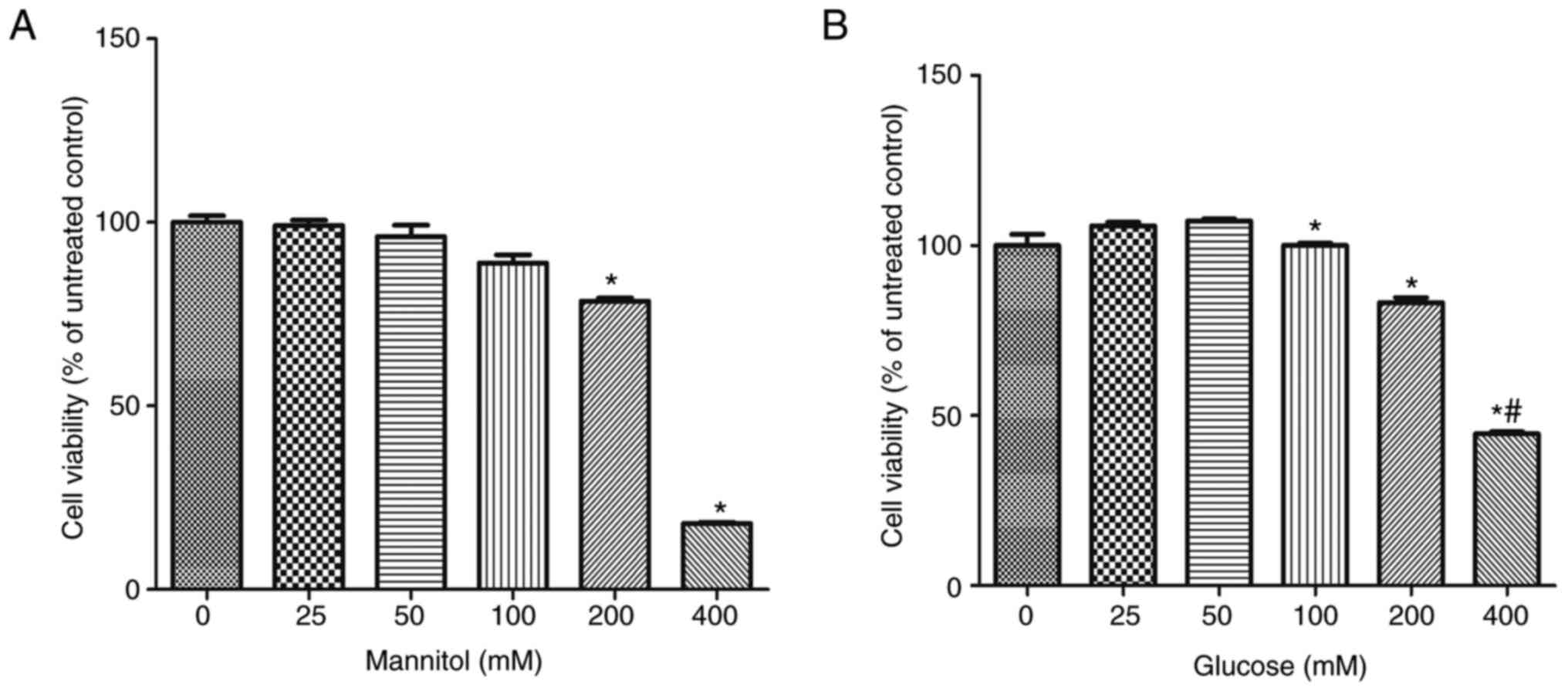
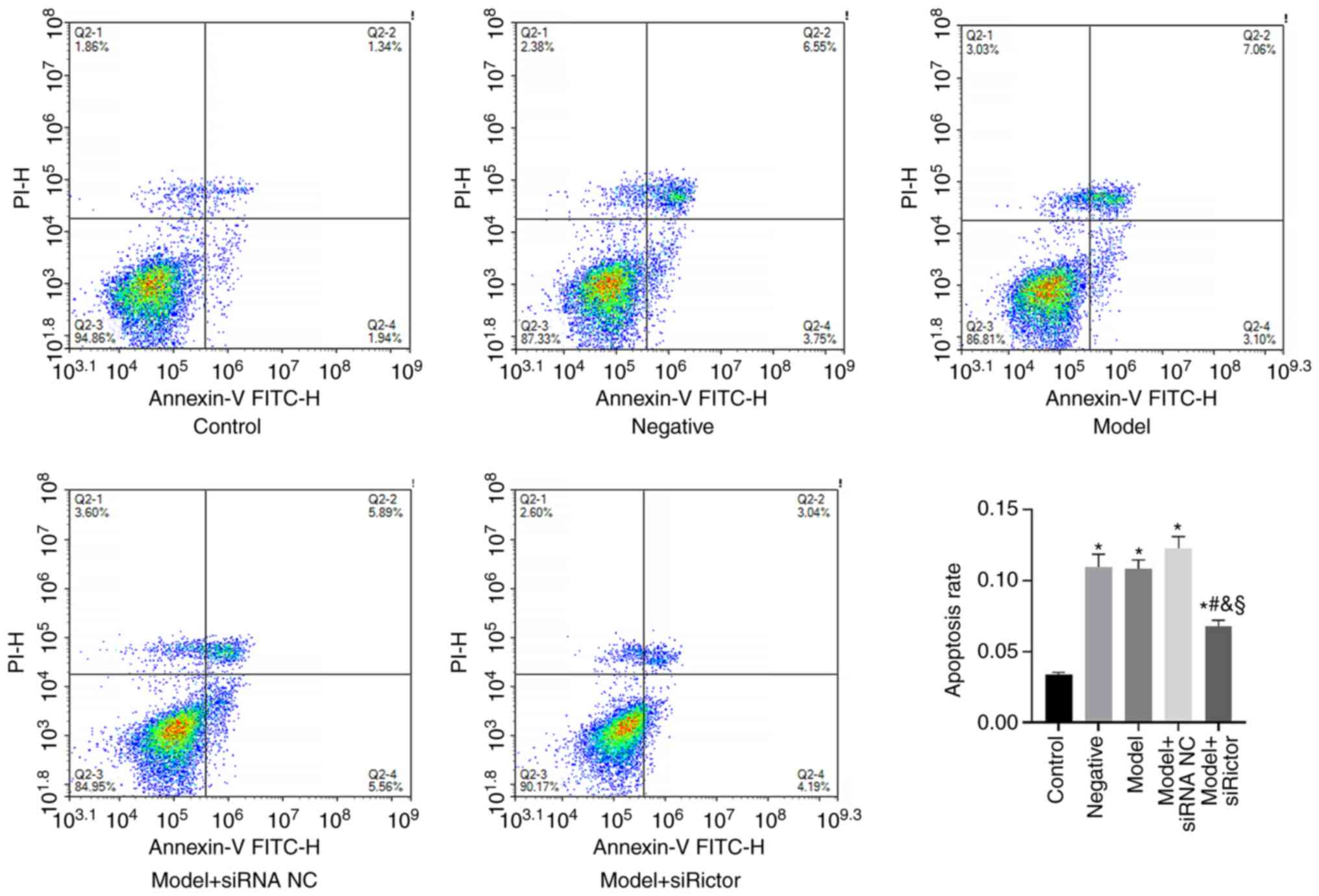
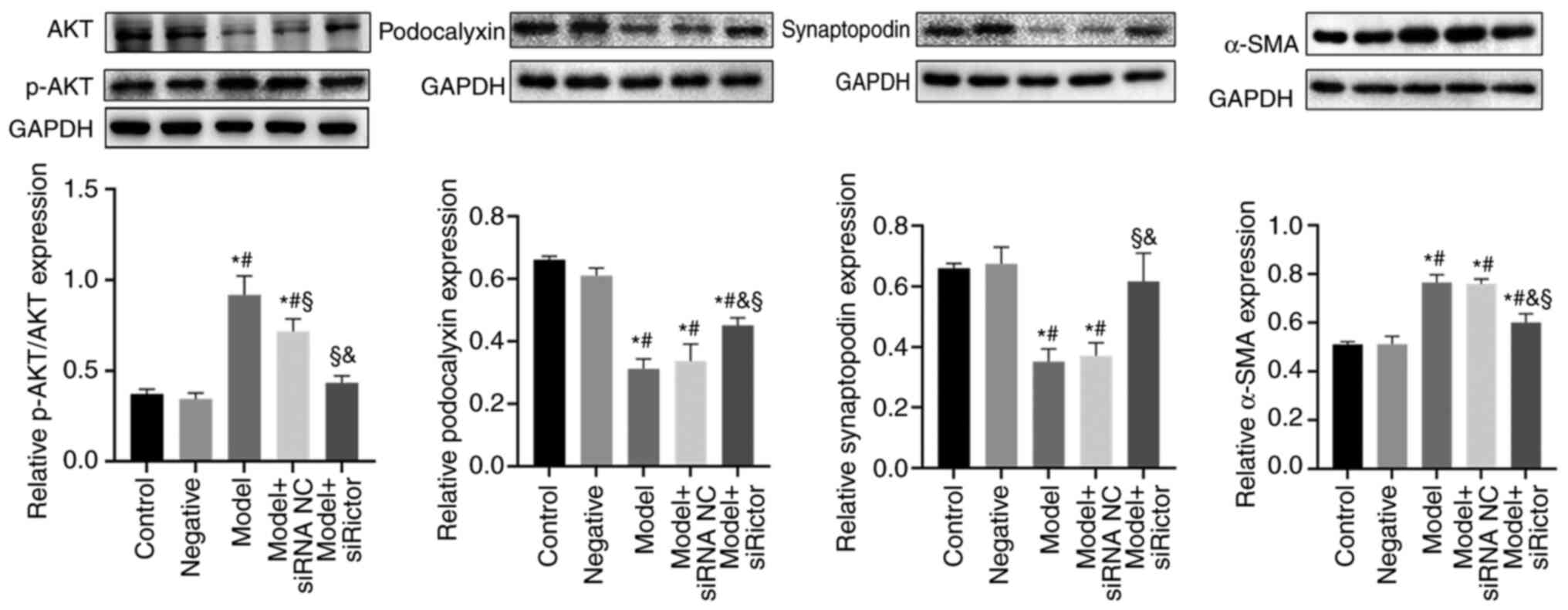
|
1
|
Gnudi L, Coward RJM and Long DA: Diabetic
nephropathy: Perspective on novel molecular mechanisms. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 27:820–830. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tryggvason K, Patrakka J and Wartiovaara
J: Hereditary proteinuria syndromes and mechanisms of proteinuria.
N Engl J Med. 354:1387–1401. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Siu B, Saha J, Smoyer WE, Sullivan KA and
Brosius FC III: Reduction in podocyte density as a pathologic
feature in early diabetic nephropathy in rodents: Prevention by
lipoic acid treatment. BMC Nephrol. 7(6)2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jo HA, Kim JY, Yang SH, Han SS, Joo KW,
Kim YS and Kim DK: The role of local IL6/JAK2/STAT3 signaling in
high glucose-induced podocyte hypertrophy. Kidney Res Clin Pract.
35:212–218. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Li S, Sun Z, Zhang Y, Ruan Y, Chen Q, Gong
W, Yu J, Xia W, He JC, Huang S, et al: COX-2/mPGES-1/PGE2 cascade
activation mediates uric acid-induced mesangial cell proliferation.
Oncotarget. 8:10185–10198. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Maezawa Y, Takemoto M and Yokote K: Cell
biology of diabetic nephropathy: Roles of endothelial cells,
tubulointerstitial cells and podocytes. J Diabetes Investig.
6:3–15. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Wu L, Feng Z, Cui S, Hou K, Tang L, Zhou
J, Cai G, Xie Y, Hong Q, Fu B and Chen X: Rapamycin upregulates
autophagy by inhibiting the mTOR-ULK1 pathway, resulting in reduced
podocyte injury. PLoS One. 8(e63799)2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kumar S and Tikoo K: Independent role of
PP2A and mTORc1 in palmitate induced podocyte death. Biochimie.
112:73–84. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Gaubitz C, Prouteau M, Kusmider B and
Loewith R: TORC2 structure and function. Trends Biochem Sci.
41:532–545. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yasuda M, Tanaka Y, Kume S, Morita Y,
Chin-Kanasaki M, Araki H, Isshiki K, Araki S, Koya D, Haneda M, et
al: Fatty acids are novel nutrient factors to regulate mTORC1
lysosomal localization and apoptosis in podocytes. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1842:1097–1108. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Ballesteros-Álvarez J and Andersen JK:
mTORC2: The other mTOR in autophagy regulation. Aging Cell.
20(e13431)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Gödel M, Hartleben B, Herbach N, Liu S,
Zschiedrich S, Lu S, Debreczeni-Mór A, Lindenmeyer MT, Rastaldi MP,
Hartleben G, et al: Role of mTOR in podocyte function and diabetic
nephropathy in humans and mice. J Clin Invest. 121:2197–2209.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Aliabadi AZ, Pohanka E, Seebacher G,
Dunkler D, Kammerstätter D, Wolner E, Grimm M and Zuckermann AO:
Development of proteinuria after switch to sirolimus-based
immunosuppression in long-term cardiac transplant patients. Am J
Transplant. 8:854–861. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ding F, Zhang X, Li X, Zhang Y, Li B and
Ding J: Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 signaling pathway
regulates transient receptor potential cation channel 6 in
podocytes. PLoS One. 9(e112972)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhang HT, Wang WW, Ren LH, Zhao XX, Wang
ZH, Zhuang DL and Bai YN: The mTORC2/Akt/NFκB pathway-mediated
activation of TRPC6 participates in adriamycin-induced podocyte
apoptosis. Cell Physiol Biochem. 40:1079–1093. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li Q, Zeng Y, Jiang Q, Wu C and Zhou J:
Role of mTOR signaling in the regulation of high glucose-induced
podocyte injury. Exp Ther Med. 17:2495–2502. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lou JS, Xia YT, Wang HY, Kong XP, Yao P,
Dong TTX, Zhou ZY and Tsim KWK: The WT1/MVP-Mediated Stabilization
on mTOR/AKT axis enhances the effects of cisplatin in non-small
cell lung cancer by a reformulated Yu Ping Feng San Herbal
Preparation. Front Pharmacol. 9(853)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Shankland SJ: The podocyte's response to
injury: Role in proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int.
69:2131–2147. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Coward RJ, Foster RR, Patton D, Ni L,
Lennon R, Bates DO, Harper SJ, Mathieson PW and Saleem MA:
Nephrotic plasma alters slit diaphragm-dependent signaling and
translocates nephrin, Podocin, and CD2 associated protein in
cultured human podocytes. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:629–637.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Dalla Vestra M, Masiero A, Roiter AM,
Saller A, Crepaldi G and Fioretto P: Is podocyte injury relevant in
diabetic nephropathy? Studies in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes. 52:1031–1035. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang C, Hou B, Yu S, Chen Q, Zhang N and
Li H: HGF alleviates high glucose-induced injury in podocytes by
GSK3β inhibition and autophagy restoration. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1863:2690–2699. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xu L, Fan Q, Wang X, Li L, Lu X, Yue Y,
Cao X, Liu J, Zhao X and Wang L: Ursolic acid improves podocyte
injury caused by high glucose. Nephrol Dial Transplant.
32:1285–1293. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sun J, Li ZP, Zhang RQ and Zhang HM:
Repression of miR-217 protects against high glucose-induced
podocyte injury and insulin resistance by restoring PTEN-mediated
autophagy pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 483:318–324.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Miaomiao W, Chunhua L, Xiaochen Z,
Xiaoniao C, Hongli L and Zhuo Y: Autophagy is involved in
regulating VEGF during high-glucose-induced podocyte injury. Mol
Biosyst. 12:2202–2212. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wei M, Li Z, Xiao L and Yang Z: Effects of
ROS-relative NF-κB signaling on high glucose-induced TLR4 and MCP-1
expression in podocyte injury. Mol Immunol. 68 (2 Pt A):261–271.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li J, Wang B, Zhou G, Yan X and Zhang Y:
Tetrahydroxy stilbene glucoside alleviates high glucose-induced
MPC5 podocytes injury through suppression of NLRP3 inflammasome. Am
J Med Sci. 355:588–596. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lei J, Zhao L, Zhang Y, Wu Y and Liu Y:
High glucose-induced podocyte injury involves activation of
mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-Induced endoplasmic reticulum
(ER) stress. Cell Physiol Biochem. 45:2431–2443. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Song S, Qiu D, Shi Y, Wang S, Zhou X, Chen
N, Wei J, Wu M, Wu H and Duan H: Thioredoxin-interacting protein
deficiency alleviates phenotypic alterations of podocytes via
inhibition of mTOR activation in diabetic nephropathy. J Cell
Physiol. 234:16485–16502. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Song S, Qiu D, Wang Y, Wei J, Wu H, Wu M,
Wang S, Zhou X, Shi Y and Duan H: TXNIP deficiency mitigates
podocyte apoptosis via restraining the activation of mTOR or p38
MAPK signaling in diabetic nephropathy. Exp Cell Res.
388(111862)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
McNicholas BA, Eng DG, Lichtnekert J,
Rabinowitz PS, Pippin JW and Shankland SJ: Reducing mTOR augments
parietal epithelial cell density in a model of acute podocyte
depletion and in aged kidneys. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
311:F626–F639. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Huang Z, Zhang L, Chen Y, Zhang H, Yu C,
Zhou F, Zhang Z, Jiang L, Li R, Ma J, et al: RhoA deficiency
disrupts podocyte cytoskeleton and induces podocyte apoptosis by
inhibiting YAP/dendrin signal. BMC Nephrol. 17(66)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Schell C and Huber TB: The evolving
complexity of the podocyte cytoskeleton. J Am Soc Nephrol.
28:3166–3174. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhang Y, Xu C, Ye Q, Tong L, Jiang H, Zhu
X, Huang L, Lin W, Fu H, Wang J, et al: Podocyte apoptosis in
diabetic nephropathy by BASP1 activation of the p53 pathway via
WT1. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 232(e13634)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Loeffler I and Wolf G:
Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal transition in diabetic nephropathy: Fact
or fiction? Cells. 4:631–652. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Xing L, Liu Q, Fu S, Li S, Yang L, Liu S,
Hao J, Yu L and Duan H: PTEN inhibits high glucose-induced
phenotypic transition in podocytes. J Cell Biochem. 116:1776–1784.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ha TS, Nam JA, Seong SB, Saleem MA, Park
SJ and Shin JI: Montelukast improves the changes of cytoskeletal
and adaptor proteins of human podocytes by interleukin-13. Inflamm
Res. 66:793–802. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Woychyshyn B, Papillon J, Guillemette J,
Navarro-Betancourt JR and Cybulsky AV: Genetic ablation of SLK
exacerbates glomerular injury in adriamycin nephrosis in mice. Am J
Physiol Renal Physiol. 318:F1377–F1390. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Daehn IS and Duffield JS: The glomerular
filtration barrier: A structural target for novel kidney therapies.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 20:770–788. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Fernández D, Horrillo A, Alquezar C,
González-Manchón C, Parrilla R and Ayuso MS: Control of cell
adhesion and migration by podocalyxin. Implication of Rac1 and
Cdc42. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 432:302–307. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Nielsen JS, Graves ML, Chelliah S, Vogl
AW, Roskelley CD and McNagny KM: The CD34-related molecule
podocalyxin is a potent inducer of microvillus formation. PLoS One.
2(e237)2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Oh J, Reiser J and Mundel P: Dynamic
(re)organization of the podocyte actin cytoskeleton in the
nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 19:130–137. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Kavoura E, Gakiopoulou H, Paraskevakou H,
Marinaki S, Agrogiannis G, Stofas A, Boletis I, Patsouris E and
Lazaris AC: Immunohistochemical evaluation of podocalyxin
expression in glomerulopathies associated with nephrotic syndrome.
Hum Pathol. 42:227–235. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Weinhold B, Sellmeier M, Schaper W, Blume
L, Philippens B, Kats E, Bernard U, Galuska SP, Geyer H, Geyer R,
et al: Deficits in sialylation impair podocyte maturation. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 23:1319–1328. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kang HG, Lee M, Lee KB, Hughes M, Kwon BS,
Lee S, McNagny KM, Ahn YH, Ko JM, Ha IS, et al: Loss of podocalyxin
causes a novel syndromic type of congenital nephrotic syndrome. Exp
Mol Med. 49(e414)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Imaizumi T, Nakatochi M, Akiyama S,
Yamaguchi M, Kurosawa H, Hirayama Y, Katsuno T, Tsuboi N, Hara M
and Maruyama S: Urinary podocalyxin as a biomarker to diagnose
membranous nephropathy. PLoS One. 11(e0163507)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Ha TS, Choi JY, Park HY and Han GD:
Changes of podocyte p130Cas in diabetic conditions. J Nephrol.
26:870–876. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Barisoni L, Kriz W, Mundel P and D'Agati
V: The dysregulated podocyte phenotype: A novel concept in the
pathogenesis of collapsing idiopathic focal segmental
glomerulosclerosis and HIV-associated nephropathy. J Am Soc
Nephrol. 10:51–61. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Kemeny E, Dürmüller U, Nickeleit V, Gudat
F and Mihatsch MJ: Distribution of podocyte protein (44 KD) in
different types of glomerular diseases. Virchows Arch. 431:425–430.
1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Wagrowska-Danilewicz M and Danilewicz M:
Synaptopodin immunoexpression in steroid-responsive and
steroid-resistant minimal change disease and focal segmental
glomerulosclerosis. Nefrologia. 27:710–715. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Hu YF, Tan Y, Yu XJ, Wang H, Wang SX, Yu F
and Zhao MH: Podocyte involvement in renal thrombotic
microangiopathy: A clinicopathological study. Am J Nephrol.
51:752–760. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Kawasaki Y, Imaizumi T, Matsuura H, Ohara
S, Takano K, Suyama K, Hashimoto K, Nozawa R, Suzuki H and Hosoya
M: Renal expression of alpha-smooth muscle actin and c-Met in
children with Henoch-Schönlein purpura nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol.
23:913–919. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Ren X, Guan G and Liu G and Liu G:
Irbesartan ameliorates diabetic nephropathy by reducing the
expression of connective tissue growth factor and
alpha-smooth-muscle actin in the tubulointerstitium of diabetic
rats. Pharmacology. 83:80–87. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Hagiwara A, Nishiyama M and Ishizaki S:
Branched-chain amino acids prevent insulin-induced hepatic tumor
cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis through mTORC1 and
mTORC2-dependent mechanisms. J Cell Physiol. 227:2097–2105.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Huo HZ, Zhou ZY, Wang B, Qin J, Liu WY and
Gu Y: Dramatic suppression of colorectal cancer cell growth by the
dual mTORC1 and mTORC2 inhibitor AZD-2014. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 443:406–412. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Yang Z, Liu F, Qu H, Wang H, Xiao X and
Deng H: 1, 25(OH)2D3 protects β cell against high glucose-induced
apoptosis through mTOR suppressing. Mol Cell Endocrinol.
414:111–119. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Cao W, Li M, Wu T, Feng F, Feng T, Xu Y
and Sun C: αMSH prevents ROS-induced apoptosis by inhibiting
Foxo1/mTORC2 in mice adipose tissue. Oncotarget. 8:40872–40884.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Wang Y, Tao J, Wang M, Yang L, Ning F, Xin
H, Xu X, Cai H, Zhang W, Yu K and Zhang X: Mechanism of regulation
of big-conductance Ca2+-Activated K+ Channels
by mTOR complex 2 in podocytes. Front Physiol.
10(167)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|